A new species of Mountain Dragon(Reptilia:Agamidae:Diploderma)from the D.dymondi complex in southern Sichuan Province,China
Kai Wang,Jia-Wei Wu,Ke Jiang,Jin-Min Chen,Ben-Fu Miao,Cameron D.Siler,Jing Che,* State Key Laboratory of Genetic Resources and Evolution,Kunming Institute of Zoology,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Kunming Yunnan 650,China
2 Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History and Department of Biology,University of Oklahoma,Norman,Oklahoma 73072,USA
3 Chengdu Museum of Nature Exploration,Chengdu Sichuan 610017,China
DEAR EDITOR,
Despite continuous studies on the cryptic diversity of the Diploderma flaviceps complex in Southwest China for the past decade, little attention has been given to other widespread congeners in China. Combining both morphological and phylogenetic data, we describe a new species of Diploderma from populations identified previously as D. dymondi in the lower Yalong River Basin in southern Sichuan Province. The new species is morphologically most similar to D. dymondi and D. varcoae, but it can be differentiated by a considerable genetic divergence and a suite of morphological characters,including having taller nuchal crest scales, smaller tympana,and a distinct oral coloration. Additionally, we discuss other putative species complexes within the genus Diploderma in China.
Mountain Dragons of the genus Diploderma Hallowell, 1861 were recently resurrected from the paraphyletic genus Japalura sensu lato (Wang et al., 2019a). Despite the recent split, Diploderma still represents one of the most diverse groups of agamid lizard from Asia, including 25 species recognized currently, with most species found in China (Wang et al., 2019a, 2019b). Although increasing attention has been paid to cryptic diversity within the genus in Southwest China during the past decade, most studies have focused on a single species complex, D. flaviceps, only (Manthey et al.,2012; Wang et al., 2015, 2016, 2017, 2019a), with few studies on other congeners that also have widespread distributions.One such example is D.dymondi(Boulenger,1906).
First described from the Jinsha River Valley at Yunnan Fu (=Dongchuan) in northeastern Yunnan Province, D. dymondi was first diagnosed by a small set of morphological characters, particularly the presence of exposed tympana(Boulenger, 1906). Based on this diagnosis, all populations of Diploderma in Southwest China with exposed tympana were identified historically as D. dymondi, and the species was recorded to have a wide distribution in Southwest China,including along the Nu River (=Salween) Basin in northwestern Yunnan Province (Wu, 1992; Yang & Rao, 2008;Zhao et al., 1999), the lower Jinsha River Basin in northern Yunnan Province and southern Sichuan Province (Boulenger,1906; Deng & Jiang, 1998; Zhao et al., 1999; Zhao, 2003), the central parts of the Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau (Boulenger,1906), and the Yalong River Basin in Sichuan Province (Deng& Jiang, 1998; Zhao et al., 1999; Zhao, 2003; Figure 1).However, later taxonomic works revealed distinct species among the populations identified previously as D. dymondi,including D. varcoae (Boulenger, 1918) from the central Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau and D. slowinskii (Rao, Vindum, Ma,Fu, Wilkinson, 2017) from the Nu River Basin in western Yunnan Province. Such discoveries suggest that D. dymondi,as currently recognized, represents a complex of unique evolutionary lineages that warrant further investigation.Interestingly, few studies have examined the taxonomic status of several populations of D. dymondi across its range (Rao et al., 2017). As different species of Diploderma occupy distinct river courses in Southwest China (Manthey et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2019a), it is highly possible that the unexamined populations of D. dymondi in different river courses along the Jinsha River represent additional diversity.
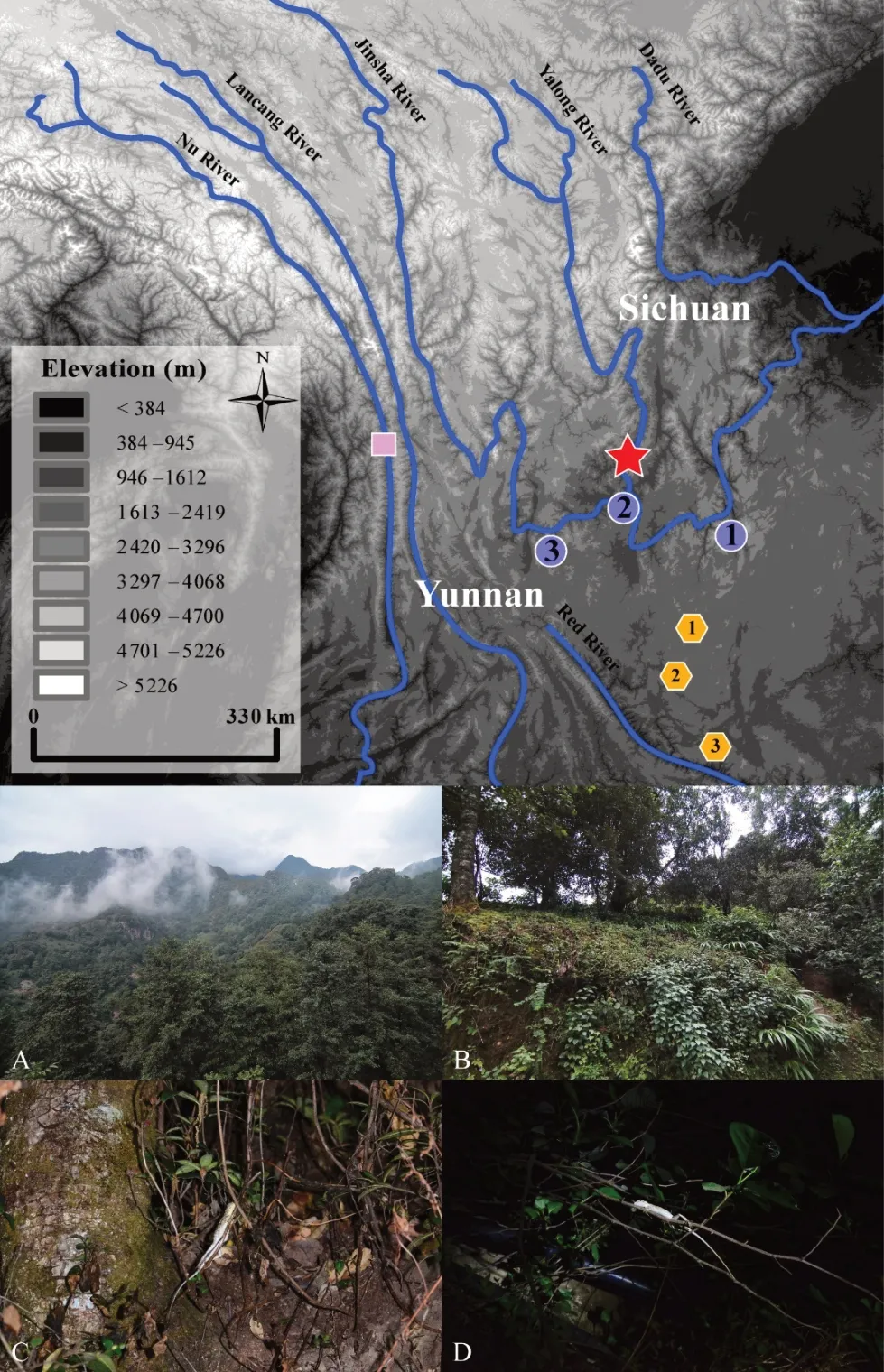
