Utilizing gastric cancer organoids to assess tumor biology and personalize medicine
Miranda Lin,Mei Gao,Michael J Cavnar,Joseph Kim
Abstract
Key words: Organoids; Gastric cancer; Cancer models; Drug sensitivity; Drug screening;Personalized medicine
INTRODUCTION
The incidence of gastric cancer (GC) has declined due to global improvements in sanitation,hygiene,and food preservation,and there has been a corresponding decrease in mortality with the implementation of early detection strategies[1,2].However,GC remains the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide,with a low 28% 5-year survival rate[1,3].Although surgical techniques such as D2 lymph node dissection have improved survival for patients with early or localized disease,there is still an urgent need to increase the number of effective therapies available to patients with advanced GC[4].
A variety of cancer models have been developed to bring new therapies to the clinic.The traditionalin vitrocancer model used to screen novel therapies is the cancer cell line (CCL)[5].CCLs are rapid-growing cancer models that are derived from a single patient and immortalized[5].CCLs have the advantage of quick development while producing abundant biological material for testing novel therapies,however due to serial passaging and wide distribution over many generations,they develop extensive chromosomal changes and lose the ability to accurately model the original primary tumor[6].Additional drawbacks include the two-dimensional nature of this cancer model and lack of structural modeling.Thus,CCLs do not meet the need for a cancer model that represents the molecular profile and three-dimensional architecture of the primary tumor.
After screening of potential new therapies in CCLs,drugs that show the most promise typically undergo testingin vivo.Patient-derived tumor xenograft (PDTX)models are the gold standardin vivomodel,created from either subcutaneous or orthotopic implantation of CCLs or patient tumor tissues into animals[7].PDTXs are beneficial in that they accurately represent genotypic and phenotypic characteristics of the primary tumor as well as interactions with the microenvironment.However,they are quite costly and require a lengthy amount of time to create,limiting their ability to provide immediate clinically actionable data[7].
Recent studies have demonstrated the potential of using next generation sequencing to predict optimal therapies for individual patients through identification of driver mutations and use of targeted therapies[8].However,sequencing can be restricted by tumor tissue availability from the patient,cost,time,and the lack of targeted drugs for cancers that do not harbor driver mutations,or when the corresponding targeted drug has not been developed[9].Thus,there is an important need for an appropriate cancer model that is able to address these limitations and identify the most effective therapy for individual patients with currently available drugs in a timely manner.
Patient-derived organoids are three-dimensionalin vitrohuman model systems that recapitulate disease development[10].The architecture of a typical GI organoid resembles the organ from which it has been derived and maintains its genomic profile[10].Organoids present an accurate model that provide quicker turnover for experimental procedures and yield results in a shorter period of time than traditional human cancer models.The first gastric organoid culture was developed in 2010 to model the self-renewing and proliferative capacity of Lgr5+vestem cells in the gastric pylorus[11].Since then,organoids have also been successfully created from GC specimens to study oncogenic events and drug sensitivities[12-15].GC organoids provide the potential to aid development of new therapies and more importantly to test and predict which therapies may work best in GC patients.
In this review,we provide a detailed description of current strides and benefits of GC organoid technology.A brief description of GC organoid culture will be followed by analysis of organoid representation of primary tumor histology,morphology,and heterogeneity,as well as organoid modeling of the subtypes of GC and carcinogenesis.This review will also discuss GC organoids as a vehicle for drug sensitivity testing and biobanking,and finally,describe investigations utilizing GC organoid technology for personalizing therapy and the promise of clinical trials using GC organoids to predict therapies for individual patients.
