Task Scheduling for Multi-Cloud Computing Subject to Security and Reliability Constraints
Qing-Hua Zhu, Senior Member, IEEE, Huan Tang, Jia-Jie Huang, and Yan Hou
Abstract—The rise of multi-cloud systems has been spurred.For safety-critical missions, it is important to guarantee their security and reliability. To address trust constraints in a heterogeneous multi-cloud environment, this work proposes a novel scheduling method called matching and multi-round allocation (MMA) to optimize the makespan and total cost for all submitted tasks subject to security and reliability constraints. The method is divided into two phases for task scheduling. The first phase is to find the best matching candidate resources for the tasks to meet their preferential demands including performance,security, and reliability in a multi-cloud environment; the second one iteratively performs multiple rounds of re-allocating to optimize tasks execution time and cost by minimizing the variance of the estimated completion time. The proposed algorithm, the modified cuckoo search (MCS), hybrid chaotic particle search(HCPS), modified artificial bee colony (MABC), max-min, and min-min algorithms are implemented in CloudSim to create simulations. The simulations and experimental results show that our proposed method achieves shorter makespan, lower cost,higher resource utilization, and better trade-off between time and economic cost. It is more stable and efficient.
I. INTRODUCTION
VIRTUALIZATION computing has enjoyed wide applications in cloud computing, where virtual machines(VMs) are created on the same set of computer hosts. The ondemand provisioning of resources and dynamic scalability makes computing power an internet commodity [1]. Singlecloud computing models (where users use a single cloud) have several challenges [2], [3], such as service and resource unavailability, regulatory compliance, network latency between end users and cloud sites, and vendor lock-in [4]. Multi-cloud computing is a viable approach to tackle these issues, where users employ multiple independent clouds that do not rely on any underlying collaboration between cloud providers. It can provide users with better quality of service (QoS) [5] using diverse geographical locations for data storages [6] and better application resilience. It can also help in avoiding vendor lock-in [7], which enables their data centers to offer users a wide variety of services [8].
Cloud task scheduling is a non-deterministic polynomialtime hard problem in general. It is challenging to efficiently find a better task scheduling solution in a multi-cloud environment because it involves not only service compositions but also the combination of many optimal objectives. In a business model, user tasks are submitted to a data center to obtain certain services in a paid manner, and cloud service providers (CSPs) tend to price their services based on the performance configuration of computing resources by a service-level agreement (SLA) [9]. Nowadays,large-scale complex applications consist of a variety of service components, which demand different combinations of security and reliability. Furthermore, on the cloud side, they require different levels of security and reliability.
Since the requirements of user’s tasks are diverse, compared with traditional single cloud computing, each task may have more opportunities to find a suited cloud service in a multicloud system to avoid poor adaptability between tasks and cloud services, excessive computing time or cost waste, and information leakage due to insufficient service security [10].Thus, a multi-cloud system is crucial to ensure the needs of users. A low level of cloud resource reliability may cause service interruption or failure and also bring unnecessary loss to users [11]. In a multi-cloud environment, a CSP is chosen according to the different needs of a user’s tasks; thus, if services fail at a CSP, the services at other providers will support corresponding tasks. To a large extent, the user can also avoid service interruption risks. Therefore, it is necessary for users to select service policies based on their own needs and employ them to multiple CSPs.
However, it is very challenging to choose a reasonable resource scheduling strategy for users in a heterogeneous multi-cloud environment, because limited cloud resources have different capacities and functions [12]. It requires a scheduling scheme that can not only efficiently complete task requests, but also maximize the utilization of VMs while meeting the user’s preferences that are translated into multiple QoS constraints. The task scheduling in this work is a nondeterministic polynomial-time hard problem. When the sum of the numbers of decision variables and constraints of the problem is large, there is no algorithm such that the desired solution can be obtained within polynomial time.
The main contributions of this work are as follows. First, in the trust aspect, we propose a matching-degree strategy between user tasks and resources to provide users with the matching resources as best as possible to satisfy the user’s resource performance, security, and reliability preferences.Second, on the basis of the previous matching results, we propose task scheduling algorithms to optimize the overall tasks execution time (i.e., makespan) and total cost in a multicloud system by taking the variance of the estimated completion time of all submitted tasks on resources as a metric.
The rest of this paper is structured as follows. Section II presents existing related works. Section III gives a description of the cloud system model and related QoS constraints.Section IV proposes a scheduling framework, and matching and multi-round allocation (MMA) algorithms. Section V conducts experimental analyses and comparisons with other scheduling algorithms to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed algorithms. Section VI summarizes this work and points out our future work.
II. RELATED WORK
Task scheduling aims to maximize the economic benefits of CSPs and achieve reasonable deployment of resources to meet user requirements. The task scheduling strategy in a cloud must satisfy the QoS requirements of user tasks, including deadline, time, economic cost, security [13]–[15], reliability[16], [17], etc. Unreasonable scheduling schemes would reduce the overall performance of cloud resources and may violate user’s QoS requirements.
Many efforts have been made on task scheduling in a single cloud environment. There are some single objective traditional scheduling algorithms, such as max-min [18], min-min [19],and first-in-first-out (FIFO) [20]. Max-min and min-min cannot efficiently utilize resources, thereby leading to a serious load imbalance problem. The FIFO processes the tasks according to their arrival time, which causes some small tasks to take too long. In fact, it is difficult to believe that single objective task scheduling methods could provide better service for cloud users.
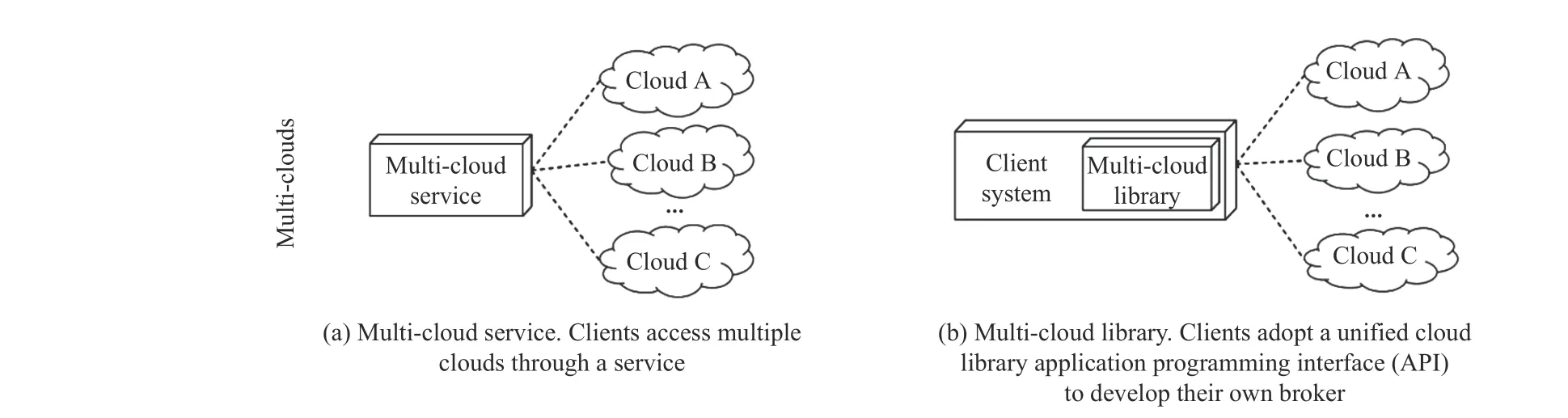
Fig.1. Multi-Cloud development architectures.
With the growth of task requests and resources, some methods based on evolutionary algorithms are adopted to optimize multiple objectives of task scheduling in a single cloud environment to promote service quality. An improved load balanced min-min algorithm is proposed in [21] by using a genetic algorithm (GA) in order to minimize the makespan and increase resource utilization. The work in [22] proposes a meta-heuristic based differential evolution (DE) algorithm to optimize the turnaround time and monetary cost for task scheduling in cloud computing. In [23], a method of initial optimization on the crossover mutation probability of an adaptive genetic algorithm using binary coded chromosomes is proposed to reduce the task execution time and cost. A multi-objective task scheduling GA-DE algorithm is proposed in [24], in which total time, cost and VM load balancing are taken into account simultaneously. However, the disadvantage of evolutionary algorithms lies in the great difficulty in compromising some factors, for example, such algorithms usually strive to increase time costs to gain economic advantage or vice versa. Thus, the existing multi-objective scheduling algorithms cannot directly be applied in a multicloud environment.
In addition, much work has been done to solve the taskscheduling problem in a multi-cloud environment. The scheduling algorithms in a multi-cloud environment are classified and analyzed in [25]. The study in [26] proposes an integrated approach to predict the workload at the next time slot, which achieves accuracy and a fast learning speed in distributed clouds. Taha et al. [27] present a SLA-based service selection approach for task scheduling in a multicloud. Lin et al. [28] propose a workflow scheduling algorithm, called the multi-cloud partial critical path, to minimize workflow execution costs while meeting deadline constraints in a multi-cloud environment. Sooezi et al. [29]propose a massive data workflow scheduling algorithm based on communications in a multi-cloud environment, which minimizes workflow execution costs subject to user-defined deadline constraints. Evolutionary algorithms are also adopted to solve scheduling problems in a multi-cloud environment.Rodriguez and Buyya [30] present an algorithm based on the meta-heuristic optimization technique and particle swarm optimization (PSO), which aims to minimize the overall workflow execution cost while meeting deadline constraints.However, these scheduling algorithms mainly focus on scheduling architectures and single objective problems instead of multi-objective ones, ignoring security and reliability constraints.
In a multi-cloud environment, the variety of resources makes security and reliability issues more prominent, but only a few studies consider their security and reliability. In [31], a multi-objective scheduling algorithm that utilizes PSO technology in a multi-cloud environment is proposed, and has the aim to minimize both the makespan and cost while considering reliability constraints. Kianpisheh et al. [32]propose a scheduling algorithm to minimize execution time and maximize the reliability with budget constraints in a cloud computing environment. A workflow scheduling strategy that takes account into security and budget is proposed in [33] to provide customers with shorter makespan with consideration of security constraints. Wen et al. [34] propose an algorithm to find deployments for workflow applications that are reliable but are less expensive and satisfy security requirements in federated clouds. The work in [35] proposes a multi-QoS(time, cost, security, and reliability) constrained task scheduling algorithm in a single cloud based on GA and PSO algorithms, which transforms the user’s QoS requirements into fitness functions for the optimization process. Although[36] proposes a GA based on QoS-aware (time, cost, and reliability) constraints perception in a multi-cloud environment, which allows users to choose a service optimization combination scheme according to their own preferences, this does not involve scheduling optimization on the underlying resources.
