Burden of diabetic foot ulcer in Nigeria:Current evidence from the multicenter evaluation of diabetic foot ulcer in Nigeria
Wisit Kaewput,Charat Thongprayoon,Narittaya Varothai,Anupong Sirirungreung,Ram Rangsin,Tarun Bathini,Michael A Mao,Wisit Cheungpasitporn
Wisit Kaewput,Ram Rangsin,Department of Military and Community Medicine,Phramongkutklao College of Medicine,Bangkok 10400,Thailand
Charat Thongprayoon,Michael A Mao,Division of Nephrology and Hypertension,Department of Medicine,Mayo Clinic,Rochester,MN 55905,United States
Narittaya Varothai,Division of Geriatrics,Department of Medicine,Phramongkutklao Hospital and College of Medicine,Bangkok 10400,Thailand
Anupong Sirirungreung,Department of Epidemiology,Fielding School of Public Health,University of California,Los Angeles,CA 90095,United States
Tarun Bathini,Department of Internal Medicine,University of Arizona,Tucson,AZ 85721,United States
Wisit Cheungpasitporn,Division of Nephrology,Department of Medicine,University of Mississippi Medical Center,Jackson,MS 39216,United States
Abstract
Key words:Type 2 diabetes mellitus;Hospitalization;Diabetes in elderly;Dysglycemia;Hypoglycemia;Hyperglycemia
INTRODUCTION
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a common chronic disease worldwide that poses a significant crisis in the global health system[1,2].The associated morbidity and mortality can be caused by the disease itself or its associated multisystem complications that can increase in incidence and severity with prolonged disease duration.This disease,which has a higher prevalence in the older population,is also increasing in the elderly population likely due to the aging population[3,4].The prevalence of individuals over 65 years of age with T2DM in Thailand reached 17.2%as reported by the InterASIA study in 2003[5].Furthermore,increased age unsurprisingly has been found to be a significant predictor of higher health-care costs among diabetic patients[6,7].
Older patients with T2DM are more susceptible to dysglycemia-related complications requiring hospitalizations and associated morbidity and mortality[8].Several recent studies showed that intensive glucose control strategies may derive less benefit and have demonstrated increased harms[3,9].Increasingly,the importance of specialized care and management for the geriatric population on clinical outcomes has been recognized,and as such the treatment approach used T2DM in the elderly population should differ from those in the younger patients[8].However,DM care quality metrics established more than a decade ago have primarily focused on prevention of hyperglycemia and its complications[9].The current state of clinical practice in relation to established quality metrics and its impact on dysglycemicrelated hospitalizations in elderly T2DM in Thailand is unknown.Thus,the aim of this study sought to determine whether prevalence of dysglycemia-related hospitalization in elderly T2DM in Thailand and the associated factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design and population
This was an analysis on the DM/HT dataset in 2014[10].This was a nationwide survey conducted annually in Thailand to evaluate the status of medical care in T2DM patients who visited the public hospitals of the Thai Ministry of Public Health and the clinics in the Thailand National Health Security Office’s program.The Inclusion criteria of this DM/HT survey consisted of T2DM patients aged ≥ 35 years who received regular medical care in the targeted hospital for at least 12 mo.Patients who received care at primary care units outside Bangkok and University hospitals were excluded from the study.A two-stage stratified cluster sampling method was used to select a nationally and provincially representative sample of T2DM patients in Thailand.The first stage of sample collection consisted of the provinces that constituted 77 strata.The second stage of sample collection was the hospitals’ levels in each province,which were stratified into five strata according to the size of the hospital.These five strata were regional (>500 beds),provincial (200-500 beds),large community (80-120 beds),medium community (60 beds),and small community (10-30 beds) hospitals.All regional (n= 25) and provincial (n= 70) hospitals were enrolled,but only 456 (62% out of 736) community hospitals were included.Of 456 community hospitals,10%,20%,and 70% were large,medium and small community hospitals,respectively (Figure1).