ORGANOID CULTURE
GC organoids can be propagated from surgically resected specimens or biopsies,and various methodologies have been proposed for their successful creation[12-16].In brief,tumor specimens are washed and centrifuged,and then minced and digested into small pieces (2-5 mm2)[16].From our experience,surgical specimens require extensive manual mincing with a scalpel and enzymatic digestion from muscle layers,while biopsies require no enzymatic digestion and only light applied pressure on a microscope slide (Figure 1)[12].Once the cells are isolated,they are then suspended in matrigel,a basement membrane matrix extracted from Englebreth-Holm Swarm mouse tumors and containing the extracellular matrix components laminin,type IV collagen,and enactin[17].Matrigel provides a gelatinous matrix for organoids to elongate and proliferate three-dimensionally.GC organoids are overlaid with organoid medium,which consists of Advanced Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium/F12,Glutamax,HEPES,and penicillin/streptomycin (Figure 2)[18].Additionally,specific factors important for gastric epithelial cell proliferation and maturation are added to promote growth of organoids,including Wnt3A,R-spondin,Noggin,hEGF,hFGF10,and gastrin (Figure 2)[10].Once plated in wells and enriched in medium,organoids are incubated at 37oC and 5% CO2[16].
Initially,GC organoids appear as clumped cells in the three-dimensional matrix.In 3-4 days,they develop into a spherical cystic body surrounded by differentiated cells,including stem cells,mucinous cells,gastric pit cells,and endocrine cells (Figure 3)[10].If the culture is healthy,GC organoids produce buds and replicate (Figure 4).Once highly confluent,organoids are passaged,i.e.,they are digested and resuspended in matrigel into additional wells.Passaging allows cultures to grow and cultivate for many months,producing substantial biological material for testing or freezing for later use[10,14,15].
ACCURATE MODELS OF GC
Retention of primary tumor characteristics and representation of tumor morphology
The current gold standardin vitromodel of GC has been the CCL[5].However,CCL cultures consist of clones of a single cell that have been distributed and passaged many times,altering chromosomal characteristics to where they no longer represent the original tumor[5].In a study of four HeLa cell line cultures,it was found that each culture had a unique genomic profile and activated different pathways in response to a hypoxic environment,demonstrating the effect of different culture conditions and serial passaging on the genomic integrity of CCLs[19].In contrast,GC organoids retain alterations found in the primary tumor even after serial passaging as evidenced by our own experience showing GC organoids retained copy number alterations after multiple passages[12]and a study showing six GC organoids maintained a stable transcriptome even after six months in culture[14].
Since faithful chromosomal segregation during mitosis requires intact tissue architecture and extracellular cues,CCLs may not represent the degree of chromosomal stability found in the primary tumor from which it was derived[20].In contrast,organoids contain a three-dimensional architecture and preserve structural integrity found in the primary tumor.They are composed of multiple cell types and represent the diversity of cell populations found in tumors (Table 1)[21].They vary morphologically depending on the original tumor's location in the stomach and tumor histology[15].GC organoids derived from intestinal-type tumor specimens resemble typical GI cancer organoids in that they are glandular and form a single lumen lined by a single layer of epithelial cells[13].Moderately differentiated intestinal type tumors develop buds,while poorly differentiated intestinal-type tumors form solid clusters[14].GC organoids developed from diffuse-type tumor specimens form either loosely cohesive isolated cells or solid cell clusters that do not surround a lumen[13,14].Mixed-type tumors develop into organoids containing all morphological patterns[13,14].
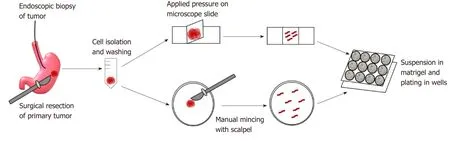
Figure 1 Creation of gastric cancer organoids.
Representation of histological and molecular subtypes
Recently,therapeutic research efforts have been enhanced by classification systems that delineate molecular features of certain GC subtypes.The classification system proposed by The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) identifies four gastric tumor subtypes:Epstein-Barr Virus-positive (EBV,9%),those with microsatellite instability(MSI,22%),genomically stable (20%),and tumors with chromosomal instability (CIN,50%)[22].The Lauren classification identifies two histological subtypes of GC based on pathology,epidemiology,and etiology:Intestinal and diffuse type adenocarcinoma.Each GC subtype contains distinct features and biomarkers that may be targeted by specific therapies.Organoids are unique in that they represent the entire genomic landscape and display distinguishable genetic properties depending on the GC subtype outlined by TCGA and Lauren classifications of the primary tumor,making them useful models for drug discovery[22,23].Chromosomal stability is maintained in MSI and EBV organoids[14].Diffuse-type organoids encompass both CIN and genomically stable subtypes,while intestinal- and mixed-type organoids display extensive chromosomal instability[14,15].GC organoids established from a genomically stable tumor contain typical CDH1 gene alterations and organoids established from MSI tumor tissues display characteristic CpG island methylator phenotype and MLH1 hypermethylation[13-15].Furthermore,EBV organoid lines retain the viral genome as well as characteristic ARID1A and PIK3CA mutations[14].In one study,a diffuse-type GC organoid line contained the CLDN18-ARHGAP6 fusion gene,which is found in genomically stable tumors.This mutation is not represented in any GC CCLs,further supporting the advantage of organoids to represent all types of GC compared to CCLs[14].