As mentioned above, in a multi-cloud environment,although some related research has been done based on multi-QoS constraints, the existing work on scheduling optimization to meet the user’s quality of service requirements is far from satisfying both performance and trust QoS constraints.Therefore, to the authors’ best knowledge, there is no reported work that optimizes the makespan and total cost in a multicloud environment while considering both security and reliability constraints. The approach proposed in this work goes beyond existing approaches by considering both performance optimization and trust QoS constraints for resource scheduling.
III. MODEL AND PROBLEM STATEMENT
A. Cloud Model
1) Multi-Cloud Architectural
The inter-cloud structure is usually classified into a volunteer federation and multi-cloud [37]. The former refers to a group of CSPs voluntarily collaborating and exchanging resources to form federation clouds. The later means that the CSPs are essentially independent of each other when an application or its broker uses multiple clouds in an aggregation. The structure of a multi-cloud system is shown in Fig.1. It is divided into:
a) Services: They carry out application provisioning and can be deployed either outside or inside of the cloud client;

Fig.2. The roles in a multi-cloud brokering scenario.
b) Libraries: It is necessary that application brokers directly deal with provisioning and scheduling application components across clouds. Inter-cloud libraries can be utilized by broker components to facilitate the usage of multiple clouds in an uniform way.
In this study, we adopt an independent inter-cloud structure with a broker.
2) Multi-Cloud Scheduling Architectural
Fig.2 addresses the multi-cloud broker architecture [38],where there are three roles: users, cloud service providers, and cloud brokers. A cloud user requests virtual resources using a service description template, which can specify a user’s preferences for resources, including requirements for resource attributes, optimization goals, and constraints. In this work,the task priority is considered during task scheduling with guarantee that users who pay more can enjoy better service. A higher priority task will be scheduled to execute earlier than a lower priority one.
Each CSP provides a variety of different VM instance types,which are defined based on hardware metrics, including CPU frequency, memory size, and data storage size. The two main functions of the cloud broker are: a) optimizing the configuration of virtual resources across a group of CSPs, and b) monitoring and managing these virtual resources. The cloud broker’s scheduler component is capable of generating an optimal deployment plan based on user’s demands on resources and cloud service offerings provided by CSPs.
B. Problem Statement
1) Cloud Security Evaluation
In practice, every cloud-computing platform faces security threats from network attacks and system vulnerabilities all the time.


In (1), a positive value of bkreflects that a security level is higher than the baseline level, whereas its negative value shows that a security level is lower than its baseline.
Let slkdenote the security level of CSPk, which can be calculated as follows [39].
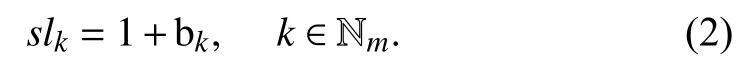
If slkis greater than or equal to the baseline level, e.g., 1,then CSPkis safe, otherwise it is not safe, and the larger the value of slk, the higher the security for CSPk. For instance,considering a percentage like evaluation result, we would say that CSPkhas a security level of 20% over or under the defined baseline if slk= 1.2 or 0.8, respectively. Therefore,CSPkis considered secure in the former and insecure in the latter.
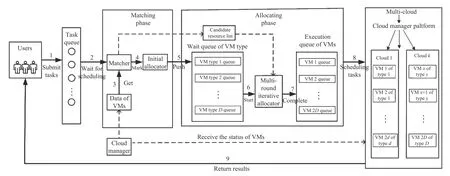
Fig.3. Two-phase scheduling framework in a multi-cloud.
2) Cloud Reliability Evaluation
The IEEE Computer Society defines software reliability[40] as follows:
a) The software does not increase the probability of a system failure during a given period; and
b) The reliability quantification indicator is the average fault-free running time of the system during a specified period.
Failures are almost inevitable for hardware and software, so cloud resources may fail at any time and affect the performance of the entire multi-cloud system. The work in[41] designs a mechanism to continuously update the reliability of cloud resources and provide reliability scheduling for cloud users. There are many VMs in each cloud, and a VM consists of several resources, thus, the reliability of a VM depends on the reliability of its each resource. Resource reliability mainly covers the reliability of disk and RAM. In [42], the reliability of the disk and RAM is 0.93 and 0.997, respectively via observations and calculations.In this work, these two values are initialized for resource reliability on the VM, and the following steps implement the VM resource reliability dynamic update.
Step 1: Assign reliability initial values to all VM instances.Set 0.93 to the disk reliability value of each VM and 0.997 to the RAM reliability value. The reliability initial value of each VM instance is obtained by multiplying the two values.
Step 2: VM reliability will be updated when each time a failure occurs on a VM. A counter initialized by zero is set for each VM’s disk and RAM. If the disk or RAM fails, the corresponding counter will increase by one, at the same time halving the reliability value of the failed disk or RAM. In this way, a discrete drop in component reliability can be simulated.
Step 3: When the number of failures reaches the threshold and the disk or RAM counter reaches the threshold (set to 1.0 here), then the VM is replaced by its backup. In this case, it implies the reliability of the resource is too low.
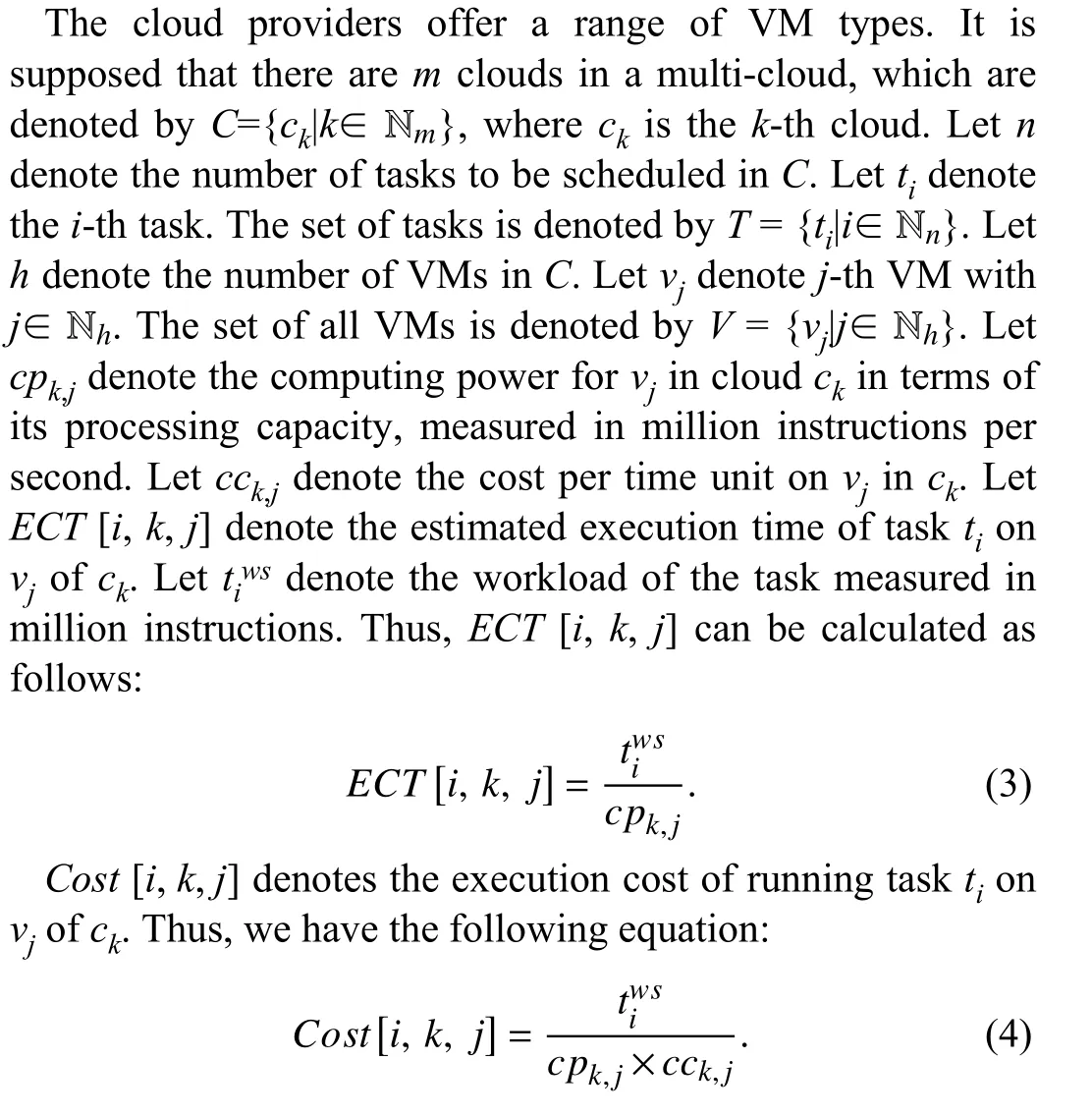
3) Time and Cost Evaluation
IV. MATCHING AND MULTI-ROUND ALLOCATION ALGORITHMS
A. Scheduling Framework
The scheduling framework shown in Fig.3 has the following main modules.
1) Matcher: It checks whether the user’s tasks in the queue are schedulable or not according to the existing VM types,then we can obtain the candidate VMs for corresponding tasks. Next, we calculate the matching degree between the task and all VM types in its candidate VMs list, and obtain the VM type with the highest matching degree for each task.
2) Initial Allocator: The tasks should be arranged in a given order by which can be visited one by one for the following scheduling process. In this work, the submitted tasks have different priorities. The tasks are sorted by their priorities. In addition, for tasks with the same priorities, they are sorted by their size in an ascending order. Then, tasks are allocated to its most matching VMs and we achieve load balancing between the same types of VMs.
3) Multi-Round Iterative Allocator: After the matching phase is completed, all tasks have been assigned the highest matching degree VMs. At this moment, if the assignment is adopted for a schedule, it would lead to the conclusion that the total completion time of some VMs is relatively large, while the completion time of some VMs is much less than the maximum. This causes some VMs to finish computing tasks early while other VMs will run for a long time, resulting in excessive total completion time. To avoid this issue, we design a multi-round iterative allocator to reallocate a task to a fitter VM, which can minimize the variance of the estimated completion time of all VMs. After the allocating phase, the tasks are reassigned to the VMs in the execution order.
4) Cloud Manager: This is a centralized management center that monitors the receipt of information from VMs provided by individual CSPs, and can obtain the type of VMs and which VMs are idle and available.
