Intervention effect of neuromuscular electrical stimulation on ICU acquired weakness:A meta-analysis
Mio Liu ,Jin Luo ,Jun Zhou ,Xiomin Zhu
a School of Nursing,Yangtze University,Hubei,China
b Affiliated Union Hospital of Tongji Medical College,Huazhong University of Science and Technology,Hubei,China
Keywords:Activities of daily living Electrical stimulation Intensive care unit Length of stay Mechanical ventilation Muscle strengths Quality of life Weakness
ABSTRACT Objective:The early use of neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES)to prevent intensive care unitacquired weakness (ICU-AW)in critical patients is still a controversial topic.We conducted a systematic review to clarify the effectiveness of NMES in preventing ICU-AW.Methods:The Cochrane Library,PubMed,EMBASE,MEDLINE,Web of Science,Ovid,CNKI,Wanfang,VIP,China Biology Medicine disc (CBMdisc)and other databases were searched for randomized controlled trials on the influence of NMES on ICU-AW.The studies were selected according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria.After data and quality were evaluated,a meta-analysis was performed by RevMan 5.3 software.Results:A total of 11 randomized controlled trials with 576 patients were included.The meta-analysis results showed that NMES can improve muscle strength [MD=1.78,95% CI (0.44,3.12,P=0.009);shorten the mechanical ventilation(MV)time[SMD=-0.65,95%CI(-1.03,-0.27,P=0.001],ICU length of stay [MD=-3.41,95% CI (-4.58,-4.24),P<0.001],and total length of stay [MD=-3.97,95% CI(-6.89,-1.06,P=0.008];improve the ability of patients to perform activities of daily living[SMD=0.9,95% CI (0.45,1.35),P=0.001];and increase walking distance [MD=239.03,95% CI (179.22298.85),P<0.001].However,there is no evidence indicating that NMES can improve the functional status of ICU patients during hospitalization,promote the early awakening of patients or reduce mortality (P>0.05).Conclusion:Early implementation of the NMES intervention in ICU patients can prevent ICU-AW and improve their quality of life by enhancing their muscle strength and shortening the MV duration,length of stay in the ICU and total length of stay in the hospital.
What is known?
· Intensive care unit-acquired weakness(ICU-AW)is a main factor that affects the recovery of ICU patients and their quality of life after discharge.
· Neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES)has been recognized as an alternative therapy to promote movement in critically ill patients,but the effectiveness of NMES in preventing ICU-AW is not clear.
What is new?
· The results of this study confirmed that the early introduction of the NMES intervention in ICU patients can prevent ICU-AW to a certain extent;for example,it can improve muscle strength;shorten the duration of mechanical ventilation,length of stay in the ICU and total length of stay in the hospital;increase walking distance and improve the ability of patients to perform activities of daily living.
· It is suggested that NMES can prevent ICU-AW in patients with mechanical ventilation and consciousness disturbance who are unable to get out of bed early.
1.Introduction
ICU-AW is a type of neuromuscular dysfunction that is commonly acquired in the intensive care unit [1]and can lead to persistent muscle weakness[2].ICU-AW is related to the severity of the disease the patient has,the duration of MV,sepsis,multiple organ failure,hyperglycemia,the use of neuromuscular blockers,long-term bedridden immobility and the length of stay in the ICU[3].ICU-AW manifests as difficulty performing daily activities,a prolonged hospital stay,hyporeflexia,muscle atrophy,and weakness,and it can lead to increased mortality [4,5].The incidence of ICU-AW has been found to be 26%-65%in conscious patients who had mechanical ventilation for 5-7 days,67%in patients who had mechanical ventilation for more than 10 days [6],70% in patients with sepsis and systemic inflammatory response syndrome[7],and 100% in patients with multiple organ failure [3],and ICU-AW has been found to affect the health of ICU patients[8].In addition,ICUAW increases nursing costs by 60%,which leads to a large financial and healthcare burden to medical and health institutions and patients’ families [9].At present,there are no completely effective treatment methods.In the case of insufficient resources in the ICU,the prevention of ICU-AW is particularly important [6].NMES is a technique that uses a 30-50 Hz low-frequency current to stimulate specific muscle groups through electrodes;the twitching or contractions of these muscles leads to functional repair.NMES has been recognized as an alternative therapy to promote movement in critical patients[10],but the topic of whether the early use of NMES can effectively prevent ICU-AW has been controversial.
Some studies have found that NMES has a positive effect on the prevention of ICU-AW,as it can effectively enhance muscle strength and shorten the duration of MV and ICU hospitalization [11,12].However,some studies have also shown that NMES does not statistically significantly improve the muscle strength of ICU patients[13,14].Three studies have systematically evaluated the effect of the early use of NMES in critically ill patients [15-17];however,complete randomization could not be performed in one of the studies due to the small sample size.In addition,there was heterogeneity among the three studies,only descriptive qualitative analysis was adopted,and contradictory conclusions across the studies were drawn,which make the evidence unpersuasive.On the basis of previous studies,in this study,strict criteria on the inclusion and exclusion of literature were implemented,randomized controlled trials on the effects of NMES in ICU patients published from the establishment of the database to April 2019 were identified,and the effects of the NMES intervention on muscle strength,mechanical ventilation time,ICU hospitalization time,total hospitalization time,mortality,ability to perform activities of daily living,functional status,maximum walking distance,and muscle length were evaluated by a meta-analysis.The aim of the study was to provide more accurate and reliable evidence for the prevention of ICU-AW.
