The effects of stereotactic body radiotherapy on peripheral natural killer and CD3 + CD56 + NKT-like cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
Tin-Tin Li ,Jing Sun ,Qun Wng ,Wen-Gng Li ,Wei-Ping He ,Rui-Chung Yng ,Xue-Zhng Dun ,,?
a Peking University 302 Clinical Medical School, Beijing 100191, China
b Radiation Oncology Department, the Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Xi Si Huan Middle Road, Fengtai District, Beijing 10 0 039, China
c Research Center for Clinical & Translational Medicine, the Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing 10 0 039, China
Keywords:Nature killer cells Hepatocellular carcinoma Nature killer T-like cells Stereotactic body radiotherapy
ABSTRACT Background:Both natural killer (NK) and CD3 + CD56 + natural killer T (NKT)-like cells play critical roles in the antitumor response.This study aimed to explore the effects of stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT)on peripheral NK and NKT-like cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC),and to identify possible surface markers on these cells that correlate with the prognosis.Methods:Twenty-five HCC patients were prospectively enrolled in our study,and 10 healthy individuals were served as healthy controls.Flow cytometry was used to determine the counts and the percentages of peripheral NK and NKT-like cells,cells with certain receptors,and cells with intracellular interferon- γ and TNF- α secretion at different time points,including time points of prior to SBRT,at post-SBRT,and 3-month and 6-month after treatment.The Kaplan-Meier method with the log-rank test was applied for survival analysis.Results:The peripheral NKT-like cells was increased at post-SBRT.Meanwhile,elevated levels of inhibitory receptors and reduced levels of activating receptors of NK cells were also observed in NK cells at post-SBRT,but the levels was not significantly different at 3-month and 6-month as compared with the baseline levels.Lower percentage of NKp30 + NK cells before SBRT and higher percentage of CD158b + NK cells after SBRT were associated with poor progression-free survival.In addition,higher percentage of CD3 + CD56 + NKT-like cells was associated with a higher overall survival rate in HCC patients.Conclusions:SBRT has an apparent effect on both peripheral NK and CD3 + CD56 + NKT-like cells.Lower percentage of NKp30 + NK cells before SBRT and higher percentage of CD158b + NK cells after SBRT are correlated with poor patients’ PFS.Higher percentage of CD3 + CD56 + NKT-like cells is associated with higher OS in HCC patients.
Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the third cancer-related cause of death worldwide [1].Recently,stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) has shown satisfactory efficacy in the treatment of HCC,particularly small HCC [ 2,3 ].In addition to destroying the tumor itself,radiation was shown to induce host’s antitumor immune response,although the effect on the immune system is still under debate.Some reports [ 4,5 ]showed that radiotherapy could reduce patients’ immune cells and inhibit patients’ immunity,which may attribute to tumor relapse.However,other studies showed opposite findings and demonstrated that radiotherapy could lead to the release of tumor-related antigens,which may activate host immune response,induce the abscopal effect,and lower the recurrence rate in some patients [6–9].Until now,T cells have been recognized as playing an essential role in the abscopal effect.
The mechanism of the human immune system is highly complex and yet to be fully elucidated.Natural killer (NK) cells and CD3+CD56+natural killer T (NKT)-like cells,as a pivotal part of the immune system,also play an essential role in the antitumor process [ 10,11 ].
NK cells are a cell type in innate immunity,which are able to kill cancer and virus-infected cells without the need for prior antigen stimulation.Their activation is mainly regulated by activating receptors and inhibitory receptors expressed on their cell surface.Activating receptors help the activation of NK cells while inhibitory receptors hinder the function of NK cells.Activating receptors of NK cells mainly include NKp30,NKp46 and NKG2D.Inhibitory receptors include CD158a,CD158b and NKG2A [ 12,13 ].NK cells have an important role in the pathogenesis of various liver diseases.In patients with chronic HBV and HCV infection,cytolytic activity of NK cells is conserved or enhanced while cytokine production is dysfunctional,which may contribute to virus presence [14].In hepatitis B virus related acute-on-chronic liver failure and HCC,the number of NK cells appears to be reduced and the function is impaired [ 15,16 ].
Previous experiments have demonstrated that CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells are mainly derived from CD4?CD8+T cell subsets in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) [ 17,18 ].One prominent feature of CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells is the co-expression of NK and T cell biomarkers on the cell surface.Thus,it functions through both non-MHC-I-restricted pathway and T cell receptormediated specific cytotoxicity [19–21].In recent years,the immunological characteristics of NKT-like cells have been described in infectious diseases and tumors [ 22,23 ].
Thus far,few studies have focused on the effects of SBRT on NK cells and NKT-like cells in HCC patients [ 24,25 ].The objective of this study was to explore the effects of SBRT on NK cells and NKTlike cells in the peripheral blood of HCC patients,and to identify NK and NKT-like cell surface markers that could predict the patients’ prognosis.
Methods
Study subjects
Twenty-five HCC patients were prospectively enrolled in the study between August 2017 and November 2018.Ten healthy individuals were enrolled as healthy controls.Of the 25 patients,blood samples in 13 patients were collected before SBRT and within a week after SBRT.They were defined as the post-SBRT group,which was used to evaluate the early effects of SBRT on NK cells and NKT-like cells.Another eight patients contributed blood samples before SBRT and at 3-month follow-up visit.They were defined as the 3-month group,which was used to assess the effects of SBRT on NK cells and NKT-like cells at 3 months after SBRT.The remaining four patients contributed blood samples before SBRT and at 6-month follow-up.They were defined as the 6-month group,which was used to evaluate the effects of SBRT on NK cells and NKT-like cells at 6 months after SBRT.
Enrollment criteria were as follows: (1) a definitive diagnosis of HCC [26]; (2) a tumor diameter of less than 5 cm; (3) Child-Pugh classification A; (4) without previous treatment for tumors;(5) without concurrent antitumor therapy or immunotherapy from the beginning of SBRT to 6 months after SBRT; and (6) positive for serum hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg).
