68Gallium-labelled PSMA-PET/CT as a diagnostic and clinical decision-making tool in Asian prostate cancer patients following prostatectomy
Janice S.H. Tan, Charles X.Y. Goh, Yen Sin Koh, Youquan Li, Jeffrey K.L. Tuan,4, Eu Tiong Chua,4, Terence W.K. Tan,4, Michael L.C. Wang,4, Lui Shiong Lee , Kae Jack Tay Ravindran Kanesvaran, Chee Keong Toh,Aaron K.T. Tong, Winnie W.C. Lam, Melvin L.K. Chua,4,8
1Division of Radiation Oncology, National Cancer Centre Singapore, Singapore 169610; 2Department of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore 169610; 3Radiological Sciences Academic Clinical Programme, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore 169857; 4Oncology Academic Clinical Programme, Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore 169857; 5Department of Urology, Singapore General Hospital, Singapore 169610; 6Department of Surgery, Sengkang General Hospital, Singapore 544886; 7Division of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Centre Singapore,Singapore 169610; 8Division of Medical Sciences, National Cancer Centre Singapore, Singapore 169610, Singapore
ABSTRACT Objective:Prostate cancers (PCa) in Asian individuals are molecularly distinct from those found in their Caucasian counterparts.There is no risk stratification tool for Asian men with rapid biochemical recurrence (BCR) following radical prostatectomy(RadP). This study aims to assess the detection rate of 68Ga-prostate-specific membrane antigen-positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PSMA-PET/CT) for diagnosis of clinical recurrence and as a treatment decision making tool in Asian patients with BCR post-RadP.Methods:68Ga PSMA-PET and CT body with/without bone scan [conventional workup (CWU)] were performed in 55 Asian patients with BCR within 36 months post-RadP. Two blinded reviewers assessed the images. Detection rates of 68Ga PSMAPET/CT were evaluated, and impact on management was reviewed by comparison with CWU.Results:Median time to BCR post-RadP was 8.1 months. Detection rate for 68Ga PSMA-PET/CT was 80% (44/55). A positive scan was significantly associated with increasing prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level [odds ratio (OR) = 1.13 (95% CI 1.05-1.30), P =0.017], but not with higher Gleason grade or shorter PSA doubling time. Compared to CWU, 68Ga PSMA-PET/CT detected an additional 106 lesions in 33/44 patients with a positive scan, resulting in a change in management in 25/44 (56.8%) patients: 10 to hormonal therapy (HT) and whole pelvis radiotherapy (RT) in addition to bed RT, and 15 to palliative HT alone.Conclusions:In the present report, we demonstrated the diagnostic and treatment decision utility of 68Ga PSMA-PET/CT in Asian men with rapid BCR. Detection of small volume nodal and systemic recurrences at low PSA levels (< 1.0 ng/mL) highlights the role of the tool in assigning patients to treatment intensification with HT-RT or palliative HT in polymetastatic disease.
KEYWORDS 68Ga PSMA PET/CT; prostate cancer; Asian; diagnostic; recurrence; prostatectomy; salvage radiotherapy
Introduction
Approximately 20%-40% of men with prostate cancer experience biochemical recurrence (BCR) following radical prostatectomy (RadP)1. Salvage radiotherapy (RT) remains the only curative treatment, but the likelihood of success of this procedure ranges from 30% to 70% depending on several pre-salvage clinical factors, including prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level at recurrence, PSA doubling time, margin status, and Gleason score (GS)2-4. The results of two large randomized phase III trials have supported the idea that combining hormonal therapy (HT) and RT improves biochemical control rates5and potentially reduces prostate cancer-specific mortality6. However, there is still no optimal stratification process for assigning appropriate patients to this treatment intensification strategy7. Furthermore, as shown in the Radiotherapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 9601 study, the lack of survival benefit from the addition of HT in patients undergoing early salvage RT emphasizes the need for early identification of those with occult metastatic disease. In this present era of personalized medicine, in addition to molecular tests with the ability to predict individual risk of distant metastases and the likelihood of benefit from salvage RT, high-resolution precision imaging represents another attractive avenue for detecting small volume metastases and potentially guiding clinical management.
68Gallium-labelled prostate specific membrane antigen ligand positron emission tomography-computed tomography (68Ga PSMA-PET/CT) has demonstrated promise as a superior imaging technique with high sensitivity and specificity in detecting small regional and distant metastases, even in patients with low PSA levels8-11. Thus,68Ga PSMA-PET/CT has also been explored as an early clinical decision-making tool. For example, identification of regional nodal metastases by68Ga-PSMA-PET/CT imaging could warrant treatment intensification with salvage RT to the pelvic nodal basin and prostate bed, in combination with HT12. In another emerging clinical scenario, detection of low volume metastatic lesions (oligometastatic disease) by68Ga PSMA-PET/CT could warrant local ablative therapies with either surgery or stereotactic body RT (SBRT) alone or in combination with HT13. Additionally, as salvage RT can only be curative if the recurrent disease is fully encompassed within the irradiated target volume, accurate localization of disease is crucial, and this exact localization of the disease site can be substantially improved with the use of68Ga PSMAPET/CT14.