2.Methods
2.1.Research design
The purpose of this study was to examine and quantify the effectiveness of NMES in the prevention of ICU-AW based on the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and metaanalyses (PRISMA)statement [18].
2.2.Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.2.1.Inclusion criteria
Regarding the subjects,ICU patients who were aged ≥18 and<85 and had duration of mechanical ventilation of>24 hour were included,and patients with a primary neuromuscular disease,limb deformity,metal prosthesis,orthopedic injury,pregnancy,or a history of cardiac arrest and those who were participating in other trials were excluded.
Regarding the intervention,the patients received NMES treatment with routine treatments and nursing care.
The control measure was either sham NMES (minimum intensity setting,no muscle contraction)or routine treatment and nursing care in the ICU.
The main outcome indicators were as follows:①muscle strength:the international MRC-score scale was used to evaluate the strength of surrounding muscles [19];②MV duration;③ICU length of stay and ④total length of stay.The secondary outcome measures were as follows:①activities of daily living,as assessed by the Barthel index for activities of daily living (ADL)[20];②functional independence,as assessed using the ICU Functional Status Score (FSS-ICU)[21];③maximum independent walking distance;and ④level of consciousness,as measured by the Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS)on a daily basis [22].
The studies included were randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
2.2.2.Exclusion criteria
Studies on NMES in combination with other interventions,studies for which the original text and data could not be obtained by various means,studies with statistical errors in the data or methodology,and duplicate studies were excluded.
2.3.Literature retrieval strategy
The Cochrane Library,PubMed,EMBASE,MEDLINE,Web of Science,Ovid,CNKI,Wanfang,VIP,China Biology Medicine disc(CBMdisc)and other databases were searched for Chinese and English articles with the following search terms:“electric stimulation/electric stimulation therapy/neuromuscular electrical stimulation/NMES/electrical nerve stimulation/electrical muscle stimulation/electrical stimulation/physical therapy” “muscle weakness/intensive care unit acquired weakness/ICU-AW/myasthenia/amyosthenia/amyasthenia/intensive care units/ICU/critically ill patients”.The article type was limited to randomized controlled trials,and the retrieval time was from the establishment of the database to April 2019.Moreover,the "snowball" method was used to identify the references that were included in the articles.Appendix A shows the retrieval strategy and results from PubMed.
2.4.Literature selection and quality evaluation
2.4.1.Literature screening
Two researchers searched the above databases independently according to the retrieval method and read the titles,abstracts,study types,research objectives and intervention measures of the articles.If an article met the inclusion criteria,the researchers additionally read the full text.After the independent screening process was completed,the screening results were cross-checked,and the differences between the results were discussed preliminarily.If there were still differences between the researchers after the discussion,the corresponding author of this paper resolved the disagreements.
2.4.2.Data extraction
Two researchers used a custom-made literature data extraction table to extract the data provided in the articles.The data that were extracted included basic information on the included article,the sample size,the research subjects,intervention measures,control measures,frequency and intensity of the intervention,and measurement indicators,and the extracted data were cross-checked by the two researchers.
2.4.3.Literature quality evaluation
Two researchers (students who were pursuing master of nursing and had completed the Evidence-Based Nursing course)evaluated the authenticity of the included articles according to the randomized controlled trial risk of bias assessment tool recommended by version 5.1.0 of Cochrane’s systematic review manual[23].The following aspects were evaluated:①the generation of random sequences;② the concealment of the distribution of random schemes;③whether the blinding method was adopted for the research subjects,intervention providers and results evaluators;④whether the subjects lost to follow-up were reported;⑤the possibility of selective reporting of the results;and ⑥other aspects.Articles with a quality grade of an A were considered to have fully met the quality evaluation standard and have a low risk of bias.Articles with a quality grade of B were considered to have partially met the quality evaluation standard and have a moderate risk of bias.Articles with a quality grade of C were considered to have not met the quality evaluation standard and have a high risk of bias.This study only includes articles with a quality grade of an A or a B.The quality grades were cross-checked by the researchers.If there were disagreements,they were arbitrated by the corresponding author.
2.5.Statistical methods
RevMan 5.3 software provided by Cochrane was used for the meta-analysis.The relative risk(RR)was used to express the effect size for binary variables,and the weighted mean difference(WMD)or standardized mean difference (SMD)was used to express the quantitative effect for numerical variables or continuous variables;each effect value was expressed with a 95%confidence interval.The χ2test was used to determine whether there was heterogeneity between studies.I2was used to determine the magnitude of heterogeneity.The larger the I2statistic was,the larger the heterogeneity.If P>0.1 and I2<50%,non-heterogeneity was considered to exist.A fixed effects model was used for the meta-analysis.If P ≤0.1 and I2≥50%,the source of heterogeneity was analyzed.If there is clinical heterogeneity or methodological heterogeneity between studies,the studies can be divided into subgroups according to the different study designs,levels of study quality and characteristics of the included populations for subgroup analysis.If there is statistical heterogeneity but no clinical heterogeneity between the studies,a random effects model can be used.When the factors that lead to heterogeneity can be measured accurately and explained completely,a Meta regression analysis can be performed.When the level of heterogeneity is excessively high,especially when there is obvious clinical heterogeneity or methodological heterogeneity,and the sources of heterogeneity cannot be addressed by other methods,a meta-analysis is not used,and only a general qualitative description of the results is provided [23].