B. Scheduling Algorithm
In this section, we propose a scheduling algorithm called matching and multi-round allocation (MMA) to achieve scheduling optimization for the entire process.
1) Matching Phase
After a series of tasks are sent to the task queue, a schedulability judgment is performed for each task, to decide whether the performance provided by a VM meets the minimum requirements of a task. If we provide users with a VM that does not meet the user’s task requirements, it violates the pre-signed SLA [43]. This will not only affect the QoS,but also seriously damage the reputation of CSPs. In the worst case, data leakage, service interruption, etc. will bring huge losses to users.

In (5), f (i, k, j) = 1 indicates that vk,jcan satisfy the security and reliability requirements of ti, thus, the rigid trust QoS schedulability conditions can be satisfied, otherwise f (i, k, j) =0. When the rigid schedulability conditions are satisfied, we must further consider the performance QoS requirement condition of task scheduling, which will allow fewer resources to be allocated to certain tasks, and decrease resource usage.Therefore, we need to make a match between the task requirements and the resource attributes, in order to meet the performance QoS requirements of the user as best as possible without causing a waste of resources.



Let FirstAllocate denote the allocated VM list obtained by Algorithm 3 in the matching phase. FirstAllocate[i]determines which VM is assigned to task ti. Algorithm 3 outputs the set of VMs that are candidates for tasks in which CandidateSet[i] denotes the candidates VM for tj.
2) Allocating Phase
In the above matching phase, Algorithm 3 finds the best virtual machine for each task. However, by this scheduling strategy, some types of VMs take a shorter time to finish their assigned tasks, while other types of VM finish their tasks in a longer time. It means the former is idle when the latter is busy.In other words, when some tasks are queuing at the overloaded VMs, it is necessary to improve upon the schedule given by Algorithm 3.
Thus, in the allocation phase, we reallocate the VMs to the tasks to balance the workload of each type of VMs gradually by using multiple iterations.
The estimated completion time (ECT) and estimated completion cost (ECC) of the task running on each VM are calculated by (12) and (13).

As a criterion for whether each VM needs to perform task migration when a round of allocating is finished, the average estimated completion time (avgECT) of VMs is calculated as follows. Let |ck| denote the number of VMs in ck, k∈ Nm.
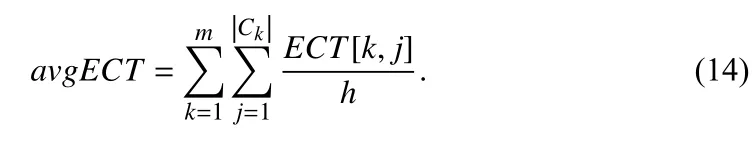
Let VA denote the variance of the estimated completion time on all VMs.
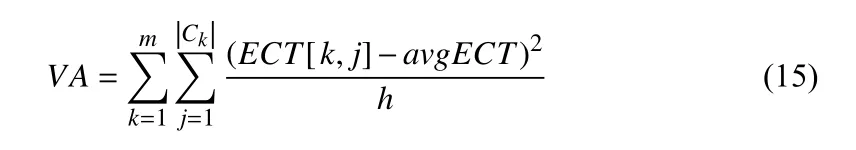
Therefore, shrinking avgECT can pave the way to reducing the total execution time and total cost of VMs. As we continually iterate through the allocation attempts, Algorithm 4 can find a point that minimizes avgECT and VA for all VMs.At this time, the execution time and cost are at the approximate equilibrium point of the relationship, which is rather difficult to find because the attributes of tasks and VMs are discrete. Hence, the execution time can be shortened and the total cost can be lower.
Algorithm 4 implements the allocation phase.



Case A: There is only one candidate VM type in CandidateSet[i] for ti. Adopt this candidate type as the current VM allocation (Line 11) and calculate the task completion time on the VM resource (Line 12).
Case B: There are two or more candidate VM types in CandidateSet[i] for ti. By the end of the execution of ti, if the task completion time of the VM assigned for tiby the previous allocation is greater than avgECT × 0.75, we find the minimal task completion time for tiamong the candidates CandidateSet[i] (Lines 14–23); otherwise, the VM assigned by the previous allocation is chosen as the current allocation(Lines 25–26).
After all the tasks have been handled, the current average completion time and current variance of all tasks on allocated VMs (avgNewECT, newECC, and newVA) are computed.Then, evaluate whether newVA and newECC are equal to or greater than those of the allocation in the previous iteration. If they are, the reallocation process terminates; otherwise, repeat the above allocation iteration.
Essentially, compared with Algorithm 3, Algorithm 4 determines the load migration of tasks so that it can shorten the task completion time, better balance the workloads among different types of VMs, reduce the cost, and improve the utilization of cloud resources.
3) Time Complexity
Now, we analyze the time complexity of the algorithms. In Algorithm 1, for Lines 1–6, the time complexity of the computing cloud security level is O(n). Then, the time complexity of Lines 7–15 is O(m×n). As a result, the time complexity of Algorithm 1 is O(m×n). In Algorithm 2, for Lines 1–5, the time complexity of initialing VM reliability value is O(h). Then, the time complexity of Lines 16–25 is O(h×n). Thus, the time complexity of Algorithm 2 is O(n×h).In Algorithm 3, for Lines 5–27, the time complexity of the first allocation is O(n×h). Now we can get the time complexity O(n×h) of Algorithm 3. In Algorithm 4, for Lines 9–29, the time complexity of multi-round reallocation is O(n).For Lines 8–40, the time complexity of Algorithm 4 is O(n).Therefore, the time complexity of our proposed algorithms is polynomial.
4) An Illustrative Example

V. EXPERIMENTS AND PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
The experimental environment includes an AMD Ryzen 5 PRO 1600 Six-Core Processor 3.4 GHz CPU, 8.0 GB memory, Windows 10 operating system, JDK7.0, and Cloud-Sim 4.0 [44], which is widely used in task scheduling simulation experiments.
Adopt the following algorithms as benchmarks to validate the effectiveness of our proposed MMA algorithm: 1) Two conventional exact algorithms: min-min and max-min[45]–[47]; and 2) three evolutionary algorithms: modified cuckoo search (MCS) [48], [49], hybrid chaotic particle search(HCPS) [50], [51], and modified artificial bee colony(MABC) [52].
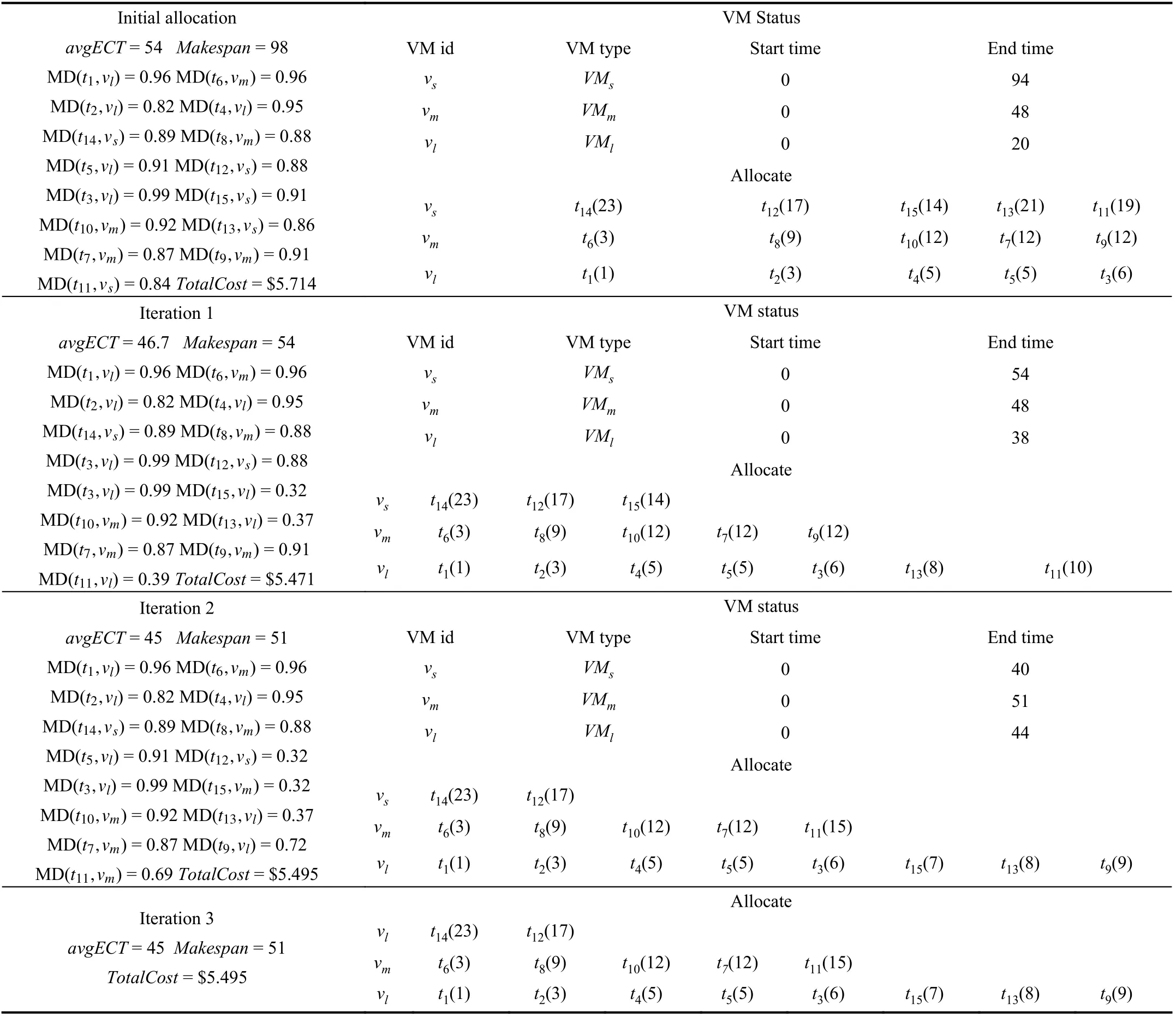
TABLE I VALUES OF THE PARAMETERS DURING THE ALLOCATING PHASE OF Fig.4

Fig.4. Execution time matrix and matching degree matrix of tasks.
The reasons to choose these three evolutionary algorithms are summarized as follows.
1) MCS can avoid to be trapped in a local optimal solution and guarantee a fast convergence to find a global optimal solution.
