Postoperative adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization improves the prognosis of patients with huge hepatocellular carcinoma
Hn Wng ,#,Hu Yu ,#,You-Wen Qin ,#,Zhen-Ying Co ,Meng-Cho Wu ,Wen-Ming Cong ,?
a Department of Pathology, Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital, The Second Military Medical University, Yangpu, Shanghai 200438, China
b Department of Hepatic Surgery, Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital, The Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200438, China
Keywords:Postoperative transcatheter arterial chemoembolization Recurrence Prognosis
ABSTRACT Background:Surgical resection of huge hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC,≥10 cm) is potentially curative.More adjuvant treatments are needed to reduce relapses in these patients.We evaluated the influence of postoperative adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (PA-TACE) on the prognosis of huge HCC.Methods:Data from consecutive patients who underwent curative resection for huge HCC in our center were retrospectively collected.Recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) were compared between patients who did and did not undergo PA-TACE.Propensity score matching (PSM) was used.Results:Among the 255 enrolled patients,93 underwent PA-TACE.The clinical outcomes were significantly better in the PA-TACE group than those in the non PA-TACE group (5-year RFS rate: 33.5% vs.18.0%; 5-year OS rate: 47.0% vs.28.0%,all P < 0.001).After PSM,similar results were obtained (5-year RFS rate: 28.8% vs.17.6%,P < 0.001; 5-year OS rate: 42.5% vs.25.0%,P = 0.004).PA-TACE decreased the possibility of early recurrence ( < 2 years,crude cohort: P < 0.001,PSM cohort: P < 0.001) but not late recurrence ( ≥2 years,crude cohort: P = 0.692,PSM cohort: P = 0.325).Multivariable Cox regression analysis suggested that PA-TACE was an independent protective factor prolonging early RFS,RFS and OS.Conclusions:PA-TACE is a safe intervention for huge HCC patients after liver resection and improves outcomes.
Introduction
Liver cancer is the fourth leading cause of malignancy and the third most common cause of cancer-related death in China [1].Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver tumor [2].Liver resection is currently the mainstay of curative treatments for HCC [3].However,the 5-year recurrence rate is as high as 70%,which suggests that more effective interventions are needed for HCC [4].
In the past,tumor size has been considered an essential factor affecting the prognosis of HCC.Based on the tumor diameter,HCC can be stratified into small HCC (<3 cm),early-stage HCC(<5 cm),large HCC (>5 cm),and huge HCC (>10 cm) [5-8].Among these classifications,huge HCC has few radical treatment methods available because of the volume.Serious operative risks and limited functional liver remnants increase the recurrence rate[9].With the advancement of surgical techniques,partial hepatectomy can be performed safely in huge HCC patients [10].However,based on a meta-analysis of 7609 patients,the characteristics of huge HCC tended to be worse than those of non-huge HCC,such as worse pathological grades,the presence of an incomplete capsule,the incorporation of satellite lesions,and higher rates of microvascular invasion (MVI) and portal vein tumors [11].As such,the management of huge HCC patients should involve more modalities and be more comprehensive.
A curative resection is defined as the absence of macroscopic or microscopic disease at the surgical margin [12].While in clin-ical practice,pathologists sample one or two tissue blocks at the resected liver closest to the tumor boundary,which means that curative resection in pathology only depends on a limited section.Meanwhile,inaccuracy of macroscopic judgment is also unavoidable.The above indicates that some defects still exist in the criteria of judgment of curative resection.As such,adjuvant therapy is valuable for huge HCC to prevent recurrence of potential residual tumors.
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) represents the current gold standard for HCC patients in intermediate stage [13].Postoperative adjuvant TACE (PA-TACE) has been shown to improve the clinical outcomes of HCC patients,especially those with a high risk of recurrence,such as patients with multinodular tumors,MVI,and gross vein tumor thrombus [14-16].Considering the biological behavior and clinical features of huge HCC,it is valuable to explore the impact of PA-TACE on the short- and long-term oncological outcomes of huge HCC patients.
