Immuno-oncology in triple-negative breast cancer
Anne-Sophie Heimes,Marcus Schmidt
Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,University Medical Center Mainz,Mainz 55131,Germany.
Abstract The immune system plays an important role in breast cancer.Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) has a higher mutational load compared to other subtypes.In addition,higher levels of tumor-associated antigens suggests that immunotherapies are a promising treatment option especially for TNBC.Our review discusses both the complexity of the immune system and the cancer immune-cell cycle.In fact,a higher level of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is associated with an improved prognosis as well as a better response to chemotherapy in TNBC.Important target structures within the cancer immune-cell cycle are the so-called“immune checkpoints”.Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICPi) block the interaction of certain cell surface proteins that serve as“brakes”of immune reactions.Recent studies have shown ICPi improved survival in early as well as advanced TNBC.However,this has the price of increasing,mainly,immune-mediated toxicity.ICPi strengthen tumor-specific T cell-mediated immunity by“releasing the brake”of the immune system.In combination with chemotherapy,ICPi are already approved for TNBC.As a further step,individualized vaccination strategies against tumor-associated neoantigens represent another promising approach.A liposome-formulated intravenous RNA vaccine encoding different tumorassociated antigens is currently being studied in TNBC and leads to neoantigen-specific immune responses.These novel strategies will improve the prognosis of patients with triple-negative breast cancer.
Keywords: Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes,cancer-immunity-cycle,immune checkpoint inhibitors,vaccination,tumor-associated antigens,neoantigens
INTRODUCTION
The role of the immune system in breast cancer has been discussed for decades[1].Especially triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC),which has a more pronounced immunogenic potential compared to other molecular subtypes,has become a focus of interest.TNBC accounts for 15%-20% of breast cancers and is associated with a significantly poorer prognosis in the first few years after diagnosis when compared with other breast cancer subtypes[2].It is now generally accepted that TNBC is not a homogeneous disease but consists of several subtypes (e.g.,basal-like 1 and 2,immunomodulatory,mesenchymal,mesenchymal stem-like,and luminal androgen receptor)[3].In TNBC,significantly more somatic mutations and neoantigens are detected than in other molecular subtypes,which speaks for an increased immunogenicity[4].Indeed,it could be shown that transcripts of immune cells as well as tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) have their strongest prognostic and predictive influence in TNBC.
Prognostic and predictive relevance of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes
A reproducible favorable prognostic influence of immune cells was shown slightly more than a decade ago using gene expression analyses[5-8].These initially retrospective results were confirmed in numerous studies using gene expression analyses[9]as well as histological detection of TILs in archival tissue of randomized studies[10].Especially in triple-negative breast cancer,there is a close association between TILs and a more favorable prognosis or better response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy[10-15].This significant association of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and TNBC is not surprising when considering that the total mutational burden is highest in TNBC[4].In addition,these authors also found that the mutational burden was highly correlated with the neoepitope load (R2=0.86).Indeed,an exhaustive analysis of immunogenic signatures in TNBC based on two large-scale breast cancer genomic datasets showed that TNBC had the strongest immunogenicity among breast cancer subtypes[16].Furthermore,these authors also confirmed that TNBC has a higher degree of immune cell infiltration and a higher expression of genes encoding for immune checkpoints than non-TNBC.However,mutational and neoantigen load seem to only incompletely explain immune responses in TNBC since other studies have described an inverse association between immune infiltration and somatic copy number alterations[17,18].Obviously,the exact relationship among immune infiltration,mutational load,and neoantigen load is not yet fully understood.Nonetheless,TILs are widely used especially in TNBC.To improve reproducibility,a standardized methodology for evaluating TILs was defined to integrate this parameter in standard histopathological practice[19].However,TILs are not yet regularly used in routine diagnostics.
