Immunostimulatory effect of ethanol extract of Chondracanthus tenellus in RAW 264.7 macrophages in vitro
Cheol Park, Da Hye Kwon, Hyesook Lee, Su Hyun Hong, Gi-Young Kim, Hee-Jae Cha, Do-Hyung Kim, Suhkmann Kim, Heui-Soo Kim, Hye-Jin Hwang, Yung Hyun Choi?
1Division of Basic Sciences, College of Liberal Studies, Dong-eui University, Busan 47340, Republic of Korea
2Anti-Aging Research Center, Dong-eui University, Busan 47340, Republic of Korea
3Department of Biochemistry, College of Korean Medicine, Dong-eui University, Busan 47227, Republic of Korea
4Department of Marine Life Sciences, School of Marine Biomedical Sciences, Jeju National University, Jeju 63243, Republic of Korea
5Department of Parasitology and Genetics, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Busan 49104, Republic of Korea
6Department of Aquatic Life Medicine, College of Fisheries Science, Pukyong National University, Busan 48513, Republic of Korea
7Department of Chemistry, College of Natural Sciences, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Republic of Korea
8Department of Biological Sciences, College of Natural Sciences, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, Republic of Korea
9Department of Food and Nutrition, College of Nursing, Healthcare Sciences & Human Ecology, Dong-eui University, Busan 47340, Republic of Korea
ABSTRACT
KEYWORDS: Chondracanthus tenellus; Immunomodulatory property; TLR4; NF-κB
1. Introduction
The disorder of the immune system damages the mechanisms of the host defense, leading to a number of pathological changes.Macrophages derived from blood monocytes are key immune cells that act as effector cells fighting against inflammation or initiating innate immune responses[1,2]. Monocytes are mononuclear phagocytic cells that can activate in response to microbial pathogens infection[2].Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is the major outer membrane component of Gram-negative bacteria, which activates monocytes through interaction with Toll-like receptors (TLRs), and resultingly triggers activation of macrophages[3,4]. Consequently, pathogens, foreign substances,and cellular debris can be eliminated through phagocytosis, the cornerstone of the innate immune response. At the same time, activated macrophages are reported to neutralize pathogens through the secretion of inflammatory cytokines and mediators or indirectly participate in immune regulation. In addition, they increase immune-enhancing activity through the processing and presentation of antigens to lymphocytes[5,6]. Currently, various drugs are used to regulate immune function to prevent and treat chronic diseases. However, most of them are toxic or have side effects, so their use is limited[7,8]. Therefore,the activation of macrophages using non-toxic natural products is considered a promising strategy to enhance host immune function.
Various types of marine organisms have long contributed to the food resources or the prevention and treatment of diseases, owing to their rich bioactive substances. Recently, many studies have shown that the extracts or ingredients of edible marine algae have significant immunomodulatory properties[9-11]. As immune modulators,they interact with the immune system to suppress or enhance host responses[12,13]. For example, various marine algae extracts possess immunostimulants and have been reported to inhibit immunodeficiency virus activity[14-16]. Certain seaweed components enhanced immunomodulatory effects through the maturation of dendritic cells and the activation of T and natural killer cells[17-19]. In other studies,polysaccharides isolated from marine algae stimulated macrophage activity while increasing the secretion and production of various cytokines and immunomodulatory mediators through activation of the TLR4 and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) pathways. They also promoted phagocytosis and enhanced the cytotoxicity of macrophages toward tumor cells[11,20-25]. These features suggest that marine algae are highly applicable as a therapeutic agent or supplement for immune regulation.Chondracanthus tenellus (C. tenellus) (Harvey) Hommersand, a red algae, is widely distributed across the coastal areas of Japan and China,including Korea. This algae is rich in sulfated polysaccharides and minerals such as calcium carbonate and has been used for the long term as a source of food in these regions. Piao et al.[26] reported that the protective effect of C. tenellus extract against ultraviolet B radiationinduced cytotoxicity in human keratinocytes was associated with strong antioxidant activity. However, despite the possibility that C. tenellus may have a variety of bioactivities, no other pharmacological efficacy studies have been conducted until now. In this respect, it is worth to estimate whether C. tenellus could be considered as a promising strategy to enhance host immune function. Therefore, in present study,we evaluated the immune modulatory effect of an ethanol extract of C.tenellus (EECT) using the RAW 264.7 cells.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Cell culture and EECT preparation
The RAW 264.7 cells (Korean Cell Line Bank, Seoul, Republic of Korea), monocyte/macrophage-like cells, were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum and antibiotics (all from WelGENE, Inc., Daegu, Republic of Korea) in an incubator with 5% COat 37 ℃. The cells were grown over to 80%-90% confluency in all experiments. EECT was obtained according to a previous study[26] and was kindly provided by Dr. Jin Won Hyun (School of Medicine, Jeju National University,Jeju, Republic of Korea). A 300 mg/mL stock solution of EECT was prepared in dimethyl sulfoxide (Invitrogen-Gibco, Carlsbad, CA,USA), and dissolved to final treatment concentrations in culture medium before used.