Patients were excluded if they had: (1) human immunodeficiency virus; (2) immune diseases; (3) portal vein tumor thrombus(PVTT); and (4) metastasis.
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital.All enrolled patients signed informed consent.
SBRT and follow-up
SBRT was performed with G4 CyberKnife (Accuracy,Sunnyvale,CA,USA) in 25 HCC patients.The prescribed doses were 49–55 Gy/5–7 Fx.The gross tumor volume (GTV) ranged from 3 to 87 mL.The planning target volume (PTV) was defined as a 3–5 mm expansion of GTV.All patients completed the radiotherapy regimen.Follow-up was conducted every three months after SBRT,which included blood routine tests,tumor marker tests,liver function tests,chest computed tomography (CT) and contrast-enhanced abdominal MRI/CT.
Preparation of blood samples
Approximately 20 mL peripheral blood was collected at four time points: prior to SBRT,at post-SBRT (within one week of completion of SBRT),and at 3-month and 6-month follow-ups.The specimens were preserved in vacutainer tubes (BD,Franklin Lakes,NJ,USA) containing EDTA.Subsequently,blood was centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C to separate blood cells from plasma.Next,PBMCs were isolated by Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient centrifugation at 2500 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C.Then,the PBMCs were washed twice in phosphate buffer solution (PBS) and resuspended in a frozen stock solution containing 90% fetal bovine serum and 10% DMSO.After gradient cooling,the PBMCs were stored in liquid nitrogen.
Detection of cells, subsets and receptors
Flow cytometry was used for measurement.The following panel was applied: Apch7-CD45 (BD Biosciences,San Jose,CA,USA,560178),BV650-CD3 (BD Biosciences,563999),BB700-CD56(BD Biosciences,566400),BV711-CD158a (BD Biosciences,563183),AF488-NKG2A (R&D systems,Minneapolis,MN,USA,FAB1059G),BV421-NKp30 (BD Biosciences,563385),PECY7-NKp46 (BD Biosciences,562101),APC-NKG2D (BD Biosciences,558071),and PECD158b (BD Biosciences,559785).Frozen PBMCs (1 × 106/vial)were thawed swiftly and resuspended in RPMI 1640 medium(Corning,Corning,NY,USA,10–040-CVR) with 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco,Grand Island,NY,USA,12662029).After the cells were washed with PBS,BD HorizonTMFixable Viability Stain 510(BD Biosciences,564406) was added,and the cells were stained at room temperature for 15 min in the dark.The cells were subsequently incubated with fluorescent antibodies in PBS for 20 min at room temperature in the dark.Immunoglobulin (Ig) G isotype antibodies were used in negative controls.The cells were washed with PBS and detected using a BD FAC Symphony A5 flow cytometer(BD Biosciences).The data were analyzed using FlowJo 10 software(TreeStar,San Carlos,CA,USA).
Detection of intracellular tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF- α) and IFN- γ
The following panel was applied: BV650-CD3 (BD Biosciences,563999),BB700-CD56 (BD Biosciences,566400),APC-INF-γ(BD Biosciences,554702),and PE-TNF-α(BD Biosciences,554513).PBMCs were stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate (25 ng/mL)(Sigma-Aldrich,Shanghai,China,P1585) and Ionomycin (1μg/μL)(Sigma-Aldrich,P1585) in a CO 2 incubator for 4 h.Unstimulated PBMCs were served as negative controls.The cells were then collected and stained with BV650-CD3 and BB700-CD56 antibodies in the dark for 25 min.Next,the cells were permeabilized in the dark for 20 min and stained with intracellular antibodies (PE-TNF-αand APC-INF-γ) at room temperature for 30 min.Finally,samples were detected using flow cytometry.
Degranulation of NK cells
PBMCs (5 × 105/well) were seeded in 24-well plates,and the volume was adjusted to 1 mL by adding RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum.PBMCs were stimulated with phorbol myristate acetate (25 ng/mL) and Ionomycin (1μg/μL).The cells were incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO 2 incubator for 4 h then stained using antibodies [BV650-CD3,BB700-CD56 and anti-CD107a (BD Biosciences,555801)]for 25 min in the dark,and detected by flow cytometry within 24 h.
Statistical analysis
Continuous data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) for normal distribution and as median (range) for nonnormal distribution.Categorical data were recorded as frequencies and percentages.For inter-group comparisons,ANOVA analysis or nonparametric test was used for continuous data,and Chi-square test or Fisher exact test was used for categorical data.For comparisons between healthy controls and HCC patients,independentt-test or nonparametric test was used.Pairedt-test or nonparametric Wilcoxon paired test was applied to data before and after SBRT.The optimal cut-off value was determined using X-tile software [27].The Kaplan–Meier method was used to assess survival time,and the log-rank test was used to compare survival outcomes.For all the tests,aP<0.05 (two-sided) was considered statistically significant.Statistical description and analysis were performed using SPSS 24.0 (SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA),Stata15.1(StataCorp,College Station,TX,USA),and GraphPad Prism 7.0 software (GraphPad,La Jolla,CA,USA).
Results
Clinical features of patients
At the outset,we examined the homogeneity of clinical features among the three groups (the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group).There were no statistical differences among the three groups in their clinical characteristics,including the baseline levels of liver function,tumor status,and radiotherapy dose.The clinical data of HCC patients were described in detail in Table 1.All included patients were HBV-related HCC,belonged to Child-Pugh A,and did not have PVTT.
