Iodine-125 implantation with transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for main portal vein tumor thrombus
Yue Zhang,Yi-Fan Wu,Zhen-Dong Yue,Hong-Wei Zhao,Lei Wang,Zhen-Hua Fan,Fu-Liang He,Tao Wang,Fu-Quan Liu
Abstract
Key words: Iodine-125;Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt;Main portal vein tumor thrombus;Metastasis;Portal hypertension
INTRODUCTION
The main portal vein tumor thrombus (MPVTT),which is the major complication of terminal hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC),is mainly caused by metastasis of tumor cells from the liver to the portal vein,seriously affecting the prognosis of liver cancer[1,2].The survival rate of a patient with liver cancer is 38% and 24% at 3 and 4 years,respectively[3].The incidence of PVTT caused by liver cancer is high[4].PVTT is classified into the following five grades:Vp0,no tumor thrombus in the PV;Vp1,presence of a tumor thrombus distal to,but not in the second-order branches of the PV;Vp2,presence of a tumor thrombus in the second-order branches of the PV;Vp3,presence of a tumor thrombus in the first-order branches of the PV;and Vp4,presence of a tumor thrombus in the main trunk of the PV or a branch contralateral to the primarily involved lobe (or both)[5,6].Methods to treat PVTT are surgery,chemotherapy,transarterial chemoembolization/transarterial embolization(TACE/TAE),radiofrequency ablation,interventional therapy,and RT[7-10].Liver transplantation is another curative treatment for end-stage liver disease;however,its application is limited by a shortage of donors and patient refusal.Treatment for MPVTT is the most difficult.Portal hypertension,which is caused by MPVTT,can lead to many complications,such as ascites and hemorrhage of the digestive tract.Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) has been widely performed for the treatment of portal hypertension,because it is minimally invasive and is reported to be effective[11,12].However,the survival rate of TIPS is less favorable because it cannot control progression of HCC.
In the past few years,the application of low-energy radionuclides,such as125I,has extended the indications of brachytherapy.Some studies have reported treatment of HCC with125I implantation.125I,which can reduce the volume of PVTT,has received widespread attention[13].However,the patients had class A or B liver function;the first-grade branch of the PV was unobstructed;and the patients had no intractable ascites.In addition,125I was implanted as particle strands,which limited the number of particles implanted and the position of125I could not be adjusted.No study has investigated the clinical effect of125I combined with TIPS,in which125I is placed between the TT and stents.Thus,we aimed to compare the clinical efficacy of TACE/TAE+125I combined with TIPS and TACE/TAE + TIPS only in the treatment of liver cancer patients with MPVTT and portal hypertension.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
This study was a nonrandomized controlled trial.
Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows:(1) age 18–70 years;(2) presence of HCC with MPVTT;(3) clear indications for TIPS treatment,such as gastrointestinal bleeding and ascites,in liver cancer patients with portal hypertension;and (4) clear indications for TACE or TAE treatment.The exclusion criteria were as follows:(1) suspected benign thrombosis;(2) active infection or serious disorders of the heart,lung,kidney,brain,and other vital organs;(3) pregnant or lactating women;(4) estimated lifetime < 3 mo;and (5) patients who could not cooperate during the treatment and observation period.
Patients
Eighty-five patients with MPVTT were nonrandomly assigned to undergo treatment with TIPS and catheter125I seed implantation (TIPS-125I group) or TIPS only (TIPS only group) between January 2007 and March 2015.HCC was confirmed according to the criteria of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases[14].PVTT was diagnosed by consensus by re-evaluation of all available computed tomography (CT)or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings by two board-certified radiologists experienced in abdominal oncological imaging.Biopsies of the confirmed PVT were performed in 31 patients who were strongly suspected to have PVTT but did not have enough imaging evidence[15].