COMPLEXITY OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
The role of the immune system in the breast cancer microenvironment is Janus-faced.In addition to tumorinhibiting acute inflammation orchestrated by type 1 T-helper cells (TH1) through CD8 lymphocytes,B cells,or M1 macrophages,tumor-promoting,TH2-directed chronic inflammation through M2 macrophages,regulatory T-cells,or immune checkpoints such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) or its ligand programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) can also occur.Furthermore,bone marrow-derived cells such as myeloid-derived suppressor cells and mesenchymal stromal cells can exert pro-tumorigenic effects through negative regulation of immune responses[20].The immunoediting,i.e.,the dynamic interaction between the immune system and the tumor,leads to different stages of tumor evolution (elimination-equilibrium-escape)[21].
Cancer-immunity cycle
To achieve the destruction of cancer cells by the immune system,different stages must be passed through step by step,which are collectively referred to as the cancer-immunity cycle [Figure 1][22].
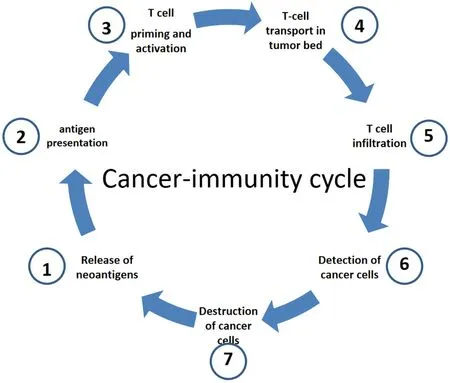
Figure 1.Cancer-immunity cell cycle (modified from[22]).In a first step,neoantigens are released by cancer cells (1).These neoantigens are then absorbed by dendritic cells (DC).Subsequently,DCs present the antigens to the T cells on major histocompatibility Complex(MHC) I and MHC II molecules (2).This leads to activation of T-cell responses against cancer-specific antigens (3) that are considered foreign or for which central tolerance is incomplete.The activated T cells are then transported into the tumor bed (4) where they infiltrate the tumor (5).Once there,the T cells can specifically recognize (6) and destroy (7) cancer cells through the interaction between their T cell receptor (TCR) and the tumor-specific antigens bound to MHC I.The destruction of the cancer cells releases additional tumor-associated antigens (1),which in turn strengthens the immune response.
Even though the cancer-immunity cycle is only partially functional in many patients with malignant tumors,it is a finely balanced interplay of stimulating and inhibitory signals in order to trigger an effective immune reaction on the one hand and to prevent an excessive immune reaction leading to the development of autoimmunity on the other hand.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Important target structures within the cancer immune-cell cycle are the so-called “immune checkpoints”.Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICPi) block the interaction of certain cell surface proteins that serve as “brakes” of immune reactions.Currently,the most relevant immune checkpoint in breast cancer is PD-1/PD-L1[23,24].The reaction of PD-1 on T cells with PD-L1,which can be expressed on both T cells and tumor cells,leads to inhibition of the T cell-mediated immunity against the tumor.However,mechanisms underlying PD-1 upregulation in tumor-infiltrating T cells are not completely understood.For instance,Liuet al.[25]showed that tumor-repopulating cells lead to PD-1 upregulation in CD8-positive T cells through a transcellular kynurenine (Kyn)-aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) pathway.Thus,tumor-repopulating cells escape immune-mediated killing by inducing high PD-1 expression through an IDO-Kyn-AhR-dependent mechanism.Importantly,a pharmacological inhibition of this pathway might also be an efficacious alternative strategy for targeting PD-1 in cancer.In addition,the A2A adenosine receptor is an important negative regulator of immune cells in protecting normal tissues from inflammatory damage[26].Again,there are several pharmacological strategies using selective antagonists to block this pathway and thereby increase anti-tumor immunity[27].
However,at present,monoclonal antibodies,so-called immune checkpoint inhibitors,which block PD-1 or PD-L1 (e.g.,pembrolizumab,nivolumab,or atezolizumab) are increasingly used to “release the brake” of the immune system and thus to increase the activity of the immune system against the tumor.The monoactivity of ICPi such as atezolizumab or pembrolizumab was present but manageable in Phase I studies in advanced and extensively pretreated TNBC[21].Especially in less heavily pretreated patients,few but longlasting responses were noticed[28].In a Phase III trial (KEYNOTE-119) in pretreated advanced TNBC,pembrolizumab monotherapy did not significantly improve overall survival compared with single agent chemotherapy,although the pembro treatment effect increased as PD-L1 enrichment increased[29].However,the effectiveness can be significantly increased by adding chemotherapy.Indeed,chemotherapy can lead to immunogenic cell death,which in turn activates the antitumor immune response[30].The combination of immunotherapy with chemotherapy should therefore achieve additive or synergistic clinical activity[31].
