Efficacy and safety outcomes with remdesivir in COVID-19 patients:A meta-analysis
Tejas Kamleshbhai Patel,Parvati B Patel,Manish Barvaliya,Vijayalaxmi,Hira Lal Bhalla
Tejas Kamleshbhai Patel,Vijayalaxmi,Hira Lal Bhalla,Department of Pharmacology,All India Institute of Medical Sciences,Gorakhpur,Gorakhpur 273008,Uttar Pradesh,India
Parvati B Patel,Department of Pharmacology,GMERS Medical College,Gotri,Vadodara 390021,Gujarat,India
Manish Barvaliya,Department of Pharmacology,Government Medical College,Bhavnagar,Bhavnagar 364001,Gujarat,India
Abstract BACKGROUND Remdesivir is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug having in vitro activity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 and is currently being used on a compassionate basis outside of clinical trials.AIM To analyze the efficacy and safety of remdesivir compared with other interventions in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients.METHODS We searched online databases to include randomized controlled trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of remdesivir compared with other interventions in COVID-19 patients.We summarized efficacy and safety data as risk ratios (RRs)with 95% confidence interval (CI) and used Mantel-Haenszel fixed or randomeffect models.We estimated the number needed to treat (NNT) to cause one additional outcome.We used the GRADE approach to assess the quality of the evidence for all outcome parameters.RESULTS We included four randomized controlled trials.We observed no significant difference in mortality (RR:0.83;95%CI:0.57–1.20;I2 = 59%) and rate of ventilation(RR:0.69;95%CI:0.41-1.18;I2 = 77%) between remdesivir- and placebo-treated patients.Remdesivir showed higher rates of clinical recovery than placebo (RR:1.10;95%CI:1.04–1.16;I2 = 0%;NNT:14.3).We observed no difference in overall adverse events between remdesivir- and placebo-treated patients (RR:1.05;95%CI:0.86–1.27;I2 = 77%).We observed less risk of serious adverse events (RR:0.75;95%CI:0.63–0.89;I2 = 0%) in remdesivir- than placebo-treated patients.The GRADE approach suggested moderate quality of evidence for all efficacy and safety outcomes.CONCLUSION We observed limited clinical benefit of remdesivir over placebo in the treatment of COVID-19.Our findings could be biased because of the small number of trials.
Key Words:COVID-19;SARS-CoV-2;Antiviral;Pneumonia;Remdesivir;Meta-analysis;Systematic review
INTRODUCTION
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was first described in China.Later it was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO).COVID-19 is highly contagious,and is associated with significant morbidity and mortality[1-4].Currently,there are no definitive proven antiviral treatments for COVID-19.Several potential therapeutic options,including remdesivir,have been evaluated for the treatment of COVID-19[5].
Remdesivir is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug having activity against several RNA viruses,including filoviruses (e.g.,Ebola virus,Marburg virus),coronaviruses (e.g.,SARS-CoV,Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus,and paramyxoviruses (e.g.,respiratory syncytial virus,Nipah virus,and Hendra virus).It is a prodrug metabolized within cells into the active nucleoside triphosphate.This nucleoside triphosphate acts as an analog of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and competes with the natural ATP substrates to selectively inhibit RNA-dependent RNA polymerase resulting in delayed RNA chain termination during the process of viral replication[6,7].Delayed chain termination at positions I and 3 are key elements of inhibition observed with SARS-CoV,MERS-CoV[6]and SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase complexes[8,9].An in vitro study by Wanget al[10]suggested that remdesivir could achieve a therapeutic working concentration against SARS-CoV-2 in Vero E6 cells.It inhibited virus infection in human liver cancer Huh-7 cells,which are sensitive to SARS-CoV-2[10].Moreover,prophylactic and therapeutic administration of remdesivir reduced the virus replication,disease severity and lung damage caused by MERS-CoV in the rhesus macaque animal model[11].
The clinical evidence of utility of remdesivir in COVID-19 patients is limited.It is primarily used on a compassionate basis outside of clinical trials in the absence of other available effective treatment options[12,13].Recently published studies have shown contradictory findings about the efficacy of remdesivir in COVID-19.The adaptive COVID-19 treatment trial (ACTT) trial suggested better clinical recovery and trends of mortality reduction with remdesivir[14],while he WHO solidarity trial did not find a significant reduction in mortality with the use of remdesivir in COVID-19[15].In this meta-analysis,we aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of remdesivir in COVID-19 patients based on evidence from published randomized controlled clinical trials.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Literature search
We searched the clinical studies of remdesivir in COVID-19 patients in PubMed,medrxiv.org,biorxiv.org,mediterranee-infection.com/pre-prints-ihu,LILACS,CNKI and Google Scholar.The PubMed search terms were:(“Remdesivir”) AND (“COVID-19” OR “SARS-CoV-2” OR “Coronavirus”).The last search was run on October 28,2020.There were no language restrictions for inclusion of the studies.
Types of participants
Patients of any age and either sex who had virologically confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection were included in the analysis.
Types of studies
Inclusion criteria:(1) Randomized controlled clinical trials;(2) Open labeled or blinded studies;and (3) Comparative trials of remdesivir with any other interventions including placebo.