2.2. Cell viability assay
The cells were exposed with EECT (50-300 μg/mL) or 0.5 ng/mL LPS (Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO, USA) for 24 h. Cell viability was measured using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) (Invitrogen, Carlsbad,CA, USA) solution, as previously described[27]. The absorbance was detected at 540 nm using a microplate reader (Molecular Devices Co., Sunnyvale, CA, USA). The LPS-treated cells were considered a positive control for activating the macrophages, while the non-treated cells were considered as negative controls. Cell morphology was observed by phase-contrast microscopy (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen,Germany).
2.3. Phagocytosis assay and morphology observation
Cells were treated for 24 h and then the phagocytic activity was evaluated using a Phagocytosis Assay Kit (Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions. The fluorescence intensity was also measured by a flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) as previous described[28].
2.4. Determination of NO production
At 24 h after treatment, the cell supernatants were collected. The collected supernatants were mixed with an equal volume of Griess reagent solution (Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co.), and then incubated for 30 min. The absorbance was detected with a microplate reader at 540 nm[29].
2.5. Determination of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and cytokine production
PGEenzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit was purchased from Cayman Chemical (Ann Arbor, MI, USA). ELISA kits for tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukin-1(IL-1)β, IL-6,and IL-10 were obtained from R&D Systems, Inc. (Minneapolis,MN, USA). At 24 h after treatment, the cell supernatants were collected and the levels of PGEand cytokines in the cell supernatants were quantified according to the vender’s instructions.Standard curves prepared from standard samples were used to calculate the PGEand cytokine production.
2.6. Western blotting assay
At 24 h after treatment, total cell lysates were prepared by lysis buffer as previously described[30]. The nuclear and cytosolic proteins were extracted using the NE-PER Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Extraction Reagents kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Rockford,IL, USA). Equal amounts of protein were subjected by SDS-PAGE and transferred to polyvinylidene difluoride membranes in sequence.The membranes were probed with primary and secondary antibodies(Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA; Abcam, Inc.,Cambridge, MA, UK; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz,CA, USA). Chemiluminescence was enhanced (R&D Systems Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA) and visualized using a Fusion FX Image system (Vilber Lourmat, Torcy, France). Quantification of the relative band density was performed using the ImageJsoftware(v1.48, NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA).
2.7. Statistical analysis
Data are represented as mean ± standard deviation (SD) of triplicate experiments. Statistically analysis was performed using Graph-Pad Prism5.03 (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA), followed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)-Tukey’s-post hoc test. In each case, P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of EECT on the viability of macrophage-like cells
Figure 1 shows that up to 300 μg/mL concentration of EECT had no cytotoxicity to RAW 264.7 cells and there were no significant differences between control and EECT-treated cells. Therefore, EECT concentrations of up to 200 μg/mL were selected for the subsequent experiments. LPS at 0.5 ng/mL used as a positive control to activate the macrophages was not cytotoxic neither.
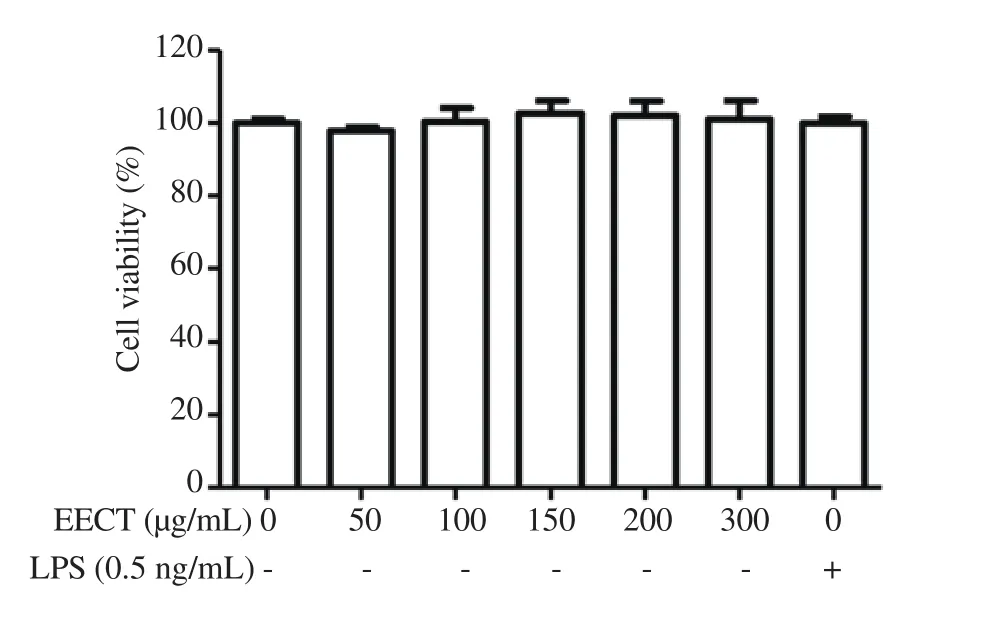
Figure 1. Effect of ethanol extract of Chondracanthus tenellus (EECT) on the viability of RAW 264.7 cells. The cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of EECT or 0.5 ng/mL LPS for 24 h. Cell viability was assessed by an MTT reduction assay. The results are expressed as mean ±SD (n=3).
