Hepatocellular carcinoma in transfusion dependent thalassemia patients: a review from a clinical perspective
Nikolaos Papadopoulos, John Koskinas
11st Department of Internal Medicine, 417 Army Share Fund Hospital, Athens 11521, Greece.
22nd Academic Department of Medicine, Medical School of Athens, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens,Hippokration General Hospital, Athens 11527, Greece.
Abstract Survival in patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemias (TDT) has increased, and complications such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are emerging. Risk factors include viral infection, mainly hepatitis C virus (HCV),iron overload, the presence of cirrhosis, and immune dysregulation. Median survival after HCC occurrence has been estimated at 12 months, while data regarding the incidence of HCC in this population are minimal.Implementing effective hepatitis B virus (HBV)/HCV antiviral treatment and universal HBV vaccination programs is expected to decrease the risk for hepatocarcinogenesis substantially. Significant hemosiderosis and hepatic fibrosis are common in patients with TDT despite chelation therapy and have been correlated with HCC development. Thus, iron overload should be monitored with liver iron concentration and ferritin levels, and effective chelation therapy should be applied. In addition, all TDT patients, particularly those with cirrhosis, should be under surveillance every six months with abdominal ultrasound ± alpha-fetoprotein levels, as this combination seems to provide better sensitivity for early HCC detection.
Keywords: Transfusion-dependent thalassemias, hepatocellular carcinoma, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, iron overload, liver iron concentration, liver stiffness measurement
INTRODUCTION
Beta thalassemia is caused by mutations in the hemoglobin beta-globin gene that leads to impaired production of beta-globin chains. Beta thalassemia major (TM) is the most severe form of beta-thalassemia,characterized by minimal to no beta-globin chain production. Individuals with beta-thalassemia major have profound and lifelong transfusion-dependent anemia (TDT), which leads to several organ pathological conditions, mainly due to iron overload.
However, as survival in patients with TDT has increased over time, mainly due to efficient iron chelation therapy, it seems that the complications from the heart that were common and fatal are reduced, and other previously rarer complications such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are emerging[1].
Traditionally, the risk of HCC development in these patients has been linked to hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections mainly transmitted by blood transfusions[2]. However, recent data highlight the risk of HCC development in HCV- and HBV-negative patients, indicating the crucial role of iron overload[3-5].
This review aims to investigate the epidemiological data and the possible mechanisms involved in developing HCC in patients with TDT, including viral hepatitis, the role of iron overload, and the immunological disturbances that characterize these patients.
HCC IN TDT EPIDEMIOLOGY
HCC is the seventh most frequently occurring cancer globally and the second most common cause of cancer mortality[6]. Its incidence rises progressively with advancing age, showing a higher prevalence among males[7]. Significant risk factors for HCC include HBV, HCV, chronic alcohol consumption, obesity, type II diabetes, and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). In general, the prevalence and etiology of HCC present a heterogeneous geographic distribution according to the predominant risk factor of each region. Thus,most cases are associated with HBV in Western Africa, Latin America, and East Asia, while most cases are associated with HCV in North America and Western Europe[8]. However, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease(NAFLD)/NASH is rapidly increasing and is expected to become the predominant risk factor for HCC in high-income regions[9]. In the United States, the incidence rates per 100,000 persons are 13.8 in men and 4.9 in women[10].
Data concerning etiological factors and treatment outcomes of HCC appear to be lacking in patients with TDT. Moreover, data regarding the incidence of HCC in this population are minimal. The majority of HCC cases are from population-based studies from Italy and Greece[11-15]. The evaluation of the total number of patients included in the updated Italian registry revealed a cumulative incidence of HCC in patients with TDT of 1.02%[12]. Overall, the study showed 60 new cases of HCC between 2002 and December 2012, among 5855 thalassemia patients who have been followed. A Greek study evaluated 57 patients with TM and thalassemia intermedia[14]. The incidence of HCC in patients with TM has been calculated as 3.5%. Data from a prospective study with 105 adults with TDT reveal a 2% incidence of HCC during a one-year observation period[16]. Furthermore, preliminary data regarding HCC survey from 1327 thalassemic patients,aged > 30 years from 13 centers, enrolled in the International Network of Clinicians for Endocrinopathies in Thalassemia and Adolescent Medicine (ICET-A), reveal a prevalence of 1.66% in TDT patients and 1.96% in non-TDT patients[17][Table 1].