There were 24 cases of hepatitis B cirrhosis,13 hepatitis C cirrhosis,15 alcoholic cirrhosis,10 primary biliary cirrhosis,eight autoimmune liver cirrhosis,and 15 other causes.According to the preoperative Child–Pugh classification,there were 16 cases of class A,36 class B,and 33 class C.There were 61 patients with hemorrhage of the digestive tract,11 with chest and abdominal dropsy,and 13 with both (Table 1).The flow chart is shown in Figure 1.
Preoperative preparation
Before TIPS,liver function tests,blood coagulation tests,routine blood tests,electrocardiography,CT and/or MRI,color Doppler ultrasonography,and esophageal radiography were performed.Gastroscopy was also performed if necessary.Before TIPS,patients’ coagulation function was corrected to a normal range.The TIPS-related concerns were explained to the patients and their family members who were later asked to sign the informed consent.This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Beijing Shijitan Hospital and conducted in accordance with all current ethical guidelines.
TIPS
First approach:Preoperative imaging showed that intrahepatic PV flow was completely or partially opened,and TT did not completely block the blood vessels.Extrahepatic portal vein (MPV) was more serious.TIPS was performed following femoral artery puncture and artery intubation of the superior mesenteric or splenic artery through femoral artery and contrast material injection through a catheter to locate the PV.Second approach:preoperative imaging showed that intrahepatic PV flow was blocked completely.TIPS was conducted after percutaneous transhepatic portal puncture was performed directly,and a catheter was placed in the PV as a marker.
Patients were assigned nonrandomly to undergo TIPS with covered stents(Fluency;Bard,Tempe,AZ,United States),under local anesthesia at the puncture site.A needle was passed from the right jugular vein to the inferior vena cava (IVC) or hepatic vein followed by a guidewire,and then the needle was passed to the PV to measure the free PV pressure (PVP).The difference between PVP and the IVC pressure represented the portosystemic gradient (PSG).The puncture set (RUPS-100;Cook,Ind,United States) was placed in the PV.Two guide wires were placed in thesplenic vein or superior mesenteric vein,through the RUPS-100.The guide wire was placed,RUPS-100 was pulled out,a 4 F catheter was inserted into the distal vessel of the TT through one guide wire,and the RUPS-100 suit was reinserted into the PV via another guide wire.Next,a pigtail catheter was advanced through the RUPS-100 to the distal end of the splenic vein or superior mesenteric vein to measure PVP and radiography was conducted.The varicose veins were embolized with coils.An 8-mm balloon was used in every patient to dilate the liver parenchyma.Both 8-mm and 10-mm covered stents were implanted.The 10-mm stent was implanted at the distal end of the TT,covering the TT,whereas the 8-mm stent was implanted in the hepatic parenchyma and at the proximal end of the TT.Measurement of PVP before and after placement of TIPS allowed assessment of the success of the procedure.If combined with percutaneous liver puncture,after TIPS,the PV catheter was pulled out,and the hepatic puncture passage was strictly blocked during the pullout to avoid intraperitoneal or thoracic hemorrhage.