3.Results
3.1.Search results
A total of 693 related studies were identified in the preliminary search,and 11 RCTs[13,24-33],including 576 patients,were finally included.A flow chart detailing the article screening process is shown in Fig.1.
3.2.Basic characteristics and methodological quality evaluation of the included articles
Nine English studies and two Chinese studies that were published in 2010-2018 and conducted in Indonesia,Greece,Brazil,Canada,Argentina,the United Kingdom,Austria,China and other countries were included.The basic characteristics of the studies are shown in Table 1.According to version 5.1.0 of the Cochrane system evaluation manual,the included articles were evaluated;2 had quality grades of an A,and 9 had quality grades of a B.The specific evaluation results are shown in Table 2,and the risk of bias assessment diagram of the included articles is shown in Fig.2.
3.3.Meta-analysis results
3.3.1.Effect of NMES on the muscle strength of ICU patients
Seven articles[13,24,25,27,29,32,33]included in this study used the MRC score to diagnose the incidence of ICU-AW;5 articles[13,24,25,27,32]used an MRC score of<48 to diagnose ICU-AW and provided the mean and standard deviation in the results,one article[29]provided the median and 25%-75% quartiles,and the remaining article [33]only recorded the number of patients with grades 0-5.Therefore,to preserve the integrity of the data,only the indicators obtained by the same evaluation method were included and consolidated.According to the heterogeneity test results,P=0.14 and I2=42%,the level of heterogeneity was acceptable.Therefore,a fixed effects model was used for the meta-analysis.The results showed that the effectiveness of the NMES intervention in improving the muscle strength of ICU patients was better than that of the control group,and the difference was statistically significant[MD=1.78,95% CI (0.44,3.12),P=0.009].See Fig.3.
3.3.2.Effect of NMES on MV duration in ICU patients
Six studies [13,24,26,27,32,33]evaluated the effect of NMES on the MV time of ICU patients.The outcome indicators were reported with different units:4 studies used d/day,and 2 studies used h/hour.SMD was used to standardize the results.According to the results of the heterogeneity test,P=0.05 and I2=55%,there was heterogeneity between the studies;to exclude clinical heterogeneity and methodological heterogeneity,a random effects model was used for the integrated meta-analysis.The results showed that the effectiveness of the NMES intervention in shortening the MV duration of ICU patients was better than that of the control group,and the difference was statistically significant[SMD=-0.65,95%CI(-1.03,-0.27),P<0.001].See Fig.4.
3.3.3.Effects of NMES on ICU length of stay,total length of stay and mortality in ICU patients
Four articles [24,26,27,32]evaluated the effect of NMES on the length of stay in the ICU.The heterogeneity test results were as follows:P=0.61,I2=0%.A fixed effects model was used for the meta-analysis.The results showed that the effectiveness of the NMES intervention in shortening the length of stay in the ICU was better than that of the control group,and the difference was statistically significant[MD=-3.41,95%CI(-4.58,-4.24),P<0.001].Three studies [24,27,32]evaluated the effect of NMES on the total length of stay.The heterogeneity test results were as follows:P=0.46,I2=0%.Thus,a fixed effects model was used for the metaanalysis.The results showed that the effectiveness of the NMES intervention in shortening the total length of stay was better than that of the control group,with a statistically significant difference[MD=-3.97,95% CI (-6.89,-1.06),P=0.008].See Fig.5.Three studies[13,26,27]evaluated the effect of NMES on the mortality of ICU patients.The heterogeneity test results were as follows:P=0.47,I2=0%.A fixed effects model was used for the metaanalysis.The results showed that there was no difference in mortality between the NMES intervention group and the control group,and the combined effect was not statistically significant[RR=1.07,95%CI (0.62,1.84),P=0.80].See Fig.6.
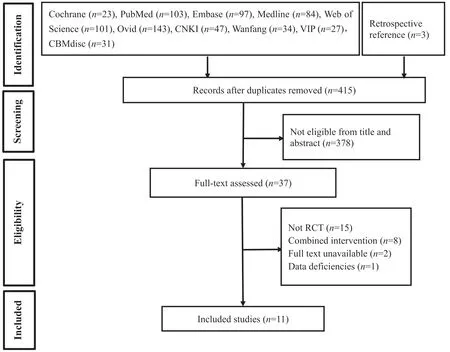
Fig.1.PRISMA flow diagram.
3.3.4.Effects of NMES on the ability to perform activities of daily living,functional state and maximum walking distance of ICU patients
Two studies [24,27]used the ADL scale to evaluate patients’ability to perform activities of daily living,with a total score of 100.The higher the score,the better their ability was.Due to a large difference in the mean,the SMD and the effect size were calculated,and the heterogeneity test results were as follows:P=0.32,I2=0%.A fixed effect model was used for the meta-analysis.The results showed that the effectiveness of the NMES intervention in improving patients’ ability to perform activities of daily living was better than that of the control group,and the difference was statistically significant[SMD=0.9,95%CI(0.45,1.35),P=0.001].Two studies [24,27]used the FSS-ICU scale to evaluate the functional status of the ICU patients after the NMES intervention.The total score ranged from 0 to 35 points.The higher the score,the better the functional status was.The results of the heterogeneity test were as follows:P=0.008,I2=86%.The causes of heterogeneity may include differences in the severity of the patient’s condition and the length of the intervention time.A meta-analysis was carried out by using a random effects model.The results showed that there was no difference between the NMES intervention group and the control group in improvements in the patient’s functional state,and the combined effect was not statistically significant[MD=9.14,95%CI(-1.14,19.43),P=0.08].Two studies [27,28]evaluated the maximum walking distance of patients,and the heterogeneity test results were as follows:P=0.82,I2=0%.A fixed effects model was used for the meta-analysis.The results showed that the walking distances of the patients in the NMES intervention group were longer than those of the participants in the control group,with a statistically significant difference [MD=239.03,95% CI (179.22,298.85),P<0.001](Figs.7-9).
