Recurrent aggressive mesenteric desmoid tumor successfully treated with sorafenib: A case report and literature review
Aikaterini Mastoraki, Dimitrios Schizas, Chrysovalantis Vergadis, Leon Naar, Alexios Strimpakos,Michail G Vailas, Natasha Hasemaki, George Agrogiannis, Theodore Liakakos, Nikolaos Arkadopoulos
Aikaterini Mastoraki, Leon Naar, Alexios Strimpakos, Nikolaos Arkadopoulos, 4th Department of Surgery, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Attikon University Hospital, Athens 11527, Greece
Dimitrios Schizas, Michail G Vailas, Natasha Hasemaki, Theodore Liakakos, 1st Department of Surgery, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Laikon Hospital, Athens 11527,Greece
Chrysovalantis Vergadis, Department of Radiology, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Laikon Hospital, Athens 11527, Greece
George Agrogiannis, 1st Department of Pathology, National and Kapodistrian University of Athens, Athens 11527, Greece
Abstract
Key words: Desmoid tumor; Aggressive fibromatosis; Case report; Pathogenesis;Therapeutic approach; Sorafenib treatment
INTRODUCTION
Desmoid tumors (DT), also known as aggressive fibromatosis, are locally advanced although histologically benign monoclonal neoplastic disorders composed of multiplying differentiated fibroblasts. They may derive from any musculoaponeurotic structure and can arise sporadically or in association with familiar adenomatous polyposis (FAP), especially with Gardner's syndrome[1,2]. DTs are classified according to their potential intra-abdominal, abdominal wall or extra-abdominal location,whereas pathological findings are identical[3,4]. The incidence of aggressive fibromatosis in the general population is approximately 2-4/1,000,000 and is typically diagnosed in young adults[5-8]. DT pathogenesis has been associated with mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene or the beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1)[9,10].Sex steroids, especially high estrogen levels, have been considered to be major determinants of tumor development. Co-relation with previous surgical trauma has also been described[11,12]. Despite benign biological behavior, DTs can be virulent,infiltrative or destructive, and often recur after excision, although their metastatic potential is limited. Both the morbidity and mortality of abdominal desmoid disease is highly dependent on its location. Therefore, desmoid evolution remains unpredictable. Some lesions grow rapidly, while others are stable or regress with either medical treatment administration or spontaneously[3,9]. A diagnostic approach is initially accomplished with ultrasonography in order to assess the tumor's site, size,margins, contour echogenicity and homogeneity. However, computed tomography(CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) play a pivotal role in evaluating the size and extension of DTs, as well as the potential involvement of adjacent structures[4].Local treatment options, such as surgery or radiotherapy (RT), are implemented in aggressively progressing or symptomatic patients[13,14]. Nevertheless, surgery remains the only potentially curative approach for extra-abdominal and abdominal wall desmoids, which is not recommended for intra-abdominal lesions because of the high recurrence rates[15]. Dacarbazine-doxorubicin administration is a hopeful therapeutic option against DTs, while several pharmacological agents have successfully been tried, including anti-estrogens, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs),imatinib mesylate, sunitinib and sorafenib[16,17]. Finally, multivisceral transplantationin selected patients in whom curative/cytoreductive surgery or conservative treatment proved insufficient can offer long disease-free intervals, relief of symptoms and even cures[18]. The aim of this investigation was to elucidate an uncommon clinical case of infiltrating intra-abdominal DT. Relevant literature is briefly presented.Clinical features, histological and immunochemical findings are discussed, while the role of current diagnostic and therapeutic options of this rare entity are commented upon.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
A 36-year-old man was admitted with increasing colicky abdominal pain, bloating and a self-palpable mass in his left abdomen.
History of present illness
The patient arrived at our emergency department with general malaise and reported loss of weight.
History of past illness
The patient referred to a past medical history of upper lip neuroblastoma at the age of 5, which was treated by surgical excision and adjuvant chemotherapy. Fourteen years earlier, he was diagnosed with a large intra-abdominal tumor in the left hypochondrium, which adhered to - but did not incarcerate - the left colonic flexure,part of the major gastric curvature, as well as the spleen. The patient underwent tumor resection along with left colectomy, splenectomy and partial gastrectomy. Final biopsy indicated the presence of a DT.
Physical examination
Physical examination confirmed a firm, tender mass in the left hypochondrium.