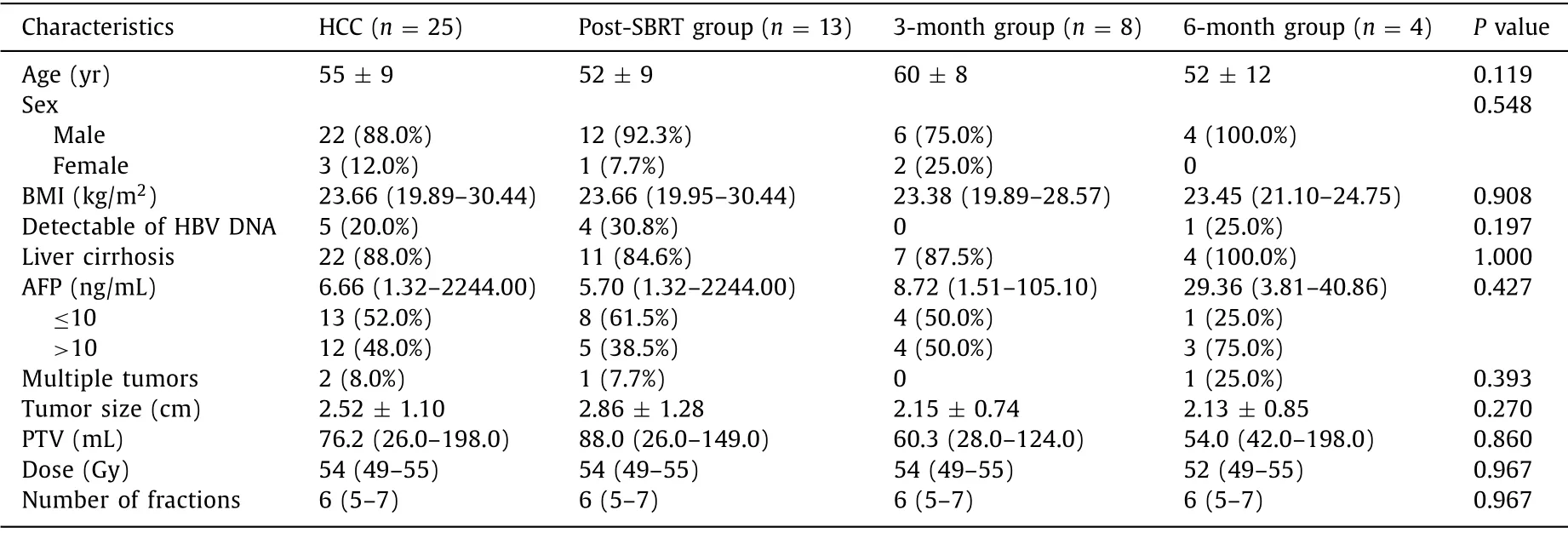
Table 1 Patient characteristics.
After a median follow-up of 20 months (range 7–28 months),eight patients were diagnosed with relapse or metastasis.Among them,two had liver relapse,three had lung metastasis,one had gallbladder metastasis,and two had multiple organ metastases.Four patients died,three of whom died of tumor relapse or metastasis,and one died of infectious shock.The 2-year local control rate,progression-free survival (PFS) rate,and overall survival (OS)rate were 88.0%,67.1%,and 76.5%,respectively.
The median age for healthy controls (eight males and two females) was 58 years (range 43–64 years),and the median body index (BMI) was 21.49 kg/m2(range 19.12–24.32 kg/m2).No significant differences were found in sex,age,and BMI between healthy controls and HCC patients.
The baseline level of NK cells and NKT-like cells in HCC patients
Human peripheral NK cells and NKT-like cells were distinguished by CD3 and CD56 in the flow cytometric gating strategy ( Fig.1A ).Compared with healthy controls,the percentages of NK cells (NK cells/lymphocytes) and their subsets (CD56dimNK cells/lymphocytes and CD56brightNK cells/lymphocytes) were decreased in HCC patients ( Fig.1B –E),whereas the percentages of NK cell receptors,intracellular IFN-γ+NK cells,TNF-α+NK cells,and CD107a+NK cells did not change significantly (data not shown).Although the percentage of NKT-like cells (NKT-like cells/lymphocytes) was not significantly different between healthy controls and HCC patients ( Fig.1 B and F),there were significantly higher percentages of IFN-γ+NKT-like cells and TNF-α+NKT-like cells in HCC patients than in healthy controls ( Fig.1 G and H).
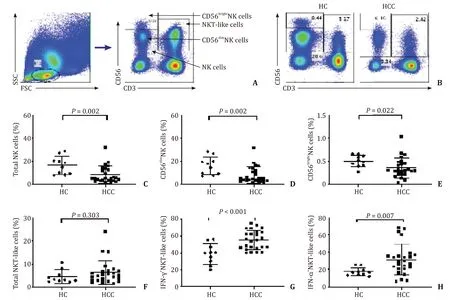
Fig.1.Comparison of the percentages of NK cells and NKT-like cells between HCC patients and healthy controls (HC) in PBMC.A : Flow cytometric gating strategy for NK cells and NKT-like cells; B - E : Comparison of the percentages of NK,CD56 dim NK,and CD56 bright NK cells between HCC patients and HC; F : Comparison of the percentages of NKT-like cells between HCC patients and HC; G,H : Comparison of the percentages of IFN- γ and TNF- α positive NKT-like cells between HCC patients and HC.NK: natural killer; NKT: natural killer T; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; PBMC: peripheral blood mononuclear cell.
Changes in NK cells in peripheral blood following SBRT
We found that the percentage of NK cells (NK cells/lymphocytes) was increased in the post-SBRT group compared with the baseline level ( Fig.2 A and B).However,the percentages of NK cells in the 3-month and 6-month groups showed no significant change compared with the baseline levels ( Fig.2 A,C and D).A possible explanation was that the number of lymphocytes changed after SBRT,which led to an increased proportion of NK cells,but it did not fully account for the increase in NK cells.Therefore,we measured the absolute NK cell counts.However,we found no change of the absolute NK cell counts in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group and the 6-month group compared with the baseline level (data not shown).The percentage of a subset,CD56dimNK cells,was increased in the post-SBRT group ( Fig.2 E),but was comparable to the baseline level in the 3-month and 6-month groups ( Fig.2 F and G).Likewise,the absolute counts of CD56dimNK cells did not show significant change.On the other hand,the percentage of CD56brightNK cells showed no significant difference in the post-SBRT group compared with the baseline level ( Fig.2 H),but was increased in the 3-month group ( Fig.2 I)and was not significantly different compared to the baseline level in the 6-month group ( Fig.2 J).