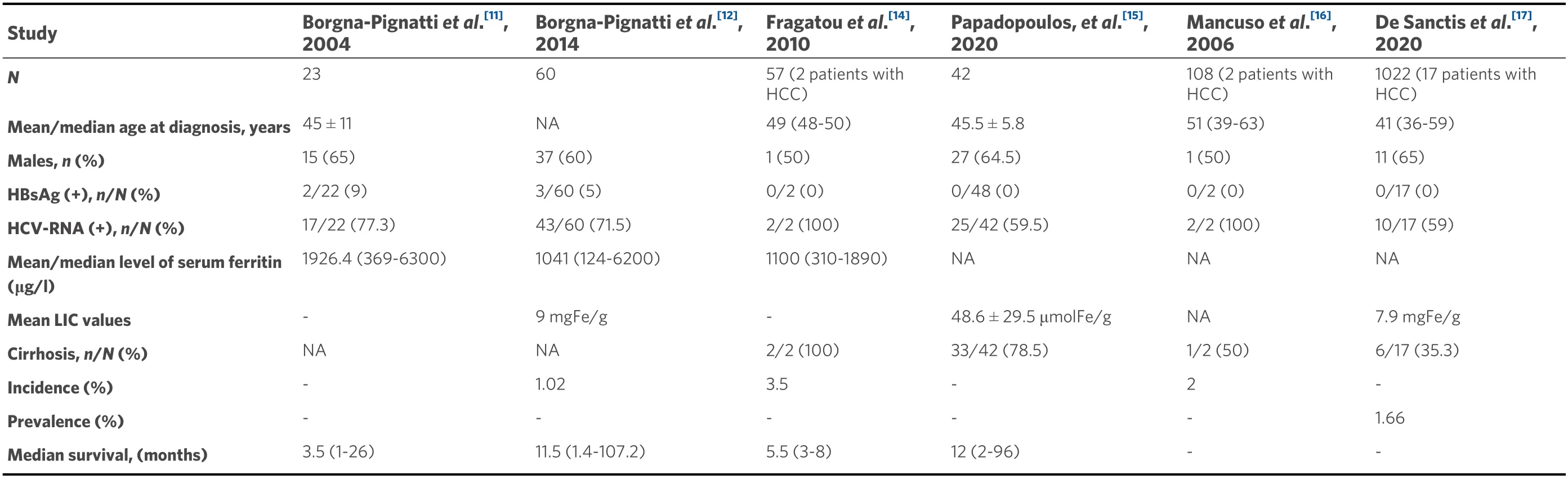
Table 1. Data regarding clinical characteristics, incidence, prevalence, and survival in TDT patients with HCC
Based on current reports, it is clear that, compared to the general population, HCC appears at a younger age in TDT patients, suggesting the presence of multiple risk factors operating early in life for this population[3]. More precisely, the median age at diagnosis is 45 years among patients with TDT compared to 64 years among the general population[7,10,12]. Moreover, as discussed above, until 2000, HCC was relatively uncommon in TDT patients, as they died younger from cardiac problems related to iron overload[18,19]. In recent years, effective iron chelation treatment has led to a significant prolongation of survival thanks to the prevention of cardiac complications. However, many TDT patients still have liver iron overload with concomitant liver fibrosis[20]. Median survival after HCC occurrence has been estimated at 12 months (range 2-96 months) in a Greek study and was mainly dependent on the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer grading system[15]. In addition, data from Italy indicate a similar median survival of 11.5 months (range 1.4-107.2 months)[12].
In most countries, incidence rates of HCC among men in the general population are two- to four-fold higher than rates among women, possibly due to the higher incidence of cirrhosis, higher levels of smoking, and greater alcohol intake[7]. Interestingly, this difference seems to be less profound between men and women in TDT patients. It is well known that the effects of testosterone may increase signaling androgen receptors in men, promoting the proliferation of hepatocytes[21]. As hypogonadism has been revealed in a significant proportion of TDT patients, we may assume that lower testosterone levels could explain the almost equal occurrence of HCC between men and women[12].
HCC IN TDT - HBV INFECTION
Chronic HBV infection is the leading cause of global liver cancer incidences and deaths[22]. The incidence rate of HCC in patients with chronic HBV infection has been estimated to be 0.6% for those without cirrhosis and 3.7% for those with compensated cirrhosis[23]. Furthermore, the overall mortality rate among all cases of chronic HBV infection has been estimated as 30%-50%[24]. Besides the increased risk of HBVrelated HCC in patients with cirrhosis, it is well known that HBV initiates the process of hepatic carcinogenesis by integrating into the host genome, thus leading to chromosomal instability and cell proliferation[25][Figure 1]. The oncogenic nature of HBVper seis further demonstrated by the fact that the risk of developing HCC is not eliminated even in non-cirrhotic patients receiving high-barrier to resistance antiviral treatment[26].
