Weekly albumin-bound paclitaxel/cisplatin versus gemcitabine/cisplatin as first-line therapy for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase II open-label clinical study
Shanshan Qin, Hui Yu, Xianghua Wu, Zhiguo Luo, Huijie Wang, Si Sun, Mingzhu Huang, Jia Jin,Zhonghua Tao, Jie Qiao, Yu Feng, Jialei Wang, Jianhua Chang
Department of Medical Oncology, Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center; Department of Oncology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai 200032, China
Abstract Objective: The aim of this trial was to compare both the efficacy and the safety of a weekly nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel) plus cisplatin vs. gemcitabine plus cisplatin in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Methods: A total of 84 participants received either 100 mg/m2 nab-paclitaxel each week on d 1, 8 and 15 of a 28 day cycle, as well as cisplatin 75 mg/m2 on d 1 every three weeks (nab-TP arm); or gemcitabine 1,000 mg/m2 on d 1 and 8, plus cisplatin 75 mg/m2 on d 1 every three weeks (GP arm). The primary end point was progression-free survival (PFS). The secondary end points were overall response rate (ORR) and overall survival (OS).Results: According to our analysis, the median PFS was 4.8 months for the nab-TP arm vs. 5.2 months for the GP arm (P=0.55). Analysis showed the median OS was 14.6 months for participants who were in the nab-TP arm vs. 15.1 months for those in the GP arm (P=0.94). Besides, nab-TP showed OS advantages over GP in patients harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation (26.7 vs. 15.3 months, P=0.046) and patients with a performance status of 0 (23.5 vs. 14.7 months, P=0.020). It was found that incidences of drug-related grade 3 or 4 toxicities were comparable between the two treatment arms.Conclusions: Therefore, it can be seen that weekly nab-TP treatment has a similar efficacy and tolerability to GP treatment for patients who are undergoing their first-line treatment for NSCLC. It could be that survival differences among platinum doublets in the context of both EGFR mutation and performance status have the potential to be the basis for our further clinical trials.
Keywords: Albumin-bound paclitaxel; cisplatin; gemcitabine; first-line therapy; advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
Introduction
Lung cancer is one of the most distressing malignancies. In addition, it is the foremost cause of cancer-related mortality and morbidity in China (1). Non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is responsible for as much as 85% of all lung cancers which have a five-year survival rate of around 15% (2). The commonly used treatment which has the potential to cure this cancer is surgery. However, many patients are not eligible for surgery as they often have been diagnosed at advanced stage. Systemic cancer therapies such as chemotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy are the best choices for these patients with advanced NSCLC. At the current time, platinum-based chemotherapy remains the first choice of first-line chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced NSCLC (3-5).Several studies have shown that drugs such as paclitaxel,docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine are considered to be acceptable platinum partners for first-line therapy for patients with NSCLC, and that these drugs show no differences in either progression-free survival (PFS) or overall survival (OS) for these patients (3,6,7).
Nanoparticle albumin bound paclitaxel (nab paclitaxel),which is a solvent-free formulation of paclitaxel, was developed to try to improve the therapeutic index of paclitaxel. A host of clinical studies confirm that this drug is more effective than its solvent-based counterpart, and that it has demonstrated an advantageous safety profile in the treatments of breast, pancreatic and lung cancers (8-10). In particular, as a first-line treatment for patients who are living with advanced NSCLC, weekly nab-paclitaxel(100 mg/m2) on d 1, 8 and 15 (three of every four weeks) as well as carboplatin administered once every three weeks demonstrated an increased efficacy when compared to other various weekly and every-three-week regimens. With an overall response rate (ORR) of 48% and a median OS of more than 11 months, results have demonstrated a distinctly stronger therapeutic efficacy as a result of the different administration schedules of this drug (11).
A combination of gemcitabine plus cisplatin over a threeweek schedule is popular in clinical practice all over the world as a first-line treatment for NSCLC (12). However,researchers have not yet conducted a direct comparison of the benefits and risks of nab-paclitaxel vs. gemcitabine.This phase II study was carried out in order to compare both efficacy and safety of weekly nab-paclitaxel plus cisplatin vs. gemcitabine plus cisplatin in chemotherapynaive participants who were living with advanced NSCLC.