Due to the specific mode of action of immune therapies,which in contrast to cytotoxic chemotherapy have no direct effect on tumor cell proliferation,a therapeutic response may be expected at a later stage.In addition,the infiltration of immune cells can lead to an initial increase in the size of the metastases,a so-called pseudoprogression.However,this pseudoprogression occurs in less than 10% of cases,while,conversely,a very rapid increase in size,a so-called hyperprogression,can occur in up to 29% of cases.Continuation of therapy with ICPi with imaging evidence of progression should therefore only be considered if the clinical condition has improved and there are no treatment-related toxicities[32].
ICPi in advanced breast cancer
A Phase I study evaluated the safety and clinical activity of the PD-L1 antibody atezolizumab in 116 patients with metastatic,extensively pretreated TNBC[33].PD-L1 expression was evaluated immunohistochemically on immune cells as well as on tumor cells.The clinical response rate was determined in the whole cohort,as well as PD-L1 expression and immune cell infiltration within defined subgroups depending on the therapy line.The clinical response rate within the total cohort was 10%.Progression-free survival (PFS) was 1.2 months and overall survival (OS) 17.6 months.Response rates and overall survival were significantly higher in the subgroup with PD-L1-positive immune cells as well as in the first line therapy.The number of TILs was shown to be an independent prognostic and predictive marker and correlated with longer overall survival and better clinical response rates.
For the PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab,several early phase studies showed the efficacy and tolerability as monotherapy.Nanda and co-workers showed in 32 heavily pretreated TNBC patients enrolled in the Phase IB KEYNOTE-012 study that pembrolizumab had an overall response rate of 18.5% and a median time to response of 17.9 weeks with an acceptable safety profile[34].Building on these encouraging findings,pembrolizumab was evaluated in the Phase II study KEYNOTE-086.In Cohort A,pembrolizumab was evaluated as second or later line of treatment for patients with advanced TNBC[35].In total,170 TNBC patients were enrolled; the objective response rate (ORR) was 5.3% in all patients and 5.7% in PD-L1-positive patients.Median OS was 9.0 months with 12.9% Grade 3/4 treatment-related adverse events (AE).In Cohort B,84 PD-L1-positive advanced TNBC patients were treated with 200 mg pembrolizumab as firstline therapy[28].ORR was 21.4%,median duration of response was 10.4 months,and median OS was 18.0 months with 9.3% Grade 3 adverse events.The authors concluded that pembrolizumab monotherapy had a manageable safety profile and showed durable antitumor activity as first-line therapy for patients with PDL1-positive metastatic TNBC.
In the adaptive,non-comparative Phase II trial TONIC,Voorwerket al.[36]evaluated several strategies (e.g.,irradiation,low-dose cyclophosphamide,cisplatin,and doxorubicin) to make the tumor microenvironment more sensitive to PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in 67 patients with advanced TNBC.In the whole cohort,the objective response rate was 20%.The majority of responses were noticed in the doxorubicin (35%) and the cisplatin (23%) cohorts.Interestingly,the authors noticed in these two cohorts an upregulation of immune-related genes and speculated that this induction approach might induce a more favorable tumor microenvironment and increase the likelihood of response to PD-1 blockade in TNBC.