The present study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of PA-TACE in patients with huge HCC who underwent liver resection in our center.To reach a more reliable conclusion,a propensity score matching (PSM) analysis was further employed.
Methods
Patients
Consecutive HCC patients who underwent curative liver resection at the Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital,Shanghai,from December 2009 to December 2010 were retrospectively analyzed.The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) HCC diameter ≥10 cm and (2) curative resection with a negative resection margin based on histological examination.The exclusion criteria included (1)palliative liver resection with microscopically positive or grossly positive resection margins; (2) gross vessel invasion or extrahepatic metastasis; (3) recurrent HCC; (4) preoperative anti-HCC treatments; (5) recurrence within one month after surgery; (6) severe liver dysfunction three months after surgery,making PA-TACE impossible; and (7) loss to follow-up within three months after liver resection.The flow chart is shown in Fig.S1.
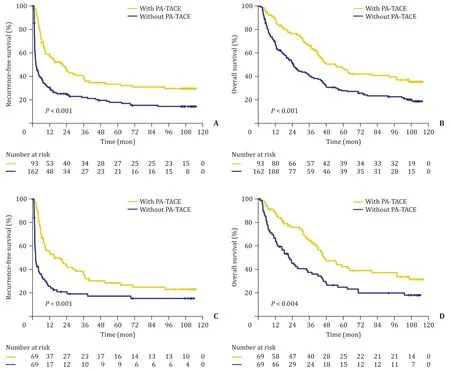
Fig.1.Cumulative incidence of recurrence-free survival ( A and C ) and overall survival ( B and D ) in huge hepatocellular carcinoma patients with and without postoperative adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (PA-TACE) before ( A and B ) and after propensity score matching ( C and D ).
Laboratory tests were done before the operation.The Child-Pugh classification system was used to evaluate liver function.The tumor size was measured in the resected specimen with the largest dimensions.The sampling was conducted by two pathologists according to the “Seven-point baseline sampling protocol” [17].The capsule data depended on the condition of the largest tumor.Tumor differentiation referred to the worst grade in the specimen and was classified based on the Edmondson-Steiner grading system [17].MVI was identified as the presence of tumor cells in a portal vein,hepatic vein,or capsular vessel of the surrounding liver tissue,which was visible only on microscopy [18].
Follow-up
Patients were regularly reexamined once every 2 months for the first year after liver resection and once every 3 to 6 months thereafter.The postoperative surveillance strategy for recurrence consisted of a liver function test,detection of the serum alphafetoprotein (AFP) level,detection of the hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid (HBV DNA) load if necessary,and ultrasonography or contrast-enhanced computer tomography (CT)/magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen.Follow-up was terminated in July 2019.The end points were recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS).RFS and OS were calculated from the date of surgery to the date of recurrence/censoring and death/censoring,respectively.Early recurrence was defined as recurrence within 2 years after surgery.
PA-TACE
Considering the malignant biological behaviors of huge HCC,all patients received the recommendation to undergo PA-TACE approximately 1-3 months after surgery when their liver function had recovered.
Using the Seldinger technique,a hepatic arterial catheter was inserted into the proper hepatic artery through the femoral artery,and TACE was conducted for the entire remnant liver.Hepatic angiography,CT angiography,or both were employed to explore any obvious tumor stains in the liver.If tumor staining was not found,chemotherapeutic agents and lipiodol were injected through the microcatheter.The chemotherapeutic regimens used included doxorubicin hydrochloride,pirarubicin and epirubicin [19].The dosage of chemotherapeutic drugs and lipiodol was determined by liver function and body surface area.
PSM
PSM was performed to reduce the effects of confounding factors [20].All variables with potential differences between the two groups (P<0.2) were included in the PSM model,including sex,red blood cell (RBC) count,HBV DNA load,hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg),hepatitis B surface antibody (HBsAb),hepatitis B e antibody (HBeAb),resection approach,transfusion,tumor size,and tumor number.The propensity score was estimated by a logistic regression analysis with nearest neighbor matching.The ratio for matching was 1:1 with a caliper width of 0.05 of the standard deviation of the logit of the propensity score.