3.3.5.Effect of NMES on the consciousness of ICU patients
Two studies [13,24]assessed the effect of NMES on the state of consciousness in ICU patients.The GCS score was used for scoring.The highest score was 15 points.The higher the score was,the clearer the consciousness.The results of the heterogeneity test were as follows:P=0.08,I2=66%.To exclude clinical heterogeneity and methodological heterogeneity,the meta-analysis was conducted by using a random effects model.The results showed that there was no difference in the consciousness state between the NMES intervention group and the control group,and the combined effect was not statistically significant [MD=0.78,95% CI (-0.07,1.62),P=0.07].
3.3.6.Effect of NMES on muscle thickness in ICU patients
Four studies evaluated the muscular thickness or area after the NMES intervention.However,due to the different measurement sites used in each study,we could not combine the data or the meta-analysis,so we only performed descriptive analysis.Acqua’s[26]study demonstrated that there was no change in the thickness of the rectus abdominis or pectoral muscles in ICU patients after the NMES intervention,but the thickness of the muscles in the conventional nursing group decreased statistically significantly.Vivodtzev’s [28]study demonstrated that NMES improved the crosssectional area of the quadriceps femoris and calf muscles in patients and maintained the balance of muscle anabolism and catabolism.Meesen’s [30]study demonstrated that NMES stimulation can prevent muscular atrophy in patients and has no effect on cardiopulmonary function.Gruthe’s [31]study showed that long-term NMES stimulation can increase the thickness of the extensor layer of the knee joint in patients.These studies,to a certain extent,help prove that NMES stimulation on muscles is beneficial and safe.
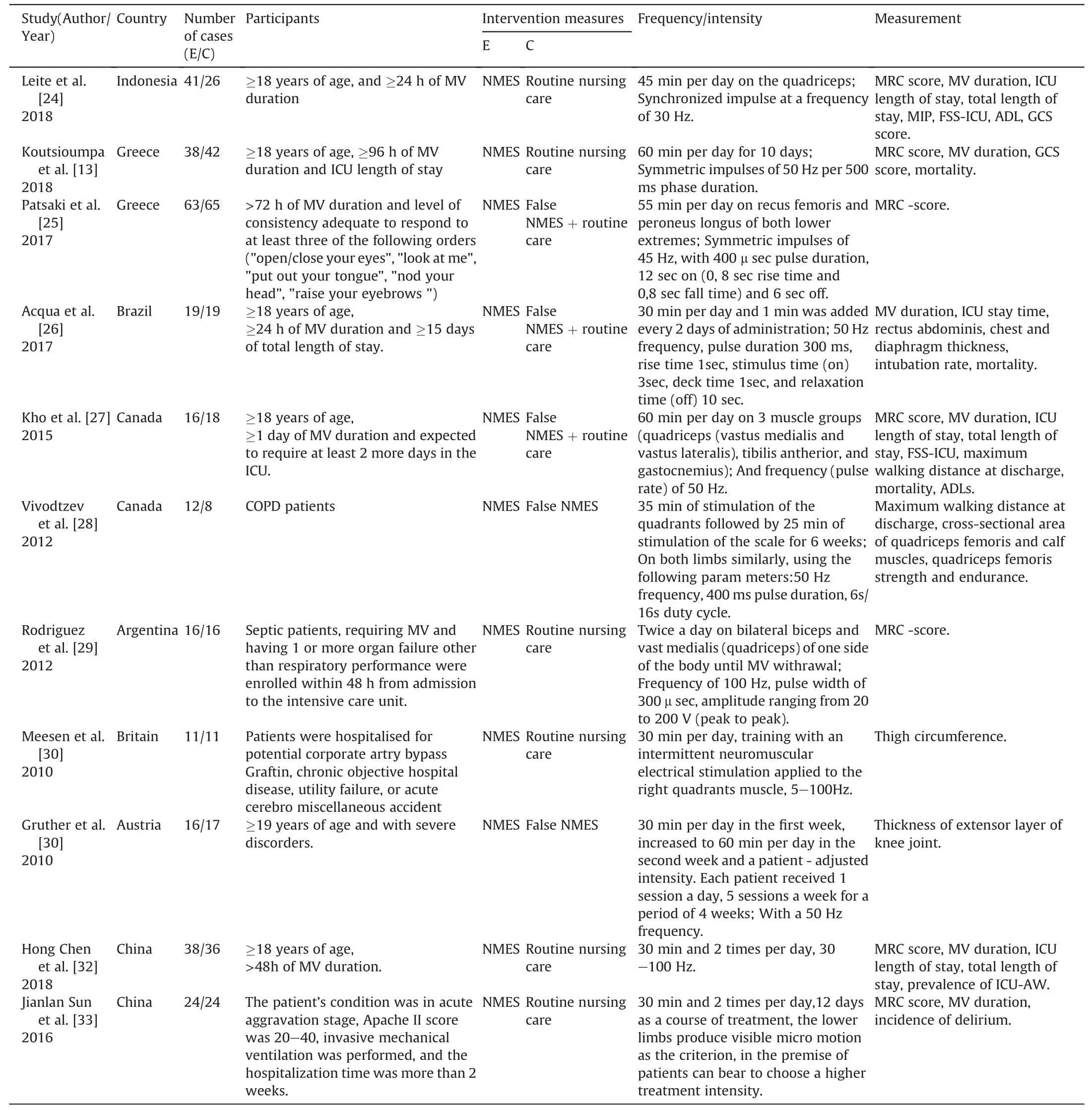
Table 1 Demographics of the studies included in the review.