TUMORIGENESIS WITH GC ORGANOIDS
Models of tumor formation,carcinogenesis,and metastasis
The initiation of GC has been studied extensively to target specific genes and molecular events leading to tumor development.Organoids have been used to accurately model this progression.Nankiet al[13]induced diffuse GC-like morphology in normal gastric organoids by knocking out the tumor suppressor CDH1,which plays a role in cell-cell adhesion[13,24].Further knockout of the oncogene RHOA,a Rho GTPase belonging to the Ras superfamily,in CDH1-KO organoids resulted in reversion back to normal morphology[13,25].This suggests malignant phenotype may be induced in normal organoids and organoids can also model reversion back to normal morphology,making them useful for studying initiating events in tumorigenesis.Organoids therefore,may serve as a valuable tool to study phenotypic consequences leading to tumor development after activation or inhibition of specific genes.
Unlike CCLs,organoids have the unique ability to model the development of cancer.Normal gastric organoids and organoids derived from a lesion with intestinal metaplasia from the same patient were not morphologically distinct,but the intestinal metaplasia-derived organoids contained the marker CDX2 while normal organoids did not[13].Similarly,organoids derived from dysplasia and invasive tumor from the same patient both expressed representative early GC mutations however,had distinctive chromosomal patterns and unique gene mutations,illustrating the ability of organoids to document the important transition from dysplasia to adenocarcinoma[14].Altogether,these studies reveal organoids created from pre-malignant lesions are accurate surrogates of the sequence of events leading to cancer,which are not possible with cell lines,and therefore serve as a useful tool for identifying and targeting key mutations of tumor development.
Lastly,organoids created from the same patient's primary tumor and lymph node metastases show varying degrees of differences,which is believed to model nichespecific changes during metastasis[14].Thus,the ability of organoids to portray the genotypic and phenotypic events during cancer progression and metastasis provides a unique platform to study important oncological events not accessible through other models.
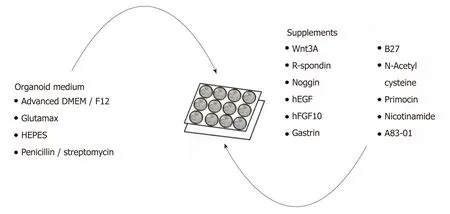
Figure 2 Complete list of ingredients for gastric cancer organoid medium.
DRUG SENSITIVITY TESTING
Current limitations of bringing drugs to clinic
The costs associated with supporting a cancer drug from preclinical development to approval by the United States Food and Drug Administration averages about $719.8 million[26].The high costs and lengthy amount of time,approximately 5 to 15 years,to bring newly developed drugs into the clinic limit the ability to provide new therapies to patients.One specific delay is the constraint associated with creating PDTX models,which are costly and require 4-8 mo prior to drug testing[7].From our experience,organoids can be utilized for drug sensitivity testing within two weeks and are less expensive than animal models (Table 1)[12].While organoids lack the ability to model angiogenesis,they provide ample biological material to rapidly test drugs prior to animal studies.