Materials and methods
Patients
Eligible participants were chemotherapy-naive patients who were living with an NSCLC that was histologically/cytologically confirmed to be non-resectable at either stage IIIB (with or without pleural effusion) or stage IV.Additionally, participants had to have at least one lesion that was measurable by the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST 1.0) (13). Further, participants had to have an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG)performance status (PS) of ≤1 (14), life expectancy that was longer than 12 weeks, and be at least 18 years old.Participants who had had prior neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy were eligible if that treatment had been completed eight months before they were enrolled in the study. Any participants who had received earlier radiotherapy had to have completed that treatment at least four weeks before entering the study. Participants were required to have adequate hematologic, hepatic and renal function, which was evidenced by a hemoglobin score of≥9.0 g/dL, an absolute neutrophil count (ANC) of≥2.0×109/L, a platelet count (PLT) of ≥100×109/L, hepatic enzyme [alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alkaline phosphatase (ALP)] levels of ≤2.5× the upper limit of normal range (ULN), total bilirubin levels (TBIL) of ≤1.5×ULN, and serum creatinine(Cr) which was deemed to be within the normal range.
Participants were excluded from taking part in the trial if they had been ever previously been treated with gemcitabine or if they were pregnant or lactating.Participants were also excluded if they had any of the following conditions: untreated or symptomatic brain metastasis; severe internal medical diseases; infections that were currently active; previous or concurrent malignancies that had occurred within the past five years (excluding cone-biopsied carcinoma in situ of the cervix or any adequately treated basal or squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)of the skin); or a history of allergies or hypersensitivity to the drugs being used in the trial.
Our study was approved by Ethics Committee of Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center on December 8th,2012, and was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of both Good Clinical Practice and the Declaration of Helsinki (15). All participants gave informed consent in writing before they commenced participation. The study was registered in clincialtrials.gov with the identifier NCT01810367 on March 11th, 2013.
Study design
Participants who had been deemed eligible were randomly assigned to either the nab-TP group, in which they received 100 mg/m230-min infusion of nab-paclitaxel weekly (on d 1, 8 and 15, every 28 d) plus cisplatin 75 mg/m2(on d 1) every three weeks; or the GP group, in which they received gemcitabine 1,000 mg/m2(on d 1 and 8) plus cisplatin 75 mg/m2(on d 1), with both drugs administered every three weeks. Randomization of participants was stratified according to age (<65 years vs. ≥65 years), histology [SCC vs. adenocarcinoma (ADC) vs.poorly differentiated], disease stage (IIIB vs. IV) and sex(male vs. female). A treatment of at least six cycles was recommended unless participants experienced disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, or they withdrew their consent.
Assessment of efficacy and safety
The efficacy of the two treatments was measured objectively using spiral computed tomography scans every two cycles, as per RECIST 1.0 guidelines. PFS, which was defined as the time from the first dose of medication to the first objective progression of the disease or the date of death from any causes, was our primary efficacy end point of interest. We were also interested in two secondary efficacy end points: that is, ORR, including both confirmed complete response (CR) and partial response (PR) rate, and OS, which was defined as the date from initiation of chemotherapy to the date of the last follow-up, or of death and safety profile. All participants who received at least one dose of nab-TP or GP were considered eligible for safety assessment. Toxicities were evaluated using the toxicity grading criteria of the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria version 2.0 (NCI-CTC 2.0) (16).
Statistical analysis
Our sample size calculation used PFS as the primary study endpoint. We assumed that the PFS time of abraxane(ABX) when combined with cisplatin treatment was 2.5 months longer than the GP treatment (4.2 months for ECOG 1594) (using the superiority test), and that the planned enrollment time on the study would be 24 months.Enrollment speed was balanced, and the rate of participants typically lost to follow-up is 5%, based on a=0.2, b=0.3(two-sided test), calculated by PASS 2008 software(Version 8.0.2, NCSS, LLC. Kaysville, USA ). Therefore,85 patients in each group should have been enrolled, and it was recommended that SCC patients should account for 50% of those participants.
Analysis was undertaken using IBM SPSS Statistics(Version 22.0; IBM Corp., New York, USA). GraphPad Prism Six Survivals, including PFS and OS, were estimated using a Kaplan-Meier curve. Differences between the treatments were measured with the log-rank test. We made use of both outpatient and telephone follow-ups, with the final follow-up of the study taking place on January 31st,2017. Comparisons among the clinical features, curative effects and frequency of severe toxicities between the two treatment arms were measured using either χ2or Fisher’s exact test. A value of two-sided P<0.05 was deemed statistically significant.