Figure 1 Distribution of Diploderma dymondi species complex in Southwest China (top) and macro- (A and B) and micro- (C and D)habitats of D.swild sp.nov.(bottom)
During herpetological surveys in southern Sichuan Province from 2017 to 2019, specimens of previously identified D.dymondi were collected from the lower Yalong River Basin, a main tributary of the Jinsha River, and a historical specimen of previously identified D. dymondi from southern Sichuan Province was examined in the museum collection. As the examined population of D. cf. dymondi forms a monophyletic group and possesses considerable genetic distances from closely related congeners based on mitochondrial marker, and given it is also morphologically distinct from all recognized congeners,we here describe this lineage as a new species.
A total of nine specimens of the new species were collected from Yanbian County, Panzhihua District, southern Sichuan Province, China (Figure 1). In addition to the newly collected specimens, a single specimen of the new species from Xichang, Sichuan Province, and 20 recognized species of congeners from the following natural history museum collections were also examined (Supplementary material(Appendix I)).
Total genomic DNA for the new species was extracted from liver tissues, and the mitochondrial gene NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 (ND2, 1 035 bp (coding region), 182 bp (tRNAs)) was amplified and sequenced by using published primers (Wang et al., 2019a). In addition to the newly generated sequences, genetic data for 18 species of Diploderma and representatives of two outgroup genera(Pseudocalotes and Acanthosaura) were obtained from GenBank(Supplementary Table S1).
To infer the mitochondrial gene tree among sampled congeners, both Bayesian inference (BI) and maximum likelihood (ML) analyses were conducted on the final alignment (Supplementary material (Methods)). To root the resulting mitochondrial gene trees, Acanthosaura lepidogaster and Pseudocalotes species were chosen as the outgroup,following recent higher-level agamid work (Wang et al.,2019b). Uncorrected genetic pairwise distances (P-distances)were also obtained for the coding region of ND2 (1 035 bp) for closely related congeners using PAUP v. 4.0b10 (Swofford,2003).
All specimens were measured by using a digital caliper to the nearest 0.1 mm, except for tail length, which was measured to the nearest 1 mm using a ruler. The morphometric characters were measured following Wang et al. (2018), with some additional morphological characteristics added (Supplementary material (Methods)). Color names and codes follow K?hler(2012).
To examine whether the putative new species occupy distinct morphological spaces with respect to morphologically similar congeners, and whether the morphological clustering coincide with the phylogenetic clades recovered from our molecular data set, Principle Component Analysis (PCA) and Discriminant Analysis of Principle Components (DAPC) were performed. Because all known species of Diploderma are sexually dimorphic (Wang et al., 2019a, 2019b), morphometric data were analyzed separately for males and females.
The resulting topologies from BI and ML analyses are highly consistent, with a few exceptions only where support values are strong in Maximum Likelihood analyses (bootstrap support[BS]>70) but not in Bayesian analyses (posterior probability[PP]<0.95; Figure 2). The genus Diploderma is shown to be a monophyletic group with strong support (Clade A, BS 98, PP 1.00; support values are given in this order hereafter). All recognized species of Diploderma (except D. laeviventre, D.micangshanense, and D. varcoae, which each only has a single individual) are shown as monophyletic with strong support (100/1.00), with two major clades, Clade B (92/1.00)and Clade C (100/1.00), observed within the genus (Figure 2).Within Clade C, all sampled individuals from Yanbian County form a clade (100/1.00). Diploderma dymondi is shown as sister to D. varcoae with strong support (Clade E, 100/1.00;Figure 2), and this whole clade forms a monophyletic group with individuals from the Yanbian population (Clade D, 65/0.94;Figure 2).