Exclusion criteria:(1) Studies of remdesivir other than SARS-CoV-2;(2) Observational studies,noncomparative studies,case reports;(3) In vitro and animal studies of remdesivir in COVID-19;and (4) Review articles,commentaries,viewpoints,or editorials.
Types of intervention
Use of remdesivir in COVID-19 patients irrespective of dose and duration of therapy was considered.All treatment modalities including placebo were considered as the comparator arm.
Risk of bias assessment
The methodological characteristics of included studies were assessed through five domains of the revised Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool for randomized controlled clinical trials (ROB-II)[16].
Data extraction
We imported the data into a Microsoft Excel 2016 spreadsheet.The extracted data included publication details,study design,study site,demographics of the study population,baseline clinical characteristics,remdesivir dose,duration and mode of administration,comparator,supportive care,and outcome variables (i.e.number of deaths,number of patients requiring invasive ventilation,clinical recovery and serious adverse events).
Types of outcome measures
Efficacy outcomes:The efficacy outcome variables were the RRs of cumulative mortality,composite mortality and ventilation,mechanical ventilation or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation ECMO) rate and clinical recovery rate of remdesivir in comparison with other interventions.In case of multiple time-point estimation of outcomes in the included studies,we used data at the end of study periods.Intention to treat data were used to estimate the efficacy outcomes.
Safety outcomes:The safety outcome variables were participants with adverse events(overall,grade 3 or 4,and serious adverse events) in the remdesivir and comparator arms.The safety population was used to estimate the safety outcomes.All patients who received remdesivir and comparator drugs irrespective of per-protocol dose and duration were considered as a safety population and included in the estimation of safety outcomes.
Data synthesis and meta-analysis
All outcomes were dichotomous variables.They were summarized as a risk ratio (RR)with 95% confidence interval (CI) using the Mantel-Haenszel method with a fixed- or random-effect model.The selection of meta-analysis model was based on the presence of heterogeneity.The fixed model effect was preferred in the absence of heterogeneity.Heterogeneity was estimated throughI2.Sensitivity analysis of efficacy and safety outcomes was performed based on risk of bias assessment and study design.The meta-analytic summary was calculated by excluding studies showing “some concern”or high risk of bias as per the ROB-II tool and those with an open-label design.
The pooled risk difference of meta-analytic summary was estimated.It was used to calculate the number needed to treat (NNT) to cause one additional outcome[17].The GRADE approach was used to analyze the quality of the evidence for each of the efficacy and safety outcomes.It was assessed based on the following parameters:study limitations,inconsistency,indirectness of evidence,imprecision,and publication bias[18,19].The meta-analysis was conducted with Review Manager version 5.4.1.
RESULTS
Of the 2289 retrieved references,we selected 46 publications for full-text evaluation(Figure 1).We included four randomized controlled trials analyzing the effects of remdesivir in COVID-19 patients.
Characteristics of included studies
Table 1 shows the general characteristics of the included studies.The included studies used remdesivir as an add-on to the standard care of treatment.Beigelet al[14]conducted a double-blind,randomized,placebo-controlled,multicenter study in North America,Europe and Asia;541 patients were assigned to the remdesivir and 521 to the placebo arms.The treatment arms were comparable at baseline for age,gender,race,median time from symptom onset to randomization,co-morbid conditions and severity status.
The WHO Solidarity Trial Consortiumet al[15]was a solidarity trial conducted by the WHO.It was a randomized,open label,parallel arm,multicenter study investigating the effect of four repurposed medications (remdesivir,hydroxychloroquine,interferon-β1a,and lopinavir/ritonavir) with local standard care.The comparator of remdesivir was a group of patients with a similar probability of allocation to receive remdesivir,but instead receiving standard care.A total of 2743 patients were assigned to receive remdesivir.The corresponding 2708 patients were assigned to receive local standard care.Both treatment arms were comparable at baseline for age,gender,comorbidity,bilateral lung lesions,respiratory support and prior impatient days before randomization.
Spinneret al[20]conducted a randomized,open-label,placebo-controlled,multicenter study in moderate COVID-19 pneumonia patients at North America,Europe and Asia.A total of 197 patients were assigned to receive remdesivir of 10 d duration,199 to remdesivir of 5 d duration and 200 to placebo.As all other included studies administered remdesivir for 10 d,we used remdesivir data of 10 d treatment duration only.The treatment arms (remdesivir 10 d and placebo) were comparable at baseline for age,gender,race,co-morbidity,and duration of symptoms before the administration of interventions and duration of hospitalization before the administration of interventions.The placebo-treated group had a higher percentage of patients with baseline oxygen requirement (19%vs13%).Compared with the remdesivir-treated group,a higher percentage of patients in the placebo arm received hydroxychloroquine/chloroquine (45%vs11%),lopinavir/ritonavir (22%vs6%) and azithromycin (31%vs21%).
Wanget al[21]conducted a double-blind,randomized,placebo-controlled,multicenter study in China.A total of 158 patients were assigned to receive remdesivir and 78 to receive placebo.Both treatment arms were comparable at baseline for age,gender,body temperature,viral load,oxygen therapy support and co-interventions(interferon alfa-2b,lopinavir/ritonavir or corticosteroid administration).The remdesivir-treated group had a higher percentage of patients with co-morbidities and a faster respiratory rate at baseline.The placebo-treated group had a higher percentage of patients with early symptom onset at baseline.