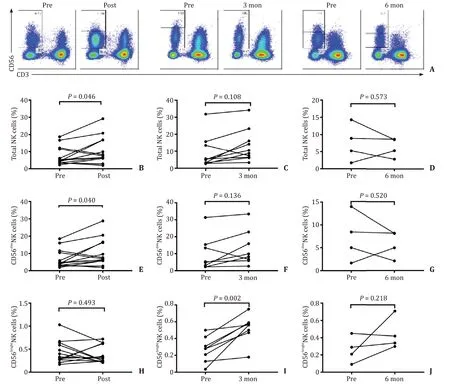
Fig.2.Comparison of the percentage of NK cells and the subsets before and after SBRT.A : Typical images of total NK cells and the subsets before and after SBRT treatment;B - D : Comparison of the percentage of NK cells in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level; E - G : Comparison of the percentage of CD56 dim NK cells in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level; H - J : Comparison of the percentage of CD56 bright NK cells in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level.NK: natural killer; SBRT: stereotactic body radiotherapy.
We further evaluated the effect of SBRT on NK cell receptors.The levels of NK cell activating receptor NKp30 and NKp46 were decreased in the post-SBRT group compared with the baseline levels ( Fig.3 A and B).However,the levels were not significantly different in the 3-month and 6-month groups compared with the baseline levels ( Fig.3 A and B).In addition,the level of NKG2D did not change significantly compared with the baseline level over the study period ( Fig.3 C).The level of inhibitory receptor CD158b increased in the post-SBRT group compared with the baseline level( Fig.3 D),but was not significantly different in the 3-month and 6-month groups compared with the baseline level ( Fig.3 D).The percentage of CD158a+NK cells and NKG2A+NK cells was comparable to the baseline levels in the post-SBRT,3-month and 6-month groups ( Fig.3 E and F).The percentage of TNF-α+NK cells in the post-SBRT group was significantly higher than the baseline level( Fig.4 A),but there was no significant difference in percentage of TNF-α+NK cells in the 3-month and 6-month groups compared with the baseline levels ( Fig.4 B and C).The percentage of IFNγ+NK cells and CD107a+NK cells were not found statistically different during the observation period ( Fig.4 D–I).
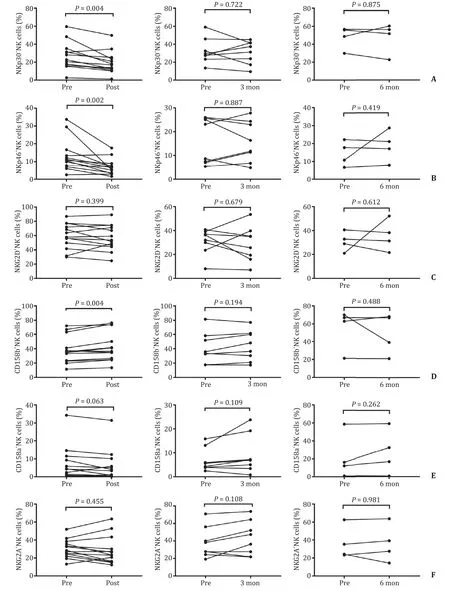
Fig.3.Comparison of the percentage of NK cells receptors before and after SBRT.A : Comparison of the percentage of NKp30 receptors in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level; B : Comparison of the percentage of NKp46 receptors in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level; C : Comparison of the percentage of NKG2D receptors in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level; D : Comparison of the percentage