Given its proposed clinical utility in numerous scenarios,there has been an acute increase in the number of studies aimed at characterizing the role of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT in prostate cancer diagnosis, but reports focusing on the Asian population are lacking. It is thus crucial to investigate the potential variation in68Ga PSMA affinity in prostate cancers in Asian individuals, particularly given the distinct molecular genotype of prostate cancers in individuals of Chinese ethnicity compared to those in Caucasian individuals15. To address this lack of data, we recruited a cohort of Asian men who experienced rapid BCR (defined as ≤ 36 months post-RadP) and underwent68Ga PSMA-PET/CT. We assessed the detection rate of this imaging modality for regional and distant metastases, as well as its utility in guiding treatment decisions for patients within our demographic of interest.
Materials and methods
Patient cohort
The present study was a retrospective review conducted in a single academic institution. Study participants were 55 consecutive patients with histologically proven prostate cancer who experienced BCR (defined as two consecutive increases of PSA > 0.2 ng/mL) within 36 months following the performance of RadP with curative intent. Patients with early BCR (PSA < 0.2 ng/mL), who were expected to receive early salvage RT, and underwent68Ga PSMA-PET/CT imaging prior to salvage treatment were also included. Other clinical information collected included patient demographics;pathological data such as pT and pN category, GS, and surgical margin status; PSA at time of relapse; and type of salvage treatment received. Ethical approval for the study was obtained from Singhealth Institutional Review Board (CIRB Ref. No: 2015/2444).
Conventional workup (CWU)
CWU included CT imaging of the thorax, abdomen, and pelvis, with or without skeletal scintigraphy to reveal potential sites of disease recurrence. Contrast-enhanced CT was performed in all patients, except in situations when contrast was contraindicated, such as in patients with impaired renal function, severe contrast media allergy, etc.CT imaging was performed using a 64-slice CT scanner, an element of the GE Discovery 690 PET/CT scanner (GE Healthcare, Waukesha, WI, USA). CT findings were interpreted by the attending radiologists. Skeletal scintigraphy was performed using a dual-head gamma camera, conducted at an interval of at least 3 hours after injection of 740 MBq of technetium-99m methylene diphosphonate.
68Ga PSMA-PET/CT image acquisition
68Ga PSMA-PET/CT images were acquired from the vertex to the upper thighs 60 minutes post injection with68Ga PSMA-11 with acquisitions of 2 minutes per bed position. The injected dose was 2 MBq/kg. Clinical data and digital imaging and communications in medicine (DICOM) files of all patients were imported onto a radiotherapy contouring software (Velocity v3.2, Palo Alto, CA, USA).
Image interpretation and delineation
All68Ga PSMA-PET/CT images were analyzed by two blinded independent nuclear medicine assessors (CG and WL) according to a recently published consensus16. There was no maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax)cutoff used to define a positive result; focal uptake of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT above surrounding background, and not associated with physiological uptake or known pitfalls (e.g.,hepatic lesions with equivocal signal) was considered suspicious for malignancy. Lesions suspicious for recurrent disease were identified and grouped as follows: 1) local recurrence, 2) regional and non-regional lymph node metastases, 3) bone metastasis, and 4) visceral metastasis(e.g., lung, liver). All68Ga PSMA-PET/CT-positive lesions were then contoured onto a template CT image to map out the pattern of relapses. Interobserver variability was addressed by obtaining an independent review by a third nuclear medicine physician (AT) in cases of discordant reporting between the two assessors (CG and WL). Intraobserver variability was addressed by ensuring that the two main assessors were highly experienced (previous review of >1068Ga PSMA-PET/CT imaging cases); all assessors adhered to the joint European Association of Nuclear Medicine(EANM) and Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (SNMMI) procedure guidelines for the recommendation, performance, interpretation, and reporting of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT data for prostate cancer.
Potential impact of 68Ga PSMA PET/CT on clinical decision making
68Ga PSMA-PET/CT was then compared to CWU to determine the number of “additional lesions” that were detected on68Ga PSMA-PET/CT, and the impact of these findings on clinical treatment. “Additional lesions” were classified based on the following criteria: 1) nodes not fulfilling the conventional CT size criteria that were positive on68Ga PSMA-PET/CT; and 2) skeletal or visceral lesions that were only positive on68Ga PSMA-PET/CT. For the present analysis, we focused on the following clinical pathways: 1) switching from prostate bed RT alone to whole pelvis RT (WPRT) combined with HT in pelvic nodal relapses, 2) salvage RT to palliative HT alone due to polymetastatic disease, and 3) SBRT to oligometastases(defined as ≤ 5 lesions)17. In addition, pelvic nodal recurrences detected by68Ga PSMA-PET/CT were contoured on a template CT image and matched against the RTOG consensus clinical target volume (CTV) borders to assess the adequacy of the WPRT coverage according to these guidelines18,19.