Worldwide, 0.3%-5.7% of thalassemia patients are hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) positive[19]. In the Italian updated registry data, the HBsAg positivity reached 5% among 60 TDT patients with HCC. In contrast, no HBsAg positivity was revealed in a Greek study with 42 TDT patients with HCC[12,15]. Thus,HBV infection does not play a significant role in HCC development in these patients, at least in Western countries. However, since the prevalence of HBV infection presents a large heterogeneous geographical distribution, its role is likely to remain important in high endemicity areas such as Asia and Africa. The most effective method to control HBV transmission is universal vaccination. Successful outcomes of nationwide vaccination programs implemented by Taiwan in 1984 proved that HBV infection and HCC incidence rates could be substantially reduced by a rigorous vaccination program[27]. Thus, HBV-related HCC, including in high-endemic areas, is expected to decrease in the coming years, even in TDT patients[28].
HBV treatment improves survival and quality of life by preventing liver disease progression and HCC. The indications for treatment in TDT patients do not differ from those recommended in the general population and are primarily based on the combination of three criteria; HBV-DNA levels, serum alanine aminotransferase levels, and severity of liver disease[29].
HCC IN TDT - HCV INFECTION
Based on previously published data, HCV infection has been proposed as the leading risk factor for liver fibrosis in TDT patients[30]. TDT patients transfused before the universal blood donors screening, which was introduced in 1992 after the discovery of HCV, were at higher risk of blood-borne HCV infection. Although the prevalence of HCV infection among these patients has dramatically decreased during the last twenty years, it remains higher than the general population. It is still a significant problem in underdeveloped countries. Anti-HCV positive was present in 87% of thalassemic patients based on an Italian registry, 39.6%-74.4% in two Greek studies, and 18%-70% in studies from the Middle East[12,15,31,32]. However, whether HCV plays a direct role or merely an indirect one through cirrhosis in the pathogenesis of HCC remains uncertain[33]. It seems that oxidative stress production enhanced by the HCV core protein would partly contribute to the development of HCC, even rarely in the absence of liver cirrhosis[34][Figure 1]. In a recent study from Greece, which reported all cases of malignant neoplastic disorders occurring in 3652 thalassemic patients diagnosed between 1985 and 2018, a strong positive association between HCV and HCC was found[13]. Moreover, it has been identified that the most frequent HCV genotype in TDT patients is 1b,which seems to play an essential role in HCC development according to a recent meta-analysis[35,36].
The new interferon-free regimens with direct-acting antiviral (DAA) agents have changed the treatment landscape of HCV infection. The indication for HCV treatment in this population is similar to that of the general population[37]. In a real-life study, DAAs achieved a sustained virological response rate of > 90%without any additional adverse events or drug-drug interactions with iron-chelating drugs[38]. However, it is well established that, in patients treated with DAAs, the absolute risk of HCC remains in patients with cirrhosis or other concomitant etiological factors[39].
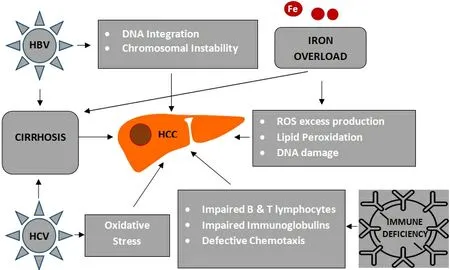
Figure 1. Hepatocarcinogenesis in patients with transfusion-dependent thalassemias (TDT). HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HBV:hepatitis B virus; HCV: hepatitis C virus; ROS: reactive oxygen species; DNA: deoxyribonucleic acid.
HCC IN TDT - CIRRHOSIS
It is well known that cirrhosis is the dominant risk factor for the development of HCC. In the Western world, up to 90% of HCC arises in the presence of cirrhosis[40]. It was estimated that up to one third of patients with cirrhosis would develop HCC during their lifetime[41]. The annual incidence of HCC depends on the etiology of cirrhosis. Thus, it has been estimated as 3.23% for HBV, 4.81% for HCV, and 1.2% for genetic hemochromatosis[42].
Significant hemosiderosis and hepatic fibrosis were common in patients with TM despite chelation therapy[43]. Worldwide available data indicate that the prevalence of cirrhosis among patients with thalassemia ranges 11.1%-78.5%[14-17].
The co-existence of specific risk factors such as iron overload and HCV or HBV infection are additive factors that increase the risk of cirrhosis in this group of patients. However, the HCC development in patients with TDT is not inextricably linked to the presence of cirrhosis[16].
Since HCC incidence is higher in patients with more advanced cirrhosis, surveillance for early HCC detection with abdominal ultrasound (US) every six months is a reasonable and cost-effective route to reduce mortality in these patients[44]. Moreover, recently published data indicate that alpha-fetoprotein levels(with 20 ng/mL as a cut-off) in combination with US is better in detecting patients with HCC, providing a sensitivity of more than 95%[45].