2) HCPS has both the high precision of simulated annealing(SA) and fast convergence of PSO [50], [51].
3) MABC has been effectively used to solve multi-modal and multi-dimensional optimization problems [52]. It uses fewer control parameters and its performance is better or similar to other algorithms [52].
A. Performance Metrics
The following performance indicators are used to evaluate the algorithms.
1) Makespan
The completion time is denoted by Makespan, which refers to the entire completion time of processing a set of user tasks on the available VMs. Makespan[k, j] represents the completion time of the tasks on vjin ck, which is defined by (16).
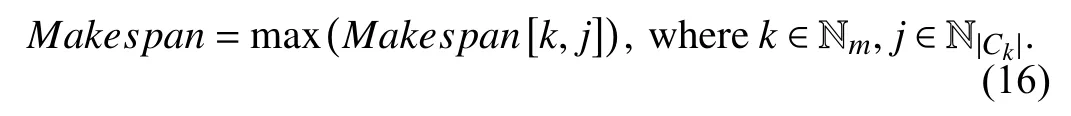
It can be concluded from (16) that the minimum completion time of the tasks is the maximum value of the latest completion time for each virtual machine to process the assigned task. The smaller the value of Makespan is, the shorter the completion time of all the tasks.
2) Total Cost
The total cost is denoted by TotalCost, which refers to how much a user has to pay to a CSP according to the agreement after successfully completing all tasks. ECC[k, j] represents the estimated completion cost of the tasks on vjin ck, which is defined by (17).
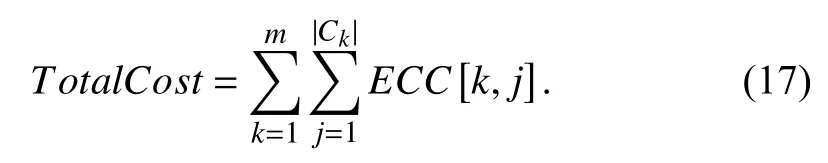
Assume that the unit price of a VM is only related to the computing performance of the virtual resource. A higher unit price indicates a more powerful computing of the virtual resource.
3) The Average Resource Utilization of VMs
AU denotes the average resource utilization of VMs. It is defined by
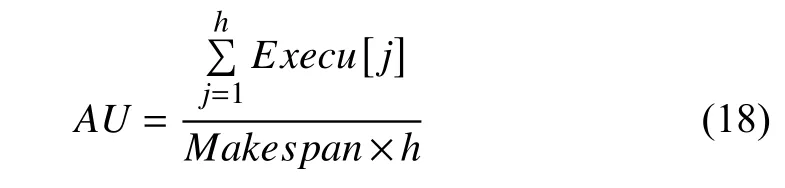
where Execu[j] is the execution time of all tasks on vj. Its value directly reflects whether cloud resources are efficiently utilized.
4) Load Balance
B denotes the load balancing of service resources. It is defined as
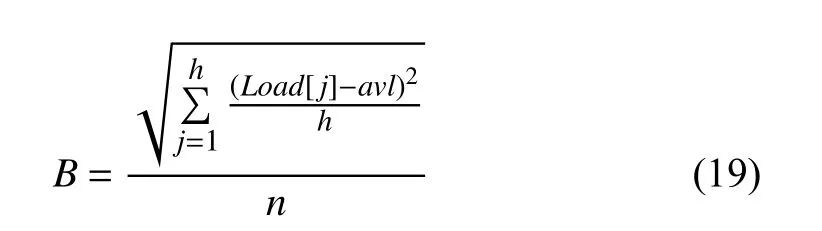
where Load[j] represents the load of vj, that is, the task completion time of vj; avl represents the average load of the VM, namely, its average task completion time. The smaller value of B implies a better workload balance.
5) Runtime Overhead
RO denotes the runtime of the algorithms. It reflects the performance of the algorithm to some extent. A good algorithm has a relatively small runtime overhead.
B. Parameter Setting
1) Parameter Setting of the MCS Algorithm
Set the number of cuckoo nests to CN = 25. The number of dimensions of the nest is the number of tasks to be processed.Set the possibility of finding the cuckoo’s eggs, Pα= 0.25.The step size factor α of Levi’s flight α(i)=b?q×(exp(10(i?1)/N_iter ?1)?1)/(exp(10)?1) (i=1,2,...,N_iter) is set to change linearly with iterations i, where N_iter is the maximum number of iterations, i is the number of iterations,and q and b are two positive numbers satisfying q < b < 1. In this work, let q = 0.39 and b = 0.4. A larger α can enhance the exploration ability of MCS and avoid falling into a local optimum in the initial stage. During the execution process of MCS, a smaller α makes MCS stably converge at a better solution.
2) Parameter Setting of the HCPS Algorithm
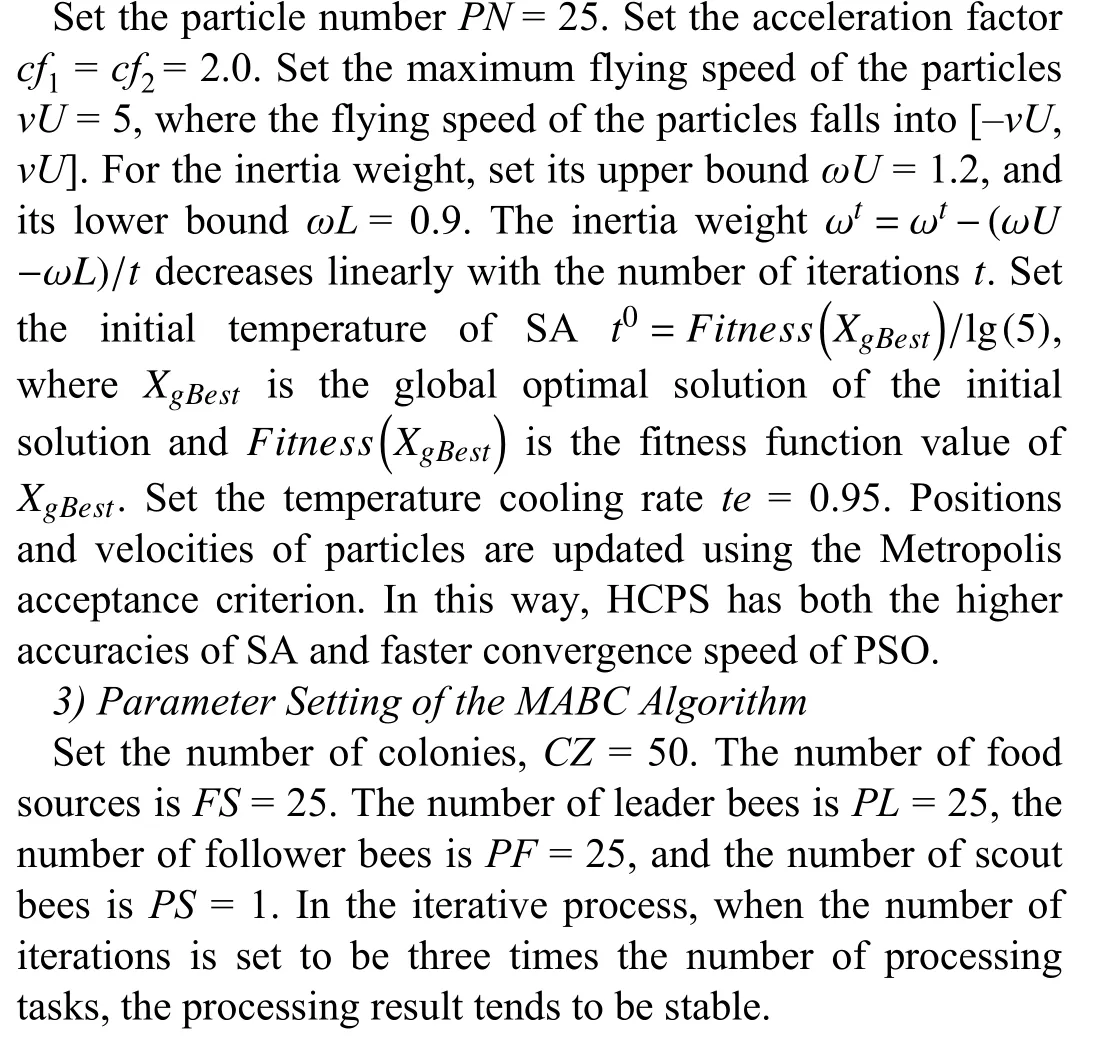
C. Experiments and Analysis for Batch Tasks
Set up the parameters for a multi-cloud and tasks as follows:1) m = 4, D = 12, h = 24, n = [10, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500] ×12; and 2) m = 4, D = 12, h = 48, n = [600, 700, 800, 900,1000, 1100] × 12, respectively. Table II presents task parameters. In order to simulate the diversity of tasks, we set up 12 types of tasks, the specific values of which are random.From task types 1 to 12, the task workload is gradually expanding and each task has a different priority due to its different user type. During simulation task expansion, tasks have different performance requirements for resources. For example, smaller tasks require-low-performance resources,and larger tasks require high-performance resources. Here, the performance of the resource is simplified to be proportional to the price of the resource.