All patients were recruited from the outpatient clinic.Written informed consent was obtained from patients before enrollment.This study was approved by both the Institutional Review Board of the Royal Thai Army Medical Department and the Ethical Review Committee for Research in Human Subjects,the Ministry of Public Health of Thailand due to the regulations of bureaucratic systems in Thailand.Welltrained research nurses reviewed medical records and collected data into a case record form.Data entry into the case record form was then transferred to the central data management of the Medical Research Network of the Consortium of Thai Medical Schools to adjudicate that the process of data collection was compiled according to study protocol.The data management team was responsible for inquiries to study sites to verify data.Site monitoring was randomly performed in approximately 10% of study sites.To focus on the hospital admission due to dysglycemia in elderly T2DM patients during 2014,we selected only patients aged ≥65 years for analysis in this study.
Data collection
Clinical characteristics,demographic information,medication,and laboratory data were collected using manual data retrieval from the medical record as described above.Body mass index (BMI) was stratified by using criteria for an Asian population[11].GFR was estimated based on age,sex,race and the most recent creatinine using the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation[12].We examined the prevalence of hospitalization due to hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia in the year 2014.Hyperglycemia complication included diabetic ketoacidosis,hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state,and hyperglycemic dehydration syndrome.
Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were presented as mean ± SD.Categorical variables were presented as count with percentage.Backward stepwise multivariable logistic regression analysis was performed to identify factors associated with hospital admission due to hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic complications.Odds ratio (OR)with 95%CI was reported.Possible interactions and collinearities were also tested.AP-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS version 22 (SPSS,Inc.,Chicago,IL,United States).
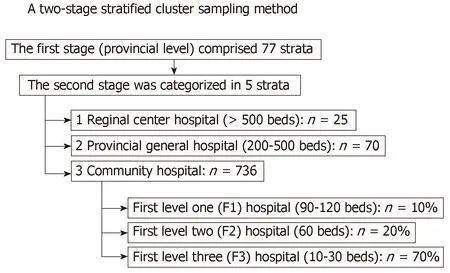
Figure1 Flow chart of the participant selection.
RESULTS
Clinical characteristics
A total of 11404 elderly T2DM patients were included in the analysis.The clinical characteristics are summarized in Table1.The mean age was 72.9 ± 5.5 years.Twentynine point four percent of the patients were aged>75 years.Thirty-one point five percent were male.The mean diabetic duration was 7.5 ± 4.4 years.Twenty point nine percent of the patients used insulin.The mean BMI was 24.3 ± 4.3 kg/m2.The mean hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) was 7.5% ± 1.9%.The mean estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 54.7 ± 21.5 mL/min per 1.73 m2(Table1).
Prevalence of dysglycemia-related hospitalizations among elderly T2DM patients
The prevalence of dysglycemia-related hospitalizations among elderly T2DM patients during the year 2014 was 4.9% (n= 558).Among elderly T2DM patients,11 (0.1%),16(0.1%),and 192 (1.7%) were admitted in hospital due to diabetic ketoacidosis,hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state,and hyperglycemic dehydration syndrome,respectively,whereas 356 (3.1%) were admitted in hospital due to hypoglycemia.
Associated factors associated with hypoglycemia-related and hyperglycemiarelated hospitalizations
In multivariable analysis,older age,female sex,had hypertension,dementia,lower BMI,insulin use,elevated HbA1c,and decreased eGFR were associated with increased risk of hospital admission due to hypoglycemia,whereas overweight and obesity were associated with decreased risk of hospital admission (Table2).
In multivariable analysis,dementia,depression,insulin use,and HbA1C 8.5% and above were associated with increased risk of hospital admission due to hyperglycemia,whereas overweight was associated with decreased risk of hospital admission (Table3).
DISCUSSION
This was a large nationwide,multicenter,one-year period cross-sectional study that examined prevalence and associated factors for hospitalization due to dysglycemia among elderly T2DM patients during the year 2014.Despite a prior study that showed an overall decreasing trend in dysglycemia-related hospital admissions among elderly Thai T2DM patients[13],our data describe that the prevalence of hypoglycemia-related hospitalization is higher than previously reported from United States[7,14],England[15],Canada[16],Italy[17],Denmark[18]and South Korea[19](Table4).This might be due to several reasons.First,the United States report consisted of combined data from both diabetic and non-diabetic patients.Second,our study included different sized hospitals,and the smaller sized hospital may have had limited availability of specialists.This may have negatively affected the quality of care for these special populations.Moreover,our study found that hypoglycemia-related hospitalization is higher than hyperglycemia in old diabetic patients.It could translate that elderly T2DM patients were likely to treat with rigorous glycemic control.