HCC IN TDT - IRON OVERLOAD
It is well known that hereditary hemochromatosis (HH) is associated with a 20-200-fold increased risk for HCC[46]. The overall standardized incidence ratio of HCC in patients with HH was estimated as 1.7 (95%confidence interval: 1.5-2.0) in a Swedish study[47].
While iron is essential for normal human physiology, its excess is toxic as there is no physiological pathway for removal from the body. In addition, free iron accelerates the Fenton reaction that generates noxious reactive oxygen species (ROS), which severely damage cells and tissues and promote fibrogenesis[48].
Iron overload is implicated in the development of HCC in other hereditary disorders such as TDT.Kountouraset al.[49]investigated the role of iron overload and HCV in the severity of liver disease in a cohort of 211 adult Greek patients with beta-thalassemia major. Based on the findings from 109 patients with liver biopsy, they demonstrated that advanced fibrosis was present with even minimal hemosiderosis.Moreover, the presence of fibrosis was independent of ferritin values or HCV history. Consistent with other reports, iron seems to have a leading role in liver disease initiation and progression[50]. Liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography, as hepatic fibrosis assessment, is closely related to the degree of hepatic siderosis in TDT patients, indicating that chelation therapy is mandatory to prevent liver disease progression[51,52].
As discussed above, iron overload in TDT patients leads to denaturation of ferritin, producing an excess of ROS into the cytoplasm of the hepatocytes, thus provoking DNA damage and genomic instability[53][Figure 1]. Free iron overproduction in hepatic tissue could be responsible for carcinogenesis, overcoming the protective effect of activation of tumor suppressor genes such asp53, which regulates cell cycle arrest,apoptosis, and senescence in response to cellular stress[54,55]. In addition, free intracellular ferrous ions react with hydrogen peroxide and activate the lipoxygenase that induces the peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in cell membranes[56,57]. This mechanism, called ferroptosis, provides evidence about the role of iron in HCC even in the absence of liver cirrhosis[57,58].
There is sufficient evidence that iron chelation therapy improves or stabilizes liver fibrosis independently of liver iron concentration or HCV prevalence[59]. However, it is uncertain whether iron chelation treatment may reduce the risk of HCC, although there is evidence that it may reduce the risk of developing HCC or even suppresses HCC growth in experimental studies[60,61]. Thus, monitoring of iron overload in patients with TDT is crucial.
Nevertheless, iron plays a significant role in the pathogenesis of liver disease and HCC in TDT patients, and effective chelation therapy is mandatory.
Iron overload measurements include liver iron concentration (LIC) using magnetic resonance imaging,which accurately reflects the total body iron stores and ferritin levels that may predict changes in the total body iron levels[62]. Annual targets of LIC 2-5 mg/g dry weight and ferritin levels < 1000 ng/mL appear to be a reasonable strategy in TDT patients[63].
HCC IN TDT - OTHER OR COMBINED RISK FACTORS Immune deficiency
Transfusion-related immunomodulation was reported several years ago and has been linked with several adverse effects in oncology[64]. Some of the reported immune abnormalities include quantitative and functional defects involving impaired B-lymphocyte function, defective chemotaxis and phagocytosis, and impaired immunoglobulin production, all of which are essential mechanisms in anticancer immune surveillance[65,66][Figure 1]. It also has been suggested that iron homeostasis is an important determinant of valid T cell-mediated immune response, as either iron overload or iron deficiency induces immunologic aberrancies[67].
“Second-hit” mechanisms
The iron-related oxidative damage can be further enhanced by several factors such as HCV infection and NAFLD, promoting liver injury and fibrosis synergistically as a “second hit” phenomenon[53,68,69].
In a landmark study, Angelucciet al.[53]described that the combination of iron overload and HCV substantially increases the progression of liver fibrosis.
Dysmetabolic iron overload syndrome is now a frequent finding in the general population, as it is detected in about one-third of patients with NAFLD[70,71]. Moreover, hepatocellular iron accumulation was associated with a higher risk of fibrosis than the absence of siderosis in patients with NAFLD, and, once again, the mechanism involves increased oxidative stress[71].
CONCLUSIONS
HCC development in patients with TDT is a complex phenomenon. Several factors such as HBV and HCV infections, iron overload, and immune dysfunction are of paramount importance. Moreover, NAFLD represents a newly emerging risk factor. The efficient antiviral treatment for HCV and HBV infections, the preventive anti-HBV immunization, and, most importantly, the monitoring and treatment of iron overload are expected to reduce HCC in these patients in the future. In all patients, particularly those with cirrhosis,surveillance programs for HCC are mandatory for early detection and application of more effective and curative treatment.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Analyzed the data: Papadopoulos N
Wrote the paper: Papadopoulos N, Koskinas J
Designed and directed the project: Koskinas J
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflicts of interest
Both authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Copyright
? The Author(s) 2021.