of CD158b receptors in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level; E : Comparison of the percentage of CD158a receptors in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level; F : Comparison of the percentage of NKG2A receptors in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level.NK: natural killer; SBRT: stereotactic body radiotherapy.
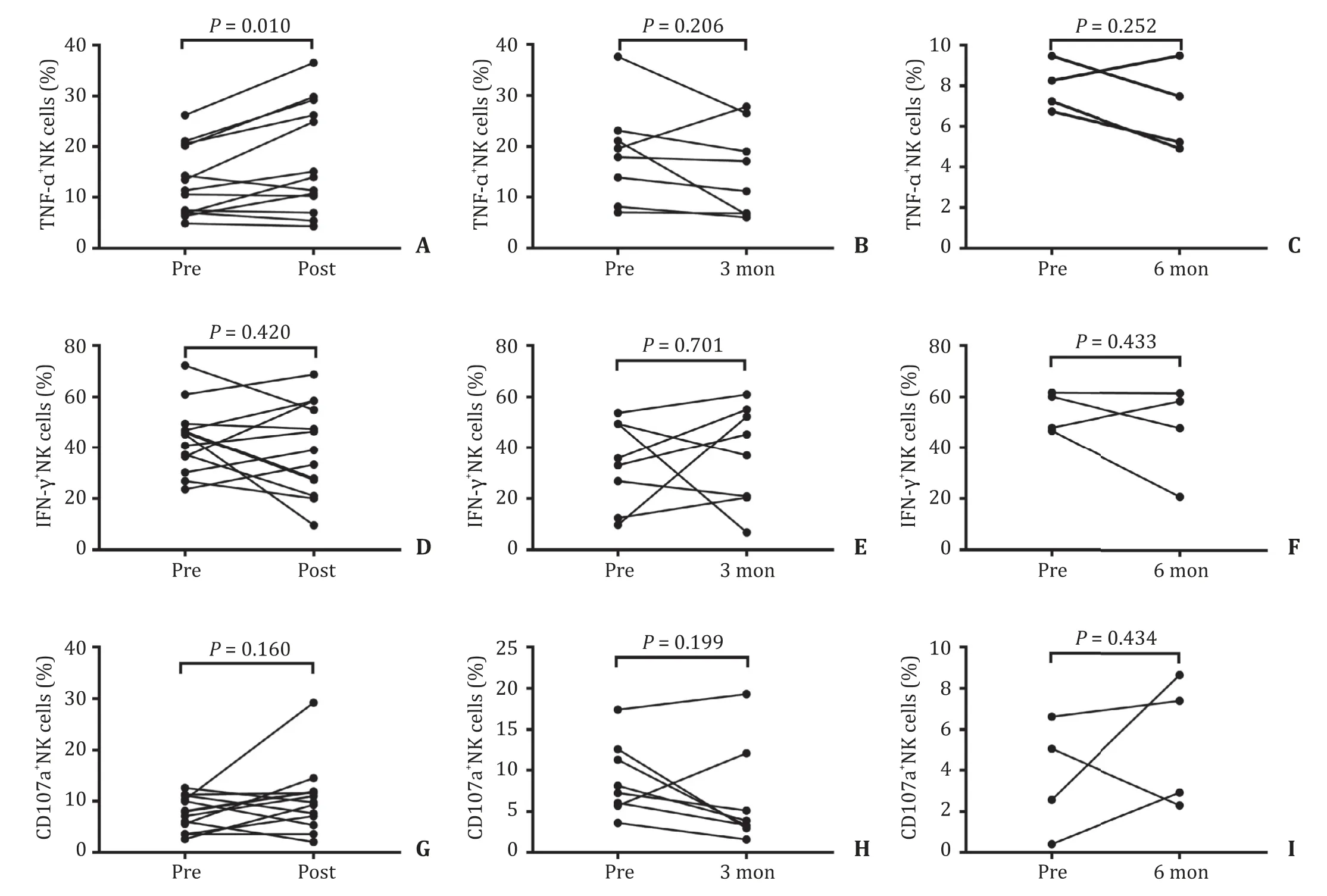
Fig.4.NK cell intracellular secretion before and after SBRT.A - C : Comparison of the percentage of TNF- α+ NK cells in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level; D - F : Comparison of the percentage of IFN- γ+ NK cells in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level; G - I : Comparison of the percentage of CD107a + NK cells in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group to the baseline level.NK: natural killer; SBRT: stereotactic body radiotherapy.
Changes in NKT-like cells in peripheral blood following SBRT
An elevated percentage of NKT-like cells was observed in the post-SBRT group compared with the baseline level in HCC patients( Fig.5 A and B).A higher percentage of NKT-like cells was also observed in the 3-month group compared with the baseline level( Fig.5 A and C).However,no significant differences were detected in the 6-month group compared with the baseline level ( Fig.5 A and D).The absolute NKT-like cell counts were only increased in the post-SBRT group (P<0.001,data not shown),but not in the 3-month and 6-month groups compared with the baseline level.In terms of intracellular detection,TNF-α+NKT-like cells were significantly higher in the post-SBRT group,but not in the 3-month and 6-month groups compared with the baseline level ( Fig.6 A–C).However,IFN-γ+NKT-like cells showed no significant differences before and after SBRT ( Fig.6 D–F).
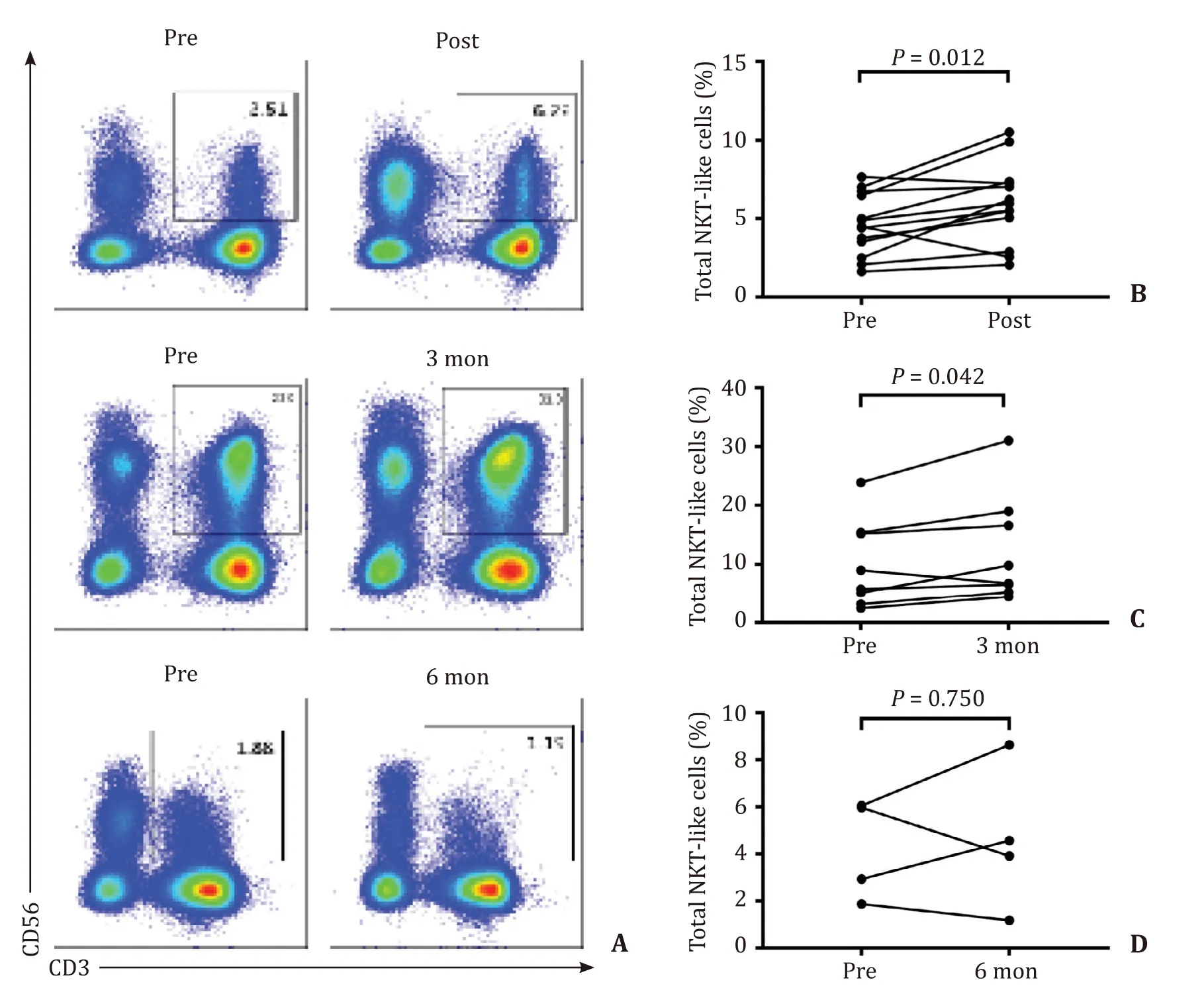
Fig.5.Comparison of the percentage of NKT-like cells before and after SBRT.A : A typical image of the flow cytometry; B : The percentage of NKT-like cells was increased in the post-SBRT group compared to the baseline level; C : The percentage of NKT-like cells was increased in the 3-month group compared to the baseline level; D : The percentage of NKT-like cells had no significant change in the 6-month group compared to the baseline level.NKT: natural killer; SBRT: stereotactic body radiotherapy.