3.2. EECT increases the phagocytic activity of macrophagelike cells
Since morphological changes of macrophages can be influenced by a variety of exogenous factors and sometimes related to their activation, we assessed the effect of EECT on the morphology of RAW 264.7 cells. As indicated in Figure 2A, the control cells were generally round or oval. However, with increasing EECT treatment concentration, the cells became irregular, large, diamond-shaped,and the surface became rough and crude. Exposure to LPS as a positive control tended to cause similar morphological changes.Next, to investigate whether EECT affected the phagocytic activity of RAW 264.7 cells, latex beads absorbed by the cells were acquired under a fluorescence microscope. The results revealed that the ability of EECT-treated RAW 264.7 cells to engulf fluorescently-labeled latex beads was enhanced compared to the control (Figures 2B and C). We also applied flow cytometry analysis and confirmed that EECT significantly enhanced phagocytosis (Figures 2D and E). The phagocytic activity of 100 μg/mL EECT-treated cells was similar to that of LPS positive control, indicating that EECT was able to activate the cells.
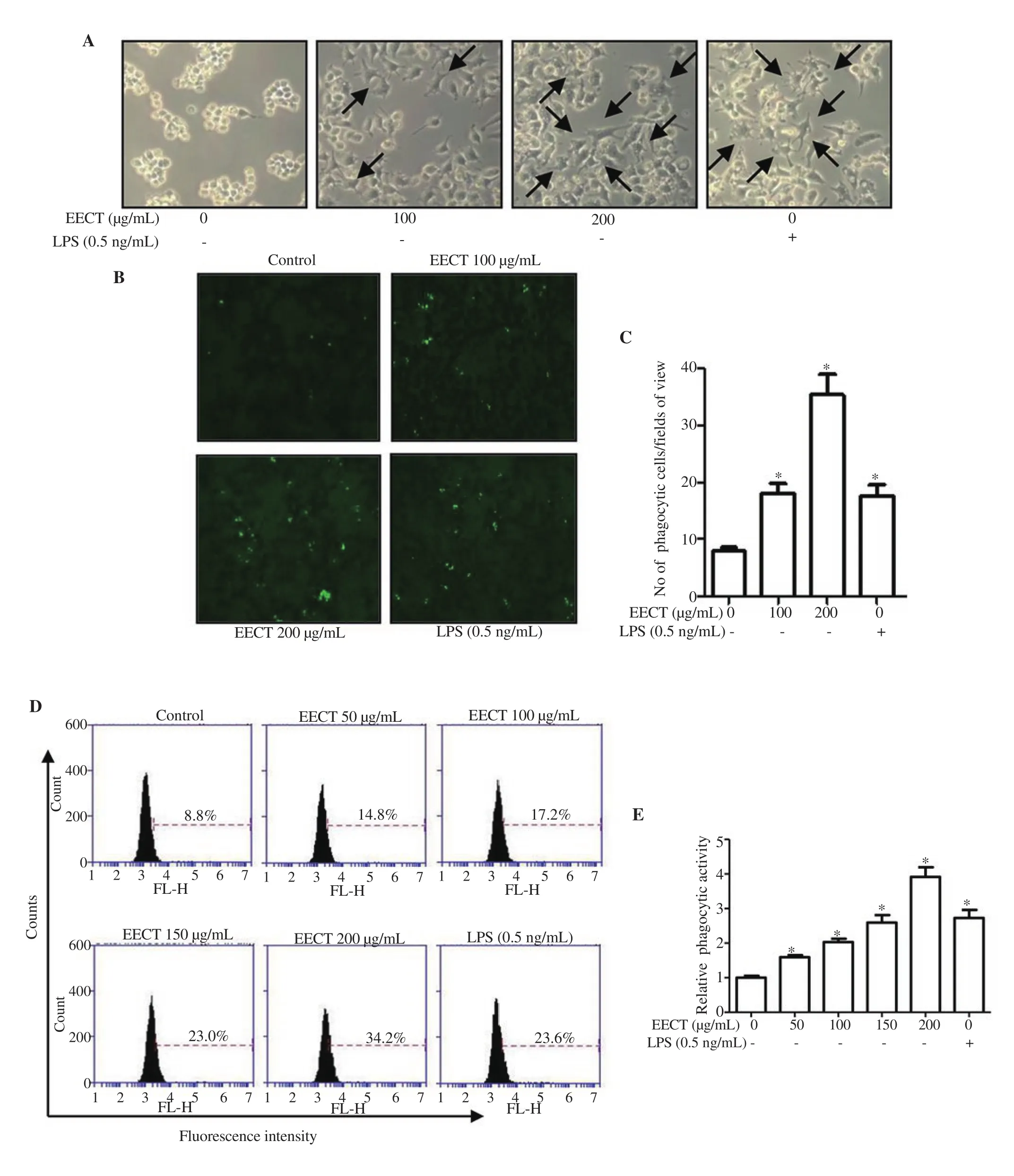
Figure 2. Increased phagocytic activity of RAW 264.7 cells by EECT. Cells were treated for 24 h. A: Representative pictures of the morphological changes(200×). B and C: Latex beads-FITC-stained cells were visualized under a fluorescence microscope (200×), and the number of phagocytic cells per field of view was counted. D and E: Phagocytic activity was measured using flow cytometry. *P<0.05 when compared with the control.
