Stem cell treatment and cerebral palsy: Systemic review and metaanalysis
Simone Eggenberger, Céline Boucard, Andreina Schoeberlein, Raphael Guzman, Andreas Limacher,Daniel Surbek, Martin Mueller
Simone Eggenberger, Daniel Surbek, Martin Mueller, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Inselspital, University Hospital Bern, Bern 3010, Switzerland
Céline Boucard, Andreina Schoeberlein, Department for BioMedical Research, University of Bern, Bern 3008, Switzerland
Raphael Guzman, Department of Neurosurgery, University Hospital of Basel, Basel 4056,Switzerland
Andreas Limacher, CTU Bern, University of Bern, Bern 3012, Switzerland
Abstract
Key words: Cerebral palsy; Perinatal brain injury; Stem cells; Umbilical cord blood;Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells; Gross motor function; Meta-analysis
INTRODUCTION
Despite advances in perinatal medicine, many infants continue to face serious risks during pregnancy, parturition, and adaptation after birth.Preterm birth and severe birth asphyxia are the most frequent complications, which may lead to brain damage of the newborn.The clinical presentation in an individual child after perinatal complications is complex.This complexity results from multiple potential causal pathways, signs and symptoms of injury.Typical pathology in these newborns include brain injury and the resulting cerebral palsy (CP).Therefore, CP summarizes a heterogeneous group of non-progressive disabilities in motor function which range from slight motor impairment of an isolated body part to the inability of walking or speaking[1].Depending on the severity, typical symptoms are difficulties in coordination, stereotypic movement, impossibility of discrete movements, evocation of primitive reflexes through voluntary movements or co-contraction of agonist and antagonist resulting in spasticity.Multiple other impairments such as seizure disorders, altered sensation or perception or musculoskeletal disorders can appear as additional symptoms[1].Although the diagnosis of CP does not require cognitive disability, about two-thirds of children with CP are confronted with it[2].Not surprisingly, CP is the most common motor disability in children with a prevalence of 2 per 1000 live births in developed countries.The prevalence of CP increases exponentially in preterm infants with decreasing gestational age[3].For example, the risk to develop CP is 30 times higher in infants born before 33 wk gestation compared to term-born infants[3].Besides prematurity, major risk factors include placental abnormalities, major and minor birth defects, low birthweight, meconium aspiration,emergency caesarean section, birth asphyxia, neonatal seizures, respiratory distress syndrome, hypoglycemia, and neonatal infections[4].Together, CP originates from a multifactorial pathology with multiple risk factors and in many cases, a distinct cause is unclear.
Due to major improvements in neonatal care, half of the children suffering from CP are preterm infants and the other half are term-born infants[5,6].This differentiation is important as prophylactic/therapeutic approaches differ in these two populations.Currently, the only intervention known to reduce the burden of CP in the term population is hypothermia.Hypothermia is associated with a significant reduction in death and disability in children subjected to perinatal asphyxia[7].However, 40%-50%of infants treated with hypothermia still die or develop significant neurological disability[8].In the preterm population, hypothermia is contra-productive and therapeutic options are lacking.One option is the antenatal magnesium sulfate prophylaxis at less than 30 wk of gestation, which reduces CP and combined CP and mortality rate at 2-years of age.However, long-term neurological benefits are lacking[9,10].New avenues to treat CP emerged and stem cell treatments are particularly promising.We review the potential of a stem cell transplant using a metaanalysis to evaluate gross motor function after randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in children with CP.
Which source of stem cells to use?
Stem cells are characterized as cells with the capacity of self-renewal and differentiation into multiple tissues[11].Their program of division and differentiation is regulated by the immediate microenvironment, also called the niche.Stem cells are grouped depending on the number of tissues they can differentiate into[12].Totipotent cells can differentiate into any cell type found in an organism.They exist for a very limited time only in the embryo shortly after fertilization.Pluripotent cells are the next stage; they occur in the blastocyst and can form cells from each of the three germinal sheets.Multipotent stem cells can also be detected in adults.Their differentiation capability is restricted to cell types within one germinal sheet.Unipotent stem cells are responsible for the renewal of a single tissue lineage.In vitro,apart from their self-renewal and differentiation capacity, stem cells can be identified by markers, which are gene products expressed by specific types of stem cells.Therefore, by means of flow cytometry, stem cells can be identified and quantified[11].
