Acupuncture improved lipid metabolism by regulating intestinal absorption in mice
Jia Han, Xin Guo, Xiang-Jin Meng, Jing Zhang, Reimon Yamaguchi, Yoshiharu Motoo, Sohsuke Yamada
Abstract
Key Words: Acupuncture; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Small intestine; Lipid metabolism; Apolipoproteins
INTRODUCTION
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has become a pandemic liver disease in the twenty-first century, and currently affects approximately one billion individuals worldwide. The prevalence of NAFLD is still increasing each year, with the high incidence of metabolic syndromes, such as obesity and dyslipidemia, especially hypertriglyceridemia[1]. Although the molecular mechanism of NAFLD is not fully understood, a considerable proportion of NAFLD patients are found to have metabolic syndrome[2]. Abnormal lipid metabolism, for example an increased fat intake, has been thought to be an initial factor leading to NAFLD[3].
Lipids are known to be one of major sources of food energy, and play a crucial role in systemic metabolism, especially in patients with chronic liver diseases like NAFLD[4]. The small intestine is the main site of dietary lipid absorption in the body. Dietary lipids are hydrolyzed and digested in the lumen of small intestine. These products are then taken up by enterocytes, and are transported, re-synthesized, assembled and secreted into circulation with lipoproteins, such as very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), high density lipoprotein (HDL) or chylomicrons (CMs), for utilization in peripheral tissues. Apolipoproteins, including apolipoprotein A (ApoA), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), apolipoprotein C (ApoC) and microsomal triglyceride transfer protein (MTP), play important roles during this process. Triacylglycerol (TG) and nonesterified fatty acid (NEFA) are packaged into large, spherical CMs and secreted into the lymphatic system; this process mainly relies on the activity of MTP and ApoB[5,6]. However, in addition to CMs, cholesterol can be secreted in HDL. In HDL, MTP showed no effect on the secretion of cholesterol, while the deficiency of ApoA1 can specifically decrease the quantities of cholesterol secreted with HDL[5,7]. The improvement of lipid metabolism helps to inhibit the progress of NAFLD.
Acupuncture is one of the most important external interventions in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). It has a long history of more than 2000 years as a treatment for many diseases on a basic of the Yellow Emperor’s Classic of Internal Medicine[8]. According to the TCM theory, all diseases were caused by a stagnation of “qi” and “blood” which is a result of the imbalance between “Yin” and “Yang”[9]. In recent years, due to its low cost and simplicity, the role of acupuncture in disease prevention and treatment has attracted increased attention from researchers, and there is a great deal of evidence to show that acupuncture can have pathophysiological consequences and alleviate symptoms in multiple organ systems, such as diseases of digestive system[10], diseases of nerve[11], as well as diseases of skin[12,13]. A number of clinical trials have shown that acupuncture has positive effects in therapy for simple obesity and that it can significantly reduce plasma lipid levels, indicating that acupuncture treatment may have important roles in the regulation of lipid metabolism, which is closely associated with the progression of NAFLD[14]. However, few modern medical studies have reported the exact mechanisms by which regulate lipid metabolism.
In a recent study, using a mouse model of methionine- and choline-deficient (MCD) diet-induced NAFLD, we investigated the effects of needling treatment at three acupoints, Zu san li (ST36), Guan yuan (CV4) and Yong quan (KI1). According to the TCM theory, most of the acupoints are located on different meridians which correspond to different systems and have different functions[8]. ST36 is located on the stomach meridian of foot-Yangming, which has a function in generating stomach qi to regulate digestion and absorption. While KI1 is located on kidney meridian of foot-Shaoyin, which is an important acupoint in regulating the motion of both qi and blood. CV4 is front Mu point of small intestine which is a key acupoint in regulating the motion of qi belonging to conception vessel. Our results demonstrated that acupuncture treatment suppressed the progression of NAFLD by controlling the intrahepatic pathological process[15]. According to TCM theory, the three acupoints are located at very important sites of the body. They have roles in the regulation of various metabolic activities, including gastrointestinal motility, glandular secretion and nerve conduction[9,10,14,16]. We therefore hypothesized that, in addition to local effects, acupuncture on ST36, KI1 and CV4 can also improve the conditions of NAFLD by regulating systemic metabolism.