3.3. EECT induces the generation of NO and PGE2 in macrophage-like cells
To investigate the effects of EECT on NO and PGEproduction,the concentrations of nitrite and PGEaccumulated in conditioned media were quantified using Griess reagent and a PGEELISA kit,respectively. As indicated in Figure 3, NO and PGEproductions were markedly enhanced compared with the control cells as the EECT treatment concentration increased. The concentrations produced by the cells treated with 150 and 200 μg/mL EECT were much higher than in LPS-treated cells.
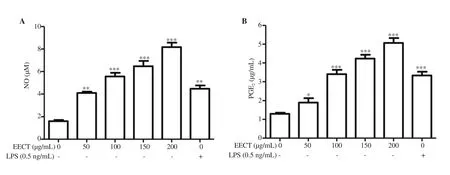
Figure 3. Induction of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) production in EECT-treated RAW 264.7 cells. At 24 h after treatment, the supernatants were collected. The amount of NO (A) and PGE2 (B) was measured by a Griess assay and ELISA kit, respectively. The data are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3).*P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 when compared with the control.
3.4. EECT enhances the secretion of cytokines in macrophage-like cells
We next performed ELISA assays to evaluate the effect of EECT on the secretion of cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10 from the RAW 264.7 cells. The result showed that EECT significantly enhanced the secretion of all tested cytokines compared with that of the control or LPS-treated cells in a concentrationdependent manner (Figure 4).
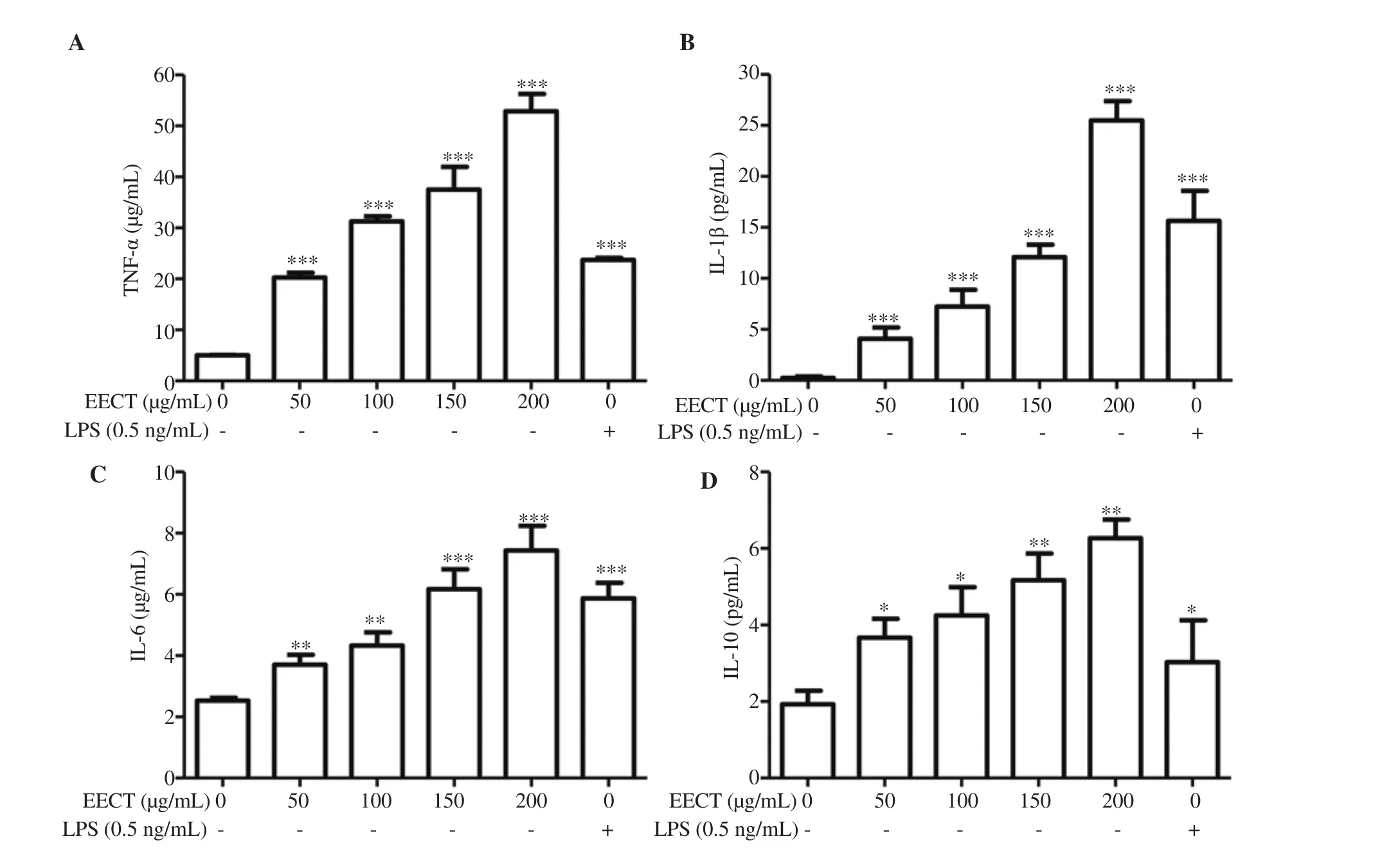
Figure 4. Increased secretion of cytokines by EECT-treated RAW 264.7 cells. At 24 h after treatment, the cell supernatants were collected. Cytokine concentrations, including tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) (A), interleukin-1(IL-1)β (B), IL-6 (C), and IL-10 (D) were measured by ELISA kits. The data are presented as mean ± SD (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 when compared with the control.
3.5. EECT enhances the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and cytokines in macrophage-like cells