Investigation of drug sensitivity testing
Organoids have the ability to accurately discriminate between different drug treatments.Previously,we created and treated organoids from a patient's gastric tumor biopsies with the cytotoxic chemotherapies 5-fluorouracil,cisplatin,oxaliplatin,and irinotecan[12].We observed varying levels of organoid sensitivity to the chemotherapies that correlated with varying IC50values.Similarly,Vlachogianniset al[27]concluded that organoids are useful for modeling patient drug response.An ErbB2-amplified GC organoid line was treated with lapatinib,an antibody that targets the EGFR and HER2 tyrosine kinases that is currently used in combination with capecitabine to treat metastatic breast cancer patients[28].While the ErbB2-overexpressing GC organoids exhibited strong sensitivity to lapatinib,a GC organoid line with ErbB2 wild-type genotype did not respond.In addition,a GC organoid line with amplified AKT1 was the only organoid line in their cohort to respond significantly to two anti-AKT antibodies,MK-2206 and GSK690693[27].As such,GC organoids have potential for drug sensitivity screening.
Creation of GC organoid biobanks for novel drug screening
Organoid biobanks have been created for various cancer types[14,29-32].They portray the diverse molecular landscape and corresponding phenotypic characteristics found within a single cancer type and provide abundant biological material for drug sensitivity screening of newly synthesized drugs undergoing preclinical development.In one particular study,9 GC organoids created from 7 patients were selected for drug screening[14].Thirty-seven cancer therapies were tested in the organoids,which showed parallel response to that of clinical response with resistance to 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin and sensitivity to oxaliplatin,epirubicin,and paclitaxel.The GC organoids also responded to recently FDA-approved therapies,napabucasin and abemaciclib,and therapies currently undergoing clinical trials,vistusertib and VE-822[14].These data highlight the potential utility of an organoid biobank to screen novel therapies for efficacy prior toin vivotrials,bypassing the additional cost and time constraints associated with screening therapies in mouse models[33].GC organoid biobanks serve as a useful tool for drug screening by bridging the gap betweenex vivoandin vivomodels by accurately portraying the genetic profile of cancers with decreased time and cost constraints.
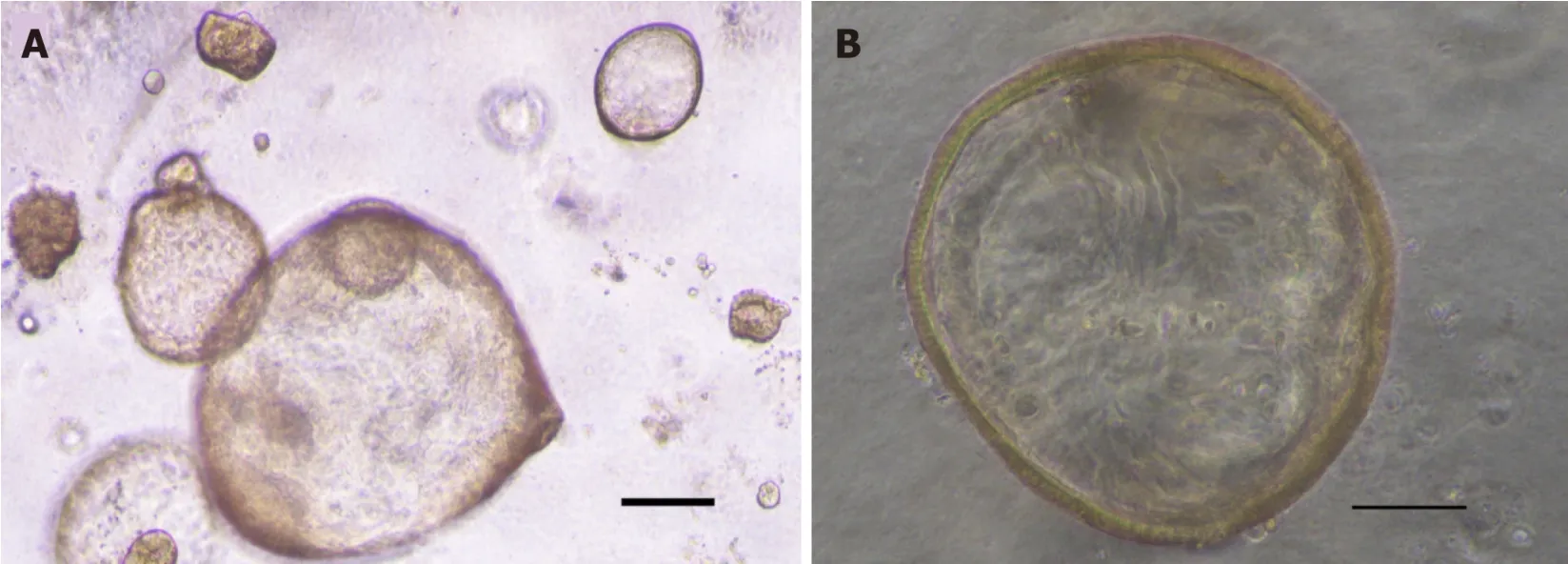
Figure 3 lmage of gastric cancer organoids.