In this study, we investigated the role of acupuncture treatment in the improvement of metabolic syndrome secondary to NAFLD by employing the above-described mouse model. Furthermore, we focused on the major organ responsible for lipid absorption, the small intestine, and observed its morphological and functional changes. Our results suggest that acupuncture may provide an alternative approach for improving metabolic syndromes in patients with NAFLD and to prevent the progression of the disease.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Experimental animals
The animals used in this study were 8-wk-old male C57BL/6J mice that weighed approximately 20 g, purchased from Sankyo Labo Service Corporation, INC. Japan. The animals were maintained at a temperature of 21-25 °C with a 12-h light–dark cycle andad libitumaccess to drinking water. All mice were fed with an MCD + high fat (HF) diet (60% fat; KBT Oriental Corporation, Saga, Japan) for 3 wk to induce NAFLD. After that, MCD diet stopped. They were then fed an HF (60% fat; KBT Oriental Corporation, Saga, Japan) diet for 2 wk to maintain their hyperlipidemia. When HF diet started, they were separated randomly into two groups: The acupoints group (AG,n= 10) and the non-acupoints group (NG,n= 10) for the needling treatment. After two weeks’ treatment, mice were anesthetized with an injection of ketamine-medetomidine and euthanized by exsanguination[17]. Whole blood samples from axillary vessels were kept at room temperature until coagulation, then all blood cells were removed by centrifugation and serum samples were frozen with liquid nitrogen for use in further experiments. The intestine was removed, photographed, and the length was measured. Then, the small intestine was cut into pieces, frozen with liquid nitrogen, or fixed in 10% neutral-buffered formalin for using in further experiments.
Acupuncture treatment
The mice were randomly separated into AG and NG. Needling treatment started as well as HF diet started. As described previously[15], three acupoints, ST36, KI1 and CV4, or corresponding non-acupoints were needled with 13-mm needles (Suzhou Medical Appliance Factory 0.25 mm × 13 mm), which were rotated slowly at 60 rotations per minute for 2 min, without retaining the needle. All mice were needled without anesthesia in a mouse retainer. The location of ST36 in mouse is 1.5 mm below the anterior tibial tubercle of both sides’ hind limbs. KI1 is located in the centre of both sides’ hind soles. CV4 is 10 mm below the mouse’s navel.
Ethics
The experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of Animal Care and Experimentation, Kanazawa Medical University, Japan. Our project code was 2019-21 (registered on July 3, 2019). All experiments were implemented in compliance with the Institutional Guidelines for Animal Experiments and the Law (No. 105) and Notification (No. 6) of the Japanese government. The number of animals used in this experiment was minimized and we attempted to minimize the animals' suffering.
Histopathology
After 24 h of fixation in 10% neutral-buffered formalin, we selected the same place of the mouse jejunum, embedded the specimen in paraffin, cut the specimen into sequential sections of 4 μm in thickness and performed hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining. Images of the sections were captured with the Nano Zoomer Digital Pathology Virtual Slide Viewer software program (Hamamatsu Photonics Corp, Hamamatsu, Japan) and the villi lengths and gland depths were measured.
Western blotting
Small intestine samples were lysed with radio immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA, SIGMA) lysis buffer containing protease inhibitor cocktail and denatured with 2 × Laemmli sample buffer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) at 95°C for 5 min. Then, the protein samples were electrophoretically loaded onto 7.5% or 12.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gels and transferred onto Immun-Blot PVDF membranes (Bio-Rad Laboratories, K.K., Tokyo, Japan). The membranes were then incubated overnight at 4°C with anti-β-actin monoclonal antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., 1:1000), MTTP antibody (Abcam PLC., 1:500), ApoA1 antibody (Abcam PLC., 1:500), ApoB antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., 1:500), and ApoC2 antibody (Bioss Inc., 1:500) diluted in self-made TBS-T buffer. After washing with TBS-T, the membranes were incubated with secondary antibody at room temperature for 1 h. The secondary antibodies used were horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody and anti-mouse antibody (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., 1:5000). After visualization by an enhanced chemiluminescence kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.), the protein bands were checked and acquired by luminescent image analyzer (FUJIFILM, LAS400).