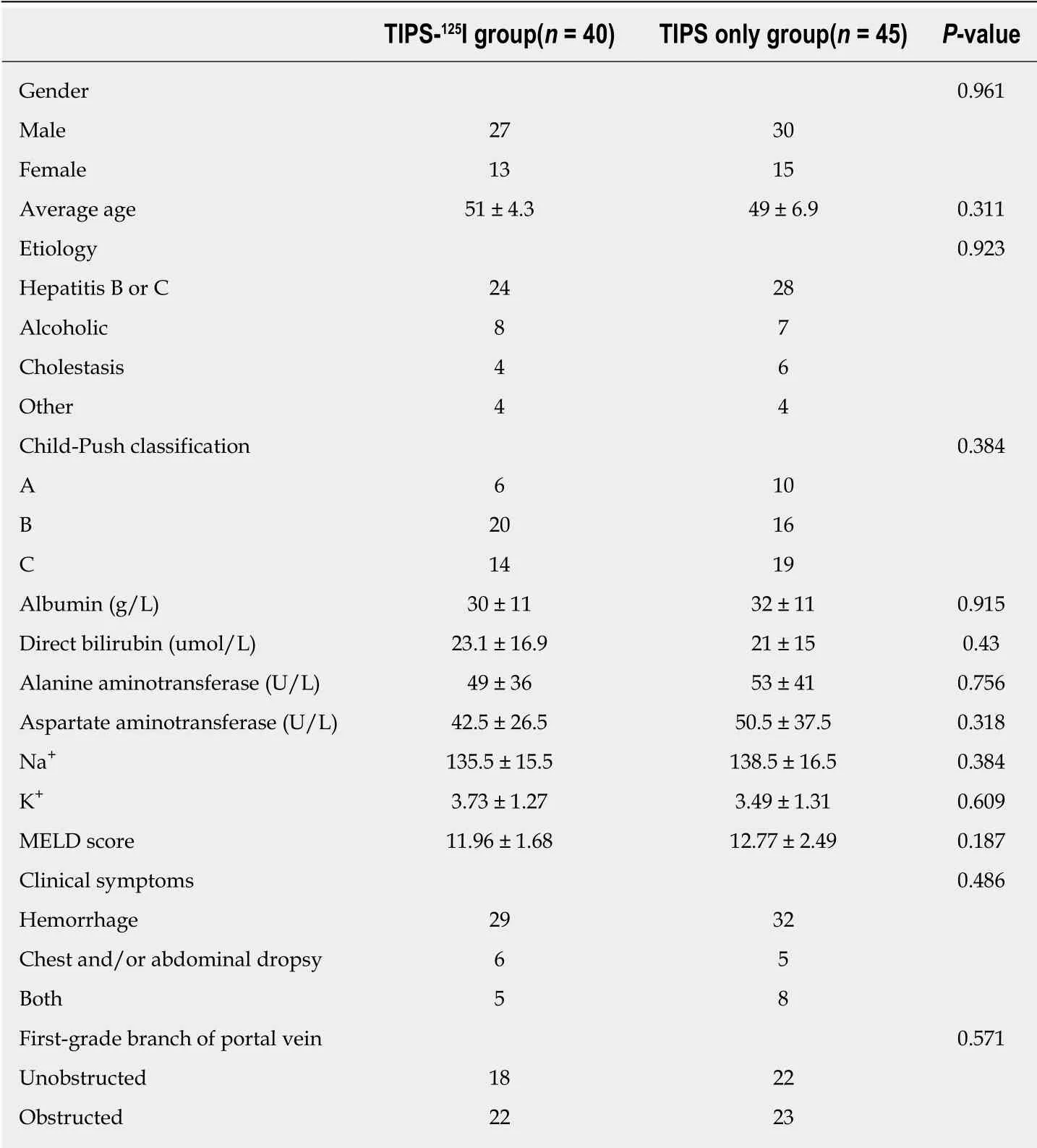
Table 1 Baseline characteristics on patients
125I implantation
In the TIPS-125I group,the patients underwent TIPS similar to those in the TIPS only group.After the shunt was successfully established,the catheter between the stent and TT was linked to the particle release gun.The catheter was slowly retreated,and at the same time,the125I radioactive particles (Tong Fu,Inc.,China) were released through the catheter up to the proximal end of the portal vein trunk and TT.The radioactive particles were arranged as neatly as possible in all TTs.After implantation,PVP was measured and portography was performed again.125I emitted characteristic electrons and photons through the recession of the electron capture surface.The electrons were absorbed by the titanium alloy wall of the sealed seeds of125I.The photons mainly emitted X rays of 27.4 and 31.4 keV as well as γ rays of 35.5 KeV.Pictures taken during the operation are shown in Figure 2.

Figure 1 Study design and flow chart.