PERSONALIZED MEDICINE
Limitations of personalized medicine
Even within GC subtypes,every patient's tumor is vastly different and therefore,could benefit from a personalized approach.Currently,after biopsy or surgical resection of the primary tumor,a patient's preserved tumor specimen may be sent for genomic sequencing,such as that offered by Foundation Medicine[8],to provide information about key driver mutations to guide treatment.While genomic testing provides invaluable biomarker and gene mutation information to help inform certain therapies and clinical trials,there are a few limitations.Optimally,a tumor percentage of 30% is required per specimen for Foundation Medicine[8]and a minimum threshold of 60% tumor percentage has historically been required for large next generation sequencing studies[22].In contrast,organoid establishment is not limited by tumor percentage and furthermore,organoids are created from minimal fresh tissue and expanded in culture,even when tumor tissue is limited[27].Finally,and perhaps most importantly,next generation sequencing testing has been criticized for lack of benefit to the majority of patients who have somatic alterations in their cancers that have no corresponding targeted therapies available in the clinic[9].These patients may benefit from functional assays using organoids to test a variety of drugs to determine the best available treatment.
Yielding drug treatment results in a clinically actionable time period
GC organoids established directly from patients may be used to test standard of care cytotoxic and targeted drug regimens,providing great potential for personalized medicine.However,GC organoids are mostly created from surgically resected tumor specimens.Surgery provides abundant tissue and serves as a good source for creating organoid biobanks for drug discovery and signaling studies.However,creating organoids from surgical specimens does not benefit the patient undergoing neoadjuvant therapies.Additionally,many patients with GC have metastatic disease and are not candidates to undergo surgery.Therefore,in order to personalize medicine for individual patients,a new avenue for organoid creation must be explored.We recently published a novel technique for successfully establishing GC organoids from esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) (Figure 1)[12].Many patients suspected to have GC will undergo EGD for diagnosis and staging.Therefore,creating organoids from EGD biopsies for drug sensitivity testing may directly yield clinically relevant results for patients who are ineligible for surgical intervention.Our technique has yielded abundant EGD derived organoids for testing multiple standard of care drug regimens and combination therapies within two weeks of organoid establishment (unpublished data),providing a valuable model for clinical prediction of the best therapies for individual patients.Furthermore,since almost every patient suspected of GC will undergo EGD,creating organoids from biopsies may serve as an additional source of abundant human biological material for biobanking.
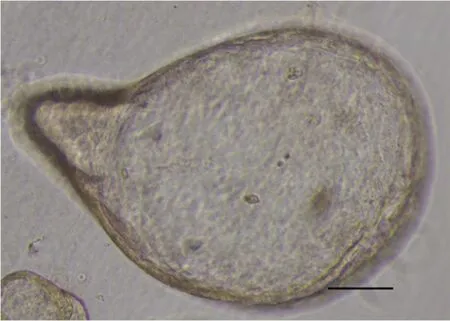
Figure 4 Gastric cancer organoid with budding.
Clinical trials using GC organoids to personalize therapy
With the ability to quickly develop large numbers of organoids that accurately portray an individual patient's tumor,GC organoids show high clinical utility for predicting drug sensitivities in patients.This unique advantage is currently being assessed in a human clinical trial where GC organoids created from patients with resectable cancer will be treated with the same neoadjuvant systemic therapy received by the patient,andin vitrocytotoxicity will be correlated toin vivoresponse(OPPOSITE trial:NCT03429816)[34].The future of personalized medicine in GC includes human trials implementing GC organoids to test various drugs and predict the best treatment for individual patients with advanced GC.