We observe low intraspecific genetic divergence within the Yanbian population (P-distances of 0.1%-0.3% ;Supplementary Table S2). However, compared to closely related congeners, individuals from the Yanbian population are observed to be 10.9%-13.1% divergent from topotypic D.dymondi, 12.1%-12.4% from D. varcoae, 16.5%-18.0% from D. slowinskii, and 15.6%-16.1% from D. flaviceps(Supplementary Table S2).
For morphometric characters PCA analyses reveal three major components with eigen values greater than one for both males and females, which together captures 81.2% and 81.5% of the total variance, respectively (Supplementary Tables S3, S4). For males, the first major principal component(PC) loads most heavily on the relative tail length (TAL/SVL)and relative head depth (HD/HL); the second major PC loads most heavily on the relative nuchal crest length (TNC/HL) and relative forelimb length (FLL/SVL); and the third major PC loads most heavily on the relative head width (HW/HL)(Supplementary Table S3). For females, the first major PC loads most heavily on relative head depth (HD/HW and HD/HL); the second major PC loads most heavily on relative forelimb length (FLL/SVL) and relative head width (HW/HL);and the third major PC loads most heavily on relative tail length (TAL/SVL) (Supplementary Table S4). For DPAC results, both males and females of the putative new species occupy distinct morphospace with respect to recognized,similar congeners, with no overlap with recognized congeners for the 95%confident intervals(Figure 3).

Figure 2 Phylogenetic relationships among species of the genus Diploderma based on both Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian analyses of mitochondrial DNA(ND2)
For pholidosis and ornamentation characters, individuals from Yanbian and Xichang are phenotypically most similar to D. dymondi and D. slowinskii, with all species possessing exposed tympana, transverse gular folds, and smooth dorsolateral stripes in males. However, the Yanbian and Xichang populations posses a suite of unique morphological characters that differentiate them from both species and all other congeners, including the presence of taller nuchal crests, exposed and relatively smaller tympana, and distinct Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) coloration of the oral cavity and tongue (for details, see comparison section below;Figures 4;Tables 1,2).

Figure 3 PCA (1) and DAPC (2) analyses of relative morphometric measurements for males (A) and females (B) of D. swild sp. nov. and closely related congeners

Figure 4 Comparisons in life of males (1 and 3) and females (2 and 4) of Diploderma dymondi (A) and D. swild sp. nov. (B), showing the different colorations of dorsal and lateral body and oral cavity and tongue

Table 1 Morphological comparisons among species of the Diploderma dymondi complex, including D. dymondi, D. slowinskii, D.varcoae,and D.swild sp.nov.(All measurements are in mm)
Taxonomic account
Diploderma swild sp. nov. Wang, Wu, Jiang, Chen, Miao,Siler, Che (Figures 1, 4 and 5; Tables 1, 2; Supplementary Table S5)
Synonyms:Japalura dymondi Deng et al., 1991: 27. Zhao et al., 1999: 110-111. Zhao, 2003: 82-83. Japalura flaviceps Deng et al., 1991: 27. Zhao et al., 1999: 111-115. Zhao,2003:84.
Holotype:KIZ 034912, adult male from Hongbao Village,Yanbian County, Panzhihua District, Sichuan Province, China(WGS 84, E101.558°, N27.104°, 2 318 m a.s.l.), collected by Ben-Fu Miao on October 15,2017.
Paratype:CIB 1871/105074, adult male from Xichang,Liangshan Prefecture, Sichuan Province, China, collector and collecting time unknown. KIZ 034913, adult female; KIZ 034914, 034894, sub-adult males, collected by Ben-Fu Miao on August 2017. KIZ 040935, adult male, collected by Ben-Fu Miao and Kai Wang on April 10, 2019; KIZ 040124, sub-adult female; KIZ 040125-27, adult females, collected by Kai Wang,Jia-Wei Wu, Gedeng Nima, and Ben-Fu Miao on April 23,2018.
Diagnosis:The new species can be diagnosed from congeners by a combination of the following morphological characteristics: (1) body length moderate, SVL 59.8-71.7mm in adult males, 57.2-76.8 mm in adult females; (2) tail long,TAL 224.4%-239.0% SVL in adult males, 200.4%-221.0% in adult females; (3) hind limbs moderate, HLL 66.9%-78.1%SVL; (4) head length, width, and depth moderate, HL 30.8%-32.5% SVL, HW 64.9%-71.9% HL, HD 50.0%-54.1% HL, HD 73.4%-80.6%HW;(4)MD 35-44;(5)F4S 18-22;(6)T4S 23-27; (7) tympana exposed; (8) tympana moderate in size, TD 26.7%-49.2% OD; (9) nuchal crest tall, clearly differentiated from dorsal crests, TNC 12.0%-12.4% HL in adult males,8.1%-11.8% in adult females; (10) transverse gular fold present, relatively shallow; (11) ventral scales of head and body distinctively keeled; (12) ventral head and ventrolateral body scales largely homogeneous in size with few enlarged scales scattered randomly; (13) gular spots absent in both sexes; (14) dorsolateral stripes distinct in males, smooth edged, Chartreuse (Color 89) in color; faint or indistinct in females, White, Cream Color (Color 12), or Spectrum Yellow(Color 79) in color; (15) ventral body white with Jet Black(Color 300) speckles or with two wide, parallel, Light Yellow Ocher (Color 13) lateral patches distributed from chest to region anterior to vent; and (16) anterior oral cavity and tongue Light Chrome Orange (Color 76), posterior parts of palate marbled Dark Neutral Gray(Color 299).