Analysis of the tissue lipid contents
To check the serum and small intestine lipids profiles, the TG, NEFA and total cholesterol (T-Cho) levels were determined using commercial assay kits (Wako Pure Chemical Co.). For the small intestine, frozen tissues were weighed and homogenized. Lipids were extracted as described previously[15]with chloroform-methanol (2/1 v/v) and dried and solubilized in 2-propanol.
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction
Quantitative Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to analyze the gene expression in tissue specimens. Total RNA was extracted from the fat and small intestine with a ReliaPrep? RNA Tissue Miniprep kit (Promega). The whole process was carrying out under RNase-free conditions in order to prevent degradation. Custom primers and a TaqMan probe for the amplification reaction were purchased from Life Technologies. The mRNA expression levels were analyzed. The relative expression levels were normalized to 18S ribosomal RNA and the fold-change in AG mice was calculated in comparison to NG mice.
Statistical analyses
All data are expressed as the mean ± SD. Statistical significance was analyzed with a 2-sided Student'st-test or Welch’st-test, as appropriate. Statistical analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel.Pvalues of < 0.05 were considered to indicate statistical significance.
RESULTS
After needling treatment, obesity caused by HF diet feeding was obviously improved in AG mice
After 2 wk of needling treatment, an apparent improvement in obesity was observed in AG mice in comparison to NG mice. General observation revealed that the AG mouse body was obviously thinner and smaller in comparison to the NG mouse body (Figure 1A). After acupuncture treatment, the body weight of the AG mice 22.6 ± 1.2 g was much lower than that of the NG mice 28.1 ± 1.0 g, indicating that acupuncture decelerated the body weight increase induced by HF feeding (Figure 1B). Moreover, the intra-abdominal fat of AG mice 213.8 ± 43.5 mg was clearly reduced in comparison to NG mice 1088.3 ± 193.0 mg (Figure 1C and D). A similar trend was also observed in the ratio of abdominal adipose tissue weight to body weight, which was significantly decreased (NGvsAG: 40.3 ± 6.8vs11.0 ± 1.9, Figure 1D). In concrete terms, the average abdominal fat weight of AG mice was only 20% of that in NG mice, while the ratio of abdominal fat weight to body weight in AG mice was one-fourth of that in NG mice.
Morphological and functional changes in AG mice
The small intestine is closely associated with lipid absorption and metabolism. Grossly, the length of small intestine in AG mice 26.7 ± 2.3 cm was significantly shorter than that in NG mice 32.7 ± 2.7 cm, meanwhile, large amounts of chyme was observed in the lumen of the AG small intestine (Figure 2A). The average length of the AG mouse small intestine was approximately 6 cm shorter than that of the NG mice small intestine. HE staining of the small intestine revealed the accumulation of a huge number of adipose droplets in the intestinal epithelium of AG mice (Figure 2B). Nevertheless, the length of small intestinal villi of AG mice was nearly 1.4 times the length in NG mice (AG micevsNG mice: 421.3 ± 67.1 μmvs302.1 ± 47.7 μm, Figure 2B). However, the depth of the small intestinal gland in NG 105.9 ± 20.0 μm and AG 98.2 ± 17.4 μm mice did not differ to a statistically significant extent (Figure 2B). The expression levels of some important apolipoproteins related to intestinal lipid absorption, including MTP, ApoB and ApoC2, were downregulated in AG mice in comparison to NG mice, while the expression of ApoA1 did not differ to a statistically significant extent (Figure 2C). The expression levels of other factors related to embolism, such as GLUT1, 3, 4, and 5, lipa, and LDLR, did not differ between the two groups to a statistically significant extent (Supplementary Figure 1).