CONCLUSION
Organoid technology has provided the ability to model GC with more accuracy than traditionalin vitromodels.They retain GC biomarkers and display varying morphology depending on the histology and molecular subtype of the primary tumor from which they are derived.GC organoids are unique in that they recapitulate important molecular events leading to carcinogenesis and metastasis unlike CCLS.They are less costly and less time-consuming to create thanin vivoPDTX models,making them an appropriate vehicle for biobanking and comprehensive drug screening.While GC organoids present a unique,in vitromodel,there are a few limitations.Unlike PDTX models,organoids are unable to mimick thein vivotumor microenvironment in that they lack blood vessels for studying cancer angiogenesis and metastasis.In addition,they are grown in optimal conditions and growthpromoting media.Despite these restrictions,GC organoids overcome current limitations in precision medicine that require minimum tumor percentage and yet,organoids provide a more relevant predictor of drug response than next generation sequencing methods.With the ability to create GC organoids from diagnostic biopsy procedures,multiple drug regimens can be tested at once to yield actionable results in a clinically relevant time interval,providing avenues for personalized medicine for GC patients.
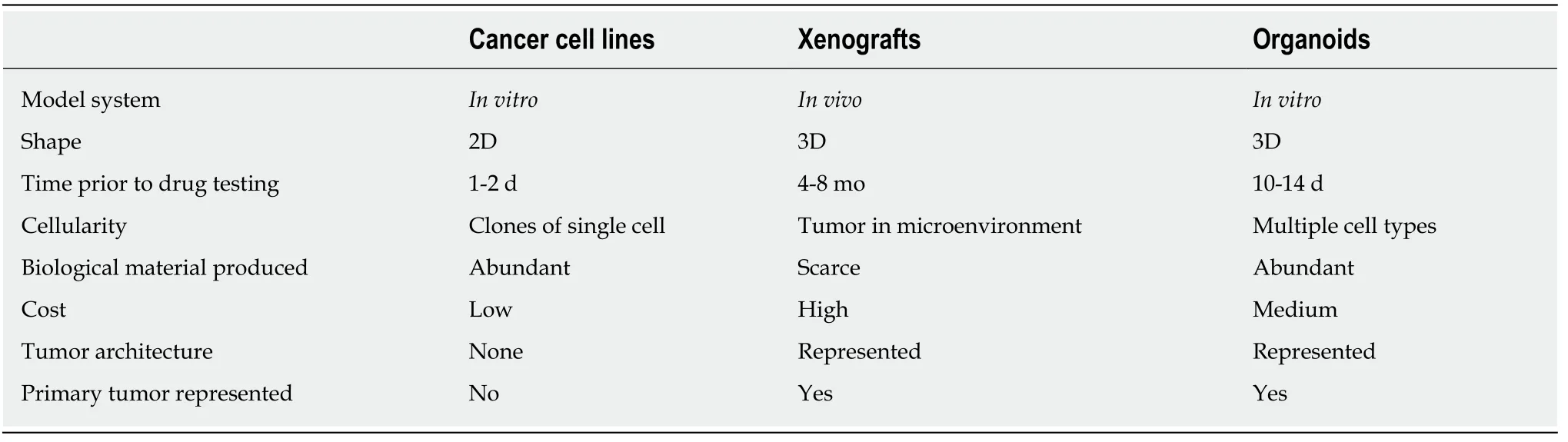
Table 1 Comparison of patient-derived cancer models
 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2019年7期
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2019年7期
- World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology的其它文章
- Recent progress of chemotherapy and biomarkers for gastroesophageal cancer
- TYMS/KRAS/BRAF molecular profiling predicts survival following adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer
- lntraoperative intraperitoneal chemotherapy increases the incidence of anastomotic leakage after anterior resection of rectal tumors
- Sarcopenia in pancreatic cancer-effects on surgical outcomes and chemotherapy