Risk of bias in included studies
Three trials were considered to have a low risk of bias for all the domains of the ROB-II tool (randomization process,effect of assignment to intervention,effect of adhering to intervention,missing outcome data,measurement of the outcome,selection of the reported results and overall risk of bias assessment).Spinneret al[20]was considered tohave some concerns for the effect of assignment to intervention domain because of imbalance in co-interventions among remdesivir- and placebo-treated patients.Hence,the overall risk of bias was considered to have some concern as per ROB-II tool(Table 2).
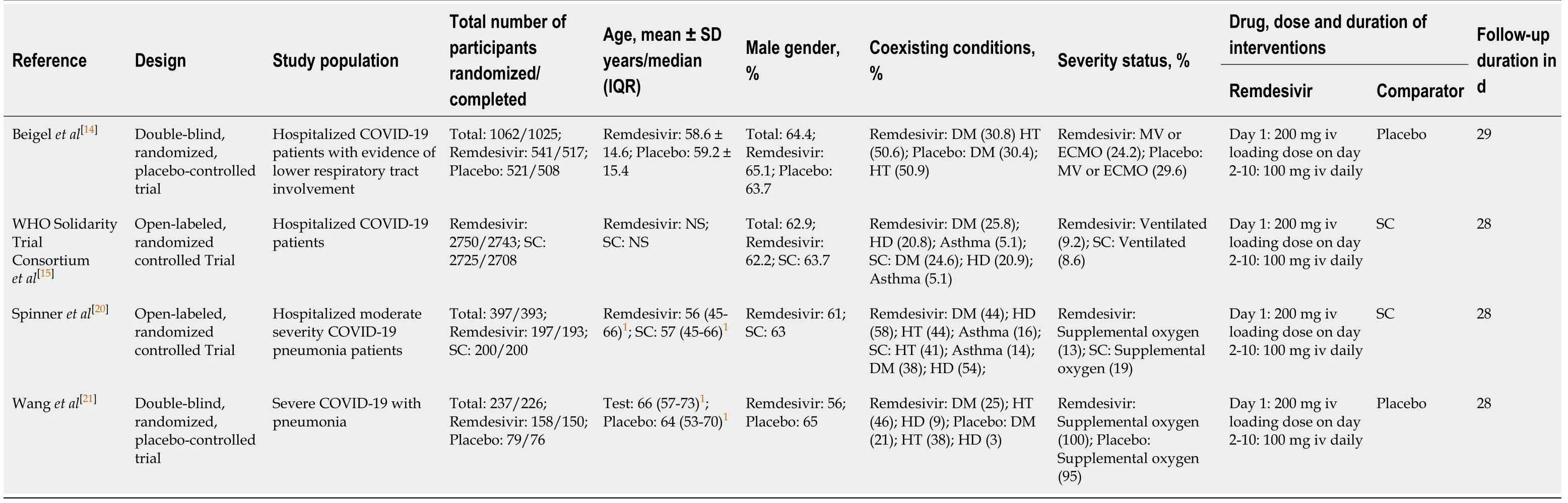
Table 1 General and baseline characteristics of included studies
Meta-analytic summary of efficacy outcomes
Mortality:As shown in Figure 2A,we observed no significant difference in the RR of mortality between remdesivir and control patients (RR:0.83;95%CI:0.57–1.20).AnI2=59% suggested a moderate degree of between-trial heterogeneity.The NNT to cause one additional reduction in mortality of COVID-19 patients with remdesivir was 100(95%CI:-25–100).The GRADE approach suggested moderate quality evidence(Table 3).The sensitivity analysis showed a similar trend in mortality (Table 4).
Ventilation:As shown in Figure 2B,we did not observe any significant difference in RR of mechanical ventilation or ECMO between remdesivir and placebo or supportive care treatment (RR:0.69;95%CI:0.41–1.18;I2= 77%) (Figure 2B).The NNT to cause one additional reduction in need of ventilation of COVID-19 patients with remdesivir was 50 (95%CI:-16.7–100).The GRADE approach suggested moderate quality evidence(Table 3).The sensitivity analysis based on study design suggested a trend of benefit with the use of remdesivir (RR:0.57;95%CI:0.410.77;I2= 0%).