Statistical analysis
The patients’ baseline characteristics and operative variables are represented by the frequencies (percentages) for categorical covariates and the means ± standard deviations (SD) or medians(ranges) for continuous covariates.Continuous and categorical variables were compared using Student’st-test or the Mann–WhitneyUtest and theχ2test or Fisher’s exact test,respectively.Kaplan-Meier curves and the log-rank test were used to compare the RFS and OS rates between different groups.The factors affecting the RFS and OS were identified by Cox proportional hazards regression models.Variables with aPvalue less than 0.1 in univariate analysis were entered into the multivariate model for further screening.Pvalues were two-sided,and aPvalue less than 0.05 was regarded as statistically significant.Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS software version 24.0 (SPSS,Chicago,IL,USA).
Results
Baseline characteristics of patients
A total of 255 patients were enrolled in our study,with 93 patients undergoing PA-TACE.No patients had serious adverse reactions.As shown in Table 1,the patients who underwent PA-TACE had a significantly higher RBC count,a lower proportion of positivity for HBsAg,and a lower proportion of transfusion than the patients who did not undergo PA-TACE (allP<0.05).After PSM,69 pairs of patients who did and did not undergo PA-TACE were selected,and none of the variables were significantly different between the two groups (allP>0.05).The median follow-up time was 108.6 months for the crude cohort and 110.1 months for the PSM cohort.No patients died within one month after surgery.The median time from surgery to PA-TACE was 43 (range: 26–92) days.No patients died within one month after PA-TACE.The RFS and OS curves after PA-TACE are shown in Fig.S2.

Table 1 Baseline characteristics of the patients before and after propensity score matching.
Impact of PA-TACE on clinical outcomes
Kaplan-Meier curves showed that huge HCC patients with PATACE had better prognosis than patients without PA-TACE.In the crude cohort,the median RFS time of the PA-TACE group and the non PA-TACE group were 20.9 and 2.6 months,respectively.The associated 1-,3-,5-,and 7-year RFS rates of the two groups were 58.8% vs.30.7%,39.4% vs.22.2%,33.5% vs.18.0%,and 31.0% vs.15.4%(allP<0.001,Fig.1 A).The median OS time of the PA-TACE group and the non PA-TACE group were 54.6 and 24.6 months,respectively.The corresponding 1-,3-,5-,and 7-year OS rates of the two groups were 89.1% vs.68.2%,66.2% vs.40.5%,47.0% vs.28.0%,and 40.9% vs.23.6% (allP<0.001,Fig.1 B).
For the PSM cohort,the PA-TACE group and the non PA-TACE group had median RFS time of 15.6 and 2.3 months,respectively.The associated 1-,3-,5-,and 7-year RFS rates of the two groups were significantly different (56.1% vs.26.0%,37.1% vs.19.5%,28.8%vs.17.6%,and 25.2% vs.15.6%,respectively,P<0.001,Fig.1 C).Meanwhile,the PA-TACE group and the non PA-TACE group had median OS of 46.2 and 22.0 months,respectively.The correlated 1-,3-,5-,and 7-year OS rates of the two groups were still significantly different (88.2% vs.66.7%,64.5% vs.37.6%,42.5% vs.25.0%,37.3% vs.20.0%,P= 0.004,Fig.1 D).
Early recurrence (<2 years) was compared between the two groups among all 255 patients in the crude cohort,while late recurrence ( ≥2 years) was compared among the 74 patients who had a postoperative period of no less than 2 years and who did not experience early recurrence.As shown in Fig.2,early recurrence (P<0.001) but not late recurrence (P= 0.692) was significantly lower in patients with PA-TACE in the crude cohort.The 6-,12-,and 24-month RFS rates of the PA-TACE group and the non PA-TACE group were 72.0%,58.8%,and 46.4% and 39.0%,30.7%,and 25.4%,respectively (P<0.001,Fig.2 A).The 3- and 5-year RFS rates of the PA-TACE group and the non PA-TACE group were 85.0% and 72.2%,and 87.6% and 71.1%,respectively (P= 0.692,Fig.2 B).