Acupuncture treatment led to the accumulation of lipids in the small intestine of AG mice with improved plasma lipid levels
The TG, T-Cho and NEFA levels of small intestinal tissue in AG mice (TG 22.1 ± 2.8 mg/g, T-Cho 3.0 ± 0.4 mg/g, NEFA 0.01 ± 0.004 mEq/g) were significantly higher in comparison to NG mice (TG 18.2 ± 2.8 mg/g, T-Cho 2.3 ± 0.3 mg/g, NEFA 0.009 ± 0.002 mEq/g, Figure 3A). However, the serum lipid levels did not change in the same way. Furthermore, the serum TG and NEFA levels in AG mice (TG 81.5 ± 16.6 mg/dL, NEFA 4.8 ± 1.9 mEq/L) were reduced in comparison to NG mice (TG 141.4 ± 34.3mg/dL, NEFA 7.8 ± 2.0 mEq/L). The serum T-Cho levels in the two groups did not differ to a statistically significant extent (AG micevsNG mice: 106.8 ± 12.9 mg/dLvs110.5 ± 14.4 mg/dL, Figure 3B).
Acupuncture treatment showed no effect in regulating the metabolism of adipose tissue
In order to explain the changes that occurred in AG mice, we firstly focused on adipose tissue itself. However, we found no significant differences in the tissue morphology of the two groups (Figure 4A) or in the expression levels of crucial genes related to the lipid metabolism of adipocytes (Figure 4B).
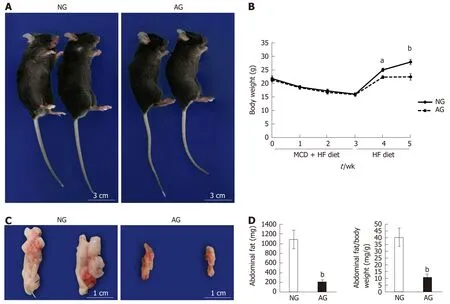
Figure 1 After needling treatment, the obesity caused by high fat diet feeding was obviously improved in acupoints group mice. A: General view of the mice; B: Body weight change of the mice; C: Appearance of abdominal fat; D: Abdominal fat weight and the ratio of abdominal fat weight to body weight (n = 10). The results are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 10). aP < 0.01, bP < 0.005. NG: Non-acupoints group; AG: Acupoints group; MCD: Methionine- and choline-deficient; HF: High fat.
DISCUSSION
In the present study, our experimental data showed that acupuncture treatment suppressed HF-induced body weight gain, reduced the accumulation of intraabdominal fat, inhibited lipid absorption in the small intestine and downregulated the blood lipid level in mice with NAFLD, suggesting that acupuncture potentially had variable beneficial effects in improving the lipid metabolism in the presence of abnormal liver metabolism.
Metabolic syndrome, which includes conditions such as obesity, dyslipidemia and insulin resistance, is closely related to the progression of NAFLD; conversely, chronic liver disease can further aggravate systemic metabolism abnormality[18,19]. Obesity, especially excess abdominal adiposity, is a high-risk factor for this disease and weight control is considered to improve the liver condition of patients with NAFLD[20]. Generally, improvements of diet and lifestyle are recommended; however, the effect on weight loss is often unsatisfactory. A large body of clinical and experimental evidence shows that acupuncture is effective for the treatment of obesity, and that acupuncture treatment is accompanied by a reduction in obesity-related complications, such as hyperlipidemia[21,22]. Indeed, in this study, the AG mice were observed to have lower body weight and less abdominal adiposity with an improved blood lipid status, in comparison to NG mice. In a recent study, we also reported that acupuncture significantly inhibited the progression of NAFLD, where reduced in ammatory responses and oxidative stress in the liver and enhanced hepatic metabolism were observed in mice with modest NAFLD after acupuncture treatment[15]. From the present results, in addition to the direct effects on the liver, the lower body weight and serum lipid levels produced by acupuncture treatment also played an important role in the improvement of the liver function, indicating that the beneficial effects of acupuncture on NAFLD not only rely on the control of the intrahepatic pathological process but also depend on the regulation of the systemic metabolism of the body.