Laboratory testing
Clinical investigation revealed a recrudescence of symptoms of anemia, as well as marked leukocytosis.
Imaging examination
Abdominal MRI revealed tumor recurrence with a large epigastric mass (maximum section 12.5 cm × 4.5 cm), which adhered to the transverse colon and the lower duodenal segment, and seemed to communicate via tissue bridging with a second abdominal lesion (7.3 cm × 4.6 cm) along the lower third of the right kidney (Figure 1). Metastatic foci were not apparent. Moreover, the liver presented diffuse focal lesions, hyperintense on T2- and hypointense on T1-weighted sequences, while contrast enhancement was present (Figure 2). Endoscopy described multiple polyps in the cecum, the ascending and the sigmoid colon, as well as the rectum. Nevertheless,incarceration of the upper or the lower gastrointestinal (GI) tract by the mass or nodal involvement was not documented.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The final histological diagnosis was recurrent aggressive intra-abdominal DT.
TREATMENT
As the tumor was highly proliferative, exploratory laparotomy was scheduled. This revealed the presence of a voluminous mass in the epigastrium arising from the posterior surface of the stomach and invading the superior mesenteric vessels,transverse mesocolon and the small bowel mesentery. As the surgical team estimated that the tumor was unresectable, a jejunojejunal bypass was performed in order to alleviate the patient's symptoms. Biopsies from both the epigastric mass and the liver were taken for histological identification. Microscopic examination of the specimen obtained from the tumor revealed spindle cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm,surrounded by a collagen network. Immunohistochemically, the tumor cells were positive for β-catenin and HHF-35, and negative for SMA, calponin, desmin,caldesmon, CD34, CD117 and DOG-1 (Figure 3). The histological findings of the hepatic lesions were consistent with focal nodular hyperplasia.

Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging revealed a mesenteric mass with heterogeneous intermediate and high signal intensity on T2-weighted images with parallel infiltration of surrounding small bowel loops.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
Postoperative course was uneventful, and monotherapy with doxorubicin as initiation treatment was warranted. The patient's tumor remained stable, and a subsequent conservative therapeutic approach with tamoxifen and NSAIDs (ibuprofen) was also implemented. Again, there was no documented tumor response, and the patient was started on sorafenib. After one year of treatment with sorafenib, a full response was noted with liquification of this voluminous abdominal mass (Figure 4).
DISCUSSION
DTs were first described in 1832 by MacFarlane[7], and the term originated from the Greek word “desmos” referring to a band or tendon-like stability. Histologically, the lesions arise from fascial or deep musculoaponeurotic structures, thus verifying their mesenchymal origin. As they can occur anywhere in the body, they can be classified as extra-abdominal, abdominal wall, and intra-abdominal types[2-4]. The worldwide incidence of these tumors is markedly low, and they comprise approximately 0.03% of all neoplasms and 3.5% of all soft tissue tumors[5]. DTs may appear at any age, with a peak prevalence between 25 and 40 years and a 2-3 fold female predominance[8,9]. We herein report the case of a 36-year-old male patient with a recurrent intra-abdominal DT, which was defined as unresectable because of its large volume and intensive infiltration of the surrounding major vascular structures that, after the failure of many regimens, responded optimally to sorafenib.
Although DT's exact etiology is still vague, and most of them arise sporadically,approximately 2% are associated either with FAP, caused by mutation in the APC gene that is located in chromosome 5q21, or Gardner's syndrome[19,20]. DTs affect 10-25% of FAP patients, with a 1,000-fold increase in the risk of developing this neoplasm[10,15]. Although extremity desmoids can also occur, most patients develop abdominal tumors, one-half of which are intra-abdominal, with the remainder involving the abdominal wall[9]. Identified risk factors include prior abdominal surgery, typically prophylactic colectomy, localization of the APC germline mutation,female sex, and a family history of DT[4,6]. These tumors are responsible for 10-14% of deaths in FAP-affected patients, making them the second leading cause of mortality after colorectal adenocarcinoma[8,10]. DTs have also been associated with episodes of antecedent trauma. Up to 30% of patients refer a history of abdominal or pelvic surgical intervention[11]. Finally, high estrogen levels have been detected in affected patients. Extra-abdominal as well as abdominal DTs tend to occur in women of childbearing age, during or following pregnancy. Trauma related to the pregnancy,including a scar from a prior Cesarean section and exposure to elevated hormone levels, may be contributory[2,4].