Another approach to increase the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade in advanced cancer is the combination with poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi).In the MEDIOLA basket trial,durvalumab and olaparib were combined in solid tumors[37].This combination showed promising antitumor activity and safety.Twenty-four of 30 evaluable patients (80%) had disease control at 12 weeks.While the above combinations are interesting and promising,the combination of ICPi with chemotherapy is currently the most straightforward approach.In a Phase Ib study,the safety and clinical activity of atezolizumab in combination with nanoparticle albumin-bound (nab)-paclitaxel was evaluated in a cohort of 33 extensively pretreated patients with advanced TNBC[38].The rationale for combining an immune checkpoint inhibitor with chemotherapy is a postulated stronger activation of T cell-mediated immunity due to an increased release of tumor-associated antigens and resulting immunogenic cell death[31].Primary endpoints of the study were safety and dose finding.Of the 33 patients enrolled in the study,24 (73%) developed Grade 3/4 toxicities.The secondary endpoint was the clinical activity of the combination of chemotherapy and ICPi.The ORR within the total cohort was 39.4% with a median duration of 9.1 months.The PFS was 5.5 months and the OS 14.7 months.The combination with nab-paclitaxel did not lead to an impairment of immune activation by atezolizumab.The results of the study show that the combination of ICPi and nab-paclitaxel is an effective treatment option with a tolerable side effect profile for patients with metastatic TNBC.
Building on these encouraging results,the Phase III study IMpassion130 confirmed the clinical efficacy of atezolizumab in combination with nab-paclitaxel as first-line therapy in a cohort of 902 patients with metastatic or locally advanced TNBC[39].Patients were randomized to either the experimental arm (atezolizumab combined with nab-paclitaxel) or the placebo arm (nab-paclitaxel + placebo) in a 1:1 ratio.The results show significantly prolonged PFS in both the intention to treat (ITT) population and the PDL1-positive subgroup: PFS was 7.2 months in the experimental arm compared to 5.5 months in the placebo arm [hazard ratio (HR) 0.80; 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.69-0.92;P= 0.002].In the subgroup of PDL1-positive (≥1% of immune cells) TNBC patients,PFS was 7.5 months compared to five months in the placebo arm.Atezolizumab in combination with nab-paclitaxel prolonged OS in PD-L1-positive patients (25.0 monthsvs.15.5 months).Based on these results,atezolizumab in combination with nab-paclitaxel is now approved as first-line therapy in advanced PD-L1-positive TNBC.In a recent analysis of IMpassion130,Schmidet al.[40]showed that atezolizumab did not significantly increase OS in the total cohort from 18.7 to 21 months at longer follow-up (HR 0.86; 95%CI: 0.72-1.02;P=0.078).In PD-L1-positive patients,however,OS was prolonged from 18 to 25 months (HR 0.71; 95%CI: 0.54-0.94).The authors concluded that a clinically meaningful overall survival benefit with atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel was found in patients with PD-L1 immune cell-positive disease.Furthermore,they postulated that atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel is an important therapeutic option in a disease with high unmet need.Surprisingly,the recently presented IMpassion131 study,which combined atezolizumab with conventional paclitaxel in advanced TNBC,did not improve PFS or OSvs.placebo + paclitaxel[41].Potential reasons for this obvious contrast with the benefit seen in IMpassion130 still need further exploration,although several hypotheses (e.g.,differences within the study population as well as different taxanes and the role of steroids) are under discussion[42].
At the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology,Cortes et al.[43]presented results of KEYNOTE-355,a randomized,double-blind,Phase III study of pembrolizumab + chemotherapy versus placebo + chemotherapy for previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic triplenegative breast cancer.They showed that pembrolizumab combined with several chemotherapy partners (nab-paclitaxel,paclitaxel,or gemcitabine/carboplatin) showed a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in PFS versus chemotherapy alone in patients with previously untreated locally recurrent inoperable or metastatic TNBC whose tumors expressed PD-L1.Furthermore,pembrolizumab + chemotherapy was generally well tolerated,with no new safety concerns.This study was recently published in full[44].Based on their findings,the authors concluded that the addition of pembrolizumab to standardchemotherapy has a role in the first-line treatment of advanced triple-negative breast cancer.The findings of Phase III studies in advanced TNBC are summarized in Table 1.