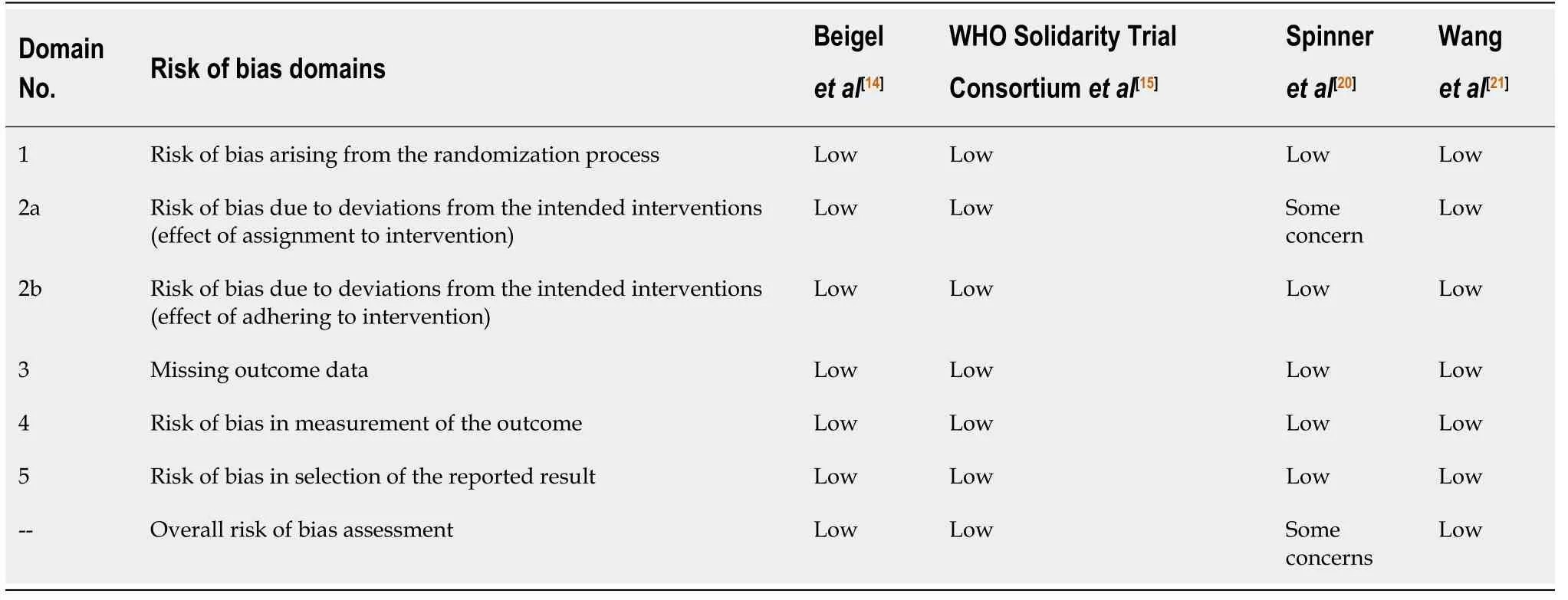
Table 2 Risk of bias assessment as per the Revised Cochrane risk of bias tool for randomized trials
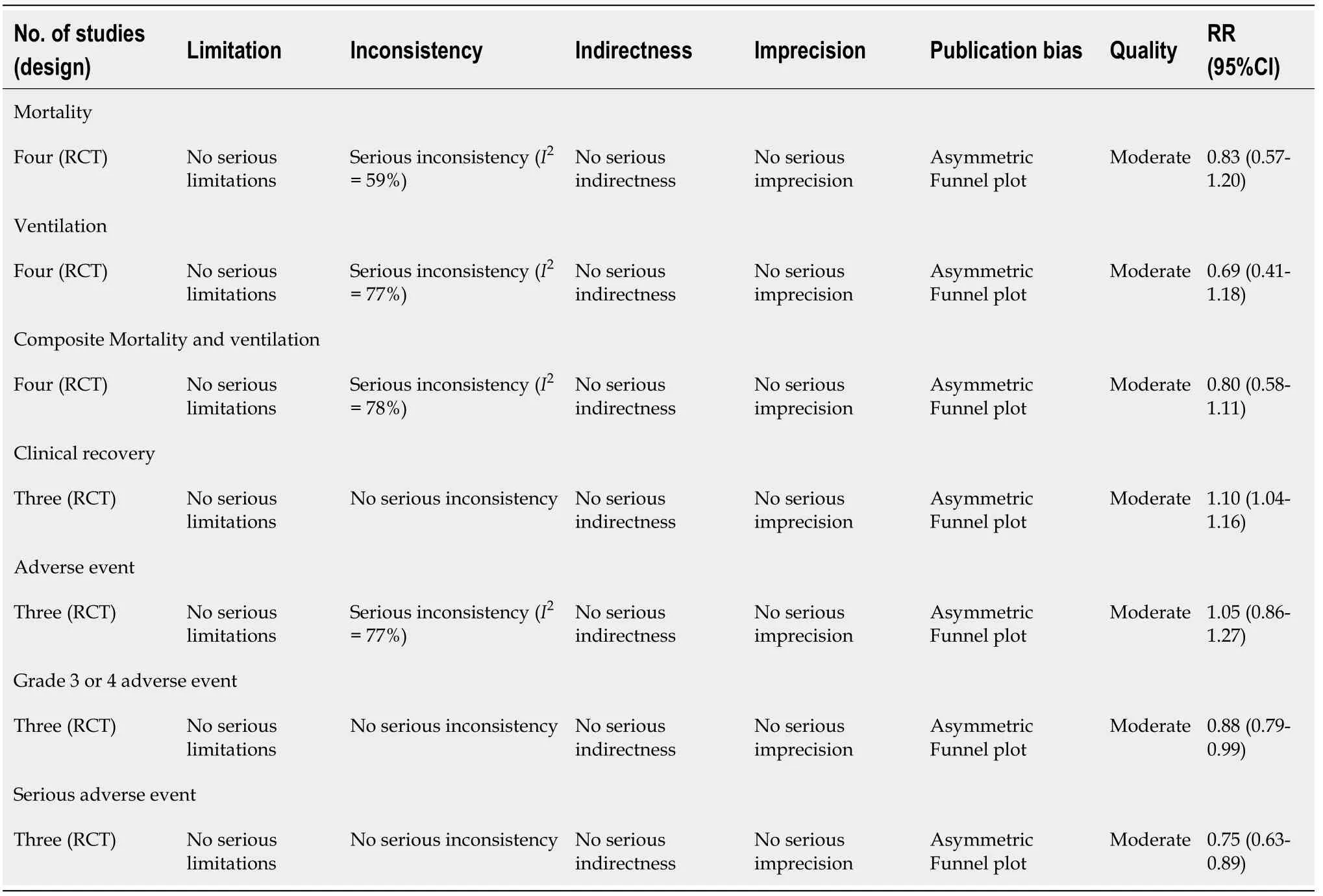
Table 3 Quality assessment for efficacy and safety parameters as per the GRADE approach
Composite mortality and ventilation:We observed no benefit of remdesivir in reducing the risk of the composite outcome of mortality and ventilation compared with placebo or supportive care (RR:0.80;95%CI:0.58–1.11;I2= 78%) (Figure 2C).This corresponds to an NNT to cause one additional participant to experience mortality and