TABLE II TASK TYPES AND PARAMETERS
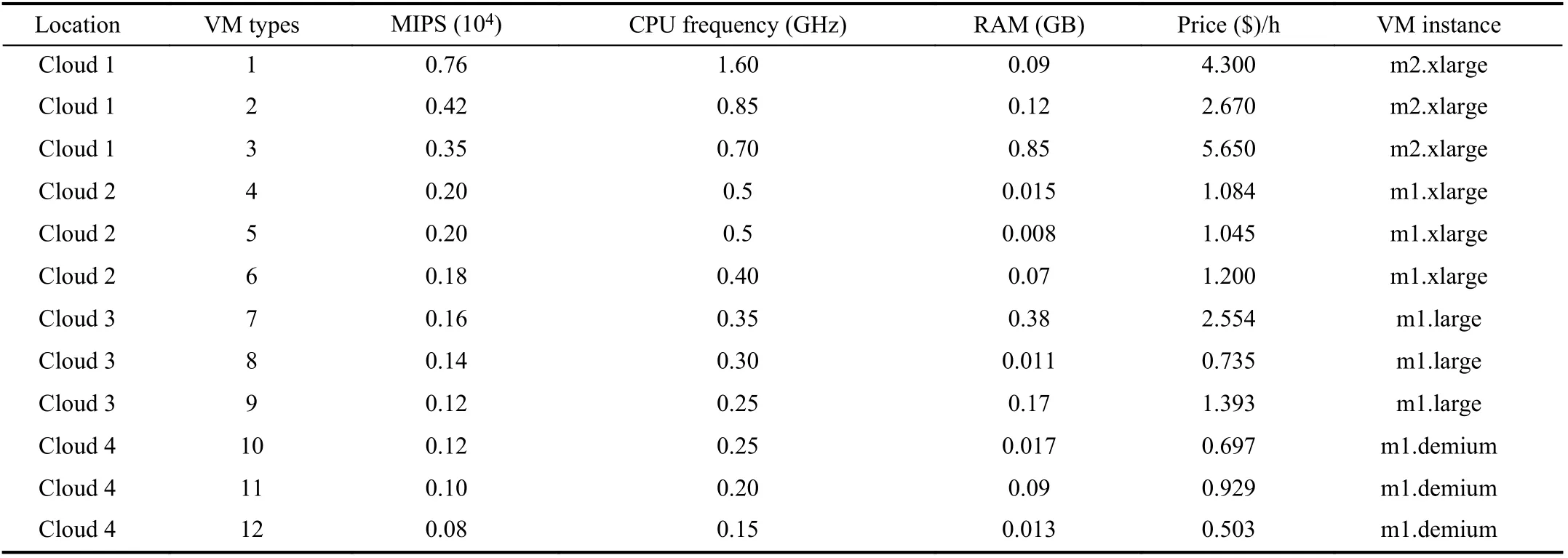
TABLE III VM TYPES AND PARAMETERS
Tables III lists the VM parameters in the experiment, which refers to the experimental data in [1]. In order to facilitate the calculation of the processing time of tasks, we assume that the processing speed of each VM is proportional to its CPU.Owing to the connection of the fiber network in a cloud and the flexible disk storage supply, this experiment assumes that these two factors are not considered.
Table IV lists the specific parameter settings for security assessment of each CSP and baseline level of SSLO parameter values, which refer to the corresponding data in [39].
1) Convergence Speeds of Three Benchmark Algorithms
Use a task example with the size of 1100 × 12 to analyze the convergence speed of our proposed MMA algorithm and threebenchmark algorithms. In Figs. 5–7, the horizontal axis, major vertical axis, and minor vertical axis represent the number of iterations in an algorithm, Makespan, and TotalCost,respectively. Because of stochastic nature of evolutionary algorithms, each of three benchmark algorithms is executed independently for 30 times to obtain the averaged objective result and the convergence speed of the algorithm as the number of iterations increases.
TABLE IV SECURITY EXPERIMENTATION PARAMETERS
Fig.5 shows the convergence speed of the MCS algorithm,which is faster than that of HCPS. It can be seen that when the number of iterations for the algorithm is greater than 50, the algorithm is close to convergence.
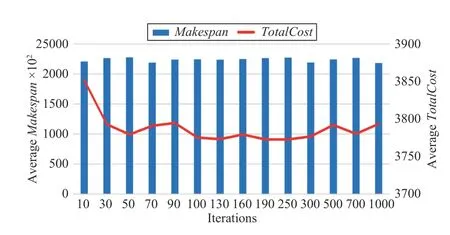
Fig.5. Convergence speed of MCS.

Fig.6. Convergence speed of HCPS.
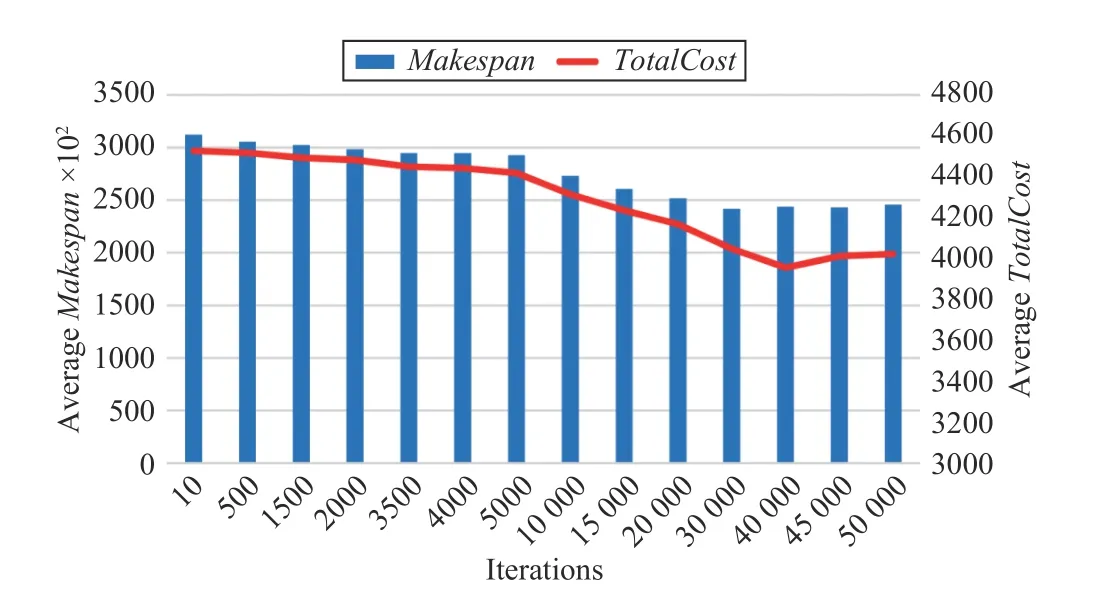
Fig.7. Convergence speed of MABC.
Fig.6 presents the convergence speed of the HCPS algorithm. It shows that with the increasing number of iterations, Makespan is continuously decreasing, and so is TotalCost. When the number of iterations is greater than about 160, the changes of Makespan and TotalCost are no longer obvious, which indicates that the algorithm has converged at this time.
Fig.7 shows that the convergence speed of the MABC algorithm is slower than the previous two algorithms. When the number of iterations for the algorithm increases to about 40 000, Makespan and TotalCost gradually keep little changes, and the algorithm is close to convergence.
2) Convergence Speed of the MMA Algorithm
MMA algorithm with the polynomial complexity can obtain an exact solution. Using the same task example with the size of 1100 × 12 as an input, the MMA algorithm takes only seven iterations to reach the termination condition and converges. In Fig.8, the horizontal axis is the number of iterations, and the vertical axis is the change in Makespan and
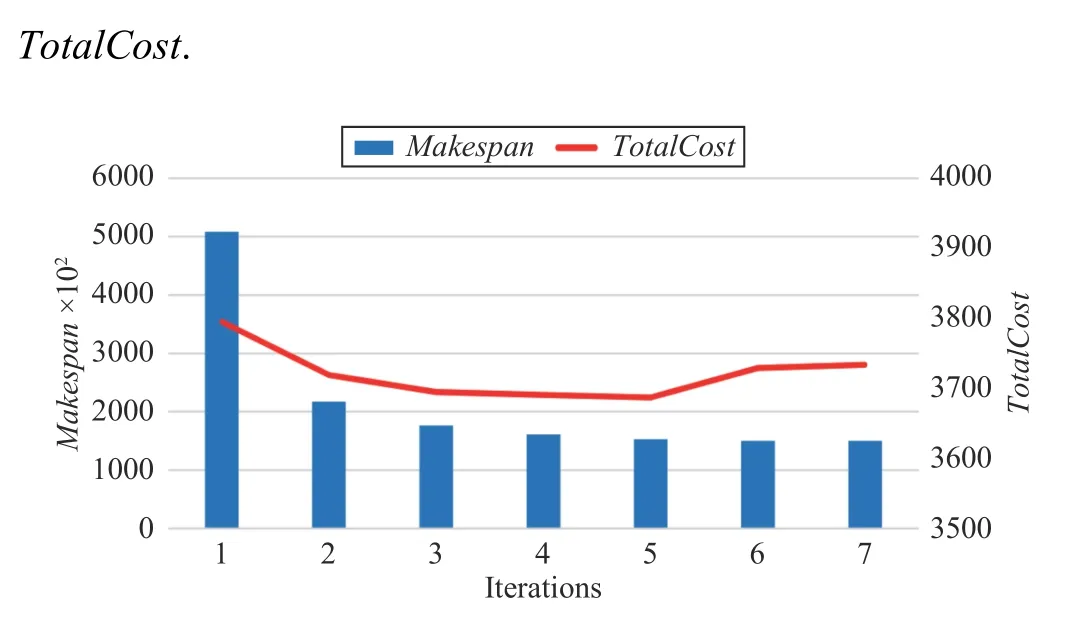
Fig.8. Convergence speed of MMA.
3) Algorithm Runtime Overhead at Different Data Scales.
The overhead of an algorithm refers to the running time taken for it to complete mapping of all tasks to the VMs.Table V shows the overhead of algorithms when the number of [10, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500] × 12 tasks are executed on 24 VMs, respectively. Table VI shows the overhead of algorithms when the number of [600, 700, 800, 900, 1000,1100] × 12 tasks are executed on 48 VMs, respectively. The unit of the runtime overhead in the table below is milliseconds. The data in Table V is the runtime overhead to obtain the desired solution.