Molecular pathophysiology in DTs indicates aberrations involving the Wnt/βcatenin pathway. Relevant alterations include mutations in either the APC or CTNNB1 genes[21,22]. Mutations in CTNNB1 have been defined in sporadic DTs with variable prevalence (39-87%)[23]. In the absence of Wnt protein, β-catenin is bound by a''destruction complex" that mainly involves the protein kinases CK1γ and GSK-3β.This complex targets β-catenin for phosphorylation, ubiquitination and degradation in the proteasome[24,25]. The majority of germline and sporadic mutations in the APC gene contribute to premature truncation of the APC protein and deprivation of the β-catenin regulatory domain, resulting in increased levels of the related protein.Moreover, non-phosphorylated β-catenin translocates to the nucleus where, along with other molecules, it activates the transcription factor TCF-4, increasing the expression of genes such as CYCD1 and MYC, and thereby promoting proliferation and enhanced survival[26-28]. Therefore, CTNNB1 gene mutations have been assessed as the most common alteration in DT development. In our patient, a specific germline mutation in the APC gene or family history of desmoid disease has not been elucidated.
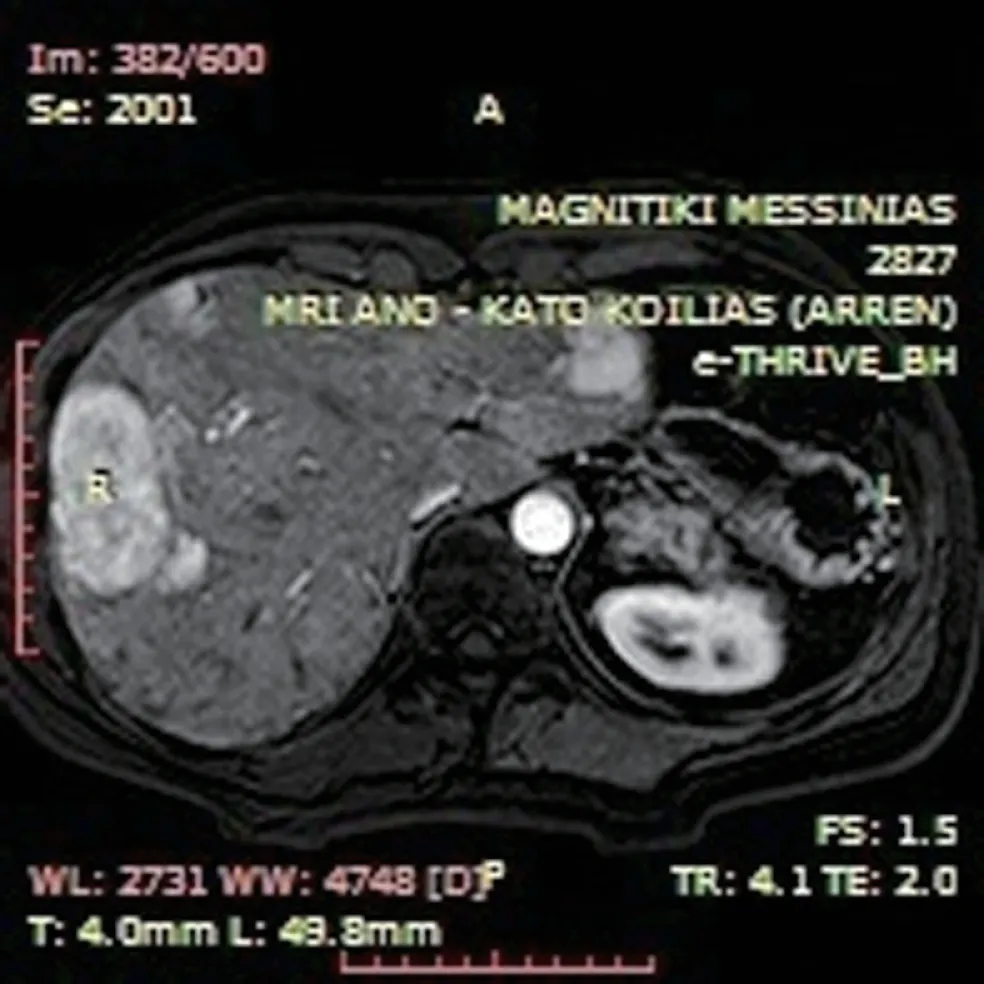
Figure 2 T1-weighted axial arterial phase post intravenous gadolinium administration image indicative of multiple hypervascular liver lesions compatible with focal nodular hyperplasia.