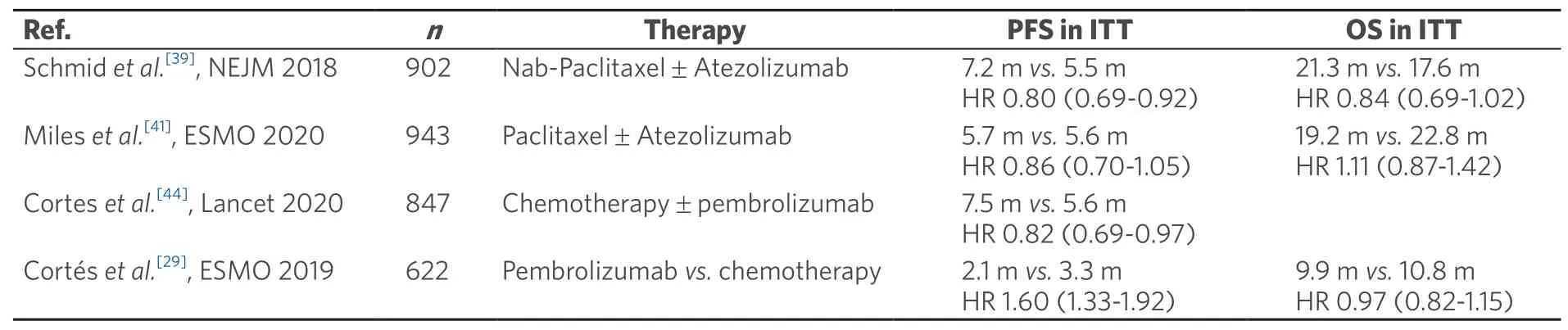
Table 1.Randomized evidence Phase III for ICPi in advanced triple-negative breast cancer
ICPi in early breast cancer
Due to the effectiveness of ICPi in advanced breast cancer,studies have also been initiated in early TNBC.In a randomized Phase II study in early TNBC,the PD-L1 antibody durvalumab was combined with an anthracycline- and taxane- containing neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) in 174 TNBC patients[45].Overall,87% of the patients were PD-L1-positive.Pathologic complete remission (pCR) was increased from 44.2% to 53.4% with durvalumab.A significant increase in pCR was found in the subgroup (n=117) who received neoadjuvant durvalumab for two weeks before the start of NACT (61%vs.41.4%;P=0.035).Immune-mediated thyroid dysfunction occurred in 47% with overall good tolerability.Interestingly,a pre-planned exploratory analysis of this study showed that both tumor mutational burden (TMB) and an immune gene expression profile (GEP) independently predicted pCR in TNBC patients[46].In patients with both high TMB and GEP,pCR rate was 82% in contrast to 28% in the group with both low TMB and GEP.These findings encourage further analysis of TMB in combination with immune parameters to individually tailor therapies in breast cancer.
Furthermore,pembrolizumab in addition to standard taxane- and anthracycline- based NACT was evaluated in the adaptively randomized I-SPY Phase II study[47].In TNBC,pembrolizumab increased pCR from 22% to 60% with an acceptable safety profile.
In the neoadjuvant Phase III study KEYNOTE-522,1174 patients with early TNBC neoadjuvant were treated with anthracycline-,taxane- and platinum- containing chemotherapy ± pembrolizumab[48].The addition of pembrolizumab significantly increased pCR from 51.2% to 64.8% (P=0.00055).This increase in pCR was observed independent of the PD-L1 status.Additionally,pembrolizumab improved event-free survival (HR 0.63; 95%CI: 0.43-0.93).Grade 3/4 toxicities were also increased with pembrolizumab (78%vs.73%).
The NeoTRIPaPDL1 Michelangelo randomized study investigated neoadjuvant nab-paclitaxel treatment with or without atezolizumab in triple negative,early high-risk,and locally advanced breast cancer,failing to show a significant increase of pCR with atezolizumab[49].Recently,however,results for efficacy and safety of atezolizumabvs.placebo combined with nab-paclitaxel followed by doxorubicin plus cyclophosphamide as neoadjuvant treatment for early-stage TNBC were presented[50].In total,333 patients with early TNBC were enrolled in the double-blind,randomized,Phase III study IMpassion031.Atezolizumab increased pCR from 41% to 58%.In the PD-L1-positive population,pCR was increased from 49% to 69%.Treatmentrelated serious adverse events occurred in 23% and 16%,respectively.The authors concluded that neoadjuvant treatment with atezolizumab in combination with nab-paclitaxel and anthracycline-basedchemotherapy improved pCR in early TNBC patients with an acceptable safety profile.The findings of Phase III studies in early TNBC are summarized in Table 2.