According to Figures 5A and 5B, the results showed that the protein expression of iNOS and COX-2 was markedly upregulated in EECT-treated cells. These results suggest that EECT could upregulate the secretion of NO and PGEby increasing the expression of iNOS and COX-2, respectively. Similarly, EECT gradually increased the protein expression of cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-10 (Figures 5C and 5D). Especially, the expressions of IL-1β and IL-6 were significantly upregulated to approximately 20-fold of control by 200 μg/mL of EECT. Meanwhile, the positive LPS control also significantly increased the expression of all these proteins.
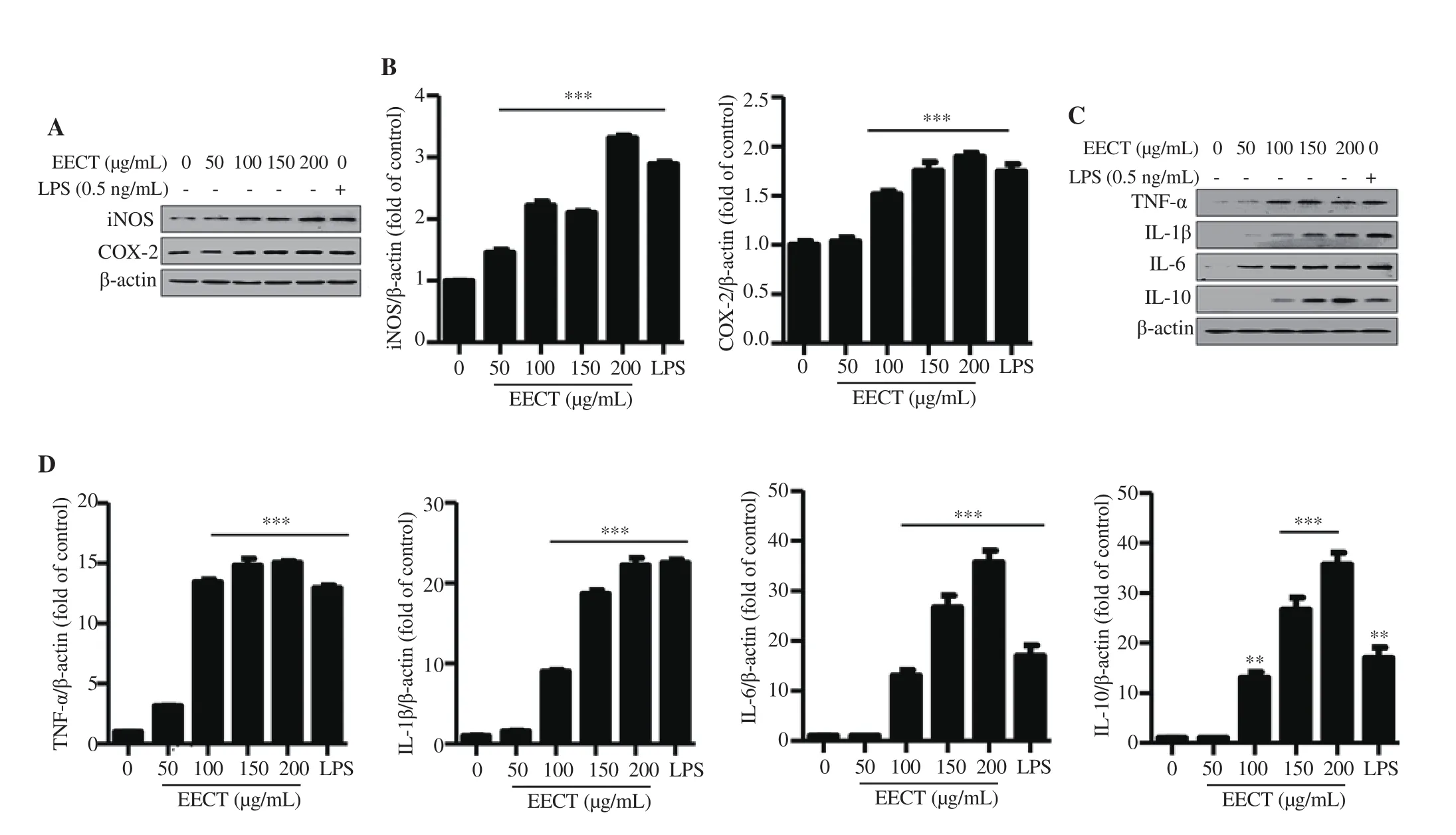
Figure 5. Induction of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), and cytokines by EECT in RAW 264.7 cells.At 24 h after treatment, the cells were harvested and total proteins were extracted. A and C: Representative bands. B and D: Quantitative analysis of protein expression. The expression of each protein was indicated as a fold change relative to the control. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3). **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 when compared with the control.
3.6. EECT activates the TLR4/myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) and NF-κB signaling pathways in macrophage-like cells
Next, we assessed whether the TLR4/MyD88 and NF-κB signaling pathways were involved in EECT-induced macrophage activation.The results demonstrated that the total protein levels of TLR4 and MyD88 in EECT-treated cells were increased in a concentrationdependent manner (Figures 6A and B). In addition, the expression of both proteins in LPS-treated cells was much higher than in the untreated control. To investigate the effect of EECT on the NF-κB signaling pathway, cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins were extracted from cells treated with EECT for 1 h, and the expression of NF-κB and inhibitor of NF-κB-α (IκB-α) was examined. Figures 6C and D show that the expression of NF-κB p65, one important NF-κB subunit for its activation, was increased in the nucleus of EECT-treated cells and decreased in the cytoplasm. The total protein expression of IκB-α, a cytoplasmic inhibitor of NF-κB, in the cytosolic fraction was gradually downregulated with increasing concentrations of EECT, whereas the level of phosphorylated-IκB-α(p-IκB-α) was upregulated compared to that in the control cells. In addition, similar trends were also found in LPS-treated cells.