Statistical considerations
All statistical analyses were performed using RStudio version 1.1.423 (with R version 3.4.3). Univariable logistic regression was used for tests of associations between clinical factors of pathological T- and N-category, GS, or International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grade obtained from a grading system for prostate cancer based on GS20, surgical margin status, interval between RadP and BCR, PSA level,and doubling time at the time of imaging with the likelihood of a68Ga PSMA-PET/CT positive result. The interval between RadP and BCR, PSA level, and doubling time were considered continuous and categorical variables; the interval between RadP and BCR was dichotomized as ≤ 6 months and> 6 months; PSA levels were categorized as < 0.5 ng/mL,0.5-1.0 ng/mL, > 1.0-2.0 ng/mL, and > 2.0 ng/mL; PSA doubling time was dichotomized as ≤ 9 months and > 9 months based on the association of this cutoff with prostatecancer-specific mortality21. All P-values were 2-sided, and significance was defined as α = 0.05.
Results
Clinical characteristics of Asian prostate cancers
Supplementary Table S1 summarizes the clinical and pathological characteristics of the 55 study patients. Median age was 69.1 [interquartile range (IQR) = 64.3-73.3] years and median follow-up from time of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT was 7.79 (IQR = 4.64-12.59) months for the cohort. Notably, a substantial proportion of patients harbored high-risk pathological characteristics such as pN+ (n = 7), GS ≥ 8 (n =16), and R0 disease (n = 25). Median PSA level at the time of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT scan was 2.19 (IQR = 0.53-4.57) ng/mL.Median interval from RadP to BCR was 8.1 (IQR = 1.9-33.8)months, an interval reflecting an unfavorable subgroup of patients. Regarding salvage therapies, 10.9% (n = 6) of patients received RT alone, 36.4% (n = 20) received combination HT-RT, and 23.6% (n = 13) received HT alone;the remaining 16 patients either underwent observation or were lost to follow-up.
Performance of 68Ga PSMA PET/CT in detecting clinical recurrences postprostatectomy
Overall, 44 (80%) of 55 patients had a positive68Ga PSMA PET/CT scan. We detected a total of 168 PET-positive lesions. Of these, 10 (6.0%) were local, 63 (37.5%) were nodal, 81 (48.2%) were skeletal, and 14 (8.3%) were visceral(Figure 1, Table 1). Detection of metastases was associated with increasing PSA at the time of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT scan[odds ratio (OR) 1.13 per 0.1 ng/mL increase, 95%confidence interval (CI) = 1.05-1.30, P = 0.017], but not with other adverse features including GS (P = 0.50) and decreasing PSA doubling time (P = 0.36) (Table 2). When stratified by PSA levels at the time of scan, 11 (of 21 patients, 52.4%) had a positive68Ga PSMA PET/CT scan with a PSA level of ≤ 1.0 ng/mL; among the lesions detected in this group, the majority were skeletal (26 of 81; Table 1). Of these lesions,none were detected by CWU. However, 17 of the 26 skeletal lesions were identified in a single patient.
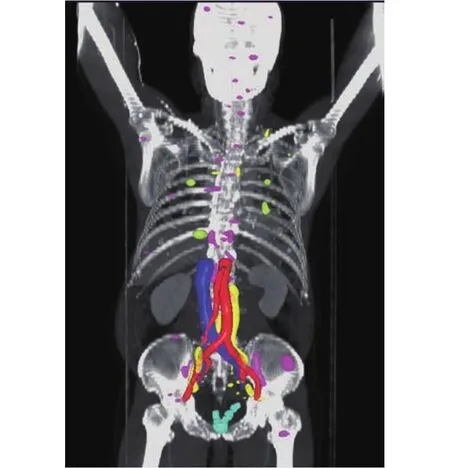
Figure 1 3D map rendering of all 68Ga PSMA-PET/CT-positive lesions according to sites of disease recurrence. Light blue =prostate bed, yellow = lymph nodes, magenta = bone, green =visceral.