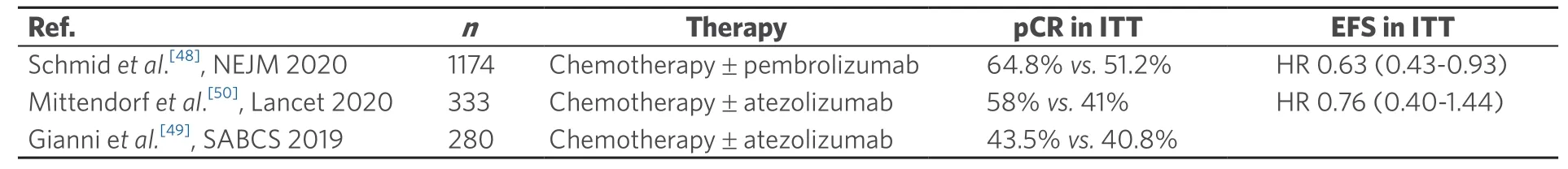
Table 2.Randomized Phase III evidence for ICPi in early triple-negative breast cancer
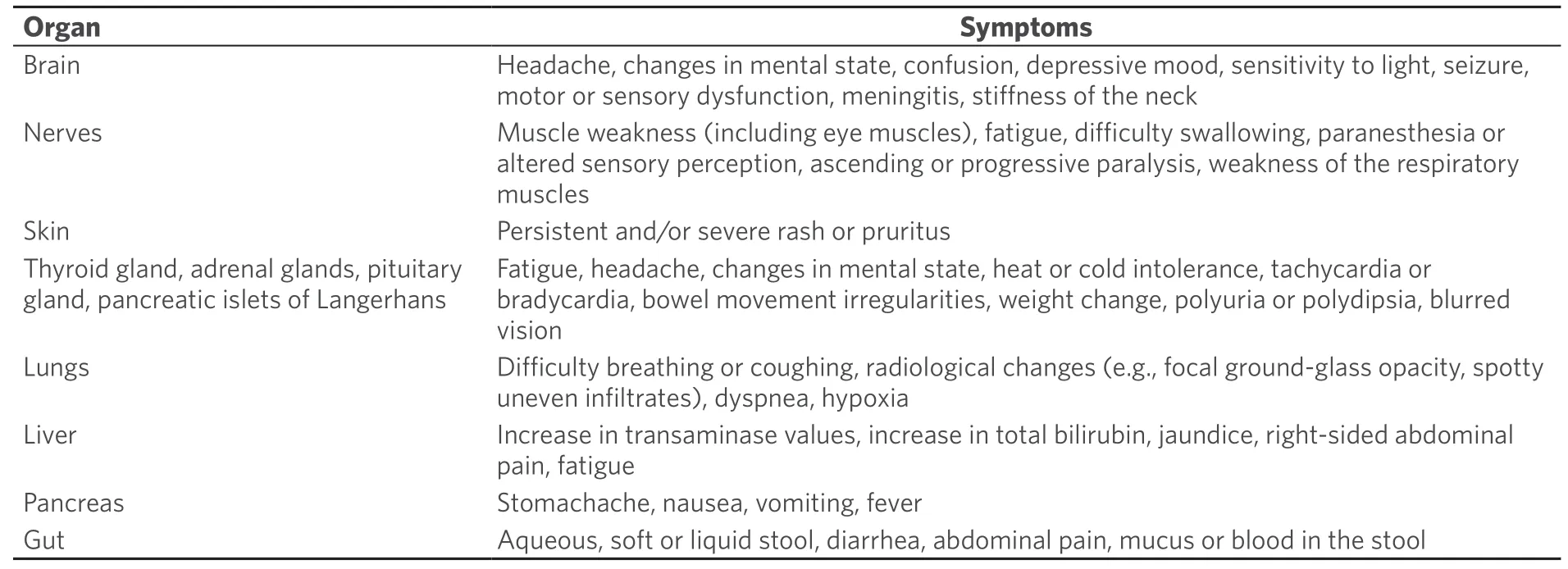
Table 3.Immune-mediated adverse effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors
In fact,all these randomized studies using ICPi in early or advanced breast cancer showed a significant advantage over standard therapy alone.In combination with an acceptable safety profile,immune checkpoint inhibitors are a promising new therapeutic option in TNBC.