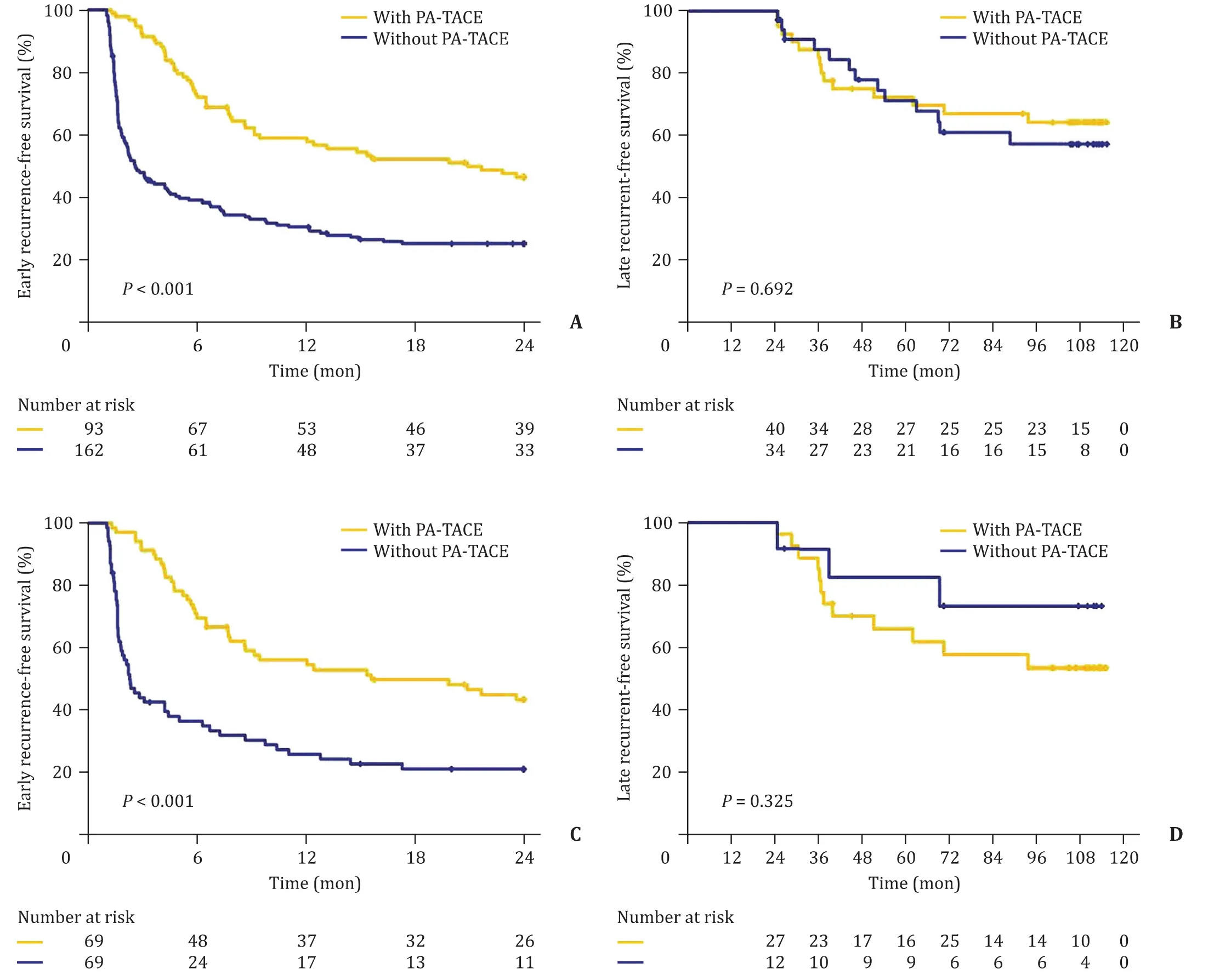
Fig.2.Cumulative incidence of early recurrence-free survival ( A and C ) and late recurrence-free survival ( B and D ) in huge hepatocellular carcinoma patients with and without postoperative adjuvant transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (PA-TACE) before ( A and B ) and after propensity score matching ( C and D ).