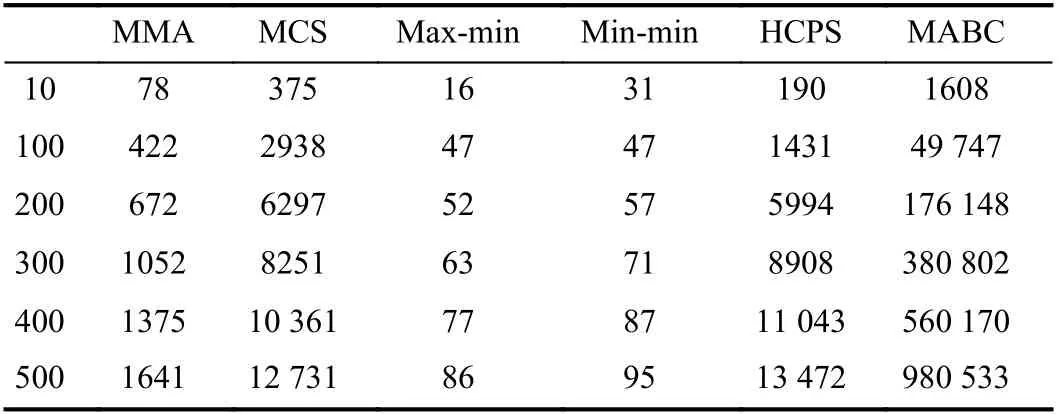
TABLE V ALGORITHM RUNTIME OVERHEAD FOR [10, 100, 200, 300, 400,500] ×12 TASKS ON 24 VMS
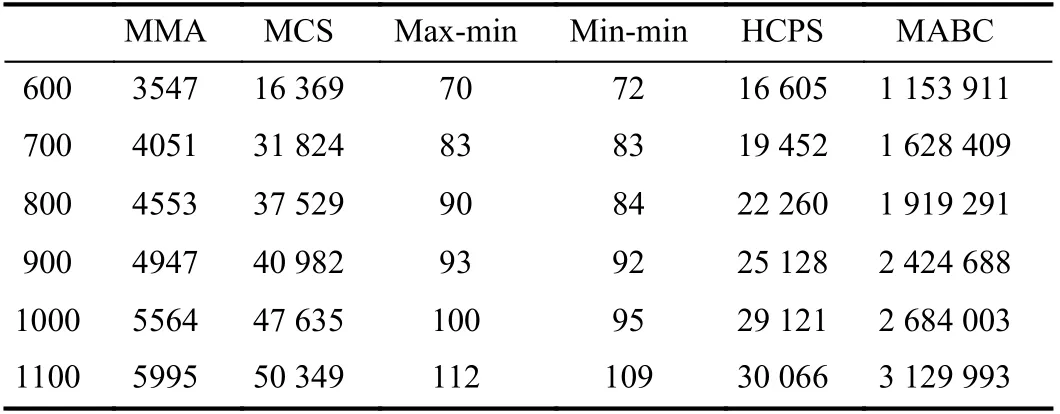
TABLE VI ALGORITHM RUNTIME OVERHEAD FOR [600, 700, 800, 900, 1000,1000]×12 TASKS ON 48 VMS
From Tables V and VI, we can conclude that as the task size increases, the runtime overhead of each algorithm increases.The max-min algorithm and min-min algorithm have very low runtime overhead due to their simple allocation operations.The MMA algorithm performs a series of operation calculations, so its overhead will be much higher. When the task size is small, the overhead of the HCPS algorithm is similar to that of the MCS algorithm. As the task size increases, the overhead of the MCS algorithm increases rapidly, while the overhead of the HCPS algorithm increases slowly. Therefore, in terms of overhead, the HCPS algorithm is superior to the MCS algorithm. The MABC algorithm has the largest runtime overhead. From the above analysis, we can see that our proposed MMA algorithm is still advantageous in terms of overhead.
4) Results of Scenario 1: Scheduling [10, 100, 200, 300,400, 500] × 12 Tasks onto 24 VMs.
Makespan, TotalCost, average resource utilization AU, and load balance B obtained by using four different algorithms to schedule tasks are shown in Figs. 9–12, respectively, where the horizontal axis represents the number of tasks for [10, 100,200, 300, 400, 500] × 12, respectively. We analyze the optimal solutions obtained by all algorithms.
Fig.9 shows that the MMA algorithm has a greater advantage as the number of tasks increases. The results of the MCS, max-min, and MABC algorithm differ slightly in the makespan. The HCPS algorithm gets the longest makespan.This means that for small-scale tasks, the advantages of the HCPS algorithm cannot be fully utilized.
Fig.10 shows the MMA and MCS algorithms always have a lower cost than others. The max-min and min-min algorithms do not achieve a better cost. Because they are traditional single-objective algorithms, they can only effectively reduce the makespan of the tasks.
Fig.11 shows that as the number of tasks increases, the resource utilization rate of the algorithm increases, where MMA algorithm has the highest utilization rate even up to greater than 95%. When the number of tasks is small, the resource utilization of the HCPS algorithm is only about 50%.However, with an increase in the number of tasks, the HCPS algorithm is almost similar to MCS and max-min algorithms,and the resource utilization rate has reached about 80%. It can be seen that HCPS algorithm has certain advantages in processing multi-dimensional functions among the three benchmarks.
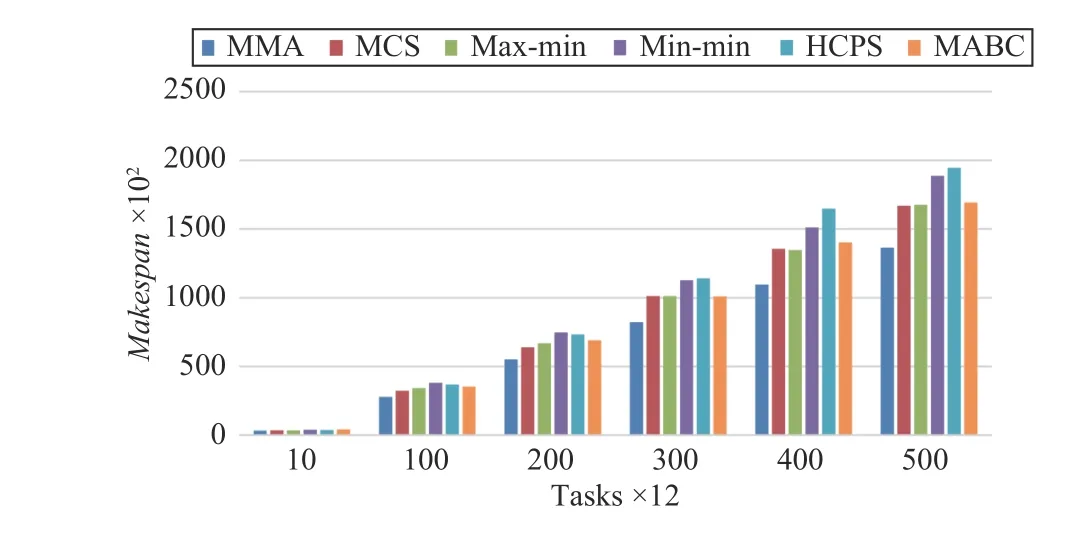
Fig.9. Makespan versus task numbers in Scenario 1.
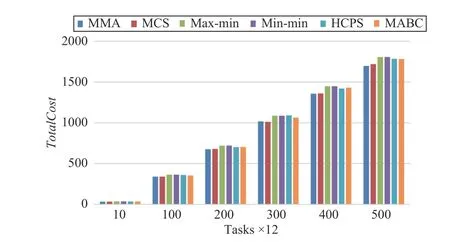
Fig.10. Total cost versus task numbers in Scenario 1.
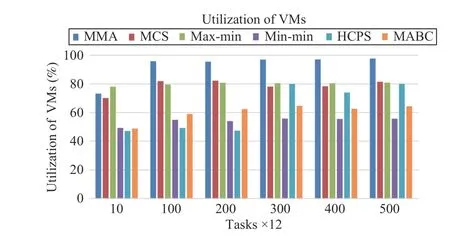
Fig.11. Average resource utilization versus task numbers in Scenario 1.
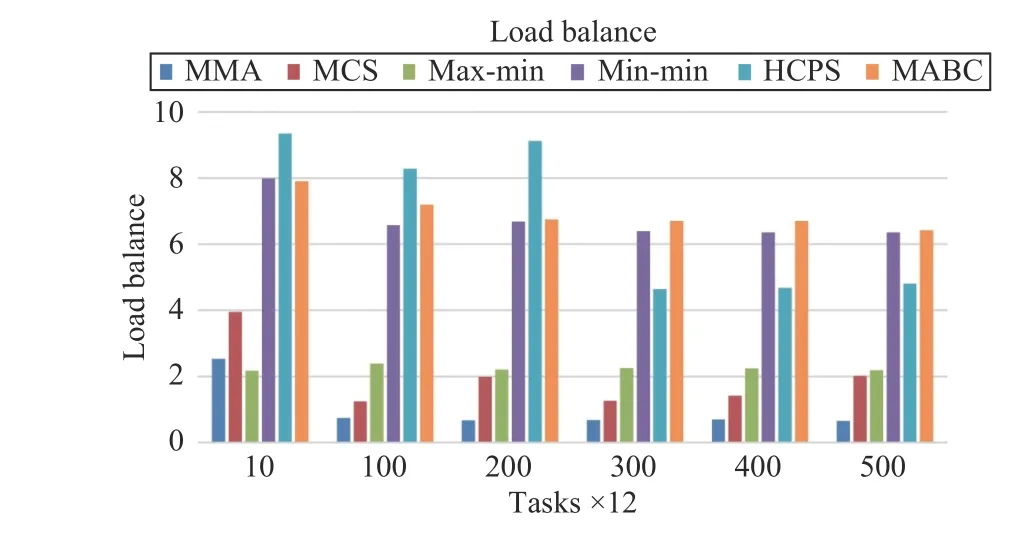
Fig.12. Load balance versus task numbers in Scenario 1.
Fig.12 shows that the proposed MMA algorithm is the most stable in terms of load balancing for different numbers of tasks. When the number of tasks increases to a certain threshold, B is less than 0.46. The MCS algorithm also has great advantages in load balancing and is superior to max-min.
5) Results of Scenario 2: Scheduling [600, 700, 800, 900,1000, 1100]×12 Tasks onto 48 VMs.
To further verify the performance of the MMA algorithm,we expanded the task scale from [10, 100, 200, 300, 400, 500] ×12 to [600, 700, 800, 900, 1000, 1100] × 12 and the number of VMs also increased from 24 to 48.
Fig.13 shows that the proposed MMA algorithm still has a great advantage in reducing Makespan when increasing the task size and the number of VMs. At the same time, MCS and max-min algorithms have the same ability to reduce Makespan. When the task scale is increased, the HCPS algorithm is better than MABC in reducing Makespan. It can be seen that the HCPS algorithm has certain advantages than MABC in processing multi-dimensional functions.
Fig.14 shows that the proposed MMA algorithm is still slightly better than other algorithms in terms of TotalCost. In addition, MCS and HCPS algorithms are very close to MMA in terms of TotalCost. max-min, min-min, and MABC perform poorly on TotalCost.
Fig.15 shows the resource utilization of each algorithm as the task scale and VM numbers increases. It can be seen that even if the task size is increased, the resource utilization of the MMA algorithm is still higher than other algorithms. The resource utilization of the max-min, MCS and HCPS algorithms can all reach 80%. However, the resource utilization of min-min and MABC algorithms can only reach about 50%.