Our study revealed that age,female sex,hypertension,dementia,insulin use,low BMI,elevated HbA1C and low eGFR are associated with hypoglycemia-related hospitalizations.Older age and its association with severe hypoglycemia is consistentwith several reports[19,20].The Korean cohort demonstrated that older patients,females,several comorbidities such as chronic kidney disease and dementia,and insulin use were associated with a high risk of hypoglycemia[19].Another previous study found that in patients who are aged ≥ 80 years,severe hypoglycemia accounted for up to one in six hospital admissions[20].Older patients may have multiple factors that can predispose them to develop hypoglycemia such as polypharmacy,age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics,decreased hormonal regulation and counter-regulation,suboptimal intake of water and/or food,decreased intestinal absorption,and cognitive impairment[21,22].They may also be burdened with diseases that affect their ability to effectively metabolize hypoglycemic agents or respond to hypoglycemia,such as heart failure,liver disease,sarcopenia[23]and kidney dysfunction[24].Female sex is associated with hypoglycemia related hospitalizations,consistent with a Korean cohort[19].Females are hypothesized to develop hypoglycemia more readily due to lower muscle mass,less tolerability of hypoglycemic symptoms,stricter diet control,and less access to medications than males[25,26].Our study found that elderly T2DM patients with hypertension areassociated with hypoglycemic admissions.This finding provides novel insights.A possible cause might be due to polypharmacy since these elderly T2DM patients with hypertension had more comorbidities and more diabetic complications that affect hypoglycemic drugs metabolism.

Table1 Baseline characteristics

Table2 Crude and adjusted odds ratios of factors that were independently associated with hospital admission due to hypoglycemic complication,using multivariate analysis
A previous community-based study in Sweden study[27]found that glycemic control is worse in patients with T2DM alone than in those with T2DM combined with hypertension.It is related to different degrees of insulin resistance and insulin secretion.Normotensive T2DM patients had reduced insulin secretion which accounts for the higher HbA1C and lower risk for developing hypoglycemia[27].Dementia in elderly T2DM patients has previously been described as correlating with a higher risk for hypoglycemia[28,29].The possible contributing factors in dementia patients included low compliance,medication errors and increased susceptibility to medication overdoses[30].Furthermore,dementia patients generally have lower dietary intake (e.g.,dysphagia),loss of functional capacity[31],increased difficulty preparing food,and higher likelihood of hypoglycemic unawareness[32,33].Consequently,these patients may not be diagnosed with hypoglycemia until they develop severe life-threatening symptoms or signs that require hospitalization.

Table3 Crude and adjusted odds ratios of factors that were independently associated with hospital admission due to hyperglycemic complication,using multivariate analysis
Exogenous insulin use as an associated risk factor for hypoglycemia makes inherent sense[34],especially when compared with medications that work primarily via other mechanisms,such as decreasing hepatic gluconeogenesis,decreasing intestinal absorption of glucose,increasing endogenous insulin sensitivity or increasing gluconeogenesis in the muscles.Elderly T2DM patients may be at higher risk for hypoglycemia as they may require insulin due to a longer chronicity of T2DM resulting in subsequent decreased endogenous insulin production,may require multiple hypoglycemic drugs,and often may have hepatic and/or renal impairments[35].Insulin should be used with caution in older adults.The administration of insulin therapy requires good visual acuity,motor skills and cognitive ability in the patient,especially for regimens that require multiple daily injections.This may be too complex for patients with several comorbidities and limited functional status.Our study also demonstrated that low BMI is associated with hypoglycemia related hospitalizations as well.A low BMI in elderly patients may cause higher risk for hypoglycemia due to lower muscle mass,suboptimal nutrition status and low glycogen storage[36,37].Our study additionally revealed that an elevated HbA1C is associated with hypoglycemic admissions.An elevated HbA1C may increase hypoglycemic risk due to more aggressive blood glucose control resulting in labile blood sugars,or a higher association with polypharmacy.