3.3.7.Publication bias analysis
Publication bias refers to the tendency of statistically significant and positive results to be published more often than negative or invalid results.In this study,we aimed to generate a funnel chart of some combined effects,as shown in Figs.10-11.The distribution of each study result on both sides of the funnel is basically symmetrical.However,due to the small number of included studies,we cannot completely exclude the possibility of publication bias.Therefore,to some extent,this bias may affect the authenticity and reliability of the research results.
4.Discussion
4.1.Effectiveness of NMES in preventing ICU-AW
This study shows that NMES can effectively improve the muscle strength of ICU patients;shorten the MV,length of stay in the ICU and total stay in the hospital;improve the ability of patients toperform activities of daily living;and increase the walking distance at the time of discharge.To some extent,NMES can prevent ICU-AW by reducing related risk factors,and it is especially suitable for patients who are under mechanical ventilation,unconscious,and unable to get out of bed in the early stage of a coma.However,the effect of NMES on the functional status,consciousness level and mortality of ICU patients during hospitalization is still unclear.Only two articles included in this study evaluated the effect of NMES on the functional status of ICU patients.Due to the high level of heterogeneity,the meta-analysis showed that the combined effect was not statistically significant,and this result needs to be further verified.Two studies evaluated the effect of NMES on the consciousness level of patients.The meta-analysis showed that there was no statistical significance between the two studies.Three studies evaluated the effect of NMES on the mortality of ICU patients.At present,there is no evidence that NMES can reduce the mortality of ICU patients,but studies with larger sample sizes still need to be conducted for further verification.
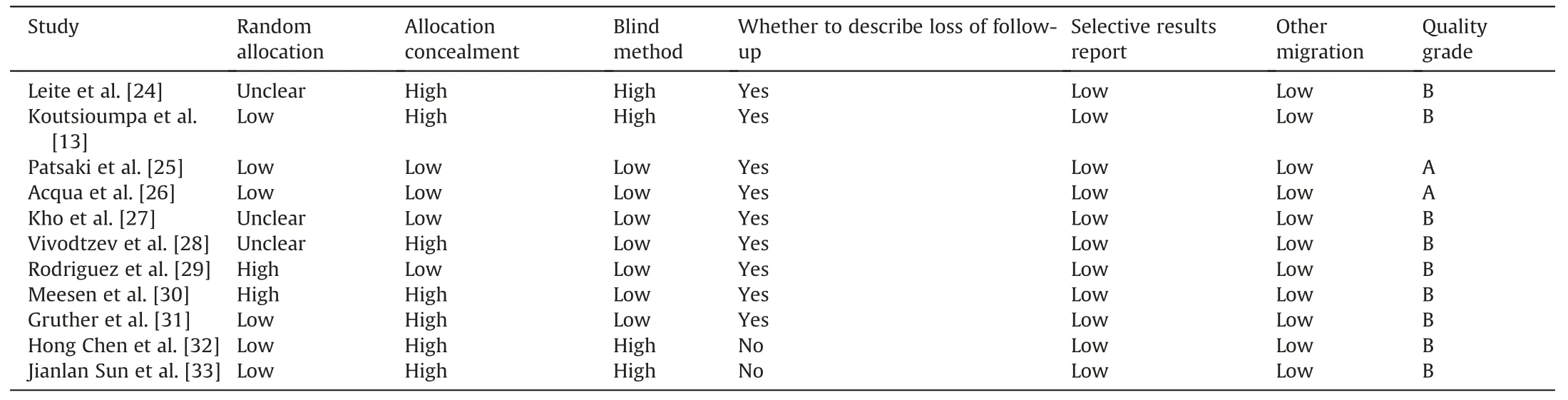
Table 2 Quality evaluation of study methodology included in the literature.
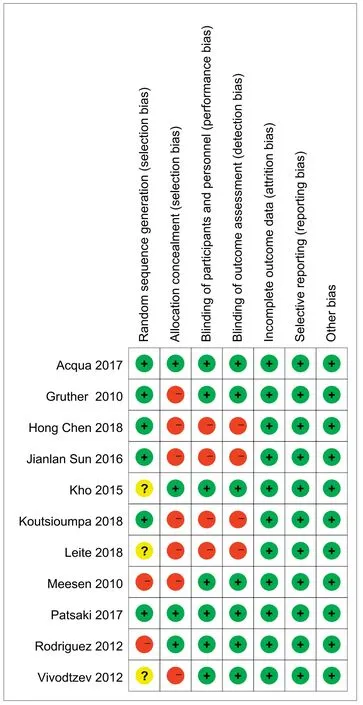
Fig.2.Risk of bias of selected studies according to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions(“+”means low risk;“-”means high risk;“?”means unclear risk).