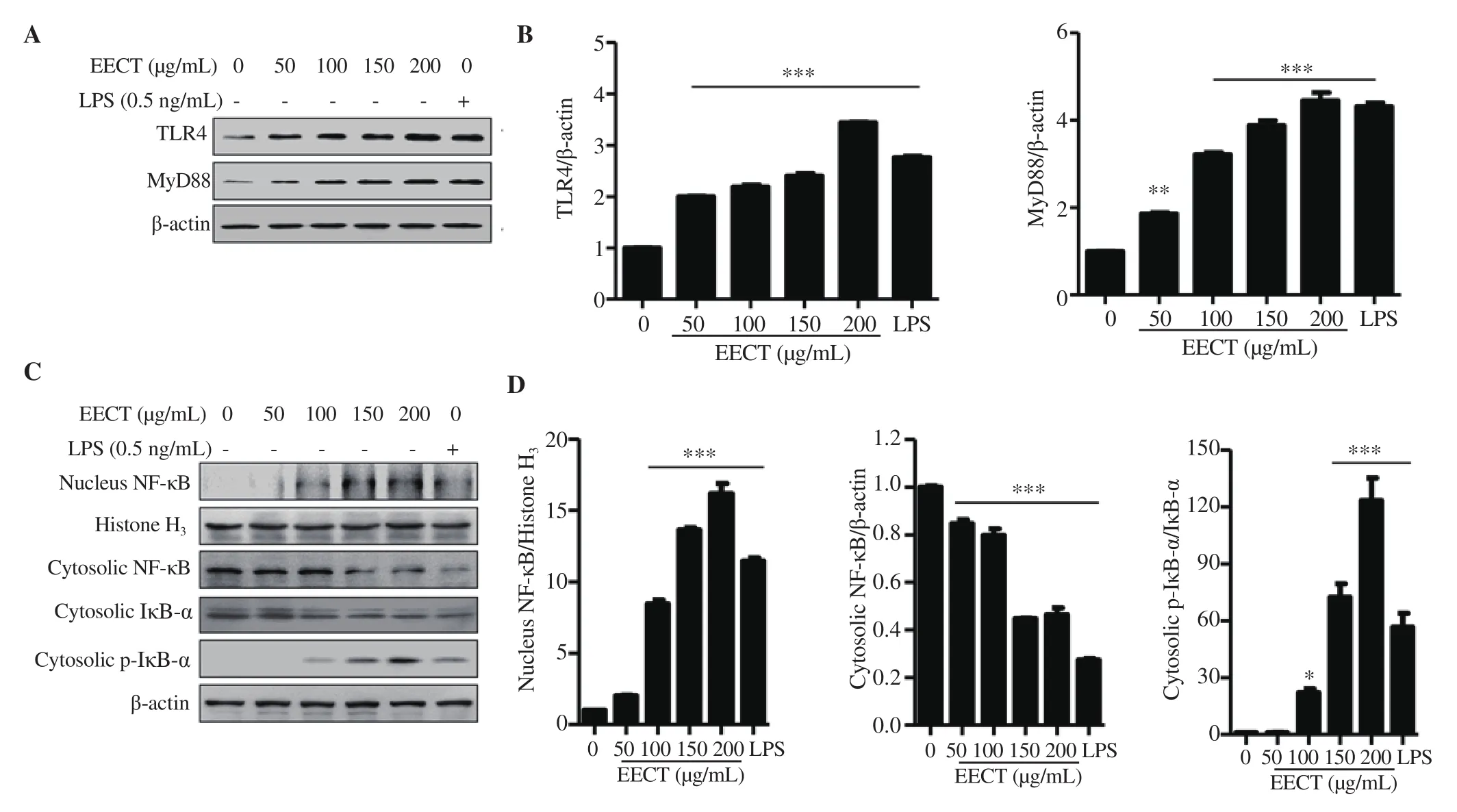
Figure 6. Effect of EECT on the expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), MyD88, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), and inhibitor of NF-κB-α (IκB-α) in RAW 264.7 cells. A and B: At 24 h after treatment, total cell lysates were prepared and the levels of TLR4 and MyD88 protein were evaluated by Western blotting assay. C and D: Nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins were isolated and the expression of NF-κB and IκB-α was observed. Histone H3 and actin were used as loading controls for nuclear and cytosolic proteins, respectively. A and C: Representative bands. B and D: Quantitative analysis of protein expression. The expression of each protein is indicated as a fold change relative to the control. Data are expressed as mean ± SD (n=3). *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 when compared with the control.
4. Discussion
More and more evidences support that immunotherapy through immunomodulation can replace conventional therapies for the treatment of immune deficiencies, infectious diseases, and cancer.Therefore, it is becoming increasingly important to find novel or more effective candidates that can enhance immunological functions.In the present study, we attempted to evaluate the immunomodulatory activity of EECT, an ethanol extract of C. tenellus, as part of an ongoing screening program for immunostimulants in marine algae. EECT activated RAW 264.7 cells to secrete NO, PGE, and cytokines and stimulated the expression of protein responsible for their production in a concentration-dependent manner. EECT also increased the expression of TLR4 and MyD88 and activated the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Macrophages originate from blood monocytes that leave the circulatory system and differentiate in other tissues, which play a critical role in both the adaptive and innate immune