Comparison of the PSM cohort was performed with 138 patients and 39 patients in the early and late recurrence subgroups,respectively.The results indicated that the 6-,12-,and 24-month RFS rates of the PA-TACE group and the non PA-TACE group were 69.6%,56.1%,and 43.6% and 36.7%,26.0%,and 21.3%,respectively(P<0.001,Fig.2 C),and the 3- and 5-year RFS rates of the two groups were 85.2% and 66.0% and 91.7% and 82.5%,respectively(P= 0.325,Fig.2 D).
RFS and OS analyses
The results of the Cox regression analysis in the crude cohort are shown in Table 2.Multivariable analysis suggested that younger age,hepatitis B e antigen (HBeAg) positivity,multiple tumors,the absence of a capsule,and no PA-TACE were independent risk factors for RFS.HBeAb positivity,multiple tumors,the absence of a capsule,and no PA-TACE were independent risk factors for OS.

Table 2 Cox regression analysis of the crude cohort.
Table 3 presents the results of the Cox regression analysis in the PSM cohort.Multivariable analysis showed that younger age,multiple tumors,and no PA-TACE were significant risk factors for RFS.Multiple tumors and no PA-TACE were significant risk factors for OS.
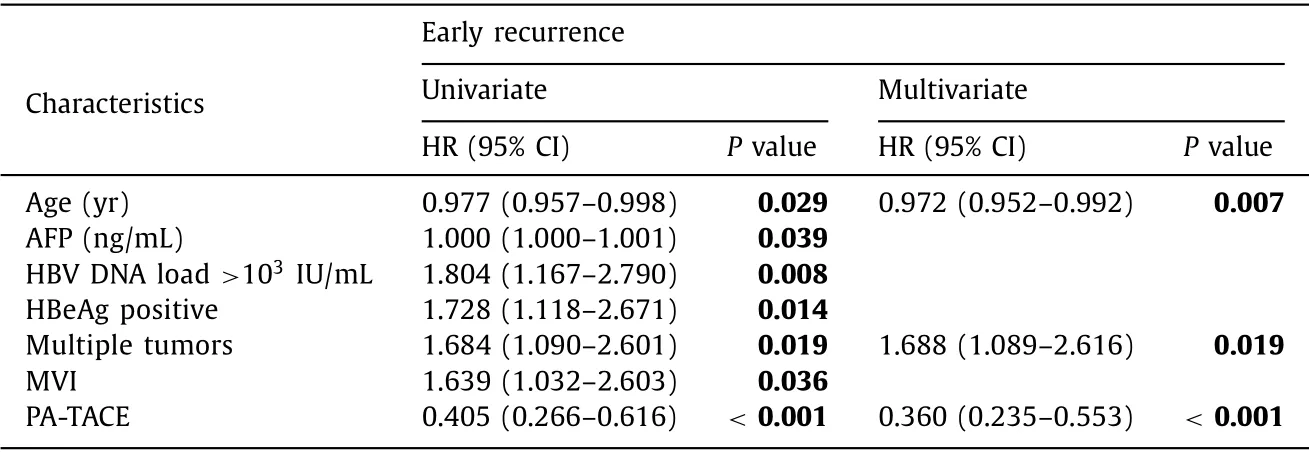
Table 5 Cox regression analysis of early recurrence for the propensity score matching cohort.
Survival analysisofearlyandlaterecurrence
Cox regression analysis of early and late recurrence in the crude cohort is presented in Table 4.According to multivariable analysis,younger age,multiple tumors,the absence of a capsule,the presence of MVI,and no PA-TACE independently affected early recurrence,and a higher platelet (PLT) count and anatomical liver resection were significantly protective factors against late recurrence.The recurrence patterns in patients are shown in Table S1.