4.2.Methodological characteristics and limitations of this study
In this study,newly published,relevant RCTs that were published before April 2019 were included,the sample sizes of the included studies were larger than those of studies included in other systematic evaluations,and a quantitative analysis was conducted on the data in the form of a meta-analysis,which allowed us to determine the differences in the main results as well as the authenticity and reliability of the results.We used robust statistical analysis tools,including a random effects model,in which the weights of small and large studies are taken into account.In addition,different conclusions were drawn on whether NMES can improve the muscle strength of ICU patients and shorten the MV and length of stay in the ICU in a study by Zhang et al.that only included 5 RCTs[34].This result may be related to differences in the inclusion and exclusion standards,study subjects,sample size and other factors.Based on the differences in the results of the two studies,it is suggested that the effectiveness of NMES in preventing ICU-AW is further verified in higher quality studies.Moreover,there are some limitations of this study.First,some outcome indicators have an obvious level of heterogeneity,which may be related to differences in the patient groups and characteristics.The pathophysiological mechanism of ICU-AW is currently unclear,and too many influencing factors inevitably lead to clinical heterogeneity among the subjects included in each study.Second,this study only included articles published in Chinese and English and ignored gray literature and articles published in other languages in the retrieval process,which may lead to some errors in the results of this study.Third,in this study,adverse effects and costeffectiveness were not assessed.