Predictive markers for immune checkpoint inhibitors
At present,the only established predictive biomarker for the response to ICPi in advanced TNBC is PDL1 status.Recent analyses show a potential role for tumor mutational load (TMB) for the response to durvalumab in early TNBC[46].In a recently published comprehensive genomic analysis of 3831 consecutive breast cancer samples,potential biomarkers [e.g.,TMB,microsatellite instability (MSI),and BRCA mutations] to guide the use of ICPIs for these patients were evaluated[51].However,for all these potential biomarkers,prospective randomized trials will be necessary to assess the predictive value for the response to immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Adverse events of immune checkpoint inhibitors
Adverse events of ICPi are mainly explained by the mode of action.ICPi block so-called immune checkpoints,which act as a “brake” on triggered immune reactions.
When this “brake” is blocked by antibodies such as ICPi,an unhindered immune reaction can occur,which can also affect the body’s own tissues through autoimmune phenomena.This is associated with a spectrum of side effects related to the mechanism of action.Side effects may affect several organs of the body and are most commonly found in the skin,gastrointestinal tract,lungs,thyroid,adrenal gland,pituitary gland,kidney,nervous system,and musculoskeletal,ocular,or cardiovascular system[52][Table 3].Duringtreatment,it is important to note that these immune-mediated side effects may occur after very different time intervals and sometimes even after the end of therapy with ICPi.
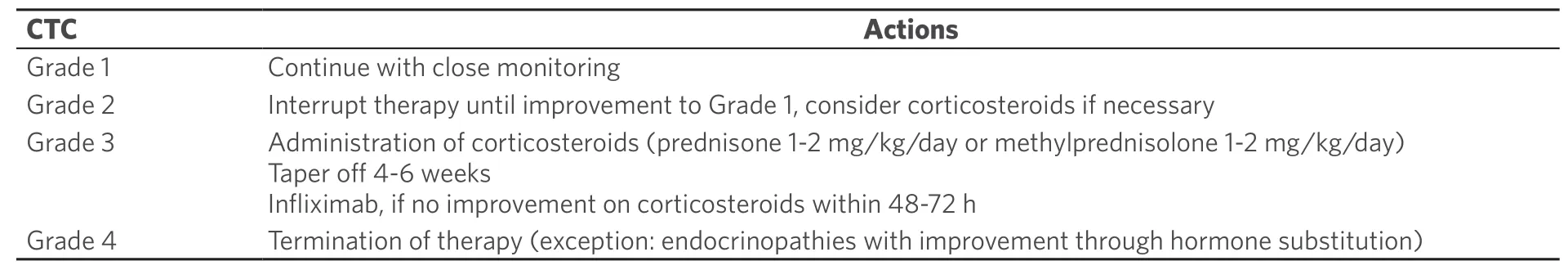
Table 4.Management of adverse effects of immune checkpoint inhibitors (modified from[52])
Management of adverse events
Early diagnosis and therapy can reduce the severity and duration of immune-mediated side effects.The proper management of these adverse events is therefore essential.Depending on the severity of the side effects,different measures are recommended.In the case of pronounced worsening of symptoms,therapy with corticosteroids or even termination of treatment with ICPi is required [Table 4][52].