Most DTs present as a deeply seated painless or minimally painful mass with a history of slow growth. Although the lesions may affect any skeletal muscle, they often develop in the anterior abdominal wall and shoulder girdle. Peripheral DTs are stable, smooth and mobile. They often adhere to surrounding structures without signs of infiltrating the overlying skin. Intra-abdominal DTs are usually large neoplasms that remain asymptomatic until their size augmentation provokes visceral compression. Symptoms of intestinal, ureteric, vascular, or neural obstruction may be the initial clinical manifestations. Pain, functional impairment, perforation of a hollow viscus, fistulas, intratumoral hemorrhage and other life-threatening complications appear as the results of local infiltration[1,3]. Notably, despite their locally aggressive and invasive nature, they do not demonstrate metastatic potential. Therefore,morbidity and mortality of the intra-abdominal desmoids depend highly on their site of occurrence, potential local infiltrative growth and tissue invasion[7,9]. In our study,the patient presented with progressing episodic abdominal pain and indigestion.Furthermore, significant loss of weight, along with a palpable mass in the abdomen,has been noticed.
CT and MRI remain the most commonly used modalities for the diagnosis of DT.On CT scans, myxoid stroma is depicted hypodense, while the collagenous component is presented as homogenous, dense soft-tissue. MRI characteristics are variable and relative to their cellularity and fibrous content. With the administration of gadolinium, DTs typically show moderate to marked enhancement, and the hypointense bands may become more apparent as collagen bundles are not enhanced by contrast material. Notably, the higher the signal intensity on T2-weighted imaging is, the more rapidly the tumor is growing. MRI is superior compared to a CT scan in elucidating the pattern and the extent of tumor development, along with revealing any recurrence. Furthermore, MRI is implemented to define a potential tumor's relation with adjacent structures in order to predict resectability; it is therefore considered the imaging modality of choice[29].
Actual guidelines for the treatment of DTs and their optimal management remain enigmatic. Due to the natural history of the disease, with some tumors remaining stable or spontaneously regressing, a wait-and-see policy for non-progressing or asymptomatic patients is a widely accepted strategy[30,31]. However, given the infiltrative growth of many mesenteric DTs, local treatment modalities are usually initially considered for aggressively progressing or symptomatic patients[32-35].Complete surgical removal of the tumor with negative microscopic margins is the standard therapeutic approach. However, this ideal goal might be unfeasible if the sacrifice of vital anatomic structures is required[36,37]. Morbidity after attempted resection is substantial, and includes bowel ischemia, adhesions and resultant obstruction, fistula formation and short bowel syndrome. In addition, recurrent disease is often more aggressive compared to the initial desmoid[38-40]. Growth factors released post-operatively, during the initial phase of wound healing, possiblytransmit signals that reinforce the activation of β-catenin, and thus surgical excision could act as a tumor enhancer in subgroups of DTs. Moreover, resection does not appear to affect survival, while the contribution of incomplete excision to local recurrence is unclear. In fact, some series report higher recurrence rates with close or positive resection margins, while recent investigations suggest that the risk of recurrence is independent of margin status[3,14]. Therefore, the overall surgical strategy should be an attempt for complete removal using a function-preserving surgical approach[5]. Finally, one study reported the use of multivisceral transplantation as a treatment option for intra-abdominal DTs that were otherwise unresectable[18]. The authors concluded that despite potential complications, the perioperative mortality was low, but it should be limited to low-grade slow-growing tumors. In our specific case, the tumor was defined as unresectable by the surgical team, and the patient underwent jejunojenunal bypass as a symptomatic treatment.
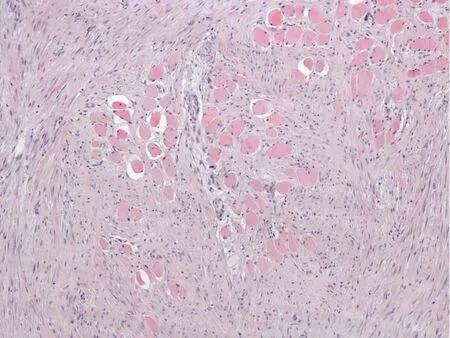
Figure 3 Desmoid type fibromatosis infiltrating the surrounding muscle fibers. Eosin - hematoxylin, × 100 magnification.