Impact of 68Ga PSMA-PET/CT on recommendation of salvage therapies
Compared to conventional imaging,68Ga PSMA-PET/CT detected additional lesions in 33 (of 44 patients with a positive scan; 75%) patients (Table 3). Of these lesions, the 106 additional68Ga PSMA-PET/CT lesions prompted a change in management in 25 (of 44; 56.8%) patients: 10 patients who had pelvic nodal relapses received WPRT and combination HT, while 15 patients with distant metastases were referred for palliative HT only. Additionally, taking into account the emerging approach of targeted ablative therapy of lesions in the oligometastatic setting22, 7 of the 15 patients with metastasis designated as oligometastatic disease (defined as ≤ 5 lesions)23would have been candidates for local ablative therapy to the metastatic lesions in addition to HT.
68Ga PSMA-PET/CT guide delineation of radiotherapy coverage of pelvic nodal recurrences
We next determined the adequacy of an existing consensus guideline18,19for delineation of pelvic nodal stations for WPRT based on the locality of regional nodes detected by68Ga PSMA-PET/CT. We observed that 13 of 33 (39.4%)regional nodal metastases that were detected by68Ga PSMAPET/CT fell outside of the consensus CTV borders (Figure 2,Table 4). Of these, 7 were common iliac nodes, 4 were localized to the obturator regions, and 2 to the perirectal regions. In particular, all of the common iliac nodes were located “out-of-field” in the L4-5 intervertebral space(Figure 2).
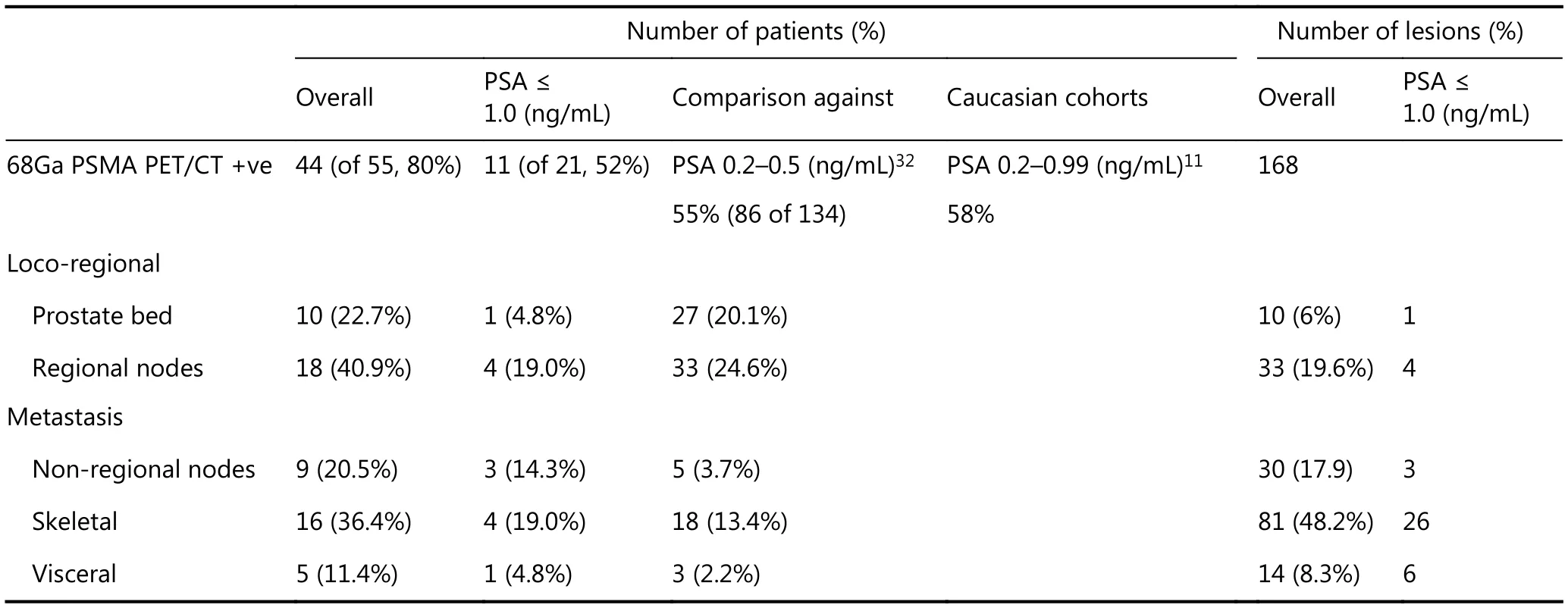
Table 1 Number of patients and lesions detected by 68Ga PSMA-PET/CT and sites of relapses in comparison with Caucasian cohorts
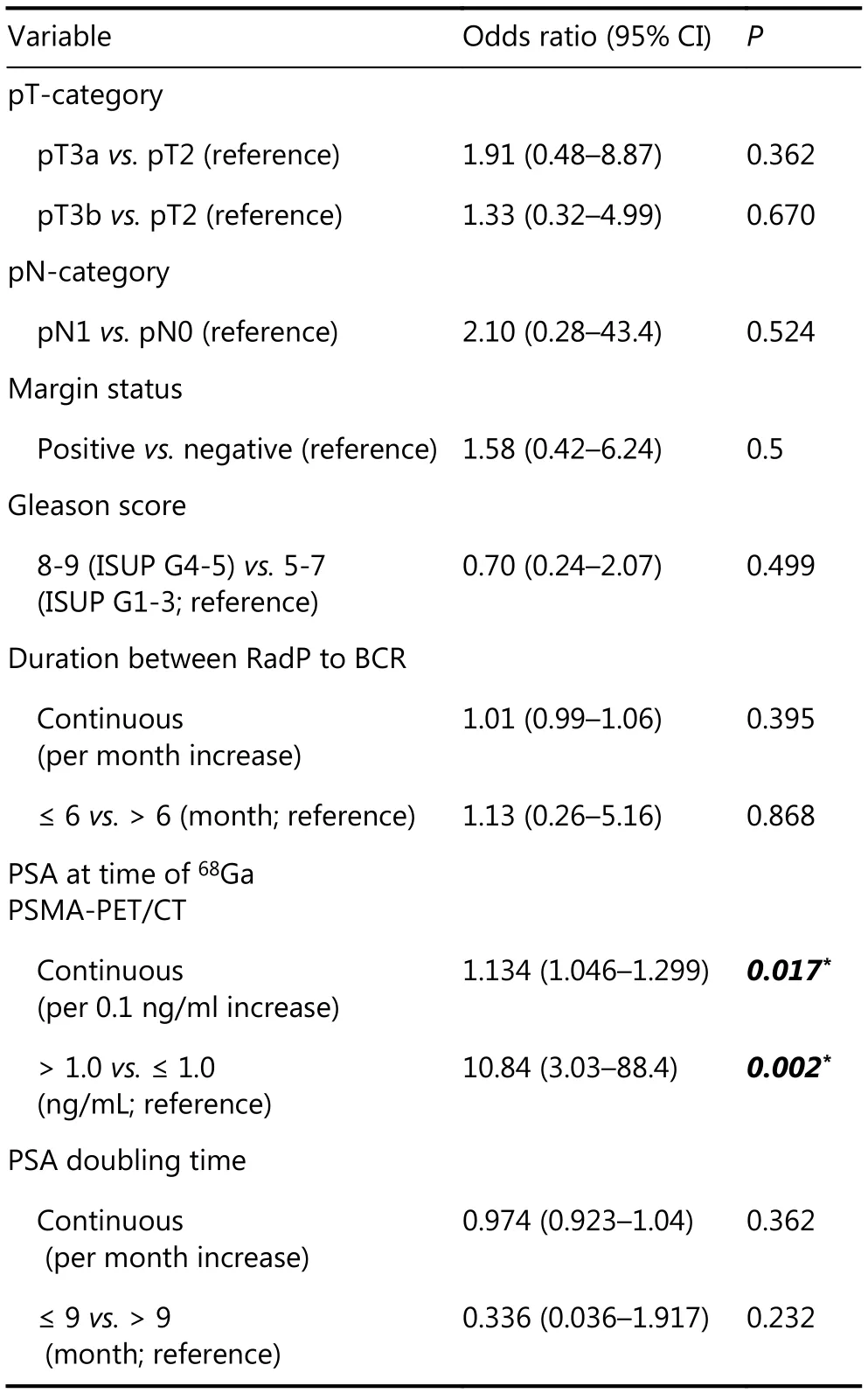
Table 2 Association of clinical covariates with likelihood of detection by 68Ga PSMA-PET/CT