TACE/TAE procedure
Before or after TIPS,class A liver function patients were treated with TACE depending on the lesion size and its blood supply.The embolization agent of iodinated oil (3–30 mL) was used.The chemotherapeutic agents used included pirarubicin (10–20 mg) and hydroxycamptothecine (5–15 mg).Before or after TIPS,patients with class B or C liver function were treated with TAE to reduce liver dysfunction.The embolization agent of iodinated oil (5–25 mL) was used.
A needle was passed from the right or left femoral artery to the hepatic artery,and hepatic arteriography was performed.Then,a catheter was placed in the artery directly supplying blood to the cancerous lesion,as closely to the focus as possible,and the embolization and infusion of chemotherapeutic drugs were performed.The interval and number of treatments depended on the size of tumor lesion,artery status,and liver function.Treatment was usually done once every 1–6 mo.In the TIPS-125I group,six and 34 patients were treated with TACE and TAE,respectively,whereas 10 and 35 patients were treated with TACE and TAE,respectively,in the TIPS only group,showing no significant difference (P=0.395).For radiofrequency ablation,patients whose lesion was ≤ 5 cm and had a rich blood supply required TACE or TAE first and radiofrequency ablation after 3–5 d.Patients whose lesions were > 5 cm required TACE or TAE once or several times initially,and then radiofrequency ablation,when the imaging showed that the lesions had no blood supply from the hepatic artery,or the catheter could not enter into the artery of the lesions.Finally,all patients underwent radiofrequency ablation an average of 1.64 times.
Postoperative routine observation and treatment
Postoperative treatment consisted of sorafenib (Nexavar;Bayer,Leverkusen,Germany);at least 400 mg/d was recommended for ≥ 20 of the last 28 d after the first TACE procedure[16].Low molecular weight heparin (5000 IU,twice daily) was subcutaneously injected for 5 d,and then warfarin was administered for 1 yr.Intravenous injection of branched-chain amino acids and oral lactulose were also administered to prevent hepatic encephalopathy (HE).Coagulation function of each patient was examined every 15 d to ensure that the International Normalized Ratio ranged from 2 to 3.Complications,including abdominal cavity hemorrhage,HE,and hepatic failure,were monitored postoperatively.
Follow-up
Scheduled follow-up was performed at 6,12 and 24 mo postoperatively.The recorded information included clinical manifestations,physical examination,shunt patency evaluation (through ultrasound and endoscopy),and laboratory tests.A telephone follow-up was performed to record the patient’s condition and details of relevant clinical events.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are presented as the means ± medians and were compared by independent samplettest or paired-samplettest accordingly.Categorical and ordinal variables are presented as frequencies or percentages and were compared usingχ2test.Time-to-event outcomes were evaluated with Kaplan–Meier curves and log-rank test.Cox regression model was used to identify independent predictors.Unbalanced factors between groups were treated as covariates.Statistical analyses were performed using IBM SPSS version 22.0 (IBM,Chicago,IL,United States) and GraphPad Prism version 7.0 (La Jolla,CA,United States).Follow-up investigators and statisticians had access to all the data and can vouch for the integrity of data analyses.
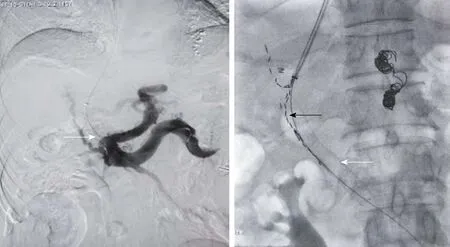
Figure 2 The two pictures in the process of the operation.
RESULTS
Baseline characteristics of patients
Eighty-five consecutive patients with MPVTT were divided into the TIPS-125I and TIPS only groups in Beijing Shijitan Hospital.All patients were followed up for 24 mo without any dropout.The baseline characteristics are presented in Table 1.