The role of RT in the management of DTs is also a subject of controversy. While many surveys have demonstrated durable local control of the disease when RT is used either before or as an adjunct to surgery, rarely is it an option for intraabdominal desmoids because of the risk of developing radiation enteritis[41,42].Therefore, effective alternative medical therapies are required so as to improve the clinical outcome of patients with tumors that are not amenable to surgical intervention. To date, several systemic treatments have been attempted. In particular,the usual first-line approach for these tumors is the administration of NSAIDs, such as sulindac. NSAIDs appear to constrain the activity of β-catenin in malignant cell lines with parallel induction of its degradation. The efficient blockade of the β-catenin pathway results in significant and durable cytoreduction, thus inhibiting the development of some DTs and obviating the need for a surgical procedure[11,12].Furthermore, as DTs are considered hormonally responsive, anti-estrogen agents,such as toremifene and tamoxifen, have been proposed alone or in combination with sulindac[6,7]. Nevertheless, the risk of their side effects, like flushing, headache and bleeding, as well as the necessity to associate contraception and anti-thrombotics at curative doses, represent evident disadvantages.
In cases where conservative treatment has failed, cytotoxic chemotherapy should be considered. Dacarbazine (DTIC) - doxorubicin (DOX) therapy is a hopeful therapeutic option in comparison with other agents including prednisolone, interferon,vinorelbine, vinblastine and methotrexate, and has been suggested as an effective therapeutic strategy to postpone the progression of life-threatening, unresectable and fast-developing mesenteric DTs[8,10,16]. DOX interferes with the expression of topoisomerase II, while DTIC is an N-methyl-type molecule that induces alkylating species. Serious adverse effects of this protocol have been documented with regard to myelosuppression and heart failure due to DOX[16]. This is the reason why lower doses are currently recommended, along with careful monitoring for blood toxicity and heart dysfunction. Finally, for patients who cannot tolerate first-line cytotoxic chemotherapy, receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitors, such as imatinib mesylate and sunitinib malate, have been reported to exert effective local control in the salvage management of unresectable DTs[13,39]. It has been suggested that this kinase-targeting therapy might be a feasible treatment of aggressive fibromatosis via blockade of platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)-α and PDGFR-β activation. The most frequent toxicities include thrombocytopenia, anorexia, diarrhea and hand-foot syndrome. There is also an increased risk of GI bleeding or perforation. On this basis,RTK inhibitors may be of clinical benefit in patients with advanced disease[5,13].

Figure 4 Computed tomography depiction of full disease response with liquification of the voluminous abdominal mass after one year of treatment with sorafenib.
Furthermore, in accordance with recent surveys, two investigational drugs targeting β-catenin are of major importance: tegatrabetan (BC-2059) and the gammasecretase inhibitor PF-03084014. In vitro, tegatrabetan directly stimulates β-catenin degradation. In culture, tegatrabetan promotes the apoptosis of DT cells. The gammasecretase inhibitor PF-03084014 stimulates the Notch pathway, which interacts with and secondly regulates the Wnt/APC/β-catenin pathway[43]. As reliable and validated predictive and prognostic factors have not yet been identified, there is no agreement on the treatment in cases of progressive DTs. Nevertheless, at least two new investigational drugs targeting the Wnt/APC/β-catenin pathway are currently being developed, while high rates of objective responses among affected patients have been reported.
CONCLUSION
The literature is limited when it comes to the subject of sorafenib utilization in patients with DT. In their study, Gounder et al[17]addressed the utilization of sorafenib in intra- and extra-abdominal DTs. After treatment initiation, patients had a clinical benefit superior to imatinib, with a reduction in pain and the need for analgesic use.This benefit was mostly noted in the patient subgroup with extra-abdominal masses.The same subpopulation also showed a better radiologic response to sorafenib when compared to patients with intra-abdominal masses[17]. Furthermore, results coming from a patient diagnosed with mammary DT showed that, similar to our case,sorafenib initiation after the failure of many traditional regimens achieved a significant arrest in tumor growth with a decrease in size, elucidated from the first months of treatment. In addition, the discontinuation of sorafenib after 1.5 years, due to tumor stability, reversed this effect with immediate tumor progression[44]. Based on the above, our case is important because it strengthens the existing data about sorafenib utilization in DTs, and at the same time documents an unprecedented response in a patient with a prior voluminous, unresectable, intra-abdominal DT.