Embryonic or pluripotent stem cells seem to be very promising due to their differentiation ability[11].However, their unlimited self-renewal and differentiation capacity combined with a lack of cell-cell-interaction and regulation through extraembryonic cells may lead to tumor formation[13].Additionally, the harvesting of pluripotent cells results in the death of the embryo raising major ethical concerns.Therefore, the main stem cell sources in CP treatment are bone marrow (BM) or umbilical cord blood (UCB)-derived stem cells.
Umbilical cord blood and bone marrow as a source of stem cells
UCB is a rich source of stem cells.It can be collected after birth and stored in public or private banks for a possible future use[14].It contains several types of stem and progenitor cells, among which hematopoietic stem cells (HSC), mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSC) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) are the most relevant.Further, the existence of embryonic-like stem cells is controversially discussed.Besides the simple isolation without ethical concerns, these cells have a remarkably low immunogenicity.Compared to stem cells from other sources, UCB cells tolerate more human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-mismatches without rejection[12].The reason for this might be the immature fetal immune system.Today, cord blood is routinely used to treat hematopoietic or immunologic disorders[15].In the last years,promising trials have shown that UCB stem cells have great potential in the treatment of various neurological diseases[16].A world-wide network of cord blood banks is available for unrelated cord blood transplantations.For therapeutic use, the mononuclear fraction is isolated from cord blood by means of a density gradient[17].The mononuclear fraction includes immunosuppressive cells such as regulatory T-cells and monocyte-derived suppressor cells[16].Each of these cell types has characteristics that are likely to contribute to neuroprotection.Notably, the composition of those cells depends on the timing of sampling (gestational age of pregnancy)[18].For example, UCB derived from preterm placentae is different in its mononuclear fraction from term-derived, and UCB from intrauterine growth restriction infants has impaired EPC[19].
BM is the major hematopoietic organ localized in the central cavities of axial and long bones[20].Differentiation and proliferation of the blood cells occur in the hematopoietic compartment.It is composed of HSC and the precursors for the different blood lineages.It used to be the main source of HSC for clinical use, until recently less invasive techniques allowed to obtain HSC from other sources such as granulocyte-colony stimulating factor-stimulated peripheral blood or UCB[21].Importantly, the stroma is responsible for the regulation of the hematopoietic process and contains MSC and EPC along with their products of differentiation like fibroblasts and endothelial cells.Compared to UCB, MSC are more frequent in BM.Although BM harvesting requires an invasive procedure, BM is still the main source for MSC[22].Notably, the number of both EPC and MSC in BM decline with age[20,23].
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells
MSC are a heterogeneous population of multipotent cells that can differentiate into bone (osteoblasts), fat (adipocytes), cartilage (chondroblasts) and periosteum(fibroblasts)[24].Their differentiation potential into the neurogenic direction is debated,but the discussion remains controversial[17].Originally, MSCs were discovered in BM as part of the mononuclear cell fraction, where they support HSC[25].Meanwhile, they have been isolated from many other sources including adipose tissue, muscle,placental tissues, and UCB.The International Society for Cell and Gene Therapy elaborated minimal criteria to define MSCs[26].It remains unclear and much discussed what MSC’s function in each source is.Some even consider the pericyte to be the cell of origin of MSCin vivo.Thus, their function could be the regulation of the capillary blood flow and permeability[27].There are high expectations for MSC as a therapy in various diseases.A special interest lies in the treatment of neurological diseases including CP[24].Also, MSC have become more and more commercialized as source of replacement for damaged structures.However, injected allogeneic MSC are rejected by the host immune system and likely to be eliminated soon after the transplantation and in contrast, autologous ones may persist for some longer time[27].Not surprisingly,the therapeutic effect of MSC is attributed not to the differentiation capacity and thus formation of new tissue, but to the secretome, which contains modulatory factors[28].These modulate oxidative stress and has angiogenetic, anti-apoptotic and antiinflammatory effects[28].MSC have different characteristics depending on their origin.Of special interest are those MSC derived from fetal tissues such as UCB, placental or cord tissues, which are believed to have a wider differentiation and greater proliferation potential[29,30].Moreover, they can easily be isolated non-invasively,rapidly and without ethical concern nor invasive procedures[31].However, we are not always successful to isolate a sufficient number of MSC from UCB for clinical use[32].