ventilation in COVID-19 patients receiving remdesivir compared with placebo of 25(95%CI:-12.5–100).The GRADE approach suggested moderate quality evidence(Table 3).The sensitivity analysis based on study design suggested a trend of benefit in composite outcome with the use of remdesivir (RR:0.69;95%CI:0.55–0.86;I2= 10%)(Table 4).
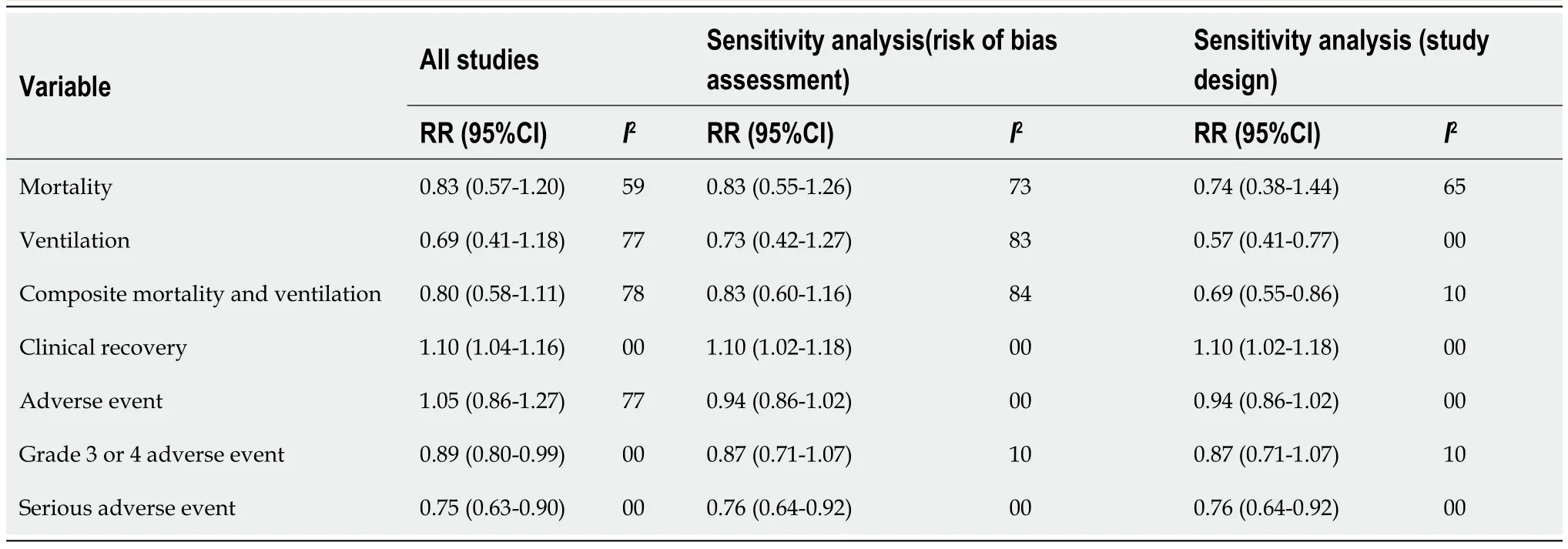
Table 4 Sensitivity analysis of efficacy and safety outcomes based on the risk of bias assessment and study design
Figure 1 Study selection – preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analysis flow diagram.