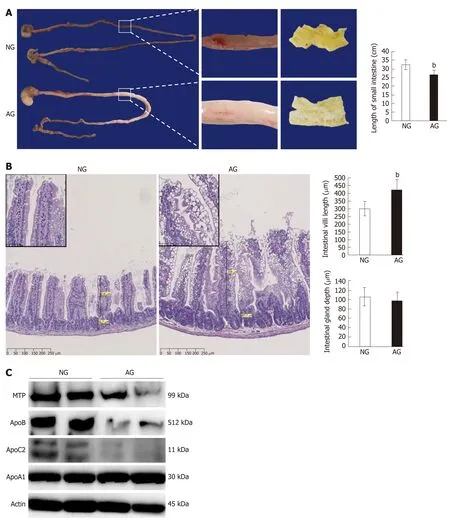
Figure 2 After needling treatment, the acupoints group mouse small intestine changed in structure, while the levels of lipid transport proteins in the acupoints group mouse small intestine tissue were significantly decreased. A: The appearance of small intestine (left) and the length of the small intestine (right); B: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of a small intestine section (left) and the length of the small intestinal villus (right upper) and the depth of the small intestinal gland (right bottom); C: Western blotting of lipid transport proteins in the small intestine. The results are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 10). aP < 0.01, bP < 0.005. NG: Non-acupoints group; AG: Acupoints group.
Furthermore, we also found more fat deposition in the intestinal epithelium with the decreased expression of some intestinal apolipoproteins in AG mice, suggesting that acupuncture may suppress lipid absorption by downregulating the expression of apolipoproteins in the small intestine, as we showed in Figure 5. At present, the mechanism underlying the effects of acupuncture in the treatment of obesity is still not fully understood, and although some related mechanisms have been reported in other studies[23,24], we suggest-at least in some situations-that the inhibition of intestinal lipid absorption plays important roles in the effects of acupuncture in the treatment of obesity. In fact, acupuncture has been widely used in the treatment of obesity in the clinical setting; thus, in view of the reduced lipid absorption, proper nutritional supplementation should be considered throughout the treatment process.
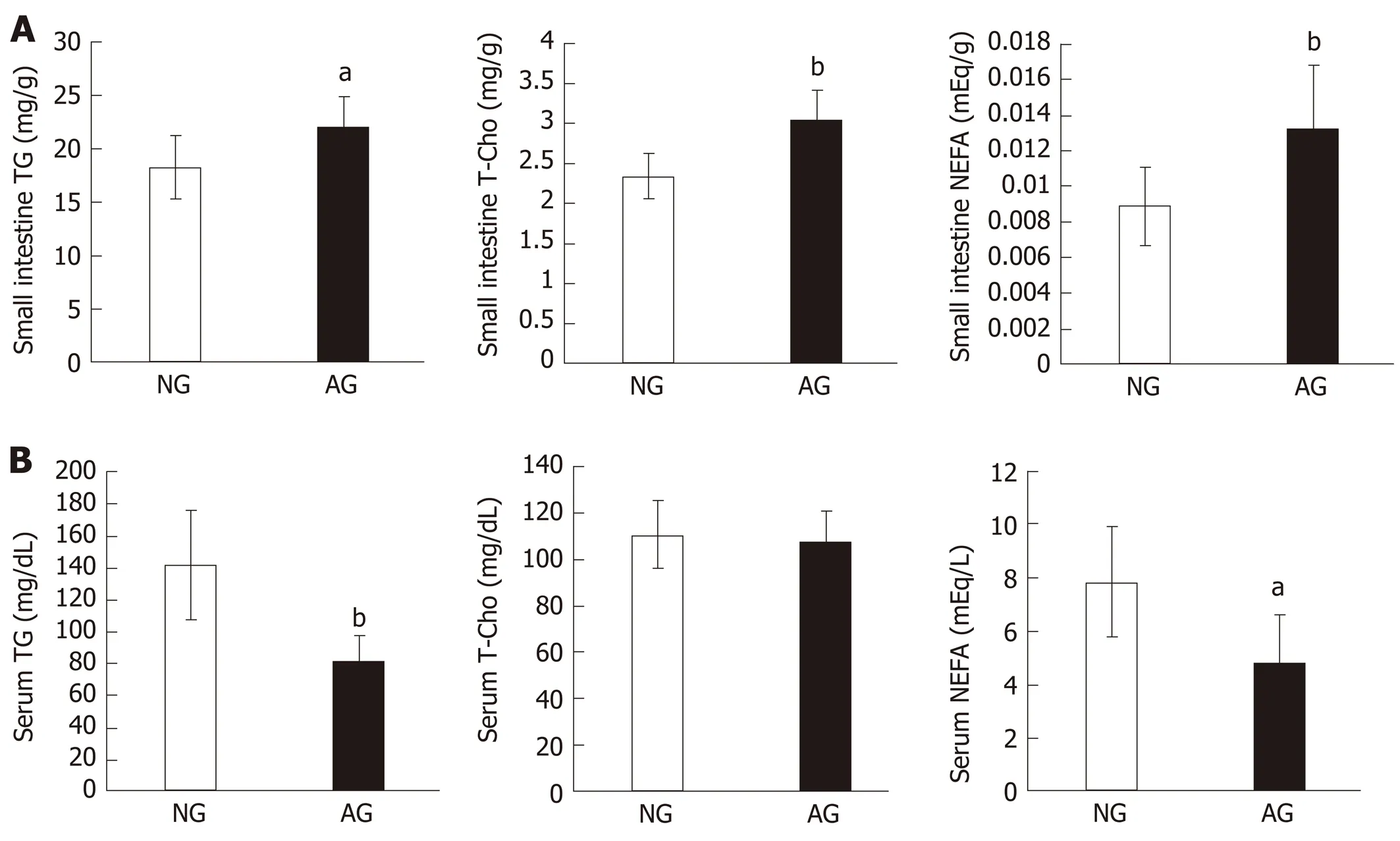