Hematopoietic stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells
Both HSC and EPC can be found in BM as well as in UCB.HSC are multipotent precursor cells with the ability to form all blood cells while maintaining a sufficient HSC-pool to provide hematopoiesis throughout life[33].Whilst HSC transplantation was the first established stem cell transplantation and exclusively for hematologic disorders, HSC now also become interesting in the field of non-hematologic diseases[34].Of special interest for a possible neuroprotective contribution is their beneficial effect in ischemic brain injury in animal models[35].EPC too are believed to possess neuroprotective features.Apart from their ability to differentiate into endothelial cells, they are believed to induce neovascularization and reduce hypoxiainduced apoptosis and destruction of blood vessels[36,37].Considering these in-vitro characteristics of both HSC and EPC, they may play a role in neuroprotective therapies such as the treatment of CP as well.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Literature search
We followed the PRISMA-statement guidelines to perform a systematic electronic search using PubMed and EMBASE databases for trials published between January 1,1990, and February 11, 2019.To be eligible for inclusion, the trial was required to be a randomized, controlled clinical trial with full-text availability in English.Further, the study population must consist of children diagnosed with any type of CP.The intervention must include any kind of stem cell treatment compared to placebo and/or standard of care such as rehabilitation.The motor outcome of both intervention and control group must be assessed and reported in the Gross Motor Function Measure (GMFM).We excluded trials that did not meet these criteria from the analysis.
We combined terms like “stem cells”, “neural progenitor cells”, “mesenchymal stem cells” or “umbilical cord blood” to match the intervention with “cerebral palsy”in both databases.We set the limitations to human-controlled clinical trials in English only.Also, we detected trials from bibliographies of other articles.We identified the potentially relevant articles through title and abstract screening and proceeded to the definite inclusion or exclusion according to their content (supplementary materials).The study selection process is illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1 Study selection process.
Meta-analysis
We defined the efficacy of stem cell therapy as a change in gross motor function.To summarize the gross motor outcome from the intervention group compared to the control group, we performed a random-effects meta-analysis using the method of DerSimonianet al[38].We pooled the standardized mean differences and the heterogeneity was quantified using the I-squared measure, taken from the inversevariance fixed-effect model.All analyses were done in Stata version 15 using the command meta version 3.04.
RESULTS
Study selection and characteristics
After applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria, we identified 8 relevant trials for further analysis (Figure 1).Four of them have been conducted in China, three in Korea and one in the United States of America.Publication dates ranged from 2012 to 2018.The study characteristics are summarized in Table 1.Five trials investigated stem cell therapy plus rehabilitation to rehabilitation only, one trial compared stem cell therapy.only to rehabilitation and two trials compared stem cell therapy only to no intervention in the control group.Two of the included studies were three-group randomized clinical trials investigating the additive effect of erythropoietin[39]or using mononuclear cells[40].Two other studies were designed as randomized controlled crossover-trials[41,42].The age in the study population ranged from 6 mo to 35 years.All patients included were diagnosed with CP.The severity of CP was measured with the Gross Motor Function Classification System, which divides the syndrome of CP into 5 levels, whereof level 5 is the most severe motor impairment[43].The type and dose of the stem cells differed in the trials.One trial used neural progenitor cells derived from aborted fetuses’ forebrains[44], while others included umbilical cord- or BM-derived stem cells[39,41,45-47].The applied dose ranged from 4 × 106to 6 × 108cells.The number of cells was not always adapted to body weight.The application route was in most cases the intravenous route.In summary, both the study population and the intervention characteristics are heterogeneous, which leads to a certain risk of bias summarized in Table 2 and Figure 2.