Table4 Rate of dysglycemia related hospitalization stratified by country
Our study also supported that a low eGFR is associated with severe hypoglycemia in elderly T2DM patients,consistent with a prior report[19].Impaired kidney function has been shown to significantly increase the risk of hypoglycemia[24].The kidney may play an essential role in glucose metabolism and serve as a defense mechanism against hypoglycemia.Furthermore,impaired renal function limits insulin and other antidiabetic drugs clearance.Patients with advanced kidney disease may also have chronic inflammation and anorexia that leads to suboptimal nutrition and a reduction in glycogen stores[24].Hence,in addition to their risk of polypharmacy,cognitive decline,dementia,sarcopenia,and frailty,older adults with diabetes and impaired renal function are at risk of hypoglycemia[24,38].
There were certain factors that appeared to protect against hypoglycemia-related hospitalizations.An elevated BMI is associated with decreased risk of hypoglycemiarelated hospitalization,consistent with a prior Korean report[19].Overweight and obese patients may have protective factors against hypoglycemia such as a higher dietary intake and more glucose reserves in the form of higher glycogen storage,muscle mass,and fat mass.
Our report describes a higher prevalence of hyperglycemia-related hospitalizations than a previous report from the United States[7](Table4).Similar to hypoglycemiarelated hospitalizations,the difference in prevalence reported may be due to differences in study design,where other study included both diabetic and nondiabetic patients and our study included patients from varying hospital sizes.
This study showed that dementia,depression,insulin use,and HbA1C were associated with an increased risk of hyperglycemia-related hospitalization.Conversely,overweight patients had a decreased risk of hyperglycemia-related hospitalization.Dementia and depression as risk factors for hyperglycemia are supported by other reports[39].It may be due to poor compliance or inability to access medications[31].Insulin use and elevated HbA1C were also risk factors for hyperglycemic hospitalizations.This could be due to an association with more advanced diabetic diseases,higher patient prevalence of comorbidities and their associated complications and poor compliance.Conversely,overweight was found to be inversely associated with hyperglycemia-related hospitalizations.This can probably be explained by the fact that improved glycemic control is associated with weight gain.
The strengths of this study included the large representative patient cohort and the adjustment for multiple clinical variables.This report is a large nationwide crosssectional study that included varying hospital sizes in Thailand.The multivariable logistical regression statistical analysis performed for assessing associated hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia-related hospitalization factors included several possible confounders such as age,gender,smoking,BMI,duration of diabetes,comorbidities,insulin use and laboratory parameter.The comorbidities included hypertension,dyslipidemia,cancer,dementia,depression,cerebrovascular disease,coronary artery disease,peripheral artery disease,peripheral neuropathy,and diabetic retinopathy.Laboratory parameters included HbA1C and eGFR for its final model adjustment.
There are several limitations of this study.First,data collection was performed using retrospective medical record review;therefore,incomplete data records with missing diagnoses cannot be verified.Second,the study population does not include patients from university hospitals.Consequently,the prevalence of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia-related hospitalization may be significantly underestimated.Third,we only measured hospitalization rates for dysglycemia.Dysglycemic events resulting in death prior to hospital admission were not captured.Fourth,we did not adjust the final statistical models for several possible confounders such as alcohol consumption and former tobacco use as this data was unavailable.One previous study had demonstrated an associated risk of hypoglycemia in T1DM patients with alcohol use[40].Conversely,another study did not show an association between alcohol consumption and risk of hypoglycemia in T2DM patients.Pietraszeket al[41]had instead reported that acute intake of alcohol does not increase hypoglycemic risk in diet-controlled T2DM subjects;an alcohol-related hypoglycemic effect only occurred when sulfonylurea was co-administered.Furthermore,long-term alcohol use seems to be associated with improved glycemic control in T2DM probably due to improved insulin sensitivity.Former tobacco use may have also affected our outcomes if patients had decided to quit smoking due to health conditions related to the dysglycemic admission.Last,this was a cross-sectional study which had duration of only one year.
Serial blood glucose monitoring is already recommended for prevention of glycemic complications in elderly T2DM patients.However,the importance of timely and more frequent blood glucose monitoring in elderly T2DM patients with associated risk factors for dysglycemic hospitalization should be emphasized.Increased awareness,dedication of resources,and early intervention to prevent complications related to the management of diabetes is key to improving both the care of elderly patients and healthcare expenditure.The American Diabetes Association guidelines recognizes the need to incorporate geriatrics components into the assessment and management of diabetes[9].By recognizing the multiple risk factors in elderly T2DM patients identified in our study,a multidisciplinary approach[9,42,43]to the individualization of a patient’s optimal glucose level and its medical management can be performed.Future clinical practice improvements can then be compared to the prevalence rates identified in this study.