Discussion
Patients with localized prostate cancer who experience BCR following definitive local therapy (RadP or RT) represent a clinically heterogeneous subgroup with distinct disease trajectories24,25. At present, conventional clinical stratification using high-risk clinicopathological indices is imprecise, and thus identification of robust clinical biomarkers is essential. Apart from molecular tests,ultrasensitive imaging capable of detecting small volume metastases is emerging as a promising new method for accurate patient risk estimation. In this domain, several retrospective series10,26-31have explored the role of PET using a variety of tracers (e.g.,11C/18F Choline,18F-NaF,68Ga PSMA, etc.), and these studies have consistently reported that molecular imaging offers substantially more information on patterns of relapses compared to conventional CT, MRI, and bone scan. However, limited, if any, data have been reported from an Asian cohort of patients with prostate cancer. In the present study cohort of 55 Asian men with rapid BCR post-RadP, we observed an 80% detection rate for local and systemic clinical recurrences with68Ga PSMA-PET/CT,comparable to the findings of a recent meta-analysis comprising predominantly Western patients11. Additionally,at PSA levels of ≤ 1.0 ng/mL we observed a 52.4% detection rate, similar to the results of the largest study cohort reported to date (n = 272)32. Among the conventional adverse clinicopathological indices, serum PSA level at the time of imaging was the only predictor of a positive scan (Table 2).Collectively, the findings from this and other studies highlight the superiority of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT for low volume early disease detection in biochemically recurrent prostate cancer.