Risk of bias
We assessed the risk of bias in individual studies using the Cochrane criteria.The risk ranged from low to high.The major source of risk of bias was patient and personnel blinding[40,44-46].The number of trials was not sufficient to estimate the risk for publication bias.
Outcome measurements
All included trials applied standardized scales to assess the neurodevelopmentaloutcome.The fine and gross motor function, cognitive function and spasticity were measured.In the following analysis, we focused on the gross motor function outcome only.The gross motor function was evaluated with the GMFM-66 or GMFM-88[43].Both scores categorize 5 sections: Lying, Sitting, Crawling, Standing and Walking.Each of these categories is expressed in the percentage of the maximum achievable points.To determine the total score, the percentages of all categories are added up and divided by five and therefore expresses the average score of all categories.Importantly, the total score varies depending on the severity of CP and the patient’s age.The observation period in the included trials was 6 months in three trials, 12 mo in another three and 24 in the remaining two trials (see Table 3 for details).Functional assessments to measure the outcomes were performed at baseline, after the observation period, and additionally at one to three points in-between.Most GMFM data were available for the 6- and 12-mo periods and therefore we decided to proceed with those for the meta-analysis.

Table 1 Intervention and study population overview

1Administation of cyclosporine.MNC: Mononuclear cells; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cells; EPO: Erythropoietin; CP: Cerebral palsy; SC: Stem cells; GMFCS:Gross motor function classification system.
Cell dose, gross motor function and safety
Three trials from the initial literature search had to be excluded from the metaanalysis due to the lack of GMFM scores in an averaged format[45], missing standard deviation or standard error in the GMFM scale[42], or no comparable outcome score of the control group given[44].One study did not provide changes in GMFM summary scores from baseline, but only absolute GMFM dimension scores at baseline, 6 months and 12 mo[40].Therefore, we averaged the dimension scores and their variations and calculated the changes from the baseline.The cell dose used in the included trials differed but improved motor outcome seems to correlate with a higher cell dose[41,42,47](Tables 1 and 3).We generated a forest plot with the available GMFM-scores at 6 and 12 mo (see Figures 3-5).Additionally, we pooled all studies; the resulting forest plot is presented in Figure 5.Besides the improvement of gross motor function, the studies assessed the serious adverse events (SAE).Overall, only two trials reported the occurrence of SAEs[39,44](Table 4).One case of hemorrhagic foci after transplantation was detected and was presumably linked to the invasive procedure[44].The other SAEs mainly consisted of infections or seizures[39].These SAEs were equally distributed between both cell recipient and control groups.There is no report of an overdose in any of the included trials.The highest dose applied was a mean dose of 5.97 × 108cells/kg and no SAEs were reported[42].Together, the included RCTs provide shortterm safety, whereas the long-term impact is unclear.
DISCUSSION
Using a systematic literature review, we identified 8 RCTs investigating the effect of stem cell treatment in children with CPvsstandard care with or without placebo.Based on our inclusion criteria, we included 5 trials in the meta-analysis with a total of 282 patients (142 control, 140 cell recipient group).By combining the outcome, we identified a significant improvement in the cell recipient compared to the control group (Figure 5).The pooled standard mean difference was 0.95 (95% confidence interval: 0.13-1.76).However, we detected a high heterogeneity (I2= 90.1%), which reflects the diverse patient characteristics and needs to be accounted for while discussing the results.Besides, our analysis only includes the results from 5 trials,which is hardly enough to represent the whole CP population.A search on clinicaltrials.gov identified 9 ongoing randomized clinical trials about stem cell therapy in CP.Therefore, evidence might grow stronger in the future with greater data acquisition.