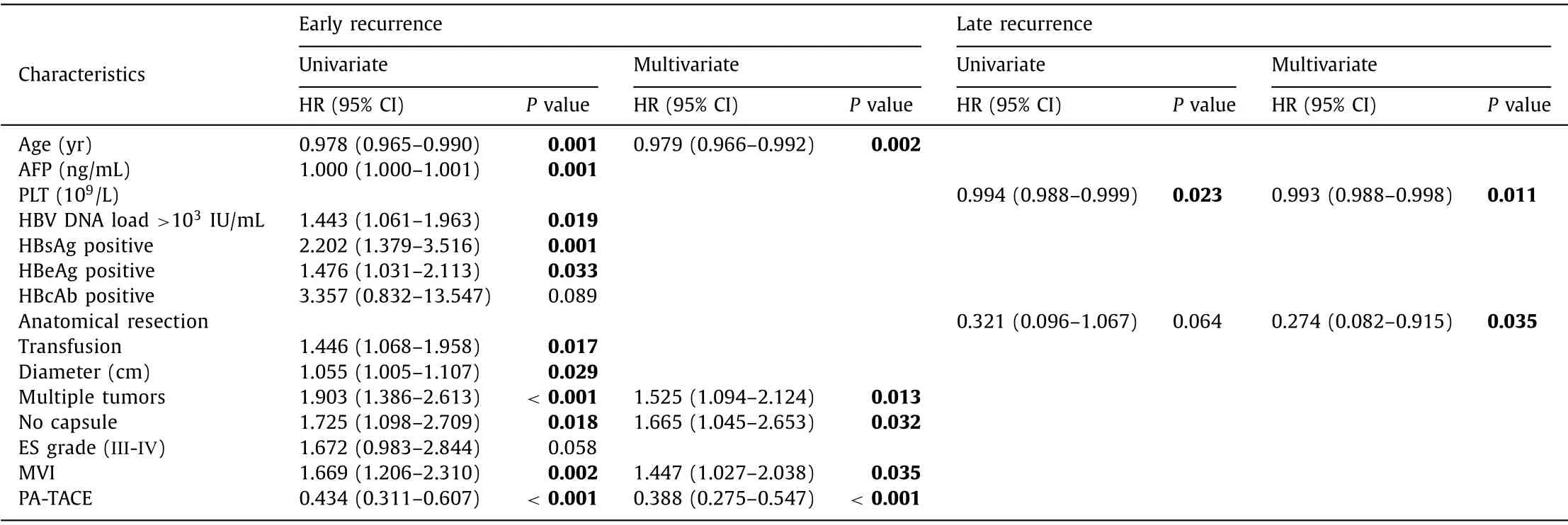
Table 4 Cox regression analysis of early and late recurrence for the crude cohort.
Cox regression analysis of early recurrence in the PSM cohort is presented in Table 5.Multivariable analysis showed that younger age,multiple tumors,and no PA-TACE were significant risk factors for early recurrence.However,univariable analysis showed that not a single variable had even marginally significant (P>0.05) association with late recurrence (data not shown); therefore,no further analysis was performed.