Results
Patient characteristics
Between April 2012 and January 2015, a total of 84 patients from the Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center took part in the study. They were randomly assigned, at a ratio of 1:1, to receive either nab-TP treatment (arm I, n=41) or GP treatment (arm II, n=43). Participants were predominantly male (83.3%) smokers (73.8%) living with stage IV NSCLC (90.4%). The baseline characteristics of the participants were evenly distributed between the two arms (Table 1). Data from seven participants did not receive response evaluation due to: adverse events (AEs) (n=4);withdrawal of consent (n=1); or death (n=2). A total of 77 patients (from the intent-to-treat set) were assessable for efficacy, while 84 patients were assessable for toxicity. The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation status of patients who were living with a histological type of ADC and NSCLC-not otherwise specified (NOS) was assessed.When data collection for the final analysis ceased, all patients had discontinued their treatment.
Efficacy results
Clinical responses for participants from both treatment arms were compared (Table 2). According to an independent radiology assessment of ORR, the GP group had a higher ORR (37.5% vs. 29.7%; P=0.471) and disease control rate (DCR) (90.0% vs. 78.4%; P=0.160) than the nab-TP group; however, statistical significance was not reached. In particular, no CR was recorded in either treatment arm. Eleven (29.7%) participants in the nab-TP arm and 15 (37.5%) in the GP arm achieved PRs. Stable Diseases (SDs) were observed in 18 (48.6%) of the participants in the nab-TP arm and 21 (52.5%) participants in GP arm. Eight (21.6%) participants in the nab-TP arm and four (10.0%) in GP arm were evaluated to have progressive diseases (PDs).

Table 1 Baseline characteristics of participants
Survival
The final date for data collection in this study was January 31st, 2017. The median PFSs were found to be 4.8 [95%confidence interval (95% CI), 4.0-5.6] months for participants in the nab-TP arm and 5.2 (95% CI, 4.0-6.4)months for participants in the GP arm (Figure 1). An increase of approximately 8% in PFS was found in the GP arm compared with the nab-TP arm [hazard ratio(HR)=1.17; 95% CI, 0.70-1.96; P=0.55]. Median OS was found to be 14.6 (95% CI, 10.0-19.2) months in the nab-TP arm and 15.1 (95% CI, 14.1-16.1) months in the GP arm (Figure 2). However, the difference in OS between the two treatment groups was not found to be statistically significant (HR=1.02; 95% CI, 0.58-1.79; P=0.94).
Analyses by strata
Sub-group analyses for PFS were undertaken and can be seen in Figure 3. These analyses demonstrated a significantly improved median PFS in the poorly differentiated (NOS) histology subgroup of the GP arm when compared with the nab-TP arm (7.3 vs. 4.0 months,P=0.017) (Figure 4). In addition, it was found that male patients in the GP treatment arm had a longer median PFS when compared with the nab-TP group; however, this was not statistically significant (5.7 vs. 4.7 months, P=0.30).Meanwhile, female patients receiving the nab-TP treatment demonstrated the opposite trend by having a longer median PFS when compared with the GP treatment(10.0 vs. 5.2 months, P=0.22).

Table 2 Overall response to treatment

Figure 1 Progression-free survival (PFS) by treatment arm(Kaplan-Meier curve) for the entire population (P=0.55). 95% CI,95% confidence interval; nab-TP, nanoparticle albuminboundpaclitaxel/cisplatin; GP, gemcitabine/cisplatin.
Sub-group analyses for OS were undertaken and presented in Figure 5. Participants who had a PS of 1 demonstrated comparable OS between the two treatment arms, while participants who had a PS of 0 showed significantly increased OS in the nab-TP arm when compared with those in the GP arm (23.5 vs. 14.7 months,P=0.020) (Figures 6A). In addition, participants in the nab-PT group who revealed an EGFR mutation demonstrated an increase in OS compared to those in the GP treatment group (26.7 vs. 15.3 months, P=0.046) (Figures 6B). There was a slight improvement in the EGFR-wild type or EGFR-unknown status subtype of more than one month in the GP arm when compared with the nab-TP arm (median,15.1 vs. 14.0 months, P=0.24). The factors of sex, age,smoking history, stage or histology did not result in any statistical differences to survival outcomes between the treatment arms. However, as with the PFS scores, female participants in the nab-TP group had a longer median OS than those in the GP group (23.5 vs. 14.7 months, P=0.23),while the OS of the male participants in the two groups were 14.1 months for the nab-TP group and 15.6 months for the GP group (P=0.57).