In the included trials, the origin (autologous or allogeneic), type (MSC,mononuclear cells, and neural progenitor cells), and source (BM, brain tissue, UCB) of the transplanted cells differed.Interestingly, in patients receiving the transplant withfewer HLA-mismatches, the improvement of gross motor function was clearly evident[39,47].We speculate that autologous cells may show a greater benefit in motor function improvement.Furthermore, the matching of HLA seems to have less relevance in case of a MSC transplant[46].For example, both studies with a significant increase in the motor outcome used a MSC transplant[40,46].These observations are further supported by the direct comparison of mononuclear fraction of BM stem cells and MSC alone[40], which clearly favors a MSC alone approach.Together, the present studies suggest that MSC are the ideal candidates to modulate the gross motor function in CP.The source may be the UCB as it is less invasive and easily accessible.However, harvesting a sufficient number of cells can only be achieved in around 40%of the samples[48], which limits the use of autologous UCB-derived MSC.Further studies are warranted especially as other easily available MSC sources such as Wharton`s jelly of the umbilical cord are very promising[49,50].

Table 2 Evaluation of the risk of bias
In order to report a proper gross motor function improvement, both the patient’s age and level of motor impairment need to be considered by using percentiles[51].However, only one of the included trials used proper percentiles and presented the results as “greater than expected”[41].Interestingly, this trial detected a significant gross motor function improvement using a higher cell dose (≥ 2 × 107cells) only.Another consideration is the use of repeated cell applications[40,46].Given that the pathophysiology of CP consists of persistent inflammation, such repetitive doses would be plausible[52].Moreover, the transplanted cells do not persist for a very long time[53], which further supports concurrent use.Eventually, the included trials do not clearly provide a specific effective dose of cells, but it should be more than 2 × 107total nucleated cells and may go up to 6 × 108without the risk of overdosing[41,42].The invasive transplantation routes such as the lumbar puncture were chosen to bypass the blood-brain barrier but resulted in a higher number of reactions like nausea and headache[40].However, the modulation of inflammatory responses by secretion of factors can be achieved peripherally[54], making the route of application less relevant for the efficacy of the cells[55].
In conclusion, stem cell therapy for CP compared with symptomatic standard care only, shows a significant positive effect on the gross motor function, although the magnitude of the improvement is limited.Especially MSC show a positive outcome.This novel treatment seems safe, at least in the short term.However, high-quality RCTs are still lacking.

Table 3 Raw motor outcome data
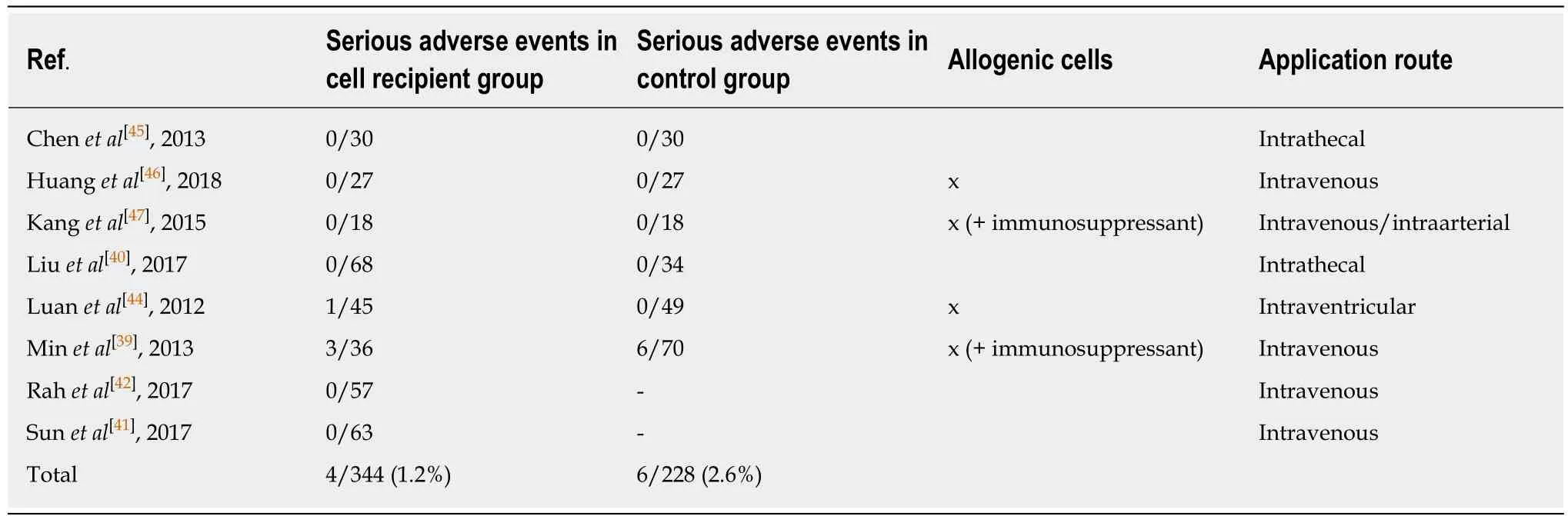
Table 4 Reported serious adverse events

Figure 2 Overall risk of bias.

Figure 3 Forest plot showing the effect size of the change in the Gross Motor Function Measure in the intervention group compared to the control group after 6 mo.