Vaccination
Improving the antigen presentation by vaccination to trigger a protective immune response against breast cancer is an obvious strategy.However,vaccinations against solid tumors such as breast cancer have thus far only shown limited efficacy.In most cases,known antigens such as HER2 were used,but these vaccination strategies have not yet shown clinically relevant success[53].A fundamental disadvantage of this approach is that the immune reactions against known self-antigens such as HER2 are mostly weak,since the T lymphocytes,which have a high affinity against these self-antigens,are subject to central tolerance.Using high-throughput mutation analysis methods such as Next Generation Sequencing (NGS),individual non-synonymous somatic mutations (the so-called mutanome) are increasingly coming into focus[54].These mutations are not subject to central immunological tolerance[55].The resulting neoantigens are therefore ideally suited for individual vaccination.With the help of complex prediction algorithms,which consider among others the MHC binding affinity,the neoantigens with the highest expected immunogenicity are selected from the mutanome of a tumor.The RNA of these neoantigens is used as vaccine and applied intravenously.In a first step,the RNA is translated into the corresponding protein in dendritic cells.The further processing of these neoepitopes is performed on the one hand via the proteasome with subsequent antigen presentation via MHC I and consecutive stimulation of cytotoxic CD8 T cells,which leads to tumor cell destruction.On the other hand,the endosomal route leads to presentation via MHC II with activation of CD4 T cells[55].While the focus of anti-tumor immunity research has long been on MHC I and CD8 T cells,it could be shown in mouse models that the majority of immunogenic mutations are presented via MHC II and recognized by CD4 T cells[56].In the meantime,the clinical efficacy of an individual RNA vaccination against the individual mutanome of a tumor in patients with advanced malignant melanoma has been described[57].
Building on these encouraging findings,we conducted a Phase I study in early TNBC after completion of standard (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy [Mutanome Engineered RNA Immuno-Therapy (MERIT)][58].The aim of this study was to demonstrate feasibility,safety,and biological efficacy of a liposome-formulated intravenous RNA vaccine encoding different tumor antigens.Patients received eight intravenous vaccinations,either with a personalized RNA vaccine based on the antigen expression profile of the respective tumor or with an individualized RNA vaccine against up to 20 neoepitopes identified by NGS.Recently,we reported at the annual meeting of the European Society of Medical Oncology preliminary results of immune responses in vaccinated patients as analyzed by interferon-gamma (IFNγ)-ELISpot,multimerstaining,TCR repertoire profiling,and single cell TCR sequencing[59].A substantial number of T cell responses against individual neoepitopes were inducedde novoand of high magnitude.In addition,the T cell response was sustained at high levels for at least six months after the last vaccination.This suggests that the individualized vaccination is highly efficient in inducing strong poly-epitopic T-cell responses in patients with TNBC in the post-(neo)adjuvant setting.In fact,as an important effector cytokine for anticancer immunity,IFNγ also has independent prognostic significance in basal-like or tiple-negative breast cancer,which supports a beneficial effect of IFNγ-mediated immune responses through vaccination[60].
With this vaccination strategy,T cell responses against tumor-specific neoantigens can be triggered.Such vaccines may lead to an increase in immunogenicity of tumors lacking spontaneous immunogenicity,which should make these tumors more responsive to treatment with ICPi.Therefore,a combination of RNA vaccination with ICPi might be useful to stimulate the body’s immune system against tumor cells,including in ICPi-experienced patients[61].
The long-term goal of this individualized vaccination against non-synonymous mutations in early triplenegative breast cancer is to hit the Achilles heel of these tumors and thus significantly improve the prognosis of affected patients.
CONCLUSION
The immune system plays an important role in triple-negative breast cancer.A high expression of tumorinfiltrating lymphocytes or immune transcripts is associated with an improved prognosis as well as an increased response to chemotherapy.Novel therapies such as immune checkpoint inhibitors have improved survival in triple-negative breast cancer.Management of side effects is of essential importance.Individualized vaccination strategies against the mutanome of a tumor are promising.
DECLARATIONS
Authors contributions
Made substantial contributions to the conception and drafted the work: Heimes AS,Schmidt M
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflict of interest
Schmidt M has been a consultant to Astra Zeneca,Celgene,Eisai,Novartis,Pfizer and Roche and has received consulting fees from these companies as well as from Lilly,Merck,Myelo Therapeutics,Pantarhei Bioscience and Pierre-Fabre.Research support was received from AstraZeneca,BioNTech,Eisai,Genentech,Myelo Therapeutics,Novartis,Pantarhei Bioscience,Pfizer,Pierre-Fabre and Roche.Heimes AS reports no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Copyright
? The Author(s) 2021.