The sensitivity of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT at low PSA levels suggests the possibility of incorporating this imaging modality into a clinical decision making algorithm for patients under consideration for early salvage RT. Moreover,as shown in Table 3, our study revealed the following key observations: 1) Of the additional 106 lesions that were detected, the majority (≈75%) from 15 patients were indeed systemic metastases (Figure 1), which would have rendered salvage RT alone ineffective; 2) nonetheless, about half of these patients had low burden disease, and thus could be candidates for prospective clinical trials investigating the role of local ablative therapy in oligometastatic prostate cancer; 3)among the 32 locoregional lesions detected, more than half were nodal recurrences, which would have necessitated the addition of combination HT and WPRT to RT of the prostate bed; 4) along these lines, we also showed that68Ga PSMA-PET/CT could actually improve WPRT coverage by nearly 40% against a consensus contouring guideline (Table 4, Figure 2). Taken together, our findings support routine usage of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT prior to salvage RT, at least in men with high-risk disease (pT3b, GS 8-10, margin negative,suboptimal lymph node dissection, and a post-RadP PSA of> 0.5 ng/mL). However, it is important to acknowledge that the detection threshold of PSMA-PET may differ in the de novo and post-surgery BCR setting; this situation may result in part from the presence of the prostate gland in the former scenario, which may influence the detection sensitivity of occult metastases at distant sites. Therefore, conclusions regarding the evaluation of this imaging modality for de novo staging should not be extrapolated based on the findings of the current study.
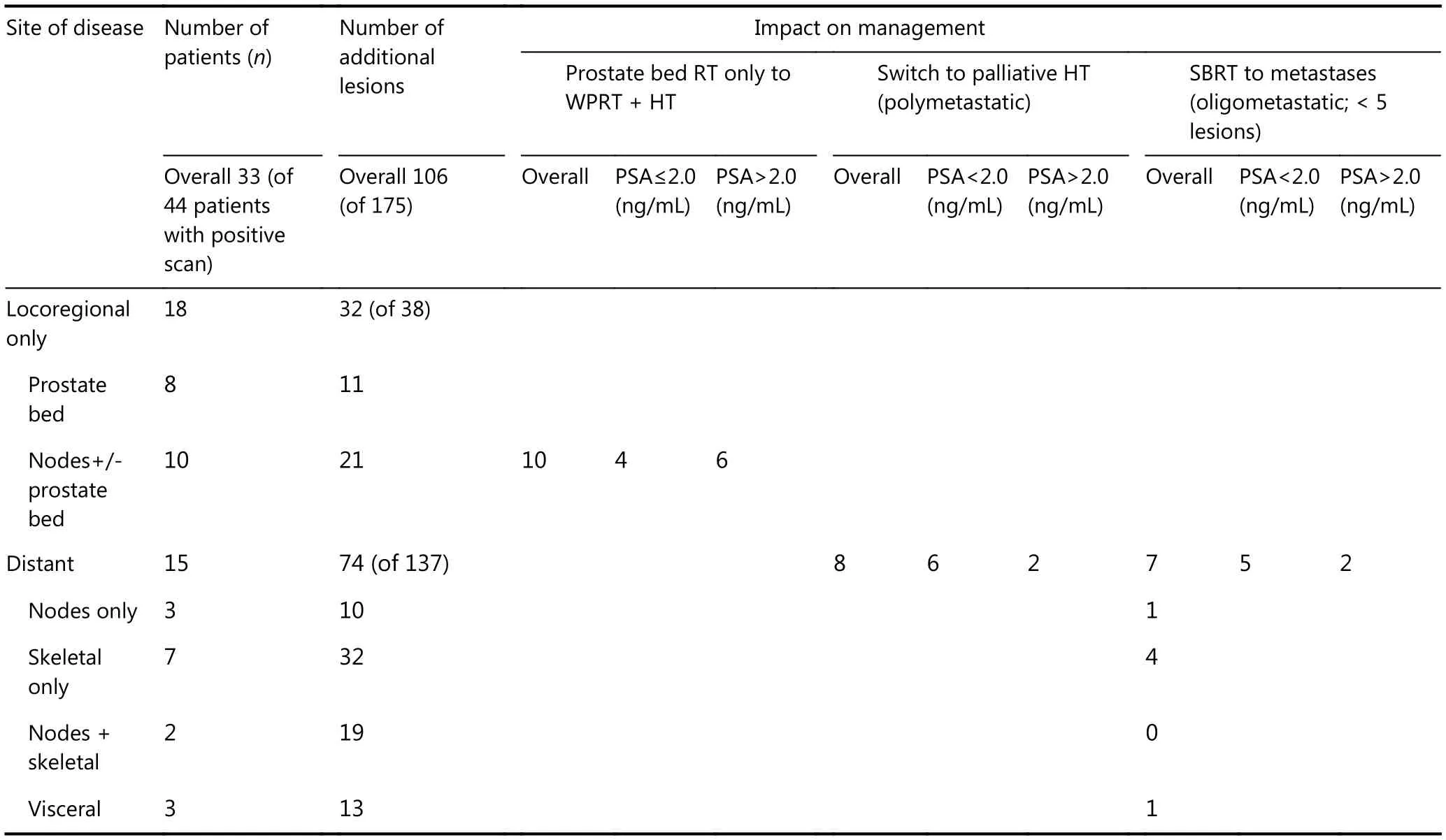