Figure 4 Forest plot showing the effect size of the change in the Gross Motor Function Measure in the intervention group compared to the control group after 12 mo.

Figure 5 Forest plot showing the effect size of the change in the Gross Motor Function Measure in the intervention group compared to the control group.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a severe, uncurable motor disability resulting from perinatal complications.It is a challenge for our health system and a burden for both patients and their families.
Research motivation
During the last years, stem cell therapy emerged as a novel treatment option.Clinical trials report promising results and create high expectations.However, most trials are of poor quality and neither randomized nor controlled, so the scientific evidence remains doubtful.
Research objectives
The aim of our meta-analysis was to investigate the effect of stem cell treatment on the gross motor function in children with CP.
Research methods
With a systematic literature search on PubMed and EMBASE, we identified the eligible randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs).We performed a random-effects meta-analysis focusing on the change in gross motor function and calculated the pooled standardized mean differences of the 6- and/or 12-mo-outcome.
Research results
We identified a total of 8 RCTs for a qualitative review.From the initially selected trials, 5 met the criteria and were included in the meta-analysis.Patients’ population ranged from 0.5 up to 35 years (n= 282).We detected a significant improvement in the gross motor function with a pooled standard mean difference of 0.95 (95% confidence interval: 0.13-1.76) favoring the stem cell group and a high heterogeneity (I2= 90.1%).Serious adverse events were rare and equally distributed among both intervention and control groups.
Research conclusions
Stem cell therapy for CP compared with symptomatic standard care only, shows a significant positive effect on the gross motor function, although the magnitude of the improvement is limited.
Research perspectives
Considering that this small number may not be enough to represent the whole CP population,our meta-analysis detected a small but significant improvement in the gross motor function favoring the stem cell group.However, the magnitude of the effect is limited.In the future, highquality research with a more homogenous study population is needed to bring more clarity.
 World Journal of Stem Cells2019年10期
World Journal of Stem Cells2019年10期
- World Journal of Stem Cells的其它文章
- Aging: A cell source limiting factor in tissue engineering
- Enhancing survival, engraftment, and osteogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells
- Genomic integrity of human induced pluripotent stem cells:Reprogramming, differentiation and applications
- Applications of single cell RNA sequencing to research of stem cells
- Characterization of inflammatory factor-induced changes in mesenchymal stem cell exosomes and sequencing analysis of exosomal microRNAs
- Unmodified autologous stem cells at point of care for chronic myocardial infarction