responses[6,31].Macrophages are professional phagocytes, and phagocytosis by activated macrophages are involved in tissue remodeling, the decomposition of foreign particles, and the continuous removal of unwanted or dying cells[2,5]. In this study, RAW 264.7 cells cultured in medium containing only dimethyl sulfoxide in cytotoxic conditions were rounded with normal morphology. However, after treatment with EECT, the cells turned into a typical active macrophage morphology that could aid in phagocytic uptake by increasing the contact area with outer substances. Especially, it is worth noting that EECT significantly increased the number of phagocytic cells and the phagocytic capacity. In addition, the number of phagocytic cells and the phagocytic capacity of LPS-treated cells were similar to those in cells treated with 100 and 150 μg/mL EECT, respectively. These results indicate that EECT can at least act as a macrophage activator that significantly improves the phagocytic uptake ability in RAW 264.7 cells. LPS used as a positive control in this study is known to be an effective stimulator of the immune system and has been widely applied to models for inducing macrophage activation[3,4]. Therefore,these results suggest that the mode of action of EECT may be similar to that of LPS.
Along with phagocytosis, activated macrophages secrete cytotoxic and immune mediators, such as NO, PGEand various cytokines, in the innate immune response[5,6]. NO and PGE, which are synthesized by iNOS and COX-2, respectively, are important mediators of inflammation, as well as the immune response, and are involved in the regulation of host innate immune responses. Since they can also improve the phagocytosis and lysis of macrophages[32,33], the increased synthesis of NO and PGEby upregulation of iNOS and COX-2 is an indicator of macrophage activation. In the present study,EECT significantly stimulated the secretion of NO and PGE, which resulted from increased iNOS and COX-2 expressions. All results were similar in the LPS-treated cells, indicating that the increase in NO and PGEproduction in the EECT-treated cells was due to the enhanced expression of iNOS and COX-2.