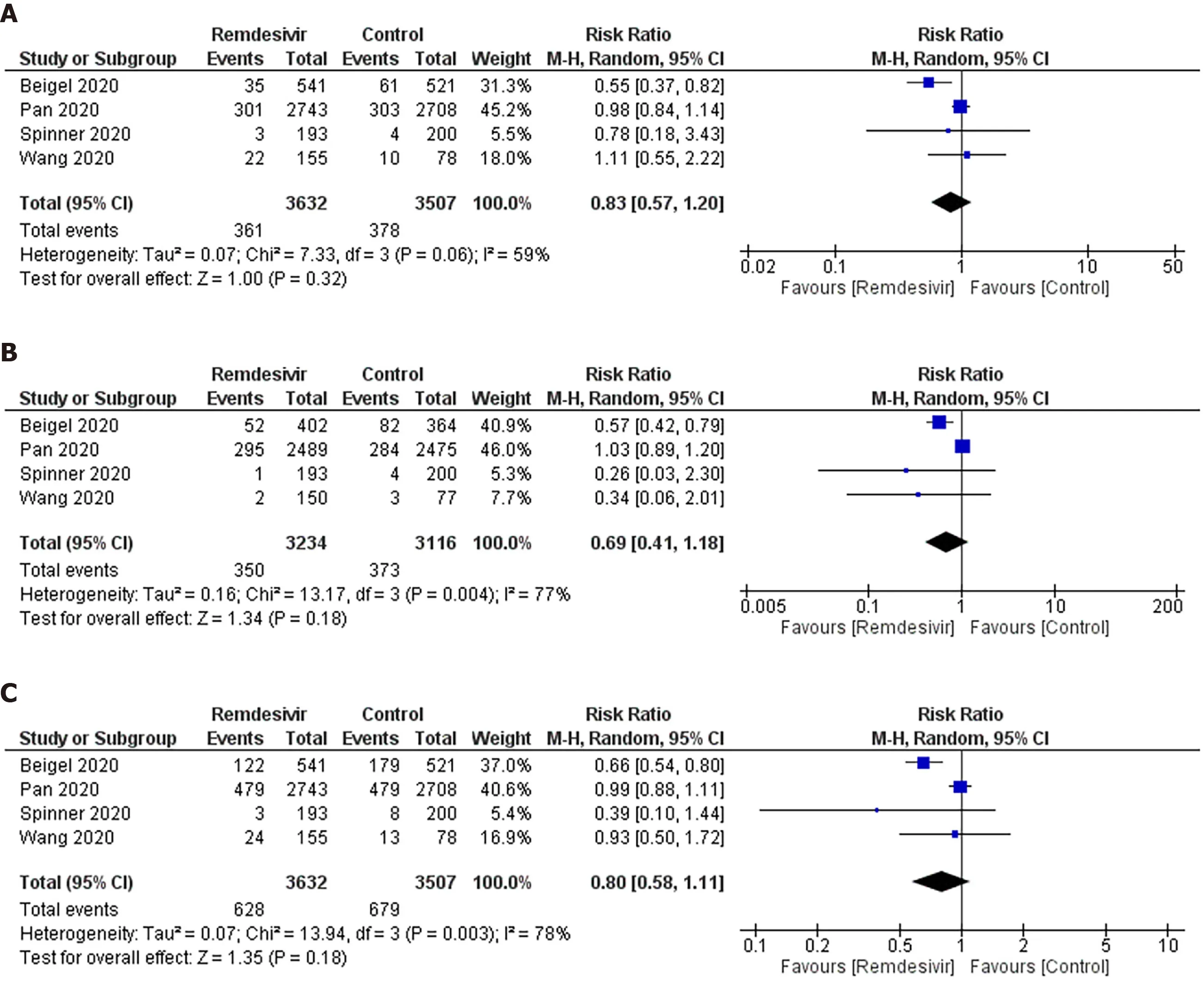
Figure 2 Meta-analytic summary through a random-effect model.
Clinical recovery:Three trials reported clinical recovery.Patients treated with remdesivir had higher rates of clinical recovery than those receiving placebo (RR:1.10;95%CI:1.04–1.16;I2= 0%,Figure 3).On sensitivity analysis,the RR was 1.10 (95%CI:1.02–1.18;I2= 0%).The NNT to cause one additional improvement in clinical recovery was 14.3 (95%CI:9.1–33.3).GRADE approach evidence quality was moderate.The sensitivity analysis showed a similar trend in clinical recovery outcome.
Meta-analytic summary of safety outcomes
Adverse events:Three trials reported 520 adverse events in 880 participants of the remdesivir groups and 466 of 794 participants in the placebo-treated groups (Figure 4).There was no significant difference in the RR of adverse events between remdesivir and placebo-treated patients (RR:1.05;95%CI:0.861.27;I2= 77%).The sensitivity analysis showed a similar trend in adverse event outcome.GRADE approach evidence quality was moderate.
Adverse events of grade 3 or 4:Three trials reported 315 grade 3 or 4 adverse events in 866 participants of the remdesivir groups and 340 of 780 participants in the placebo groups (Figure 5A).Patients receiving remdesivir were 11% less likely to experience grade 3 or 4 adverse events than placebo-treated patients (RR:0.88;95%CI:0.79–0.99;I2= 0%).GRADE approach evidence quality was moderate.The NNT to cause one additional participant to experience fewer serious adverse events compared with placebo,was 20 (95%CI:11.1–100).The sensitivity analysis did not suggest a reduced risk of adverse events in the remdesivir arm (RR:0.87;95%CI:0.71–1.07;I2= 10%).