Figure 3 After needling treatment, large amounts of lipids accumulated in the small intestinal epithelium of acupoints group mice. This did not occur in the serum. A: Lipid levels in the small intestine; B: Lipid levels in the serum. The results are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 10). aP < 0.01, bP < 0.005. NG: Non-acupoints group; AG: Acupoints group; TG: Triacylglycerol; T-Cho: Total cholesterol; NEFA: Nonesterified fatty acid.
After dietary fat is digested by the intestinal lipase system in the lumen of the small intestine[25], the predominant lipids cross the apical membrane and enter the enterocytes in a protein-independent or -dependent manner[26,27]. When the lipid concentrations in the lumen are much higher than the intracellular levels, the passive uptake becomes the main way for enterocytes to absorb lipids[28]. In this study, an HF diet resulted in a high lipid concentration in the lumen, permitting the uptake of a large amounts of lipids by the enterocytes. However, when these lipids cannot be secreted into the lymphatic system or circulation, they are stored as cytosolic lipid droplets in the enterocytes[29]. Monoacylglycerol and free fatty acids are packaged into ApoB-rich chylomicrons for secretion into lymphatic vessels, in which MTP deliver lipids to the nascent ApoB and assist in folding[30,31]. The inhibition of MTP can lead to the degradation of ApoB, which causes the downregulation of chylomicron secretion[32,33]. The decreased expression of MTP and ApoB in the AG intestine may result in the accumulation of lipids by reducing chylomicron secretion in the enterocytes. In addition to chylomicron, cholesterol is secreted in MTP- and ApoBindependent HDL pathways, with ApoA1 playing a pivotal role in HDL secretion[34]. The expression of ApoA1 in the NG and AG groups did not differ to a statistically significant extent (Figure 2C). Thus, less abdominal adipose tissue and lower plasma TG and NEFA levels were found in AG mice; however, the cholesterol levels in plasma (Figure 3) and liver tissue[15]did not differ to a significantly extent between the two groups.