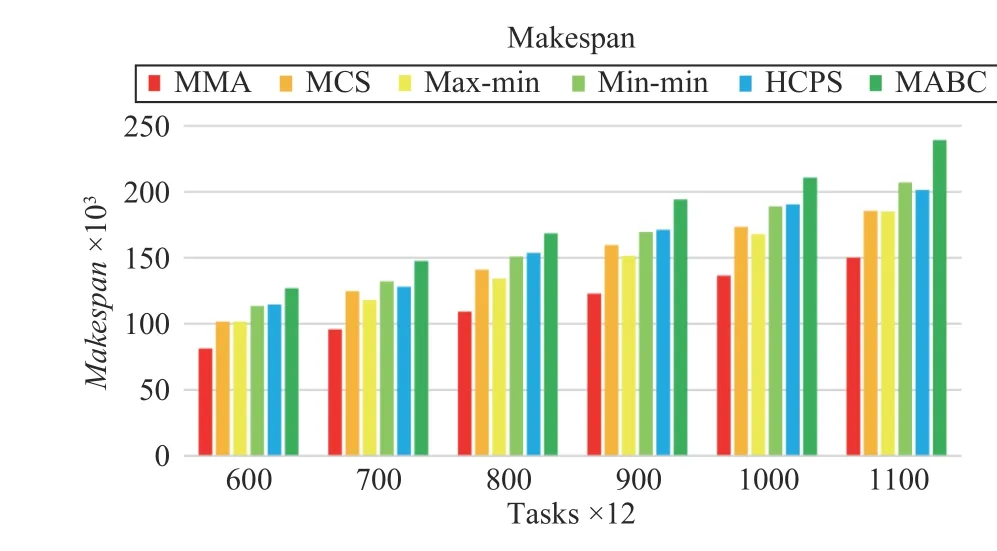
Fig.13. Makespan versus task numbers in Scenario 2.
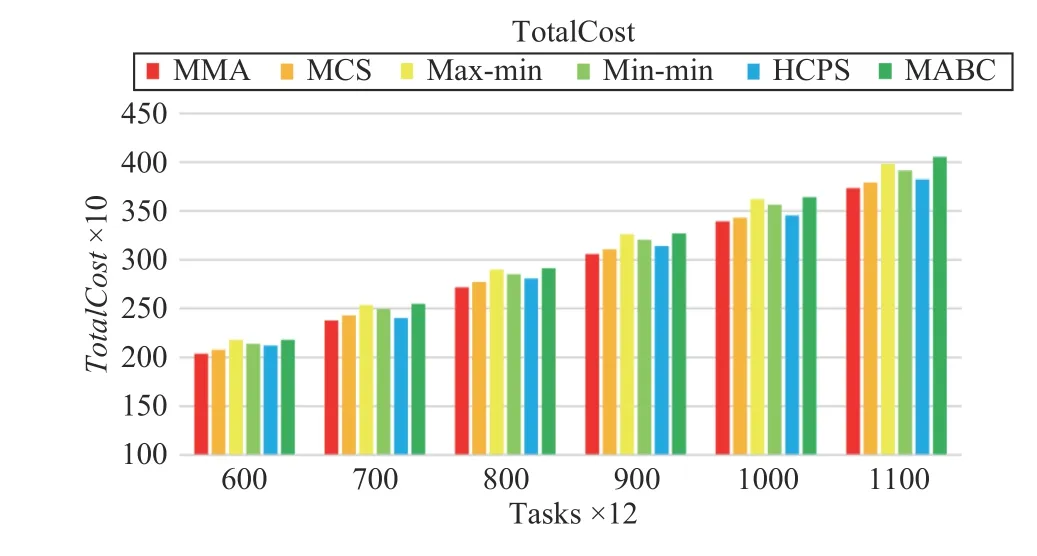
Fig.14. Total cost versus task numbers in Scenario 2.
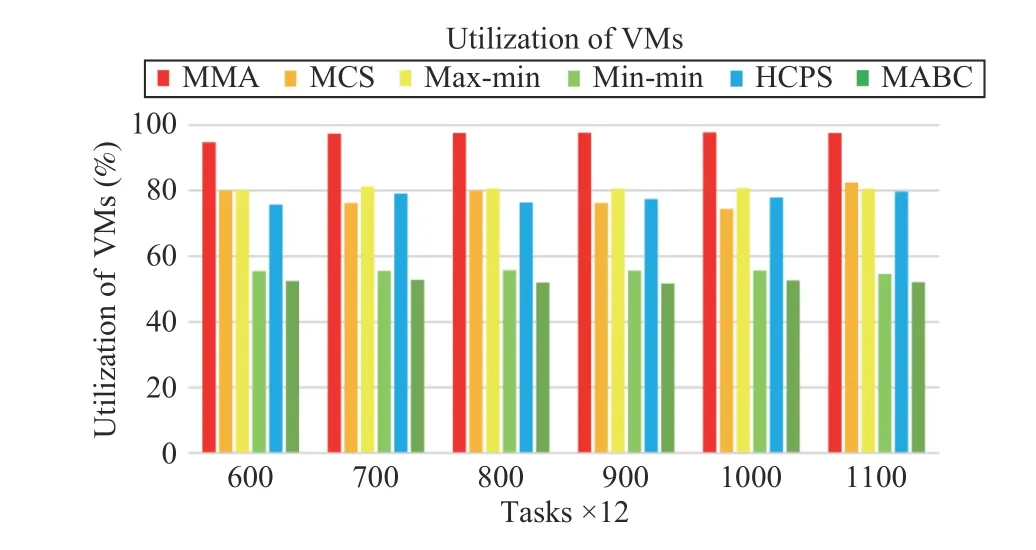
Fig.15. Average resource utilization versus task numbers in Scenario 2.
Fig.16 shows that even if the task scale and VM numbers increases, the MMA and MCS algorithms do very well in load balancing. We can also find that the min-min and MABC algorithms cannot do well in load balance, because the former always allocates tasks to high-performance VMs, and the latter has difficulty in finding a better solution.
Therefore, the above results of experiments show that our proposed MMA algorithm has great advantages in many metrics.
D. Experiments and Analysis for Workflow Tasks
For workflows, Table IV is also used for security assessment of each CSP and the baseline level of SSLO parameter values.
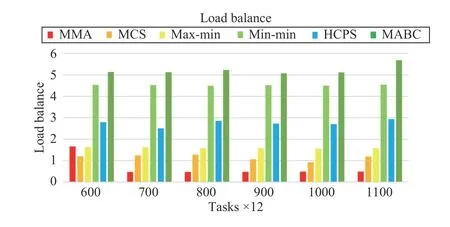
Fig.16. Load balance versus task numbers in Scenario 2.
We take four real-world scientific workflows [53] as the input, which are CyberShake_1000, Epigenomics_997,Inspiral_1000, and SIPHT_1000. In this work, we focus on the scheduling of cloud resources under the constraints of security and reliability, thus, we simplify details of data transmission among data-intensive workflow tasks and handle the precedence among the tasks.
By the MMA algorithm and benchmark algorithms, we conducted scheduling simulations for these four types of workflows. A directed acyclic graph (DAG) can characterize the dependencies among the tasks of a workflow, where vertices represent the tasks and a directed edge denotes the precedence constraint between two tasks. The highest priority is assigned to one or more tasks (vertices in a DAG) which have no predecessor (parents) tasks, are called entry tasks.Except for the entry tasks, a task can be executed only after its parent tasks are finished. The priorities of entry tasks are numbered Level-1. Then, we number the level of each successor (child) vertex of Level-1 vertices. In a top-down manner, each task can be assigned with a unique priority(Level-number). Therefore, the proposed MMA algorithm can be employed to schedule a workflow under the addressed security and reliability constraints.
1) Convergence Speed
Since the convergence speed of each algorithm for the four workflows are similar, we present the convergence speed of algorithms only for a CyberShake_1000 workflow.
For a CyberShake_1000 workflow, Figs. 17–20 show the convergence speeds of different algorithms. The execution of needs only three iterations to obtain a solution, which has both lower TotalCost and shorter Makespan than those by three benchmark algorithms.
For the other workflows, i.e., CyberShake_1000,Epigenomics_997, and Inspiral_1000, Algorithm 4 performs three iterations at most to obtain a good solution.
2) Runtime Overhead
Due to the polynomial computational complexity of the MMA algorithm, its runtime overhead is significantly lower than that of each evolutionary algorithm. Table VII presents the runtime of algorithms.
3) Scheduling Results for Workflows
Figs. 21–24 plot the performance of different algorithms in makespan, cost, average resource utilization, and load balancing for four types of workflows, respectively. Figs. 21–24 indicate that MMA algorithm can obtain the best performancewhen it schedules four types of workflows compared with the scheduling results obtained by benchmark algorithms.