In conclusion,prevalence of dysglycemia-related hospitalization in elderly T2DM patients in Thailand was higher than developed countries at 4.9%.Elderly T2DM patients should be evaluated for risk factors of dysglycemia and may benefit from more frequent blood glucose monitoring and individualization of care in order to prevent dysglycemia-associated hospitalizations.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
The prevalence of older individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is increasing due to the aging population and improved medical care.These patients are very susceptible to disease and treatment-related hospitalizations,resulting in higher health care costs,morbidity,and decreased quality of life.However,data of treatment-related complications,especially dysglycemia-related hospitalizations,are lacking
Research motivation
This study would provide further support to the importance of regular monitoring of blood glucose,and glucose control should be individualized for the elderly T2DM patients.To further investigate the association between each variable and dysglycemia were assessed using multivariate logistic regression.Furthermore,it would motivate future research on whether more intensive monitoring of T2DM patients may allow earlier detection and prevention of dysglycemia-related hospitalization.The authors conducted a nationwide cross-sectional study based on the DM/HT study of the Medical Research Network of the Consortium of Thai Medical Schools.
Research objectives
We conducted this study to determine the prevalence and associated factors for hospitalizations due to dysglycemia among elderly T2DM patients in Thailand using nationwide patient sample.
Research methods
We conducted a nationwide cross-sectional study based on the DM/HT study of the Medical Research Network of the Consortium of Thai Medical Schools.This study evaluated adult T2DM patients from 831 public hospitals in Thailand in the year 2014.We examined the prevalence of hospitalization due to hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia.Hyperglycemia complication included diabetic ketoacidosis,hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state,and hyperglycemic dehydration syndrome.The association factors between dysglycemia-related hospitalizations were assessed using multivariate logistic regression.
Research results
In this study,a total of 11404 elderly T2DM patients were enrolled in this study.The mean age was 72.9 ± 5.5 years.The prevalence of hospital admission due to diabetic ketoacidosis,hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state,hyperglycemic dehydration syndrome,and hypoglycemia among elderly T2DM patients in the year 2014 was 0.1%,0.1%,1.7% and 3.1%,respectively.Increased hospitalization due to hypoglycemia was associated with older age,female sex,had hypertension,dementia,lower body mass index,elevated hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C),decreased kidney function,insulin use.Increased hospitalization due to hyperglycemia was associated with dementia,depression,lower body mass index,elevated HbA1C,and insulin use.
Research conclusions
We found that prevalence of dysglycemia-related hospitalization in elderly T2DM patients in Thailand had higher than developed countries.Elderly T2DM patients,especially in patients with associated factors,should be closely monitored blood glucose.
Research perspectives
Serial blood glucose monitoring should be recommended to prevent glycemic complications especially,in the elderly T2DM patients with associated factors cannot be over-emphasized.The early intervention to prevent further complications and adequate control of diabetes is a key to the reduction of complications of diabetes itself and treatment-related complications.Among elderly T2DM patients with multiple morbidities,the glucose control should be individualized.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank the Medical Research Network of the Consortium of Thai Medical Schools (MedResNet) Thailand which granted access to the diabetes and hypertension dataset in the DAMUS website (http://www.damus.in.th/damus/index.php).
 World Journal of Diabetes2019年3期
World Journal of Diabetes2019年3期
- World Journal of Diabetes的其它文章
- Do we need to screen every patient in intensive care unit for diabetes in community with high prevalence of diabetes?
- Optimized health care for subjects with type 1 diabetes in a resource constraint society:A three-year followup study from Pakistan
- Targeted genotyping for the prediction of celiac disease autoimmunity development in patients with type 1 diabetes and their family members
- Screening the RFX6-DNA binding domain for potential genetic variants in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Antidiabetic treatment on memory and spatial learning:From the pancreas to the neuron
- Crosstalk between gut microbiota and antidiabetic drug action