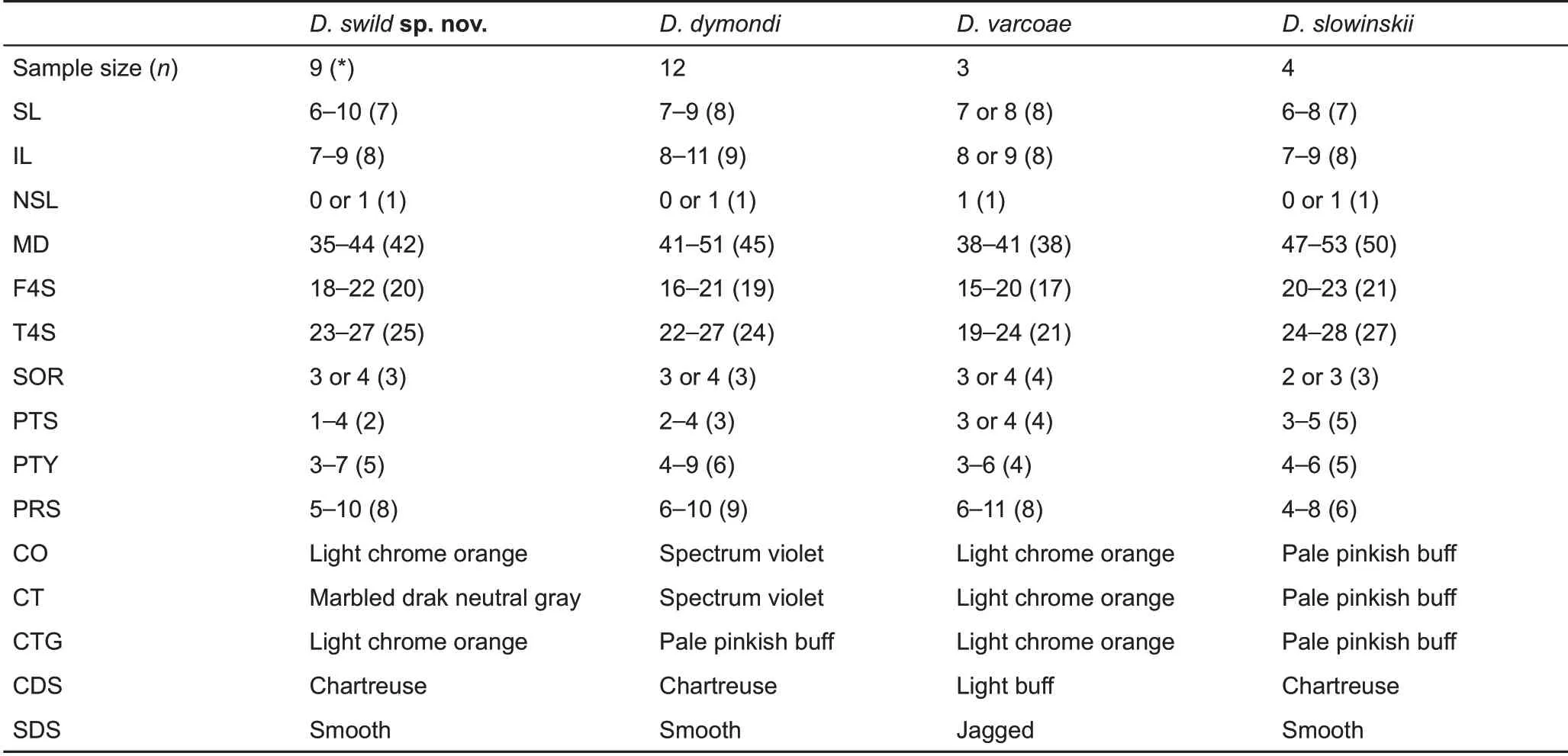
Table 2 Pholidosis and coloration comparisons among species of the Diploderma dymondi complex, including D. dymondi, D.slowinskii,D.varcoae,and D.swild sp.nov.
Comparisons:The new species is morphologically most similar to, and confused historically with, D. dymondi, in which both species have exposed tympana and green, smoothedged dorsolateral stripes in males. However, D. swild sp.nov. can be differentiated from D. dymondi by having relatively taller nuchal crest scales (TNC 12.0%-12.4% HL in males, 8.1%-11.8% in females vs. 4.6%-6.6% in males,4.4%-6.0% in females), smaller tympana (TD 26.7%-49.2%OD vs. 49.4%-61.2%), a distinct coloration of oral cavity(Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) vs. Spectrum Violet (Color 186) or Jet Black (Color 300)), and tongue (Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) vs. Light Flesh Color (Color 250)) (Tables 1, 2), as well as by presence of enlarged scales on the ventral surface of head scales(vs.absent).