Change in PSG before and after TIPS
The PSG in the TIPS-125I group decreased from 26.96 ± 5.73 to 13.1 ± 5.9 mmHg (t=20.88,P< 0.05) after TIPS.In the TIPS only group,it decreased from 26.12 ± 5 to 12.6 ±5.4 mmHg (t=22.94,P< 0.05).The PSG before and after TIPS was significantly different between the two groups (Table 2).Preoperative PSG did not differ significantly between the two groups (t=1.103,P=0.273).After the operation,PSG still did not differ significantly between the groups (t=0.625,P=0.534) (Figure 3).
Time-to-event outcomes
The rates of symptom recurrence at 6,12 and 24 mo were 7.5%,22.5% and 35%,respectively,in the TIPS-125I group,whereas those in the TIPS only group were 31.1%,62.2% and 82.2%,respectively,which were significantly different [log rankP< 0.05,hazard ratio (HR):0.227,95% confidence interval (CI):0.129–0.401,Figure 4A] (Table 3).The rates of stent restenosis at 6,12 and 24 mo were 12.5%,27.5% and 42.5%,respectively,in the TIPS-125I group,whereas those in the TIPS only group were 42.2%,68.9% and 84.4%,respectively,with significant differences (log rankP< 0.05,HR:0.313,95%CI:0.182–0.536,Figure 4B) (Table 3).Median overall survival (OS) was 11.75 mo in the TIPS-125I group and 7.70 mo in the TIPS only group (P=0.009).The rates of survival at 6,12 and 24 mo were 80%,45% and 20%,respectively,in the TIPS-125I group,whereas those in the TIPS only group were 64.4%,24.4% and 4.4%,respectively,with significant differences (log rankP< 0.05,HR:0.527,95%CI:0.332–0.834,Figure 4C) (Table 3).The survival rates also differed significantly depending on the Child–Pugh classification (log rankP< 0.001,Figure 4D).
Cox regression
Cox regression identified that etiology of liver cancer,clinical symptoms,albumin,aspartate aminotransferase,Na+,and K+had no significant effect on the survival rate.The treatment was the significant factor affecting survival rate (P< 0.001 HR:4.178,95%CI:2.340-7.459).Child–Pugh classification,Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score,and direct bilirubin were also independent prognostic factors for survival(Table 4).The OS is shown in Figure 5.
DISCUSSION
For patients with MPVTT,the ideal operation should improve survival rate,reduce PVP,and avoid ascites and gastrointestinal bleeding.TIPS can achieve these,in addition to improving the survival rate of patients.125I has a good therapeutic effect and can improve the survival rate of patients[17,18].However,125I implantation documented in the literature was combined with percutaneous liver puncture or TACE in the form of particle strands,which had some disadvantages,such as limited number of particles being implanted.Moreover,the position of125I cannot be adjusted in these procedures.125I combined with TIPS can fix the particles between the stent and the TT without the need for particle strands.This approach allows for easier adjustment of the position of125I and the amount of125I being implanted.However,there has been no research on125I combined with TIPS for the treatment of PVTT.Thus,we investigated the efficacy of TIPS combined with125I in the treatment of PVTT.Overall,our study revealed the following outcomes:(1)125I combined with TIPS in the treatment of PVTT can significantly improve patients’ survival rate and reduce stent restenosis and symptom recurrence;and (2) TIPS can reduce PVP and relieve clinical symptoms;and (3) TIPS combined with125I is safe and feasible.