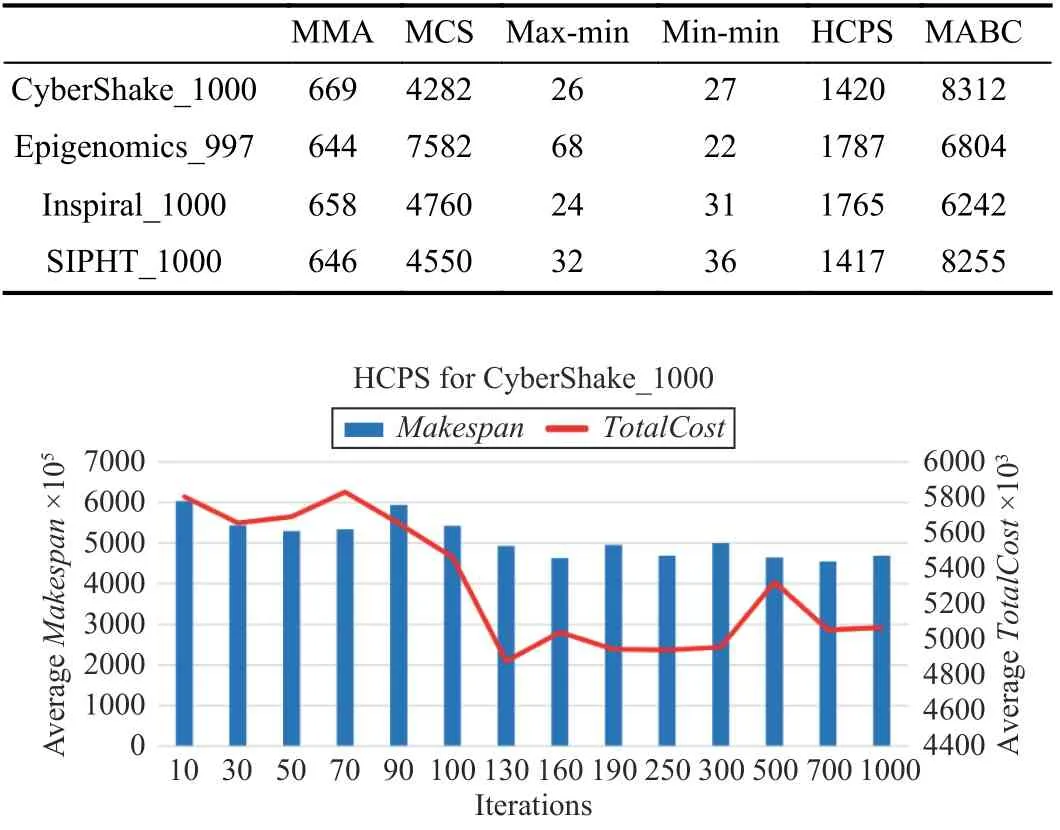
TABLE VII ALGORITHM RUNTIME OVERHEAD FOR WORKFLOwS ON 48 VMS
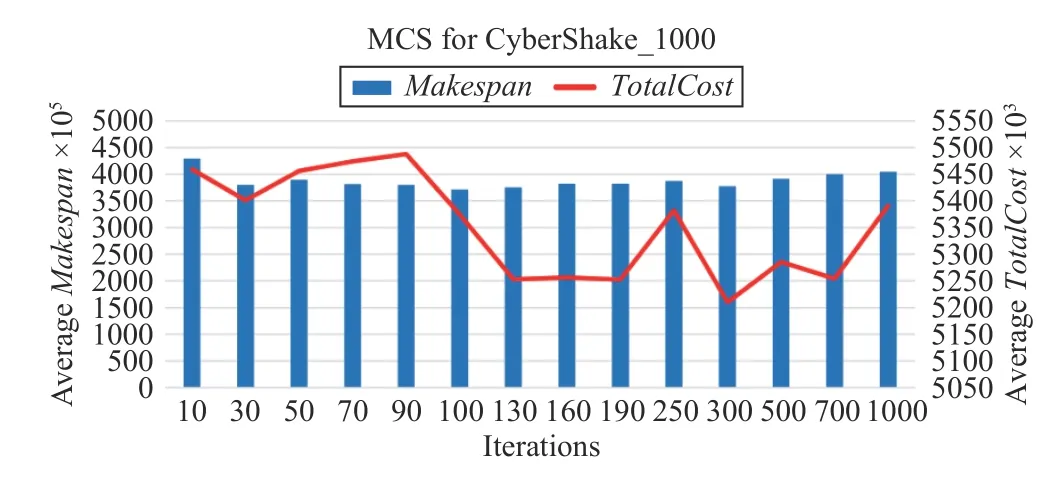
Fig.18. Convergence speed of MCS for CyberShake_1000.
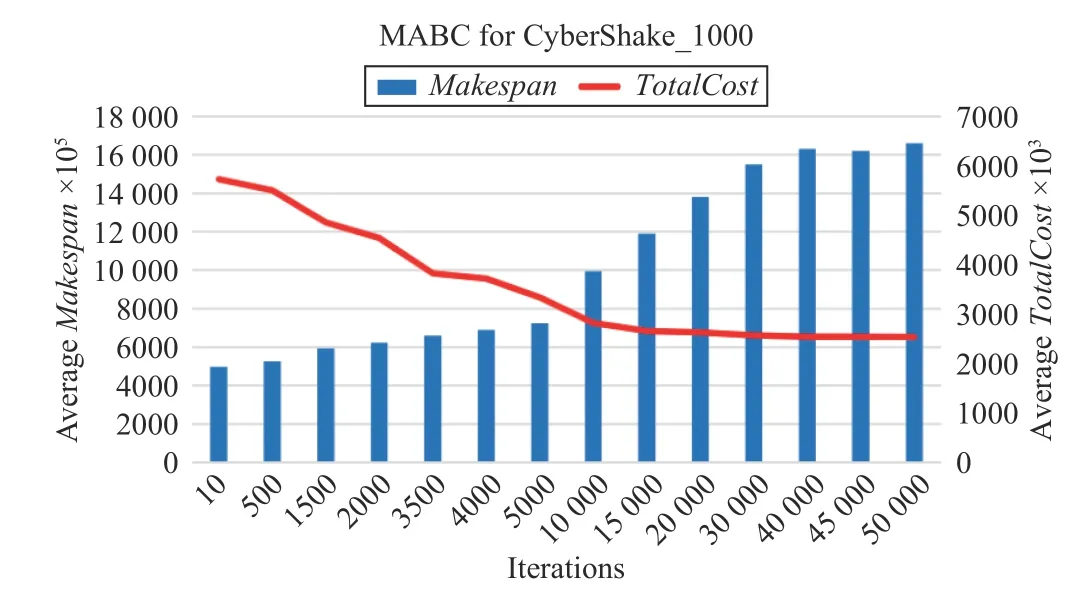
Fig.19. Convergence speed of MABC for CyberShake_1000.
VI. CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE WORK
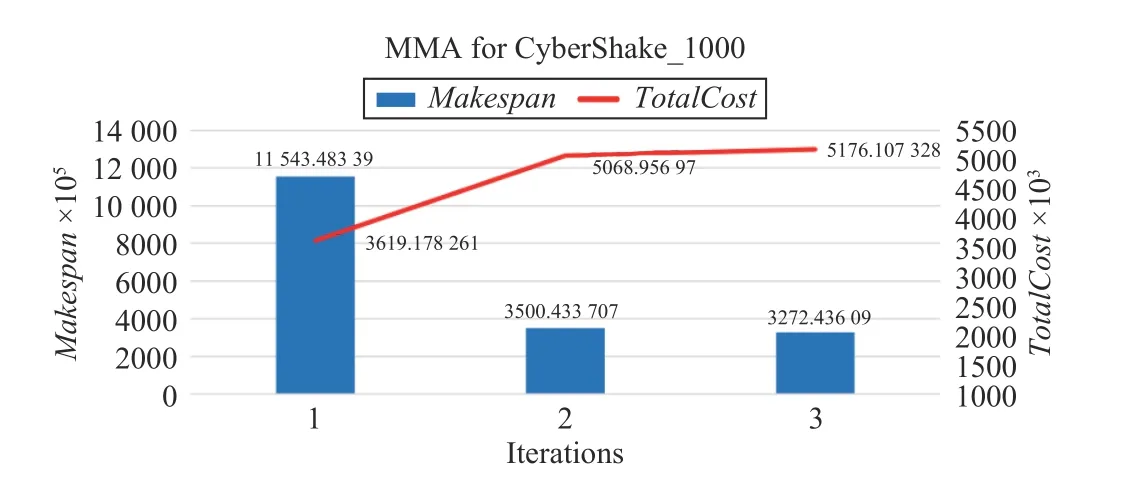
Fig.20. Convergence speed of MMA for CyberShake_1000.
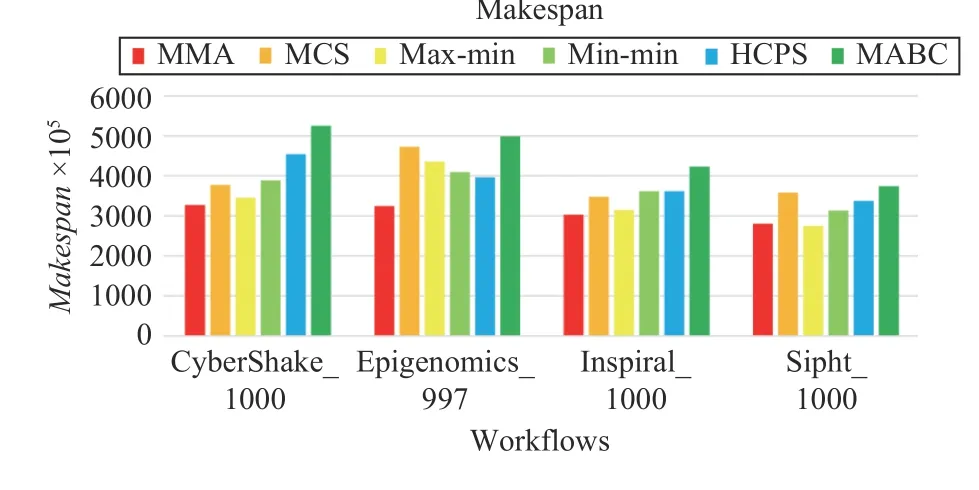
Fig.21. Makespans of different workflows.

Fig.23. Average resource utilization of different workflows.
Aimed at the problem of tasks scheduling in a multi-cloud environment subject to security and reliability constraints, we propose a matching strategy and resource allocation algorithms for user tasks in a multi-cloud system with heterogeneous types of VMs. Candidate resources are initially allocated for the tasks so that they meet the user’s performance and trust QoS demands while achieving the best matching degree. Upon this pre-allocation scheme, multiple rounds of re-allocation are performed to find a schedule that can optimize tasks execution time and cost by minimizing the variance of the estimated completion time, provide the user with matching resources as much as possible, satisfy the user’s performance and trust QoS requirements, and balance the workload well among different types of VMs. Hence, the overall completion time and cost are reduced, and resource utilization and workload balancing are improved to obtain higher QoS for users.
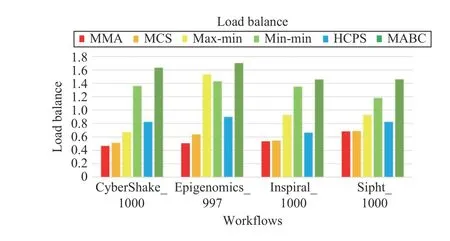
Fig.24. Load balance of different workflows.
Our proposed method can be applied to scheduling cloudcomputing resources in the scenarios of both batch tasks and workflows. For example, a large amount of different types of business-to-business transaction packages, or real-world workflows, may be submitted to a multi-cloud system to be processed. These tasks should be scheduled efficiently to be processed under the security and reliability requirements in a multi-cloud system. In this work, we do not consider some features of the task itself, such as deadlines and data transmission among the workflow tasks. Our future work will focus on such issues.
 IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica2021年4期
IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica2021年4期
- IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica的其它文章
- Adaptive Pseudo Inverse Control for a Class of Nonlinear Asymmetric and Saturated Nonlinear Hysteretic Systems
- Property Preservation of Petri Synthesis Net Based Representation for Embedded Systems
- Dynamic Evaluation Strategies for Multiple Aircrafts Formation Using Collision and Matching Probabilities
- Residual-driven Fuzzy C-Means Clustering for Image Segmentation
- Vibration Control of a High-Rise Building Structure: Theory and Experiment
- Decoupling Adaptive Sliding Mode Observer Design for Wind Turbines Subject to Simultaneous Faults in Sensors and Actuators