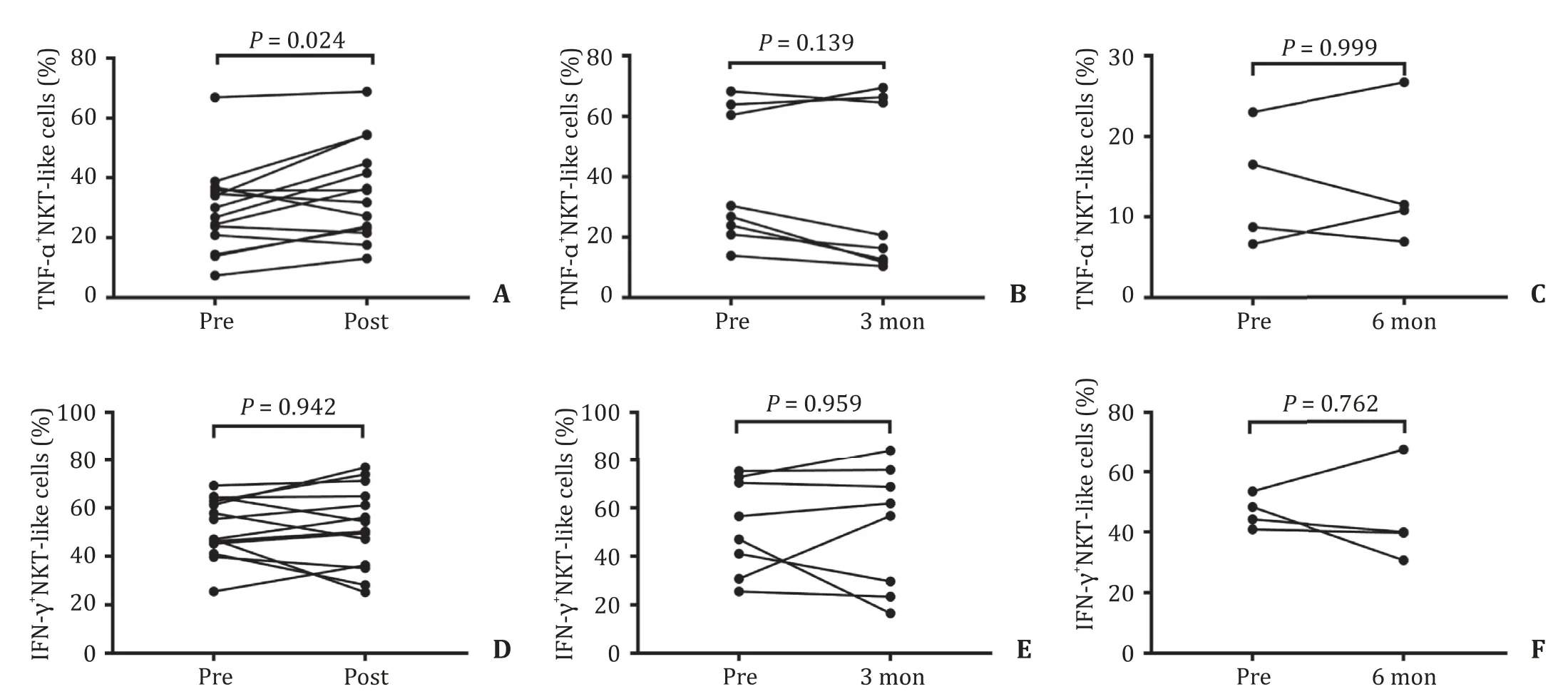
Fig.6.NKT-like cell intracellular secretion before and after SBRT.A : The percentage of TNF- α+ NKT-like cells increased in the post-SBRT group compared to the baseline level; B : No significant difference was found in TNF- α+ NKT-like cells in the 3-month group; C : No significant difference was found in TNF- α+ NKT-like cells in the 6-month group; D - F : The secretion of IFN- γ was not significantly different in the post-SBRT group,the 3-month group,and the 6-month group compared to the baseline level.NKT:natural killer T; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; IFN: interferon- γ; SBRT: stereotactic body radiotherapy.
Correlations with clinical outcomes
Moreover,we tried to analyze the corrections between the patient’s survival rates and the above-mentioned immune phenotypes,which significantly changed with SBRT.We put the above-mentioned immune phenotypes into the X-tile software one by one,and analyzed the correlation between their expressions with PFS and OS.There were two phenotypes,the percentage of NKp30+NK cells and CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells,which could find the optimal cut-off value.The optimal cut-off value for the percentage of NKp30+NK cells in NK cells was 18.01% in HCC patients before SBRT.Patients were divided into two groups based on the cut-off value.We found that patients with a higher percentage of NKp30+NK cells (>18.01%) had better PFS than patients with a lower percentage of NKp30+NK cells ( ≤ 18.01%)(P= 0.016,Fig.7 A).However,there were no significant differences in OS between the two groups.(P= 0.279,Fig.7 B) In addition,the optimal cut-off value for the ratio of CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells/lymphocytes was 3.77% before treatment.We divided patients into two groups: a higher percentage of CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells(>3.77%) group and a lower percentage of CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells ( ≤3.77%) group.There were no significant differences in PFS between the two groups (P= 0.242,Fig.7 C).The result showed that patients with a higher percentage of CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells(>3.77%) had higher OS than patients with a lower percentage of CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells ( ≤3.77%) (P= 0.032,Fig.7 D).