Figure 3 Forest plot per stratification for progression-free survival (PFS). NSCLC-NOS, non-small-cell lung cancer-not otherwise specified; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; MT, mutant type; WT, wild type; NA, not available; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; PS, performance status; nab-TP, nanoparticle albumin-boundpaclitaxel/cisplatin; GP, gemcitabine/cisplatin; HR, hazard ratio; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval.
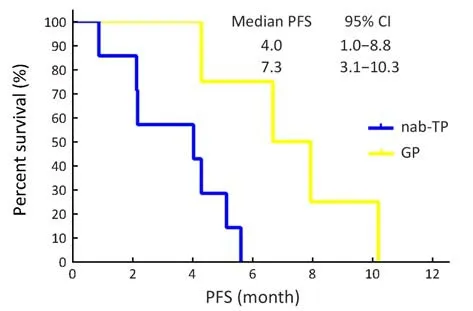
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier progression-free survival (PFS) curves for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer-not otherwise specified(NSCLC-NOS) histology (P=0.017). nab-TP, nanoparticle albumin-bound paclitaxel/cisplatin; GP, gemcitabine/cisplatin;95% CI, 95% confidence interval.
Safety
In terms of the safety profile, grade 3 and grade 4 AEs were compared between the two treatment arms (Table 3).Overall, rates of severe toxicity incidences were low. In the nab-TP arm, the most frequent grade 3 and 4 AEs were leukopenia (n=5, 12.2%), sensory neuropathy (n=3, 7.3%)and febrile neutropenia (n=2, 4.9%). In the GP arm, the most frequent grade 3 and 4 AEs observed were leukopenia again (n=4, 9.3%), as well as thrombocytopenia (n=3, 7.0%)and anemia (n=3, 7.0%). No significant difference was found between AE occurrences in either arm, suggesting that the nab-TP group had a comparable tolerability to GP group for patients living with advanced NSCLC.
Post-discontinuation therapies
In general, both the use and the type of second-line therapy were balanced in the two treatment arms (Table 4). In the nab-TP arm, some 45.9% of participants (17 out of 37)received second-line therapy, compared to 52.5% of participants in the GP arm (21 out of 40). The most frequently used regimens in both treatment arms were pemetrexed, epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs) and docetaxel. One participant in the nab-TP arm was given GP as a secondline therapy, while none of the participants in the GP arm were administered nab-TP treatment.
Discussion
This randomized, open-label, phase II clinical study directly compared both the efficacy and safety profiles of a combination of weekly nab-paclitaxel plus cisplatin with gemcitabine plus cisplatin as a first-line therapy for patients who were living with advanced NSCLC. Analysis did not find any significant differences in PFS and OS between the two groups. Additionally, both clinical responses and incidences of drug-related grade 3 or 4 toxicities were comparable between the nab-TP and GP treatment arms.According to the power level in our sample size calculation process, it may be because the test efficiency is not enough that our research results were insignificant between the two groups. For this is a phase II study, it is worth further exploration in the future.
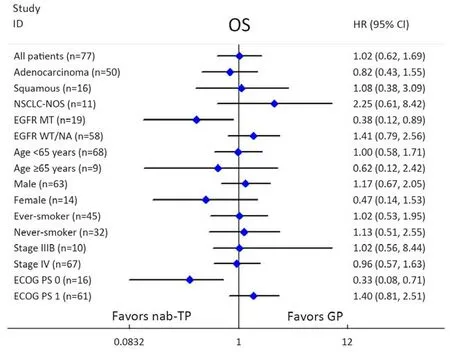
Figure 5 Forest plot per stratification for overall survival (OS). NSCLC-NOS, non-small-cell lung cancer-not otherwisespecified; EGFR,epidermal growth factor receptor; MT, mutant type; WT, wild type; NA, not available; ECOG, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; PS,performance status; nab-TP, nanoparticle albumin-boundpaclitaxel/cisplatin; GP, gemcitabine/cisplatin; HR, hazard ratio; 95% CI, 95%confidence interval.