The central and enteric nervous systems play important roles in gastrointestinal motility and gastric emptying is closely associated with the synthesis of intestinal apolipoproteins[35,36]. Many studies have confirmed that acupuncture has a regulating effect on gastrointestinal motility through the pathways of the nervous system[37]. Food retention was clearly observed in the AG intestine (Figure 2A), suggesting that gastrointestinal motility may be relatively repressed in these mice. Thus, decreased expressions of intestinal MTP and ApoB in AG intestines might be a response to the activation of an ileo-jejunal negative feedback loop caused by weaken gastrointestinal motility[36].
The present study also demonstrated some changes in intestinal morphology. Overloading of nutrients can induce intestinal epithelial cell proliferation[38]; thus, food retention in the lumen and lipid accumulation in the enterocytes may increase the burden of small intestinal metabolism, which contributed to the longer villi in AG mice. Furthermore, intestinal enlargement is often found in obese and/or diabetic animals, which may result from hunger perception-induced neural stimulation[39]. The improvement of metabolic syndrome after acupuncture treatment may normalize the size of the intestine in AG mice. The specific mechanism needs to be confirmed by further studies in the future.
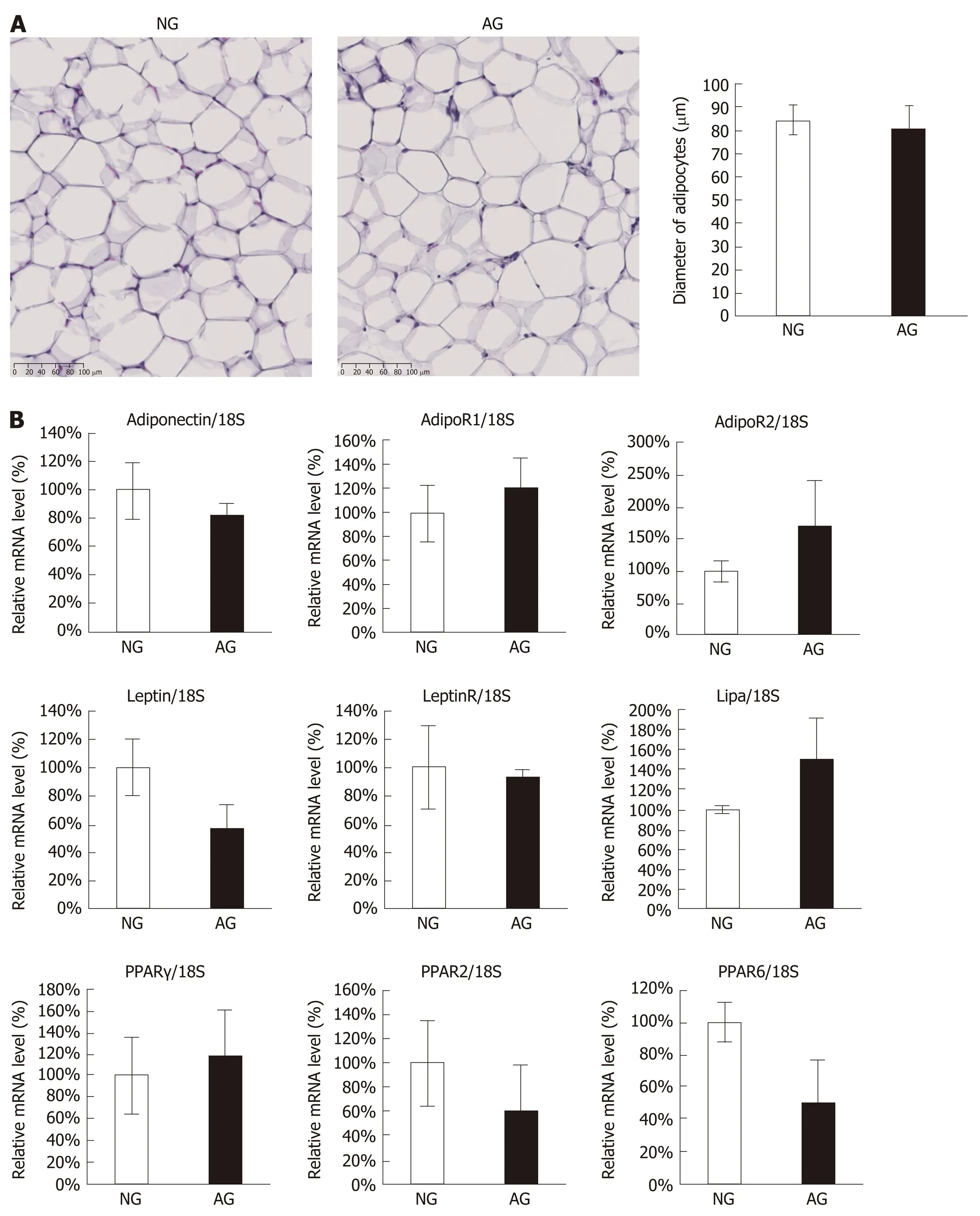
Figure 4 Acupuncture treatment did not seem to regulate the adipose tissue itself. A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining of abdominal adipose tissue (left) and the diameter of adipocytes (right); B: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction of abdominal adipose tissue. The results are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 10). NG: Non-acupoints group; AG: Acupoints group.