Diploderma swild sp. nov. is also similar to D. slowinskii and D. varcoae morphologically, where all three species have exposed tympana. However, the new species can be differentiated from D. slowinskii by having a smaller maximum body size (maximum SVL reaching 76.8 mm vs. reaching 99.5 mm), fewer middorsal scales count (MD 35-44 vs. 47-53), distinct oral coloration in life (Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) vs. Light Flesh Color (Color 250)), and by the presence of distinct, white lip stripes (vs. absent); and from D. varcoae by having much larger nuchal crest scales (TNC 12.0%-12.4%HL in males, 8.1%-11.8% in females vs. 4.0%-7.1% in males,3.8%-6.1% in females), smaller tympana (TD 26.7%-49.2%OD vs. 55.1%-67.3%), different shape and color of dorsolateral stripes in males (Smooth edged, Chartreuse(Color 89) or Yellow Green (Color 103) vs. strongly jagged,Light Buff (Color 2)), different ecology (arboreal vs. terrestrial),and by the presence of a transverse gular fold (vs. absent)(Tables 1,2).
Compared to other members of the same clade (Clade C,Figure 2), the new species differ from D. flaviceps by having a longer tail (TAL>200.4% SVL vs.<193.9%), taller nuchal crests(TNC 12.0%-12.4% HL in males, ≥8.1% in females vs. ≤6.1%in males, ≤5.6% in females), different shape and coloration of dorsolateral stripes in males (smooth edged, Chartreuse(Color 89) or Yellow Green (Color 103) vs. strongly jagged,Cream Color (Color 12)), as well as by the presence of dark distinct radial stripes around eyes (vs. absent), and by the absence of hollow, rhomboid shaped patterns along dorsal midline of the body (vs. present); from D. micangshanense by having exposed tympana (vs. concealed), different shape and coloration of dorsolateral stripes in males (smooth edged,Chartreuse (Color 89) or Yellow Green (Color 103) vs. strongly jagged, Cream Color (Color 12)), a distinct coloration of oral cavity and tongue (Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) vs. Light Flesh Color (Color 250)), and by the presence of a transverse gular fold (vs. absent); from D. splendidum by having exposed tympana (vs. concealed) and a distinct coloration of oral cavity and tongue (Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) vs. Light Flesh Color (Color 250)); from D. zhaoermii by having exposed tympana (vs. concealed), a distinct shape of dorsolateral stripes in males (smooth edged vs. strongly jagged), a distinct oral coloration in life (Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) vs.Light Flesh Color (Color 250)), and by the absence of distinct gular spots in males (vs. present); and from all island congeners (D. brevipes, D. luei, D. makii, D. polygonatum,and D. swinhonis) by having exposed tympana (vs.concealed) and by the presence of a transverse gular fold (vs.absent).
For congeners in the different Clade (Clade B, Figure 2), the new species differs by having exposed tympana (vs.concealed) and a shallow transverse gular fold (vs. prominent and deep). Additionally, D. swild sp. nov. differs from all members of Clade B except for D. laeviventre (including D.chapaense, D. batangense, D. vela, D. yulongense, and D.yunnanense) by having smooth edged, dorsolateral stripes in males (vs. strongly jagged), and from all but D. chapaense and D. yunnanese by having a distinct coloration of oral cavity and tongue (Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) vs. Light Flesh Color (Color 250)), heterogeneous ventral head scales and ventrolateral body scales (vs. homogeneous), and taller nuchal crests (TNC 12.0%-12.4% HL in males, ≥8.1% in females vs. ≤6.1%). Furthermore, D. swild sp. nov. differs from D. laeviventre by having fewer middorsal scale count(35-44 vs. 57-59), different scale texture of ventral scales(strongly keeled vs. smooth), and by the absence of distinct gular spots in both sexes (vs. present); and from D.chapaense and D. yunnanense by having a transverse gular fold (vs. absent), and by the absence of distinct W-shaped ridges on occipital head (vs. present) and the absence of gular spots(vs.present).
For congeners that do not have genetic data, the new species differs from all by having exposed tympana (vs.concealed). Additionally, D. swild differs from D. brevicaudum by having a much longer tail (TAL≥200.4% SVL vs. ≤150.0%);from D. drukdaypo by having a longer tail (TAL≥200.4% SVL vs. ≤175.1%), distinctively keeled ventral scales (vs. smooth or feebly keeled), and strongly developed nuchal crests (vs.feebly developed); from D. grahami by having strongly developed nuchal crests (vs. feebly developed) and by the absence of grangular scales on the head and body (vs.present); from D. hamptoni by having parallel dorsolateral stripes (vs. diagonally away from dorsal midline toward posterior direction); from D. iadinum by having a longer tail(TAL≥200.4% SVL vs. ≤196.4%), a distinct dorsal coloration(Clay Color (Color 18) to Warm Sepia (Color 40) vs. Yellowish Spectrum Green (Color 128) to Emerald Green (Color 143)), a distinct coloration of oral cavity and tongue (Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) vs. Light Flesh Color (Color 250)), and by the absence of gular spots in both sexes (vs. present); and from D. fasciatum by having a longer tail (TAL≥200.4% SVL vs. ≤180.5%), a distinct coloration of oral cavity and tongue(Light Chrome Orange (Color 76) vs. Light Flesh Color (Color 250)), and different ornamentation patterns on the dorsal bodies in males and females (two smooth edged dorsolateral stripes vs. single hourglass-shaped transverse marking on mid dorsum).