Macrophages produce multiple pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines to regulate the balance of inflammatory and immune responses. Early pro-inflammatory cytokines induced by activated macrophages have multiple functions in the inflammatory process and also promote the secretion of other cytokines[5,6]. They have also been reported to enhance the immune function of macrophages because they are multifunctional cytokines that play an important role in rejecting tumor cells and activating T cells. The release of anti-inflammatory cytokines is also necessary for the immune response, as sustained production of pro-inflammatory cytokines can negatively affect the repair of damaged tissue[5,34]. In the present study, the secretion of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-10, was markedly enhanced in EECT-stimulated cells. The LPS-treated cells showed a similar tendency. Therefore, our findings indicate that the ability of EECT to enhance macrophage function included the increased production of immune mediators and cytokines.
TLRs play a key role in the innate immunity system and trigger immediate host defensive response such as inflammation[3,4].Among the TLRs, TLR4 plays a crucial role in the inflammatory and immune responses and activates TNF receptor-associated factor 6 through the MyD88-dependent pathway, one of the adapter molecules. TNF receptor-associated factor 6 further serves as a key mediator of signal transduction pathways that regulate the expression of immunomodulatory-related downstream gene by promoting the activation of NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways[35,36].Therefore, we found that EECT could promote the activation of TRL4 signaling pathway, which is accompanied by upregulation of TRL4 and MyD88 expression. Especially, the expression levels in the 150 μg/mL EECT-treated cells were similar to those of the 0.5 ng/mL LPS-treated cells but were higher in the 200 μg/mL EECT-treated cells.
NF-κB is an important transcription factor in macrophage activation that modulates many immune regulatory mediators[1,37]. Inactive NF-κB dimer (p65/50) interacts with IκB-α in the cytosol to form complexes. As IκB-α is phosphorylated and degraded subsequently through the ubiquitin-proteasome system, the NF-κB dimers are released from the NF-κB/IκB-α-complex and translocate to the nucleus to initiate transcriptional activity of the target genes[38,39].Our immunoblotting results suggested the expression of NF-κB and IκB-α was decreased in the cytoplasm of EECT-treated cells compared to the control cells, whereas the expression of p-IκB-α and nuclear NF-κB (p65) was increased by EECT. Similar trends were also found in LPS-treated cells. Based on these data, we found that EECT induced both degradation of IκB-α by phosphorylation and translocation of NF-κB from the cytosol to the nucleus,which is similar to the mode of action of LPS. In addition, these results suggest that EECT has an immunomodulatory activity by increasing the production of immunomodulatory mediators and cytokines through activation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Consistent with our results, several previous studies have shown that seaweed-derived polysaccharides increased immune effects by the activation of TLR4/NF-κB[21,25]. However, additional research should be conducted to determine the link between TLR4 and the NF-κB signaling pathway, and other signaling pathways involved in the immune effects of EECT. Nevertheless, our results could provide the important information to understand the mechanism of the immunomodulatory potential associated with macrophage activation by the red algae C. tenellus.
In conclusion, our findings indicate that the phagocytic ability of RAW264.7 cells was significantly improved after treatment with EECT, and the cell morphology changed correspondingly. EECT increased the production of immunomodulatory mediators and cytokines, which might be due to the upregulated expression of their respective genes. Moreover, the underlying mechanism of the EECT-mediated activation of macrophages was related to the activation of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Therefore, the EECT used in this study could potentially be used as a candidate for medication or dietary supplements to increase immune activity. However, for this purpose, it is necessary to investigate the bioactive components contained in EECT, as well as additional molecular mechanisms and immune properties of C. tenellus in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Funding
This research was a part of the project titled ‘Omics based on fishery disease control technology development and industrialization(20150242)’, funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries,Republic of Korea.
Authors’ contributions
Collecting data, drafting the manuscript and critical revision of the manuscript were done by DHK, CP, HL and YHC. YHC, CP and HJH designed the study. Data analysis and interpretation were done by GYK, HJC, HSK and HJH. SHH contributed to the design of manuscript. In addition, YHC was responsible for supervision,as well as SK and HJH contributed to project administration and funding acquisition.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2021年6期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2021年6期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Total flavonoids from Saussurea involucrata attenuate inflammation in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages via modulating p65, c-Jun,and IRF3 signaling pathways
- Ginseng ameliorates pulmonary toxicity induced by silicon dioxide nanoparticles in rats
- Caffeic acid and protocatechuic acid modulate Nrf2 and inhibit Ehrlich ascites carcinomas in mice
- Potential of polyphenols in curbing quorum sensing and biofilm formation in Gramnegative pathogens