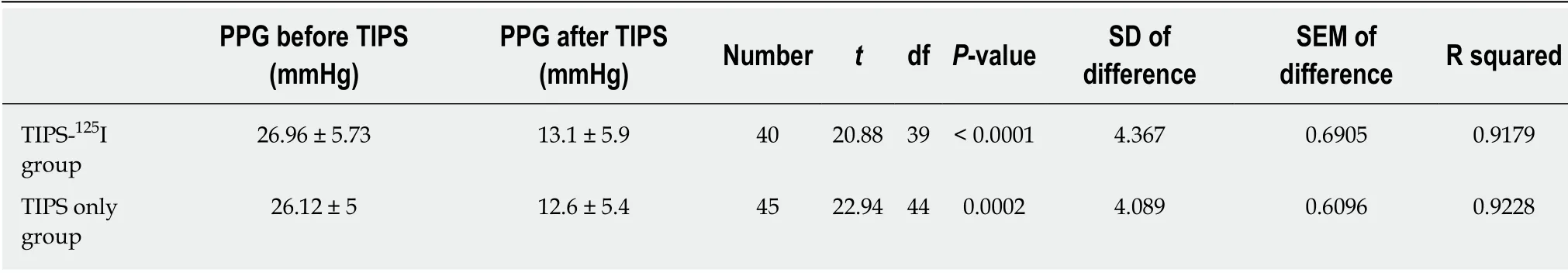
Table 2 The portosystemic pressure gradient before and after transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt was significantly different in the two groups
TIPS can effectively reduce PVP and prevent the occurrence of portal hypertension and its complications.It can improve patients’ quality of life and give them the opportunity to be treated for their primary lesion[12,19-21].However,it is unable to control the development of TT.Bettingeret al[21]studied a group of 40 HCC patients treated with TIPS,showed that TIPS implantation is an effective and safe treatment for portal hypertension in these patients,without significant impairment in liver function.Nevertheless,patients with PVT had a median OS of 5.2 (4.3-6.0) mo,whereas that in patients without PVT was 17 (3.2–18.7) mo.
Recently,the application of125I in treating PVTT has shown a curative effect[18,22-24].A retrospective matched cohort study[2]has suggested that TACE combined with125I seed implantation may be a good choice for selected hepatitis B HCC patients with PVTT.Linet al[18]found the median OS in HCC patients with PVTT,treated with125I brachytherapy was 7 mo in the MPV group,which was lower than that in other groups,such as the right or left portal vein group and segmental branches of portal vein group.Luoet al[8]compared the therapeutic effect between the group treated with125I + TACE + stent implantation (group A) and the group treated with stent implantation + TACE (group B).The median survival time was 9.3 ± 0.9 mo (95%CI:7.6-11.0 mo) in group A and 4.9 ± 0.5 mo (95%CI:4.0-5.8 mo) in group B.Median progression-free survival time in groups A and B was 1.8 ± 0.1 mo (95%CI:1.6-2.0 mo)and 1.5 ± 0.1 mo (95%CI:1.3-1.7 mo),respectively (P< 0.001).Median stent patency period was 9.2 ± 1.1 mo (95%CI:7.0-11.4 mo) in group A and 4.8 ± 0.5 mo (95%CI:3.9-5.7 mo) in group B (P< 0.001).
Radiotherapy (RT),which is recommended for patients with HCC and PVTT,can provide better PVTT control and OS.Liet al[25]and Imet al[26]showed that high dose RT combined with other treatments provides a significantly better survival outcome than monotherapy for unresectable HCC patients with PVTT,like TACE,especially for patients with PVTT involving main trunk.The defect of RT with high irradiation dose is the occurrence of adverse reactions,such as gastrointestinal reactions,bone marrow depression and liver function damage.125I seeding can release continuous low doses of X and γ rays that can damage the DNA in the nuclei of the tumor cells.In our research,the uniformly distributed125I seeds,which have a half-life of 59.6 d and a radiation diameter of 1.7 cm,were positioned close to the TT and fixed by TIPS stent[27].The close contact with MPVTT makes it possible to deliver γ-ray irradiation to the TT continuously,which greatly inhibits tumor cell growth by inducing apoptosis and shrinking the MPVTT.Therefore,TIPS combined with125I can avoid injury of the surrounding normal tissue with low radiation dose accumulation in the TT,and then can effectively restore the blood flow of the obstructed MPV.Certainly,there are also potential risks as migration of the125I seeds and heterogeneity of the radiation area.