Table 3 Summary of additional lesions detected by 68Ga PSMA PET/CT, and the influence on subsequent treatment
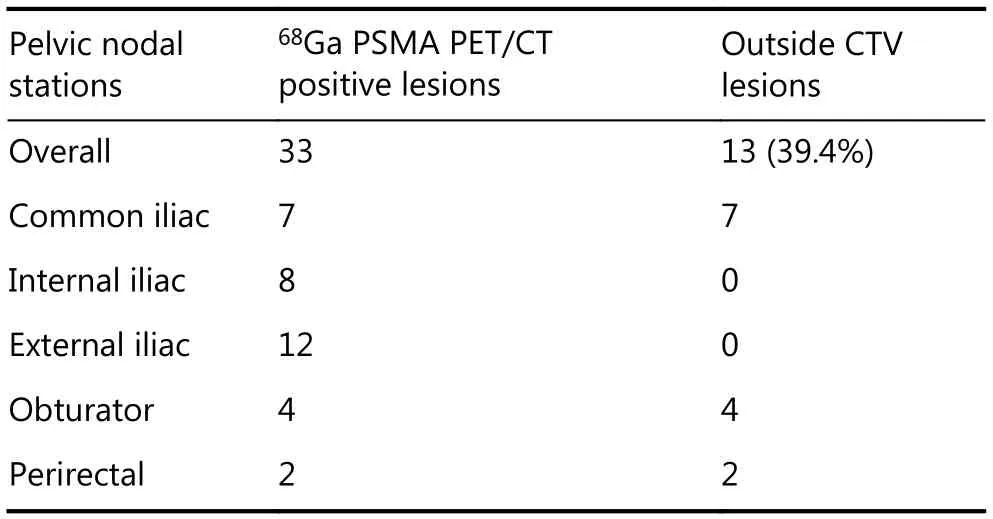
Table 4 Pelvic nodal recurrences by anatomic regions, including number of lesions that fall outside of the consensus clinical target volume (CTV) borders18,19
The main limitation of our study is the paucity of data regarding the true sensitivity and specificity of68Ga PSMAPET/CT, owing to the lack of histopathological confirmation of the PSMA-positive lesions, although it is arguable whether biopsy confirmation is clinically indicated in the presence of consecutive PSA increases and the co-occurrence of multiple68Ga PSMA-PET/CT-positive lesions. Moreover, targeted biopsies of the prostate bed and nodal recurrences (68Ga PSMA-PET/CT-positive nodes are often < 1 cm) can be technically challenging. Another limitation relates to the predominance of Chinese individuals in our prostate cancer cohort. It remains to be seen if PSMA expression and68Ga PSMA affinity vary between prostate cancers found in different racial groups; notably, it has been shown that prostate cancers found in African-American individuals are molecularly distinct from those found in Caucasian white individuals33,34. In the same vein, a recent study reporting on whole genome sequencing of 65 prostate cancers in Chinese individuals revealed several obvious differences compared with genomic profiling studies from Western cohorts; in particular, a lower frequency of the TMPRSS2-ERG fusion mutation (< 10%), and high frequencies of allelic PCDH9 losses (23%) and PLXNA1 gains (17%) that were unique characteristics of Chinese tumors15. Finally, our evaluation of the clinical impact of68Ga PSMA-PET/CT was not based on a prospectively designed clinical workflow, and did not consider the eventual survival outcomes of patients.However, such an analysis will require long-term follow-up in the context of a prospective clinical trial.