We also explored whether the percentage change of peripheral NK and NKT-like cells after SBRT could be an indicator for the prognosis.After analysis by X-tile software,only the percentage of CD158b+NK cells in the post-SBRT group had an optimal cut-off value.The optimal cut-off value for the percentage of CD158b+NK cells was 41.17%.Patients with a higher percentage of CD158b+NK cells (>41.17%) had poorer PFS than patients with a lower percentage of CD158b+NK cells ( ≤41.17%) (P= 0.003,Fig.7E ).OS showed no significant difference between the two groups(P= 0.273,Fig.7 F).
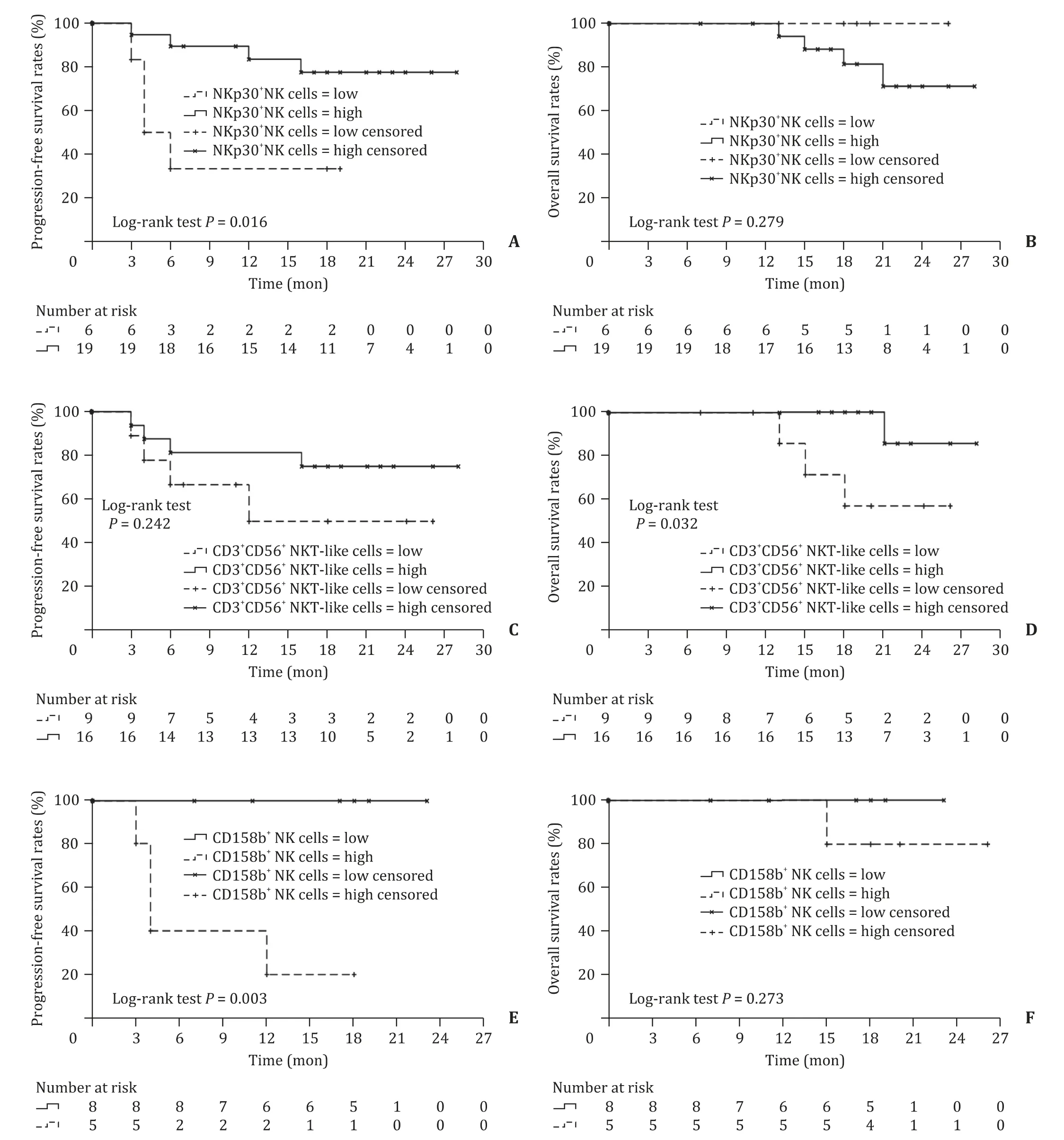
Fig.7.Correlations with survival.A : The progression-free survival in correlation to the percentage of NKp30 + NK cells in HCC patients before SBRT; B : The overall survival in correlation to the percentage of NKp30+ NK cells in HCC patients before SBRT; C : The progression-free survival in correlation to the percentage of CD3+ CD56+ NKT-like cells in HCC patients before SBRT; D : The overall survival in correlation to the percentage of CD3+ CD56 + NKT-like cells in HCC patients before SBRT; E : The progression-free survival in correlation to the percentage of CD158b+ NK cells at post-SBRT; F : The overall survival in correlation to the percentage of CD158b + NK cells at post-SBRT.HCC:hepatocellular carcinoma; SBRT: stereotactic body radiotherapy; NK: natural killer; NKT: natural killer T.