Description of holotype:Medium sized agamid species, SVL 58.84 mm, body not compressed dorsally; tail long, slender,TAL 239% SVL; limbs moderate, forelimb 48.8% SVL, hind limb 78.1% SVL. Head moderate, head width 65.8% head length, head depth 52.0% head length, head depth 78.9%head width; snout relatively long, snout-eye distance 39.2%head length. Rostral rectangular, three times longer than height, separated from nasal by single scale; nasal polygonal in shape, separated from first supralabial by single small scale; supralabials 7/7, each with single, strong, lateral keel,last one longest; supralabials and orbit separated by three scale rows, medial row much larger, all distinctively keeled with lateral keels; supraciliaries 7/7, first anterior three each overlapping one-third of its total length with succeeding one,remaining ones overlapping between one-third to one-fourth of their length; two distinctively enlarged, sub-pyramidal shaped scales posterior-superior to orbit, with anterior one more laterally elongated; enlarged, convex, keeled scales between posterior orbit and anterior tympanum, 7/8, forming lateral ridge between orbit and tympanum on each side;tympana exposed, somewhat oval in shape, relatively small,TD 42.2% OD; enlarged, conical scales posterior-superior to tympana,well developed,4/5.
Dorsal head scales mostly homogeneous in size and shape, with few ones distinctively enlarged and randomly distributed, all scales distinctively keeled; four enlarged,keeled scales forming Y-shaped arrangement on dorsal snout anterior to orbit, with tip of such Y-shaped arrangement three small scales posterior to rostral; interparietal spear-tip in shape, with tip pointing posteriorly, parietal eye indistinct; 5/6 enlarged, convex scales in C-shaped arrangement on each side of temporal head, with opening of C-shaped arrangements facing each other and symmetrical along dorsal midline; single, distinctively raised, conical scale on lateral temporal region on each side, superior to lateral ridge between orbit and tympanum; enlarged, raised, conical scales post-occipital on each side of head,well developed,2/3.
Dorsal body scales distinctively keeled, heterogeneous in size and shape; nuchal crest 11, in tall triangular shape,clearly differentiated from dorsal crest; dorsal crest highly serrated, well developed, differentiated from remaining dorsal scales; middorsal scale count 38; distinctively enlarged dorsal body scales somewhat conical in shape, tips raised at posterior ends; some enlarged dorsal body scales arranged in two paravertebral rows on each side of body, with first row about single scale-row away from dorsal crest, second row along superior border of dorsolateral stripe, further away from dorsal crest; remaining enlarged dorsal scales scattered randomly. Dorsal forelimb scales homogeneous on upper arm,heterogeneous on lower arm, with few enlarged, subpyramidal scales on posterolateral side; dorsal hind limb scales heterogeneous, with enlarged conical scales on posterolateral thigh.
Mental pentagonal in shape, in contact with first pair of supralabials and chin shields; chin shields 7/8, two or three scale rows separated from infralabials; infralabials 8/9, each bearing single, strong, lateral keel; remaining ventral scales distinctively keeled, largely homogeneous in size and shape;small number of enlarged scales scattered randomly on posterior half of ventral head, largest of these roughly three times size of nearby background scales; post-rictal conical scales 10/7, distinctly enlarged and raised, resulting in spiky appearance. Gular pouch present, distinct in life, indistinct after preservation; lateral gular fold present in life, absent after preservation; transverse gular fold present, shallow. Ventral body scales distinctively keeled, largely homogeneous in size and shape, with small number of enlarged scales scattered on ventrolateral body only. Ventral limb scales largely homogeneous in size and shape, all distinctively keeled;Finger IV and Toe IV longest; subdigital lamellae well modified, 20/21 beneath Finger IV, 25/24 beneath Toe IV. Tail scales distinctively keeled,carinate in lateral rows.
Coloration of holotype in life:The background color of the dorsal surface of the head is Straw Yellow (Color 53). Four distinct, Jet Black (Color 300) transverse patterns are scattered evenly between the snout and the posterior margins of the orbits on the dorsal surface of the head. The anterior most pattern is U-shaped, compared with the remaining patterns which are X-shaped. Irregular, Jet Black (Color 300)pigmentation patterns are present on the occipital and temporal regions of the head. Distinct, Jet Black (Color 300)radial stripes are present around the eyes, 10/10, with two inferior stripes below the eyes intercepting with the white lip stripe on each side of the head. Within the oral cavity, the anterior parts of the roof, sides of the mouth, and the tongue are Light Chrome Orange (Color 76), and the posterior parts of the palate and visible parts of the deep throat are marbled Dark Neutral Gray(Color 299).
Two smooth-edged, dorsolateral stripes run from the occipital region of head to the pelvis, one on each side. The most anterior parts of the dorsolateral stripes from the neck to the pectoral region are white, which then sharply transition to Chartreuse (Color 89) posteriorly. The dorsal region of the body between dorsolateral stripes is nearly uniform Sepia(Color 286), with some fade, Jet Black (Color 300), triangular patterns. The background coloration of dorsal limbs and lateral surfaces of the body inferior to the dorsolateral stripes is Olive Brown (Color 278). Straw Yellow (Color 53), Medium Lime Green (Color 115), or White scales are scattered randomly on lateral surfaces of body inferior to dorsolateral stripes. Straw Yellow (Color 53) or Buff (Color 5) colored scales are arranged in transverse bands on dorsal surfaces of forelimbs and hind limbs. A distinct white stripe is present on the ventrolateral surface of thigh on each side, extending from pelvis to two third of the thigh. The background coloration of dorsal and lateral surfaces of the tail is uniform Sepia (Color 286). Four Light Buff (Color 2) bands are evenly distributed on the anterior half of the tail and gradually become indistinct posteriorly. The ventral surfaces of head, limbs, and body are uniform white with no distinct ornamentations. The ventral surface of the tail is uniform Light Buff(Color 5)(Figure 4).