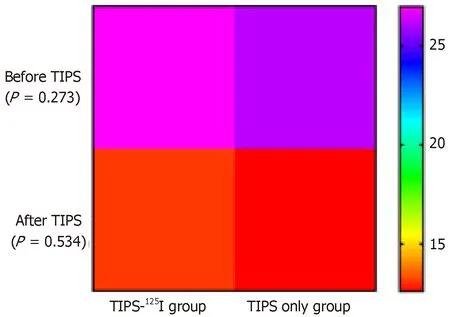
Figure 3 Heat map.
Although a sufficient amount of radiation[17]can reduce the degree of impairment to the surrounding normal tissue and improve the therapeutic effect on the PVTT,the cases reported in the literature had strict controls.For example,the first-grade branch of the PV was unobstructed,and the patients had no intractable ascites.At the same time,the patients must be categorized as class A or class B according to the Child–Pugh classification.The number of implanted particles was fixed.The patients included in our study had different characteristics compared with those reported in the literature.In our study,the clinical symptoms were worse.There were 16 patients categorized as class C liver function,with hemorrhage of the digestive tract and chest and abdominal dropsy,and obstructed first-grade branch.Thus,our results were able to demonstrate that125I combined with TIPS can improve patients’ survival rate,reduce stent stenosis rate,and reduce symptom recurrence rate.
Our study had several limitations.First,the radiation dose was not uniformly distributed.Second,the number of enrolled patients was small,and it may have influenced the accuracy of the results.Finally,we did not analyze the particle removal rate.Therefore,the results should be interpreted with caution,and large randomized clinical trials are warranted.
In conclusion,TACE/TAE+125I combined with TIPS is effective in treating MPVTT and its complications,in improving the quality of life of patients,and in reducing the mortality rate.
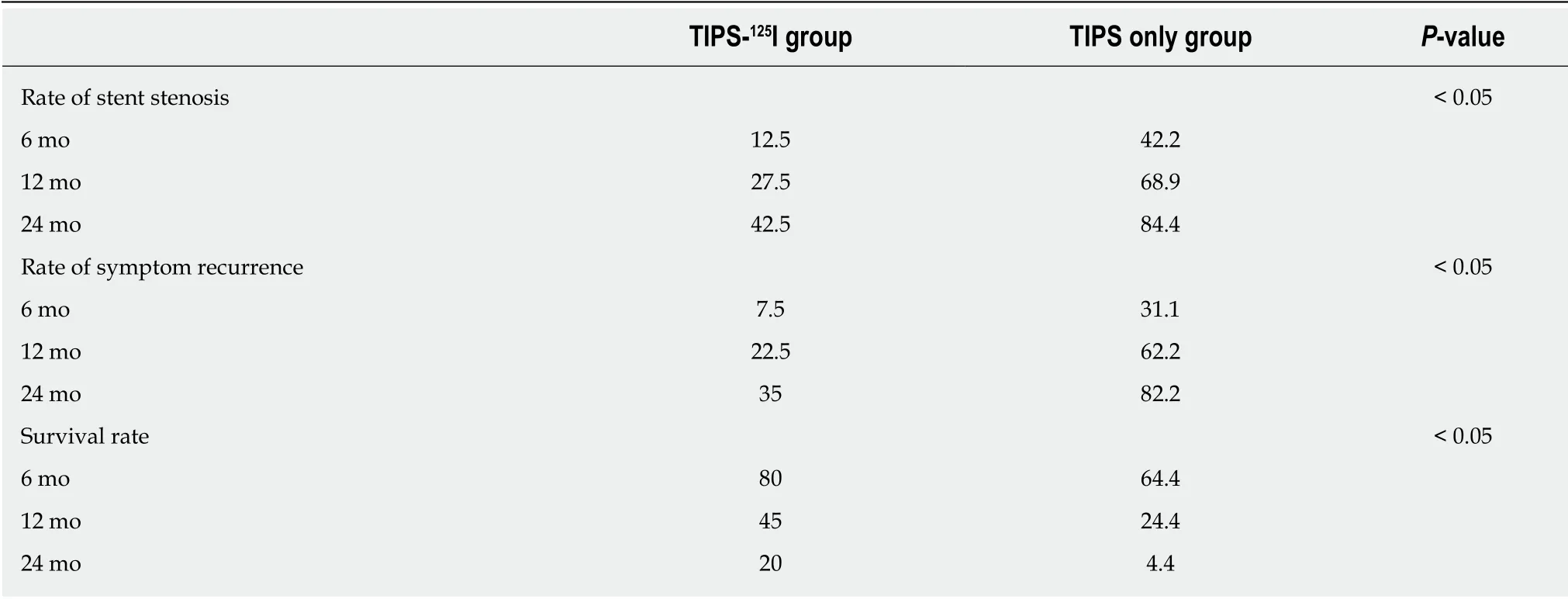
Table 3 The rates of symptom recurrence,stent restenosis and survival during follow-up

Table 4 The multivariate analysis of survival
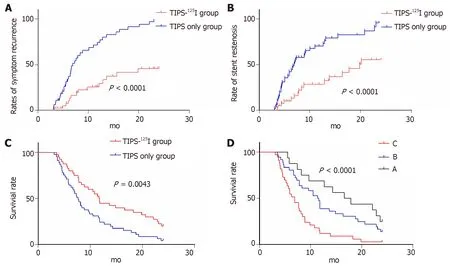
Figure 4 Kaplan-Meier curves of post-operation symptom recurrence,stent stenosis and survival.

Figure 5 COX plots of overall survival in epatocellular carcinoma patients with main portal vein tumor thrombosis.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
The main portal vein tumor thrombus (MPVTT),which is the major complication of terminal hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and causes portal hypertension,seriously affects the prognosis of liver cancer.MPVTT causes portal hypertension,which leads to many complications,such as ascites and hemorrhage of the digestive tract.
Research motivation