Discussion
In our study,the percentages of peripheral NK cells and its subsets were significantly reduced in HCC patients before SBRT treatment compared with healthy controls.Patients with a lower percentage of NKp30+NK cells had a poorer PFS than patients with a higher percentage of NKp30+NK cells.This finding is consistent with other recent studies on NKp30 as an important prognostic biomarker,including studies on liver diseases such as HCVrelated liver fibrosis,early stage of the end of radiofrequency ablation of HCC [ 28,29 ].In addition,observations on other cancers including leukemia,lung cancer,and prostate cancer have similar reports [30–32].
The servant ran after his master and told him what had happened, and then, not wishing to lose the saddle as well as the horse, he went back to fetch it
One possible explanation for these is that activating receptor NKp30 on NK cells could play a crucial role in antitumor response in HCC patients.The NKp30 receptor is expressed on all resting and activating human NK cells.The NKp30 receptor is capable of mediating direct killing of virus-infected and tumor cells.Its downregulation is a mechanism by which tumors evade innate immunity [33–35].
The immune response induced in HCC patients by radiation therapy is complicated and has not been fully explored,with studies giving contradictory findings.Navarro-Martín et al.showed that radiotherapy could promote antitumor immunity by increasing the immunoactive component and reducing inhibitory effects of regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in lung cancer patients [36].Another study showed that lymphopenia may occur after radiation treatment [37].What was more perplexing was that different radiation regimens,such as routine radiation therapy versus SBRT,had different effects on antitumor immunity [38].Very limited data were reported regarding the effects of SBRT on NK cell changes in HCC patients [ 24,25 ].One limitation in the previous studies was that most HCC patients had received other treatments before SBRT,which made it more challenging to interpret the results.Furthermore,these studies only described the proportion of NK cells,not specific NK cell surface markers.
In this study,none of the enrolled patients received other treatments before SBRT.We found that the absolute counts of NK cells and its subsets did not change in HCC patients after SBRT,while the percentage of NK cells in lymphocytes was increased.It is likely that after SBRT,the reduction of other types of lymphocytes,such as T cells,led to an increase in the proportion of NK cells without increasing the absolute counts.This indicates that some immune cells are sensitive to SBRT and decreased in numbers after radiotherapy,whereas NK cell numbers better tolerate the SBRT treatment.
However,in further observations,we found that the proportion of the NK cell activating receptors was decreased and the proportion of NK cell inhibitory receptors was increased in HCC patients receiving SBRT.This change usually occurred after SBRT.It is known that the antitumor processes of NK cells mainly depend on the balance between activating receptors and inhibitory receptors on their surface.If activating receptors are upregulated and inhibitory receptors are down-regulated,it would enable NK cells to inhibit tumors [ 39,40 ].Our research indicated that SBRT may inhibit the antitumor response of NK cells in the short term by changing the expression of NK cell receptors,i.e.,by increasing inhibitory receptors and reducing activating receptors.It seemed that these exhausted phenotypes only occurred at the post-SBRT group,and were not significantly different in the 3-month and 6-month groups compared with the baseline levels.
Furthermore,our study found that not all patients had the same changes in NK cell receptors after SBRT.Some patients with higher CD158b at the post-SBRT group had lower 2-year PFS.A study on hepatitis C virus infection also showed that the high frequency of CD158b expression may be related to persistent virus infection [41].There are two points of application value for such findings.First,the expression of CD158b on NK cells after SBRT may serve as a helpful indicator for assessing the prognosis.Second,the inhibition of CD158b receptor expression on peripheral NK cells in the course of SBRT may further improve survival rate.This can be further explored in future research with combined SBRT and immunotherapy.
Intracellular cytokine TNF-αwas increased in HCC patients after SBRT.However,this change did not seem to affect patient’s survival.This may be worth exploring in future studies.
As for the percentage of NKT-like cells,we did not find significant differences between healthy controls and HCC patients.This result is consistent with a previous study,which demonstrated no change in CD3+CD56+cells in peripheral blood of HCC patients compared with healthy donors,but a significant decrease in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in tissues [42].Further,we found that HCC patients with higher percentage of CD3+CD56+NKTlike cells achieved higher 2-year OS.This is in line with previous reports,which showed that CD3+CD56+cells play an active role in antitumor immunity in a variety of tumor types,including HCC [ 43,44 ].
Additionally,we noticed a significant increase in the percentage of NKT-like cells in HCC patients after SBRT.The expansion of CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells suggests that SBRT could trigger NKTlike cells-related immune response,which was mainly expanded using cytokines in the past [45].
In conclusion,SBRT shows an effect on NK cells and CD3+CD56 + NKT-like cells.Although SBRT does not change the total number of NK cells,it changes the distributions of NK cell activating and inhibitory receptors.Lower percentage of NKp30+NK cells before SBRT and higher percentage of CD158b+NK cells after SBRT are correlated with poor patients’ PFS.Moreover,higher percentage of CD3+CD56+NKT-like cells is associated with higher OS in HCC patients.
Acknowledgments
We thank all patients and volunteers who participated in this study and all staff in Radiation Oncology Department of the Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital for their help in collection of samples.
CRediTauthorshipcontributionstatement
Tian-TianLi:Data curation,Formal analysis,Methodology,Software,Writing - original draft.JingSun:Resources,Writing - review & editing.QuanWang:Data curation,Formal analysis.Wen-GangLi:Methodology,Resources.Wei-PingHe:Methodology,Resources.Rui-ChuangYang:Methodology.Xue-ZhangDuan:Conceptualization,Funding acquisition,Project administration,Supervision,Validation,Writing - review & editing.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81972856).
Ethicalapproval
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Fifth Medical Center of Chinese PLA General Hospital.
CompetinginterestNo benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
 Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International2021年3期
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International2021年3期
- Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International的其它文章
- MEETINGS AND COURSES
- Reply to: Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A cost-effective alternative for low-resource settings
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A cost-effective alternative for low-resource settings
- Transarterial chemoembolization as adjuvant treatment after surgery:The cure of huge hepatocellular carcinoma?
- RELEVANT CONTENT
- Variations of the hilar biliary confluence from postoperative cholangiography in Chinese population