Coloration of holotype in preservation:Although ornamentation structure remains largely the same following preservation, most coloration fades in intensity and shade.Specifically, the Jet Black (Color 300) transverse patterns on the dorsal surface of head fade and become Raw Umber(Color 22), the Chartreuse (Color 89) dorsolateral stripes become Pale Cyan (Color 157), the Medium Lime Green(Color 115) scales of lateral body become Cyan White (Color 156), and the Sepia (Color 286) color of the dorsal body and limbs becomes Olive Color(Color 16)(Figure 5).
Variations:Detailed morphometric and pholidosis variation are summarized in Supplementary Table S5. Like other congeners, sexual dimorphism is evident in D. swild sp. nov.,where males (KIZ 034912, 040935, CIB1871/105074) differ from females by having a longer tail (TAL 224.4%-239.0%SVL in males vs. ≤221.0% in females), taller nuchal crest(TNC 12.0%-12.4% HL in males vs. 8.1%-11.8% in females),and distinct coloration and ornamentation, including differences in lateral body ornamentation (almost uniform Olive Brown (Color 278) or Clay Color (Color 20) in males vs.white, Chamois (Color 84), or Light Greenish Yellow (Color 87)with Sepia (Color 279) or Jet Black (Color 300) reticulated patterns in females), dorsolateral stripes (distinct, smoothedged, Chartreuse (Color 89) in male vs. indistinct, jagged,white, Cream Color (Color 12), or Spectrum Yellow (Color 79)in females), gular coloration (uniform white in males vs.uniform white, Cream Yellow (Color 82), or Dark Spectrum Yellow (Color 78) with few black speckles in females), and coloration of ventral body (white in males vs. speckled white or speckled white with two parallel, Light Yellow Ocher (Color 13)lateral patches in females).
Etymology:The specific name "swild", which is a noun, is derived from the name of the Chinese Conservation Organization, Swild Studio (西南山地工作室). We name the species after the organization in honoring its continuous contributions on promoting citizen science, nature photography, and public outreach on the wildlife conservation in Southwest China, particularly in the Hengduan Mountain Regions where the new species is native. Suggested English Common Name: Swild Mountain Dragon; Suggested Chinese Common Name:山地龍蜥(Pinyin:Shan Di Long Xi).
Natural history:The new species is arboreal, inhabiting broad-leaf forest at elevation between 1 800-2 200 m a.s.l.(Figure 1). To date, the new species has been collected from the type locality in Yanbian County and Xichang of Liangshan Prefecture, Sichuan Province only, but individuals were also recorded from Huili County, further east from the type locality(personal communication). Although the type locality of the species is protected by the Ertan National Natural Reserve,much of the protected area is at high elevation where the species is far less abundant. As little is known about the distribution range other than few isolated localities, we propose to list the species as Data Deficient (DD) for IUCN assessment, and we call for future ecological study to determine its conservation status.
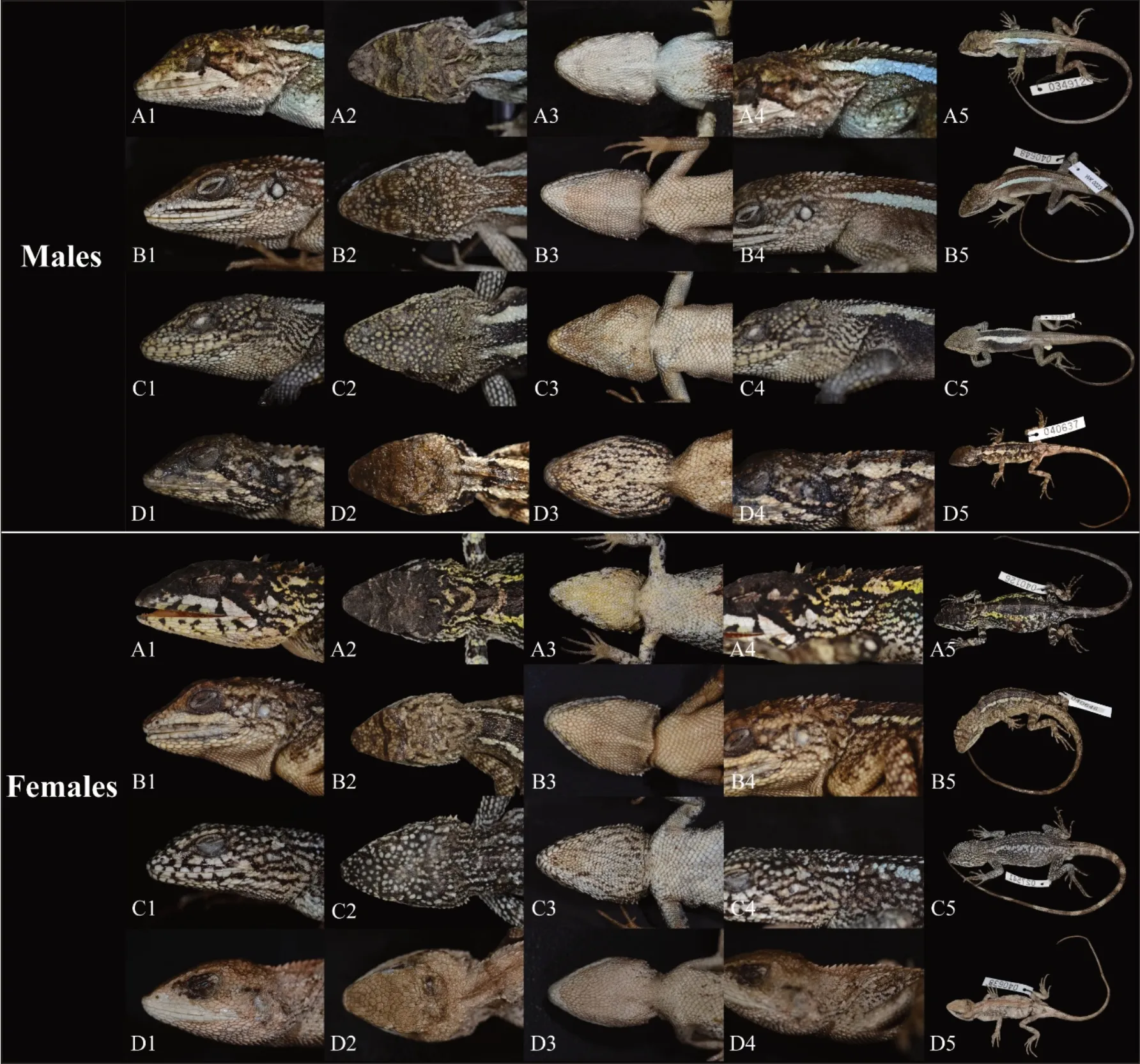

Figure 5 Comparisons between males and females of Diploderma swild sp. nov. (A), D. dymondi (B), D. slowinskii (C), and D. varcoae (D)in preservative, depicting differences in the lateral (1), dorsal (2), and ventral (3) head regions, the nuchal crest (4), and in overall body ornamentation(5)(Photos by Kai Wang)