For patients with MPVTT,the ideal treatment should improve survival rate,reduce portal vein pressure,and avoid ascites and gastrointestinal bleeding,and the main objectives are to eliminate TT and recanalization of the PV.
Research objectives
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) has been widely performed for the treatment of portal hypertension because it is minimally invasive and is reported to be effective.
Research methods
Some studies have reported that treatment of HCC with 125I implantation can reduce the volume of PVTT,which can improve the survival rate of patients.Thus,data analysis was adopted to analyze patient outcome in two groups with different treatments (plus or non-plus 125I implantation).However,125I implantation documented in the literature was in the form of particle strands,which cannot be adjusted in position and implanted in limited numbers.
Research results
125I combined with TIPS can fix the particles between the stent and the TT without the need for particle strands.
Research conclusions
This approach allows for easier adjustment of the position of125I and the amount of125I being implanted.It can significantly enhance the survival rate of patients.TIPS combined with 125I can also reduce stent restenosis rate and symptom recurrence rate,and it is safe and feasible.However,the radiation dose is not uniformly distributed and particle fixation needs to be strengthened.
Research perspectives
In the present study,we used 125I combined with TIPS for the treatment of MPVTT and fixed the125I particles between the stent and TT,without the need for particle strands.This approach allows for easier adjustment of the position of125I and the amount being implanted.The direction of future research should aim to find new methods that are minimally invasive and more effective.
 World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2019年4期
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology2019年4期
- World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology的其它文章
- Significance of HER2 protein expression and HER2 gene amplification in colorectal adenocarcinomas
- Validated model for prediction of recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation in Asian population
- Predictive factors of histological response of colorectal liver metastases after neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- Up-regulation of tumor necrosis factor-α pathway survival genes and of the receptor TNFR2 in gastric cancer
- Identification of genomic features associated with immunotherapy response in gastrointestinal cancers