Figure 3 Meta-analytic summary of clinical recovery data through a fixed-effect model.
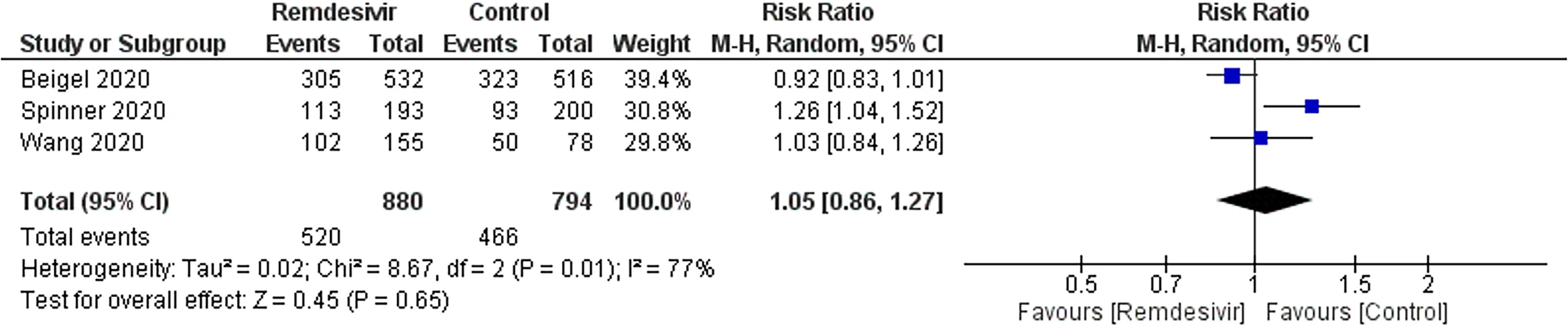
Figure 4 Meta-analytic summary of adverse events data through a random-effect model.
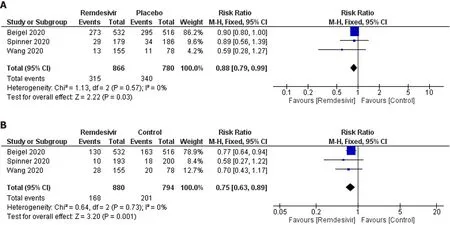
Figure 5 Meta-analytic summary through a fixed-effect model.A:Grade 3 or 4 adverse events data;B:Serious adverse event data.
Serious adverse events:Three trials reported 186 serious adverse events in 880 participants of the remdesivir groups and 201 of 794 participants in the placebo-treated groups (Figure 5B).Participants were 25% less likely to experience serious adverse events in the remdesivir group compared with the placebo-treated group (RR:0.75;95%CI:0.63–0.89);I2= 0%;GRADE approach evidence quality was moderate).On sensitivity analysis,the RR was 0.76 (95%CI:0.64–0.92;I2= 0%).The NNT to cause one additional participant to experience fewer serious adverse events compared with placebo,was 16.7 (95%CI:11.1–50).The sensitivity analysis showed a similar trend in this outcome.
DISCUSSION
The findings of this pooled analysis suggest a trend of limited clinical benefits with the use of remdesivir in COVID-19 patients.More evidence based on double-blind randomized controlled trials is required to evaluate its benefit in reducing mortality and the need of invasive ventilation in the severe COVID-19 patients.
Currently no effective antiviral drugs are available to treat COVID-19.Only dexamethasone showed a mortality benefit in severe COVID-19 patients requiring respiratory support[22].During the initial period of the pandemic,remdesivir was used on a compassionate basis outside of randomized controlled trials in COVID-19 patients based on in vitro and animal studies.In May 2020,the Food and Drug Administration(FDA) granted the emergency use authorization to use remdesivir in severe COVID-19 patients.In October 2020,emergency use authorization was extended to all hospitalized patients[23].Our meta-analysis suggests no major safety concerns with its use.Our findings support the emergency use authorization by the United States FDA in the absence of availability of better antiviral drugs.However,remdesivir alone does not seem to be a promising option.The discovery of better antiviral drug should go beyond it.
Included studies presented earlier findings of efficacy based on randomized controlled trials.Beigelet al[14](the ACTT trial) reported a mortality benefit.Three other studies including the WHO solidarity trial observed no difference at the end of the study period[15,20,21].In case of ventilatory support requirement,Beigelet al[14]suggested a beneficial effect.Two smaller trials observed a trend of reduced risk of ventilation[20,21],while the WHO solidarity trial did not find any difference[15].A noncomparative study by Antinoriet al[24],reported 22.2% of the patients on invasive ventilation showed improvement after remdesivir treatment.In case of clinical recovery,three trials reported trends of improvement[14,20,21].Beigelet al[14]and Spinneret al[20]found that remdesivir was superior to placebo in shortening of clinical recovery time,whereas Wanget al[21]did not find any statistically significant clinical benefit with remdesivir in severe COVID-19 patients.Beigelet al[14]found that the median recovery time was shorter in patients treated with remdesivir than it was with placebo treatment (10 dvs15 d),whereas in the study by Wanget al[21]the recovery time was 21 d in the remdesivir group compared with 23 d the placebo group.The WHO solidarity trial did not report clinical recovery with the study medications[15].Moreover,there was a decreased duration of initial hospitalization (12 dvs17 d) and a reduction in the number of days in which patients received oxygen (13 dvs21 d) if they were on oxygen at baseline,in the remdesivir-treated group as compared to placebo.However,it did not reduce the reoccurrence of a need for oxygen[14].Noncomparative studies by Antinoriet al[24]and Greinet al[25]also observed that remdesivir can provide a greater benefit to patients with pneumonia requiring oxygen therapy or non-invasive ventilation than to those receiving mechanical ventilation.Thus,early intervention with remdesivir can provide increased clinical benefit with fewer adverse events[24].None of the studies included in the present review focused on virological cure.Severe COVID-19 patients have high viral loads and generally need an longer duration to become negative than those with low viral loads[26,27].A study by Antinoriet al[24]found a 100% SARS-COV-2 negative conversion rate with remdesivir,and it occurred after a median period of 12 d (interquartile range 9.25–16.75) after starting the treatment.