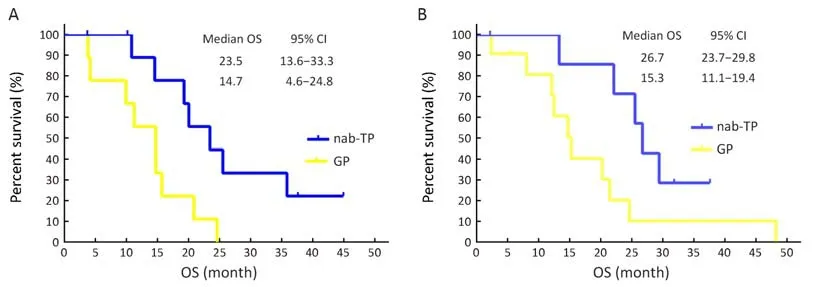
Figure 6 Kaplan-Meier overall survival (OS) curves for (A) patients with a performance status of 0 (P=0.020) and (B) patients harboring epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation (P=0.046). nab-TP, nanoparticlealbumin-bound paclitaxel/cisplatin; GP,gemcitabine/cisplatin; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval.
Sub-group analyses found a significant difference in PFS in favor of the gemcitabine and cisplatin treatment in the NSCLC-NOS histological type (7.3 vs. 4.0 months,P=0.017), while the nab-TP group demonstrated stronger OS than the GP treatment group for participants who had an EGFR mutation (P=0.046) as well as for participants who had a PS of 0 (P=0.02). It is therefore an important finding of this study that the efficacy is equivalent between nab-TP and GP treatments, and that selected populations such as patients with EGFR mutation or those who have a stronger PS may survive longer if they are treated with albumin-bound paclitaxel and cisplatin.
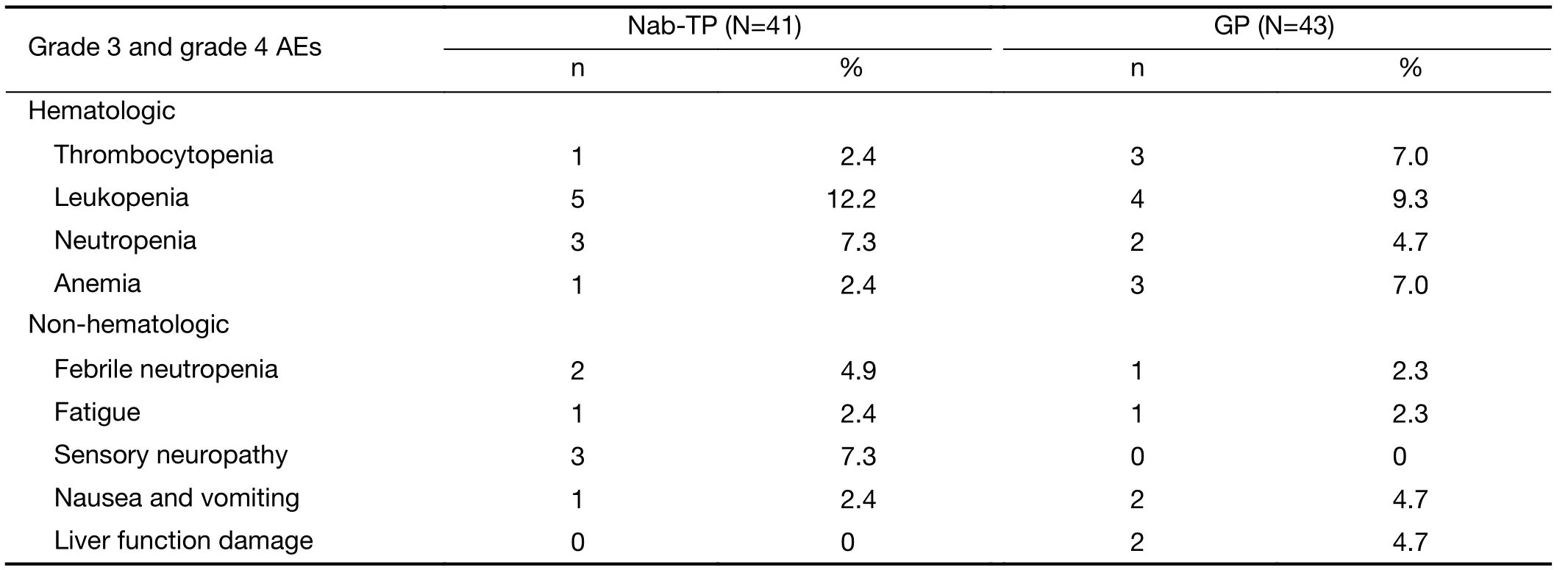
Table 3 Toxicity profile

Table 4 Second-line chemotherapy summary
A previous phase III trial (n=1,052) from Socinski and colleagues compared weekly nab-paclitaxel/carboplatin to solvent-based paclitaxel/carboplatin as a first-line therapy for patients living with advanced NSCLC. These authors found an improvement of approximately 10% in PFS(median, 6.3 vs. 5.8 months; P=0.214) and OS (median,12.1 vs. 11.2 months; P=0.271) in their nab-PC arm when compared with their sb-PC arm (17). A comparison of our data with the data from that study suggests that like patients’ survival was improved, with a median OS of 14.6 months. There are several reasons why this might be the case. Firstly, participants in our study had a mean age of 55 years, while those in Socinski’s study were older, with a mean age of 60 years. This means that stronger overall health and fewer comorbidities may have contributed to longer survival rates. Secondly, a higher proportion of participants who were living with ADC were enrolled in our study; 56% compared to 49% in Socinski’s study. ADC is a favorable prognostic factor in the NSCLC population as a whole (18), and so it might explain our longer survival rates. In addition, while both cisplatin and carboplatin are platinum-based regimens, they may have some differences.