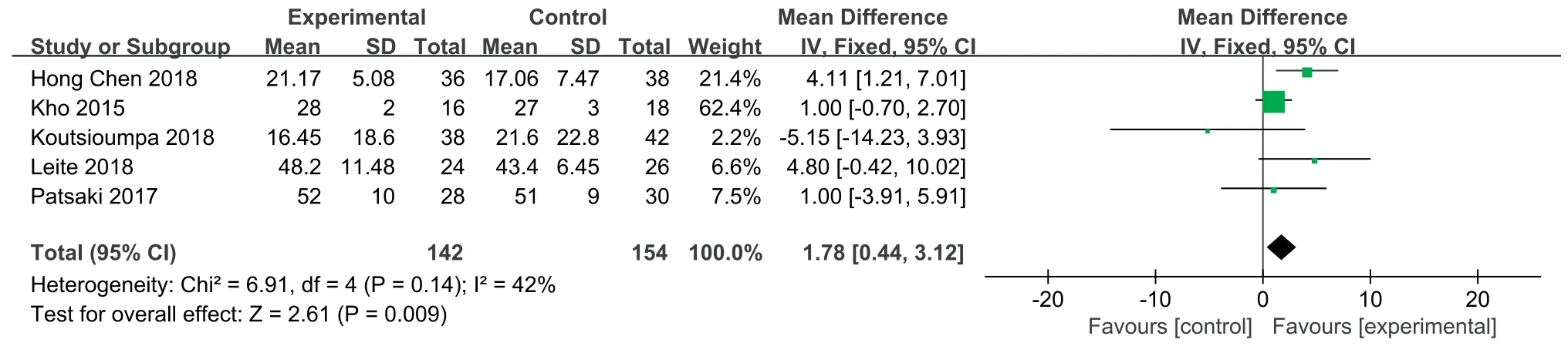
Fig.3.Effects of NMES on muscle strength of ICU patients.
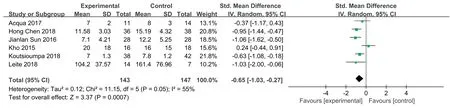
Fig.4.Effects of NMES on MV duration of ICU patients.
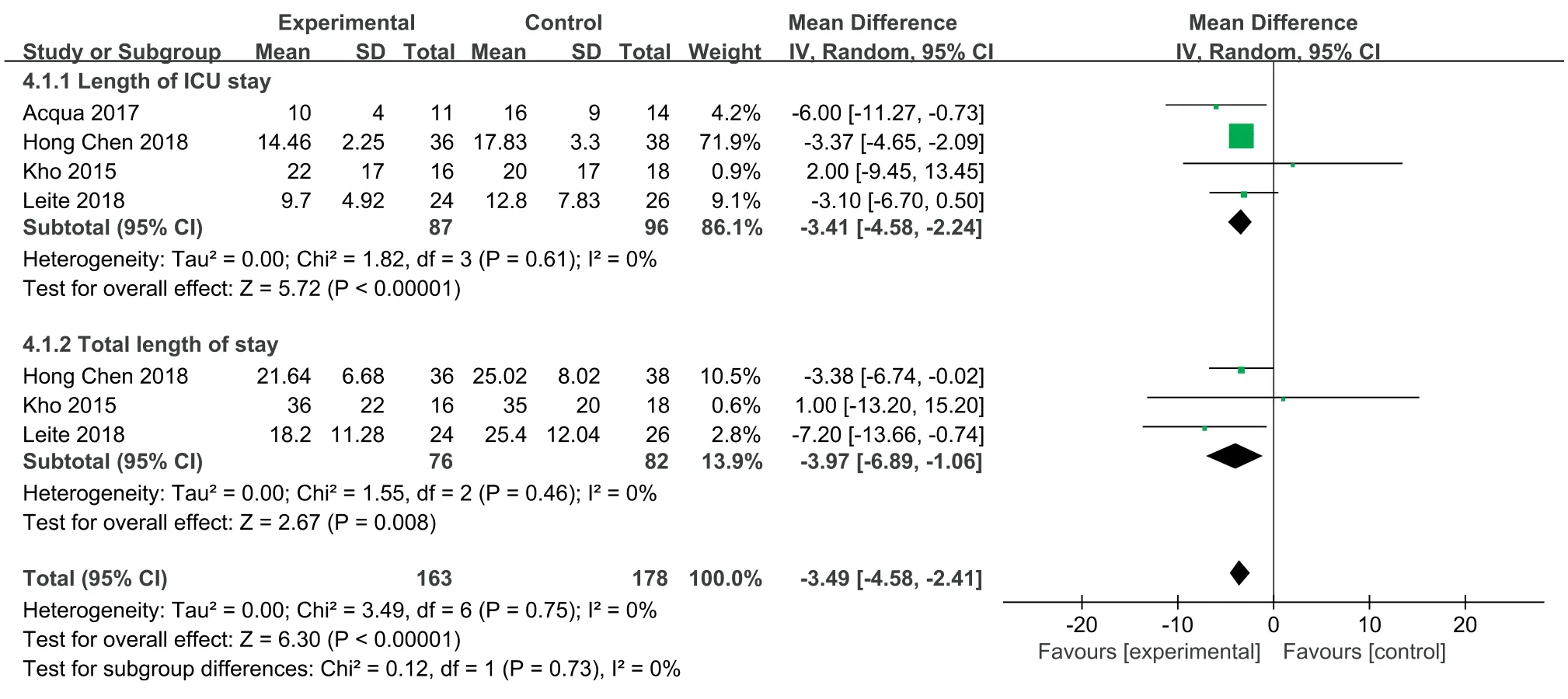
Fig.5.Effects of NMES on ICU length of stay and total length of stay.
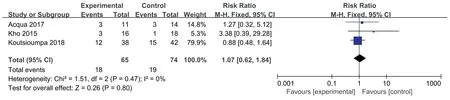
Fig.6.Effect of NMES on mortality.
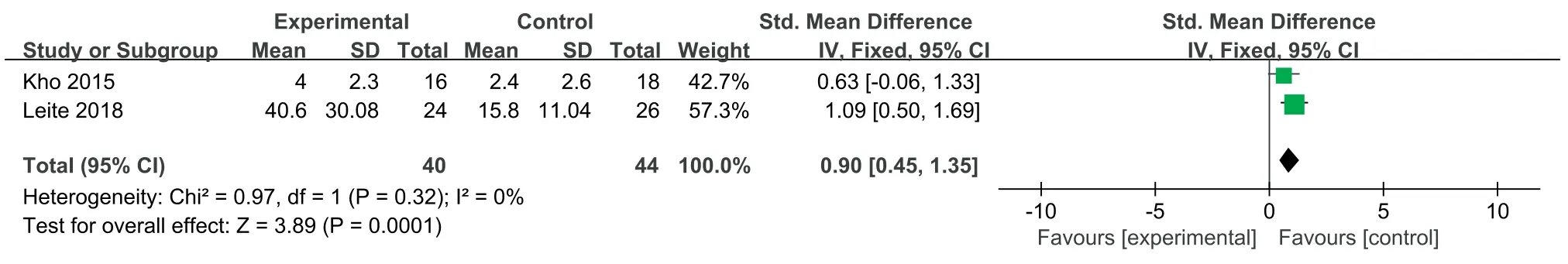
Fig.7.Effects of NMES on patients’ daily living ability (ADL).
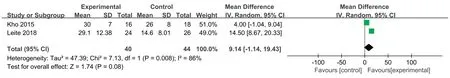
Fig.8.Effects of NMES on functional status during hospitalization.

Fig.9.Effect of NMES on walking distance at discharge.
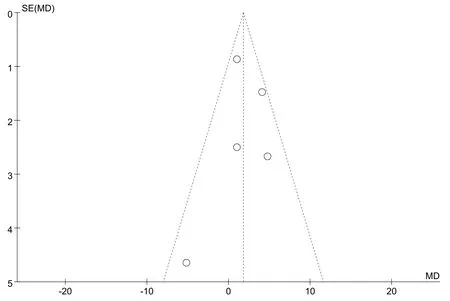
Fig.10.Funnel diagram of the effects of NMES on muscle strength.
5.Conclusion
The early implementation of the NMES intervention in ICU patients can effectively increase muscle strength;shorten the MV,length of ICU hospitalization and total length of hospitalization;promote patient recovery;improve the quality of life of patients after discharge;and prevent the occurrence of ICU-AW to a certain extent.However,there is no evidence that proves whether NMES can improve the functional status of patients during their stay in the ICU,promote the early awakening of patients and reduce the mortality of patients in the ICU.In the future,a large-scale and multicenter high-quality study should be conducted to further verify the effectiveness of NMES in preventing ICU-AW in different cohorts and evaluate the clinical feasibility of NMES.