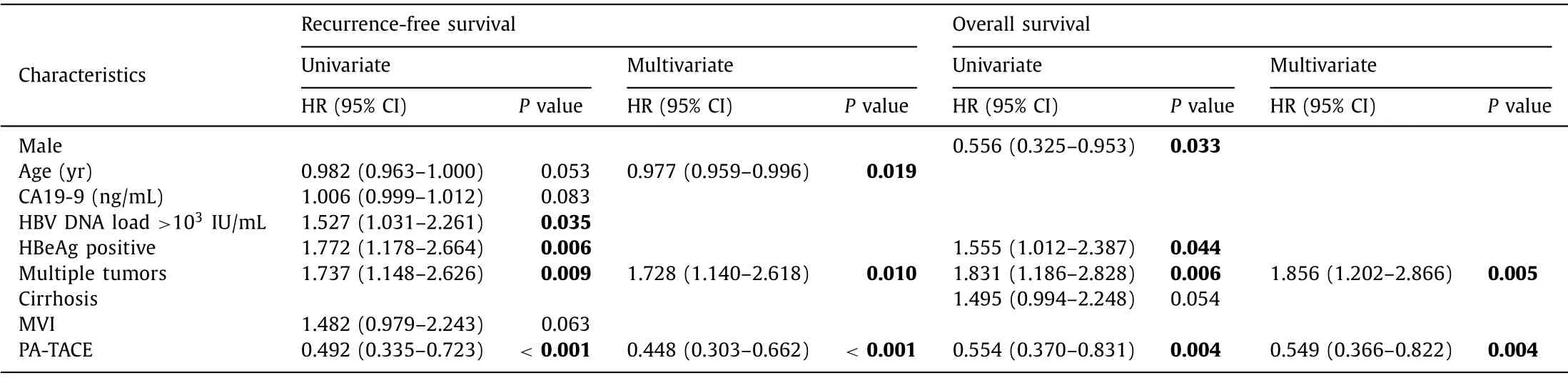
Table 3 Cox regression analysis of the propensity score matching cohort.
Discussion
The main reason for the extremely low OS of HCC is that most patients are diagnosed at an advanced stage,which means a large tumor size,multiple tumor nodules,and poor liver function.In other words,huge HCC has become one of the major concerns of the hepatologists over a long period of time.Numerous scholars have explored the best initial treatment method for these patients.For example,Min et al.and Zhu et al.found that liver resection resulted in a better prognosis than did TACE [ 21,22 ].Although some studies found that radiotherapy could be a safe and effective treatment option for these patients,the study cohorts all had unresectable huge HCC [ 23,24 ].Therefore,liver resection is the firstline therapeutic approach for huge HCC.However,due to distant recurrence,many patients have poor clinical outcomes after liver resection [8].Interestingly,recent studies have repeatedly shown that the multidisciplinary management of HCC patients is associated with higher rates of adherence to therapy and better patient survival [ 25,26 ],which means that the use of more treatment modalities before or after surgery is worth attempting to improve the prognosis of huge HCC patients.Consequently,we investigated various adjuvant therapies and found that there were controversial results regarding the use of PA-TACE.
TACE remains a valuable therapeutic modality for unresectable HCC because it induces tumor shrinkage and tumor necrosis.Although numerous patients have undergone TACE as an adjuvant therapy,patient selection is still controversial [ 27,28 ].A randomized controlled study confirmed that HCC patients with an intermediate (tumor size>5 cm) or high risk of recurrence (single tumor with MVI; 2 or 3 tumors) could benefit from PA-TACE [29].Another randomized controlled trial also suggested that PA-TACE is suitable for HCC patients with a solitary tumor ≥5 cm and MVI [30].Nevertheless,Liu et al.found that PA-TACE was an independent protective factor in the subgroup with tumors ≤5 cm but not in the subgroup with tumors>5 cm [31].The controversial results led us to hypothesize that the range of tumor size considered an indication for PA-TACE should be more stringently limited.The impact of PA-TACE on huge HCC patients warrants further investigation.
According to the results of our center,PA-TACE is safe for huge HCC patients.The curative effect of PA-TACE was encouraging.The median time of RFS and OS were significantly increased,showing that PA-TACE can serve as a part of new personalized treatment strategies.This conclusion was confirmed by PSM analysis,which also showed the improvements of median time of RFS and OS.In addition,the results regarding early and late recurrence demonstrated that PA-TACE only influences recurrence within 2 years.There is a consensus that early recurrence is likely due to residual cancer,while late recurrence suggests the probability of a newborn tumor [32].Considering the different origins of early and late recurrence,we conjecture that it is tremendously difficult to achieve the curative resection of huge HCC in absolute terms because of its highly malignant biological behavior,which means that there are tumor cells left after the operation that cannot be detected by imaging or serological examination; PA-TACE destroys those residual tumor cells,preventing or at least delaying intrahepatic recurrence.TACE is a type of endovascular operation that addresses the hematogenous metastasis of HCC [33],therefore,it has a beneficial effect on the prevention of early recurrence but not late recurrence.Another meaningful result was that anatomical resection could reduce the possibility of late recurrence,possibly because regular resection provides an excellent foundation for liver regeneration and therefore an appropriate liver context for avoiding long-term recurrence.We did not find any significant risk factors associated with late recurrence in the PSM cohort,which might be a type II error due to the small sample size.Furthermore,a recent study found that preoperative TACE was also correlated with improvement of RFS and OS after liver resection of huge HCC [34].Based on the above evidence,we recommend that adjuvant TACE and anatomical liver resection should be employed for all cases of huge HCC because of its superior ability to destroying the micrometastatic foci while preserving the functional liver parenchymal cells [ 35,36 ].