Individuals were observed foraging both on trees and on the ground during the day, but only resting on twigs or thin stems of bushes at night from about 1 m to 2-3 m above ground(Figure 1). Road-killed individuals are common at the type locality, especially at low-elevation site (about 1 200 m a.s.l.).Possible predators may be lizard-eating snakes such as Ptyas nigromarginatus, Lycodon liuchengchaoi, and Elaphe carinata,which are all common at the type localities. No sympatric distribution between the D. swild sp. nov. and D. dymondi were observed in the field. Based on our field surveys, the new species inhabits the moister, montane area that is further away from the much dryer main course of the Jinsha River,where D. dymondi inhabits (Figure 1). Such differences in abiotic habitat may indicate ecological divergence between the two otherwise similar species. Further ecological studies are needed to gain a better understanding on the ecology of these mountain dragons in this region.
NOMENCLATURAL ACTS REGISTRATION
The electronic version of this article in portable document format represents a published work according to the International Commission on Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN),and hence the new names contained in the electronic version are effectively published under that Code from the electronic edition alone (see Articles 8.5-8.6 of the Code). This published work and the nomenclatural acts it contains have been registered in ZooBank, the online registration system for the ICZN. The ZooBank LSIDs (Life Science Identifiers) can be resolved and the associated information can be viewed through any standard web browser by appending the LSID to the prefixhttp://zoobank.org/.
Publication LSID:
urn: lsid: zoobank. org: pub: 31EEFAD0-0452-44DD-B60E-
66360C922836
Diploderma swild LSID:
urn: lsid: zoobank. org: act: 2CB71FB0-D2C7-4215-9BA0-7C954BE49CBA
SCIENTIFIC FIELD SURVEY PERMISSION INFORMATION
Permission for field surveys in Sichuan Province was granted by the Forestry Department and National Reserves of China.Project approval (BBCJ-2014-001) was issued by the Kunming Institute of Zoology,Chinese Academy of Sciences.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary data to this article can be found online.
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
AUTHORS'CONTRIBUTIONS
K.W., J.W.W., and B.F.M. collected specimens in the field. K.J. supervised the morphological data collection. K.W. and J.M.C. collected morphological data. K.W. conducted genetic analyses and submitted to GenBank, which was supervised by C.D.S. and J.C.. K.W. wrote the manuscript with inputs from other authors.C.D.S.and J.C.revised the manuscript.All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank D. Hollis (ROM) for editing the English language of the manuscript; Mr. J. Ren for taking photographs at CIB; Mr. G. Nima and Mr.L. He for their great assistances in the field; Dr. V. Deepak for his helps in examining specimens and taking photographs; Drs. Y. Wang and J. Li(CIB), Drs. R. Brown and L. Welton (KU), Mr. W. Addison (NMNH), Mr. J.Vindum and Ms. L. Scheinberg (CAS), and Drs. J. Hanken and J. Losos(MCZ) for their great supports in allowing us examine specimens or facilitate specimen loans.
- Zoological Research的其它文章
- Nest sanitation facilitates egg recognition in the common tailorbird,a plaintive cuckoo host
- Postural effect on manual laterality during grooming in northern white-cheeked gibbons(Nomascus leucogenys)
- Non-invasive genetic analysis indicates low population connectivity in vulnerable Chinese gorals:concerns for segregated population management
- Genetic diversity and temporal changes of an endemic cyprinid fish species,Ancherythroculter nigrocauda,from the upper reaches of Yangtze River
- Immunodetection of ephrin receptors in the regenerating tail of the lizard Podarcis muralis suggests stimulation of differentiation and muscle segmentation
- A soluble FcγR homolog inhibits IgM antibody production in ayu spleen cells