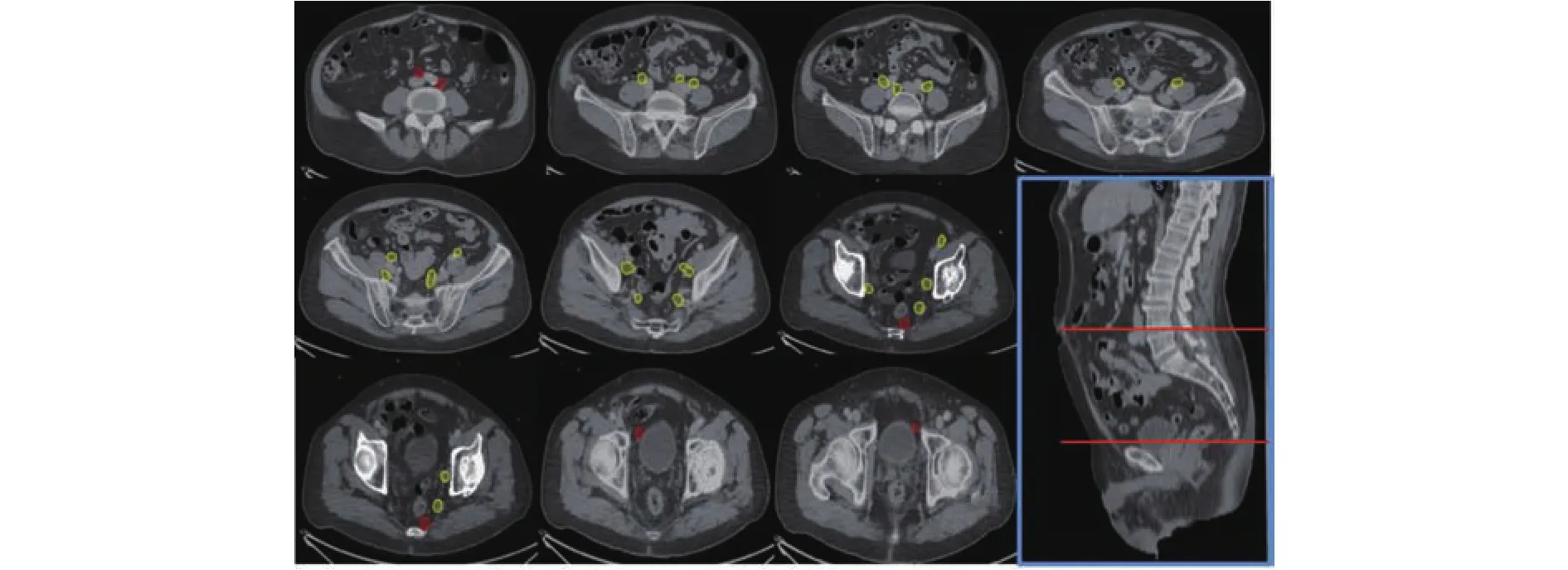
Figure 2 Locality of all pelvic nodal metastases detected by 68Ga PSMA-PET/CT. Yellow contours represent lesions within the consensus clinical target volume (CTV) borders, while red contours represent those not covered by the consensus CTV18,19.
Conclusions
In the present study, we demonstrated that68Ga PSMAPET/CT is a highly effective imaging tool for small volume and occult metastases in Asian men with prostate cancers who experience rapid BCR post-surgery. Importantly, we highlighted the significant impact of the improved detection achieved with this tool on clinical management. Precision treatment of this subgroup of men with unfavorable clinical characteristics could eventually entail the incorporation of contemporary molecular assays and imaging to allow more accurate clinical prognostication and to guide more individualized therapeutic approaches.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Varian, Paolo Alto, CA through a structured research agreement. MC is supported by the National Medical Research Council Singapore Clinician-Scientist Award (Grant No. NMRC/CSA/0027/2018), and the Duke-NUS Oncology Academic Program Proton Research Program. This work was presented in part at the ESMO Asia Congress 2017 and ASCO GU Symposium 2018.
Conflict of interest statement
This work is supported in part by Varian through a structured research agreement. MC reports speaker's fees from Astellas, speaker's fees from Janssen, grants and speaker's fees from Ferring, non-financial support from Astrazeneca, speaker's fees and non-financial support from Varian, grants from Sanofi Canada, grants from GenomeDx Biosciences, non-financial support from Medlever, outside the submitted work.
 Cancer Biology & Medicine2019年1期
Cancer Biology & Medicine2019年1期
- Cancer Biology & Medicine的其它文章
- Application of next-generation sequencing technology to precision medicine in cancer: joint consensus of the Tumor Biomarker Committee of the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology
- Methods of computed tomography screening and management of lung cancer in Tianjin: design of a population-based cohort study
- Reactive capillary hemangiomas: a novel dermatologic toxicity following anti-PD-1 treatment with SHR-1210
- Perioperative rh-endostatin with chemotherapy improves the survival of conventional osteosarcoma patients: a prospective non-randomized controlled study
- Identification of portal vein tumor thrombus with an independent clonal origin in hepatocellular carcinoma via multi-omics data analysis
- Clinicopathologic and molecular characteristics of 44 patients with pure secretory breast carcinoma