Emerging evidence supports the notion that nabpaclitaxel is an effective tool in the treatment of various malignancies, especially cancers that have a squamous histology (19-21). A phase II trial recently compared the efficacy and safety of first-line nab-paclitaxel and carboplatin to gemcitabine and carboplatin in 127 advanced SCC of the lung (22). Sub-group analysis suggested that the squamous histology was a predictive factor in the efficacy of nab-paclitaxel treatment, with a marginally improved ORR (46% vs. 30%, P=0.085) and an improvement of approximately 18.8% in PFS (median, 5.7 vs. 4.8 months, P=0.657) when compared to the gemcitabine arm. In addition, in the sub-analysis of participants who were living with SCC (n=450) in Socinski’s study (cited above), nab-paclitaxel and carboplatin led to a significantly better ORR when compared with solvent-based paclitaxel and carboplatin(41% vs. 24%; P<0.001), resulting in an approximately one-month longer median OS (10.7 vs. 9.5 months;P=0.28). However, in our study, we did not measure any advantages of the nab-paclitaxel treatment in the SCC subgroup, whether in ORR, PFS or OS. This may be a result of our relatively small sample and the low proportion of SCC patients in that sample. Importantly, a significant difference in PFS, in favor of gemcitabine and cisplatin,was found in the NSCLC-NOS histology (7.3 vs. 4.0 months, P=0.017), noting that the OS of the GP arm in the histology sub-group was also superior to that of the nab-TP arm (13.8 vs. 8.5 months, P=0.23), although this was not statistically significant. This may suggest that gemcitabine and cisplatin should be a preferred regimen for treating such pathological groups of patients.
A novel and important finding of this trial was revealed during the sub-group analyses for survival in the context of EGFR mutation status, since a significant survival difference in favor of the albumin-bound paclitaxel/cisplatin treatment arm was found in patients who had an EGFR mutation. This important correlation between EGFR mutation and the efficacy of albumin-bound paclitaxel and cisplatin has not been reported before. While targeted drugs are always being developed for patients with EGFR mutation, and while these drugs have demonstrated strong therapeutic efficacy and moderate adverse reactions,finding a suitable chemotherapy regimen is also an alternative option, particularly after EGFR-TKIs resistance(23-25). Considering the relatively small number of participants in this study, more research is needed to validate the survival benefits of albumin-bound paclitaxel and cisplatin in those patients with EGFR mutation, as well as to investigate the underlying mechanisms of those benefits.
Conclusions
It has been demonstrated that a treatment of weekly nabpaclitaxel plus cisplatin offers similar efficacy and tolerability to gemcitabine plus cisplatin for first-line treatment of patients who are living with advanced NSCLC. Survival differences among platinum doublets according to both EGFR mutation and PS have the potential to be the basis for further clinical trials.
Acknowledgements
None.
Footnote
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2019年2期
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2019年2期
- Chinese Journal of Cancer Research的其它文章
- Extensive exploration of T cell heterogeneity in cancers by single cell sequencing
- Synthesis and evaluation of 64Cu-radiolabeled NOTA-cetuximab(64Cu-NOTA-C225) for immuno-PET imaging of EGFR expression
- Nomograms based on HPV load for predicting survival in cervical squamous cell carcinoma: An observational study with a longterm follow-up
- Alisol B 23-acetate-induced HepG2 hepatoma cell death through mTOR signaling-initiated G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis: A quantitative proteomic study
- Histogram analysis of apparent diffusion coefficient predicts response to radiofrequency ablation in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Efficacy of endoscopic treatment on patients with severe dysplasia/carcinoma in situ of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A prospective cohort study