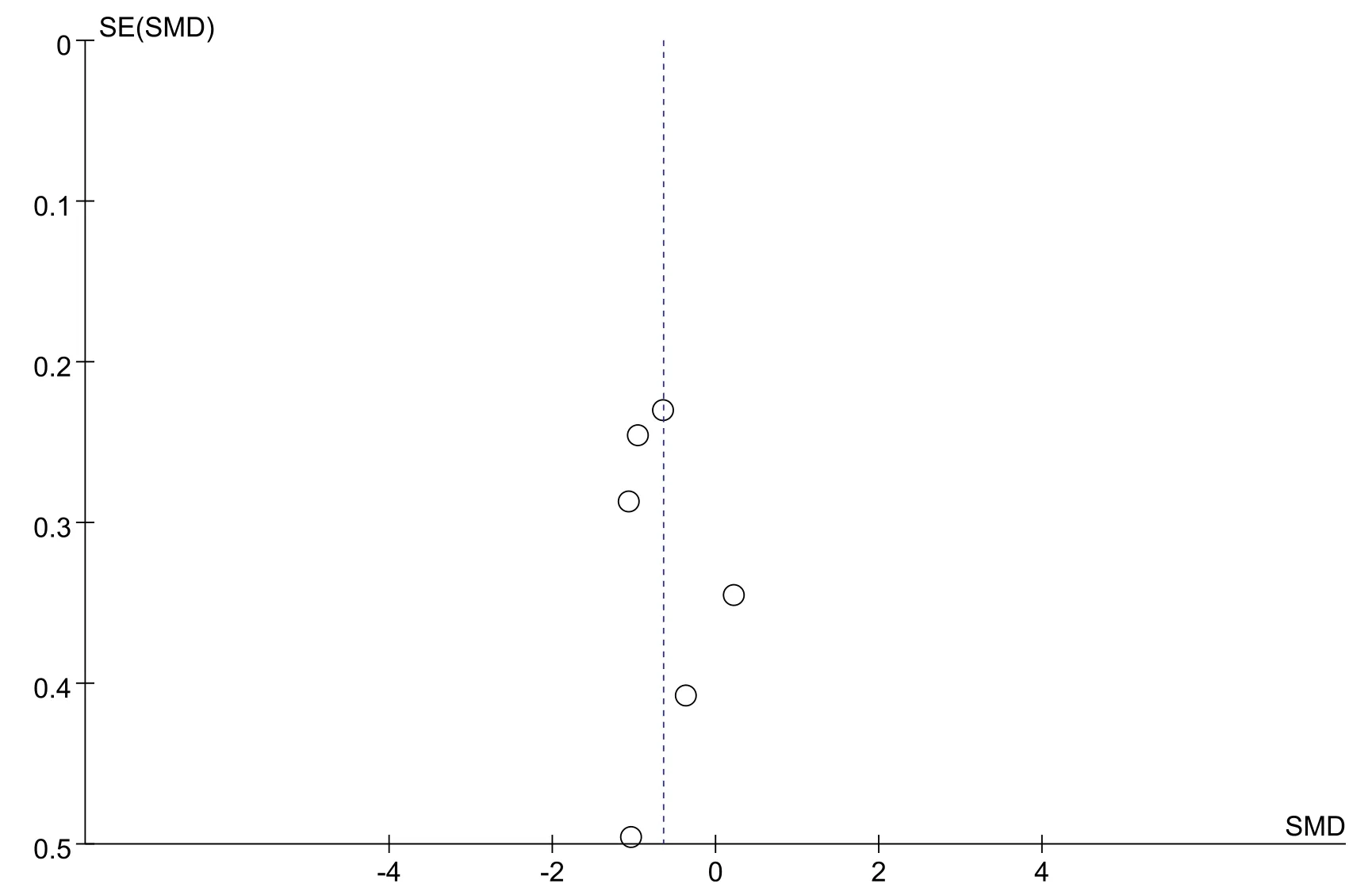
Fig.11.Funnel diagram of the effect of NMES on MV duration.
Funding
This work was supported by the Chinese Nursing Association research program [ZHKY201611].
Authors’ contribution
Miao Liu:Conceptualization,design,Literature retrieval,Analysis and interpretation,Writing-Original Draft,Writing-Review and Editing.Xiaomin Zhu:Literature retrieval,Literature quality evaluation,Data extraction,Writing-Review and Editing.Jun Zhou:Literature retrieval,Literature quality evaluation,Writing-Review and Editing.Jian Luo:Conceptualization,design,Analysis and interpretation,Writing-Original Draft,Writing-Review and Editing,Supervision,Project administration,Funding support.
Declaration of competing interest
None.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Miao Liu:Conceptualization,Formal analysis,Writing-original draft,Writing -review &editing.Jian Luo:Conceptualization,Formal analysis,Writing-original draft,Writing-review&editing,Supervision,Project administration,Funding acquisition.Jun Zhou:Writing -review &editing.Xiaomin Zhu:Writing -review &editing,Data curation.
Appendix A.Supplementary data
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnss.2020.03.002.
 International Journal of Nursing Sciences2020年2期
International Journal of Nursing Sciences2020年2期
- International Journal of Nursing Sciences的其它文章
- Exercise for fatigue in breast cancer patients:An umbrella review of systematic reviews
- Antiretroviral therapy improves neurocognitive impairment in people living with HIV? A meta-analysis
- Psychometric properties of the Chinese Version of the Readiness for Hospital Discharge Scale for people living with HIV
- Experiences of graduates in Massachusetts of the United States from a RN-to-BSN program
- Analysis on nursing competence and training needs of dementia caregivers in long-term care institutions
- Investigation for the transcultural self-efficacy of nurses in Guizhou,China