To the best of our knowledge,this is the first study to confirm the influence of PA-TACE on the recurrence and prognosis of huge HCC in a large-scale Chinese population.Moreover,PSM adequately balanced the clinicopathological parameters that might be confounding variables.Additionally,the difference in early and late recurrence provided us with more information about how PA-TACE works.
There are also some limitations in our study.First,potential biases were still inevitable due to the retrospective nature of our study.However,the following factors reduce the probability of bias influencing our results: (1) we did not include patients who experienced recurrence within one month after surgery or those who had severe liver dysfunction three months after surgery because it was not possible to perform PA-TACE in those patients.Excluding those patients meant that the included patients were afforded an equal opportunity to undergo PA-TACE.(2) PSM was performed to balance the baseline characteristics and reduce the effects of other parameters on patient prognosis.(3) The number of patients lost to follow-up three months after surgery was relatively small,meaning that losing patients to follow-up did not have a significant impact on the statistical analysis.(4) Our center is one of the largest liver surgery centers in Asia,performing over 3000 liver resections for HCC annually.The large department and number of doctors also reduce the probability of bias.(5) All huge HCC patients were considered at high risk of recurrence,making it less likely that patients with a low risk of recurrence would be selected intentionally for PA-TACE.The drugs and dosages involved in PA-TACE could vary across medical centers.It is important to formulate a PA-TACE protocol that considers both safety and effi-cacy.Additionally,a background of HBV infection existed in most patients included.Whether the results obtained in this study can be generalized to HCV-related or alcohol-related HCC needs further investigation.
In conclusion,the results of the current study indicate that PATACE is a worthwhile intervention in the management of patients with huge HCC.PA-TACE is a safe adjuvant treatment and is associated with improvement of RFS and OS after liver resection.In addition,anatomical liver resection could reduce the risk of late recurrence.
Acknowledgments
None.
CRediTauthorshipcontributionstatement
HanWang: Conceptualization,Data curation,Formal analysis,Writing - original draft,Writing - review & editing.HuaYu: Conceptualization,Data curation,Writing - review & editing.You-Wen Qian: Data curation,Writing - review & editing,Funding acquisition.Zhen-YingCao: Data curation.Meng-ChaoWu: Project administration.Wen-MingCong: Conceptualization,Funding acquisition,Writing - review & editing.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81472278 and 81502086) and the Scientific Research Foundation of the Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (20154Y0140).
Ethicalapproval
This study was conducted in accordance withtheDeclaration ofHelsinkiand the Ethical Guidelines for Clinical Studies of Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital of Shanghai.This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Eastern Hepatobiliary Surgery Hospital,and written informed consent forms were obtained from all participants.
Competinginterest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Supplementarymaterials
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at doi:10.1016/j.hbpd.2020.12.018.
 Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International2021年3期
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International2021年3期
- Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International的其它文章
- MEETINGS AND COURSES
- Reply to: Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A cost-effective alternative for low-resource settings
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: A cost-effective alternative for low-resource settings
- Transarterial chemoembolization as adjuvant treatment after surgery:The cure of huge hepatocellular carcinoma?
- RELEVANT CONTENT
- Variations of the hilar biliary confluence from postoperative cholangiography in Chinese population