The present study was associated with some limitations. Firstly, the present study did not employ metabolic cage or pair feeding; thus, the quantities of feed and feces were not monitored. Consequently, in addition to the reduced absorption of the small intestine, the positive effect of acupuncture on weight loss may also have been associated with restrained feeding or the promotion of fecal excretion. Secondly, the metabolism of other nutrients also affects the progression of NAFLD, but only lipidrelated indicators were observed; thus, the roles of acupuncture in glucose and energy metabolism may also directly or indirectly inhibit intestinal lipid absorption. Finally, the treatment of NAFLD by acupuncture was found to have a short-term (only 2 wk) effect, which led to a dramatic difference in body weight between the two groups. Rapid weight loss may also exacerbate conditions associated with this disease, such as portal fibrosis or necroinflammation, the side effects of acupuncture as a treatment to promote weight control need to be investigated during long-term treatment.

Figure 5 Schematic illustration of the critical roles of acupuncture in intestinal lipid absorption under non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. MCD: Methionine- and choline-deficient; HF: High fat.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the results of the present study suggest that acupuncture inhibited lipid absorption in the small intestine by downregulating the expression of intestinal apolipoproteins, causing some changes in the intestinal morphology. We suggest that, in addition to the control of the intrahepatic pathological process, acupuncture may improve the outcomes of patients with NAFLD by regulating the systemic metabolism of the body.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research results
Acupuncture treatment can suppress intestinal lipid absorption by downregulating the expression of apolipoproteins in the small intestine, and then improve obesity and hyperlipidemia. In fact, acupuncture has been widely used in the treatment of obesity in the clinical setting; thus, in view of the reduced lipid absorption, proper nutritional supplementation should be considered throughout the treatment process. Acupuncture treatment normalized the size of the intestine and contributed to the longer villi. The specific mechanism needs to be confirmed by further studies in the future.
Research conclusions
We suggest that, in addition to the control of the intrahepatic pathological process, acupuncture may improve the outcomes of patients with NAFLD by regulating the systemic metabolism of the body.
Research perspectives
In future study, the quantities of feed and feces need to be monitored by using metabolic cage. In addition to lipid, the role of acupuncture in another nutrients metabolism should be investigated. The side effects of long-term treatment need to be further observed.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Yuka Hiramatsu, Yonenaga Chikako, Yamabe Yukie, Tanaka Asari and Manabu Yamashita for their expert technical assistance and Professor Yasuo Iida from Department of Mathematics for his biostatistics review certificate.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年34期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年34期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Peliosis hepatis complicated by portal hypertension following renal transplantation
- Endoscopy-based Kyoto classification score of gastritis related to pathological topography of neutrophil activity
- Golgi protein-73: A biomarker for assessing cirrhosis and prognosis of liver disease patients
- Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid improves liver glucose and lipid homeostasis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via AMPK and mTOR regulation
- Potential applications of artificial intelligence in colorectal polyps and cancer: Recent advances and prospects
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for Budd-Chiari syndrome: A comprehensive review