Remdesivir has a better or comparable tolerability profile than placebo.The findings of safety analyses should be interpreted cautiously as rare and serious adverse events are usually identified with the widespread use of any drug outside of clinical trials[28,29].Limited information is available for the use of remdesivir in pregnant women and patients with hepatic or renal impairment[30,31].This is especially important from the aspect of high prevalence of acute kidney injury during and its associated mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients[32].Abnormal liver function test values are common in COVID-19 patients[33,34].
Our study has several limitations.Although there was a meticulous search to identify published studies on PubMed and Google Scholar as well as preprint versions of studies on Medrxiv and other databases,we could identify only four published randomized trials to date.The findings of this study could indicate trends rather than confirmation due to non-consideration of the impact of co-morbidities and severity status.We could not analyze the impact of remdesivir on virological cure.While this study was under peer-review,few meta-analyses of remdesivir against COVID-19 have been published.The earlier studies included randomized and observational studies[35,36],did not perform sensitivity analyses[37-39]and did not include quality assessment of efficacy and safety parameters as per the GRADE approach[37-39].
CONCLUSION
The benefits of remdesivir over placebo were significant only in causing higher rates of clinical cure.Use of remdesivir can be continued on a compassionate basis in the absence of specific antiviral drugs.The evidence is based on only four clinical trials.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
There are no specific antiviral drugs currently available to combat coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by novel virus severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.This has promoted the evaluation of various previously approved drugs as an effective treatment for COVID-19.Remdesivir is one such repurposed drug currently under investigation against COVID-19.
Research motivation
This study investigated whether remdesivir is an effective and safe option to treat COVID-19 patients.
Research objectives
In this study,the authors aimed to provide a meta-analytic summary of the efficacy and safety outcomes in COVID-19 patients with the use of remdesivir as compared with control interventions.
Research methods
A literature search was conducted to identify studies published through October 28,2020.Randomized controlled trials of remdesivir plus any other interventions including placebo were included.The quality assessment of all included studies for methodological characteristics was performed with the revised Cochrane risk of bias assessment tool for randomized controlled clinical trials.The efficacy outcome variables were mortality,need for mechanical ventilation,composite mortality and ventilation and clinical recovery rate.The safety outcome variables were overall adverse events,grade 3 or 4 adverse events and the serious adverse events rate.
Research results
We included a total of four randomized controlled trials in this meta-analysis.Three studies were considered to have a low risk and one study was considered to have some concerns in the overall risk of bias assessment.Remdesivir- and placebo-treated patients did not differ in mortality,rate of mechanical ventilation and composite mortality and ventilation rate outcomes.A sensitivity analysis suggested a reduced risk of ventilation and composite mortality and ventilation with remdesivir on exclusion of open-label studies.Remdesivir-treated patients showed higher rates of clinical recovery than placebo-treated patients.Remdesivir and placebo-treated patients did not differ in the overall occurrence of adverse events.Remdesivir-treated patients were at lower risk of grade 3 or 4 adverse events and serious adverse events than placebo-treated patients.The GRADE approach suggested moderate quality of evidence for all efficacy and safety outcomes.
Research conclusions
The effect of remdesivir over placebo was not significant for mortality or the rate of ventilation.However,remdesivir may provide higher rates of clinical cure.There are no major safety concerns with the use of remdesivir.Its use can be continued on a compassionate basis in the absence of specific antiviral drugs.
Research perspectives
The current evidence is based on four clinical trials only.More evidence based on double-blind randomized controlled trials in different disease-severity populations is required to evaluate the benefits of remdesivir in COVID-19 patients.
 World Journal of Meta-Analysis2021年1期
World Journal of Meta-Analysis2021年1期
- World Journal of Meta-Analysis的其它文章
- Should we use full analgesic dose of opioids for organ procurement in brainstem dead?
- Magic and forensic psychiatry:A case study and review of the literature
- Health-related quality of life in patients that have undergone liver resection:A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Mortality of critical care interventions in the COVID-19:A systematic review
- Risk factors,manifestations,diagnosis and treatment of cholelithiasis in children
- Non-invasive diagnosis of Crohn’s disease:All that glitters is not gold
