Multiplex gene expression profile in inflamed mucosa of patients with Crohn’s disease ileal localization:A pilot study
Francesco Giudici,Letizia Lombardelli,Edda Russo,Tiziana Cavalli,Daniela Zambonin,Federica Logiodice,Ornela Kullolli,Lamberto Giusti,Tatiana Bargellini,Marilena Fazi,Livia Biancone,Stefano Scaringi,Ann Maria Clemente,Eloisa Perissi,Giovanni Delfino,Maria G Torcia,Ferdinando Ficari,Francesco Tonelli,Marie-Pierre Piccinni,Cecilia Malentacchi
Abstract
Key words: Crohn’s disease;Ileum;Colon;Messenger ribonucleic acid;Th1/Th17;Microbiota;Inflammation
INTRODUCTION
The pathogenesis of Crohn’s disease (CD),one of the major inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) together with ulcerative colitis (UC),has been extensively investigated.It is generally accepted that both genetic and environmental factors contribute to the etiology of the disease.In CD patients,strong associations between genes involved in maintaining intestinal barrier function,epithelial anti- microbial defence,innate immune regulation,reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation,autophagy,and metabolic pathways have been identified[1,2].
Environmental risk factors involved in the progression of the disease include smoking,low-fiber and high-carbohydrate diet,gut microbiota (GM) alteration,and treatments with antibiotics or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs[3].
CD is characterized by a transmural inflammation which can potentially affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract[4].However,recent studies reported a selective location in the terminal ileum in 50% of the patients and location in the colonic district in 20% of the patients.Ileum and colon district were involved in the remaining 30% of the patients.A different clinical course and surgical requirement was reported according to disease’s localization but currently the reasons underlying the differences in the clinical course have not been defined.In addition,the immunological pathways involved in colonic inflammation are different from those involved in ileal inflammation[5].
The mutual interplay between GM and the immune system is involved in the pathogenesis and prognosis of intestinal diseases[6]as the GM is a key modulator of intestinal inflammation[7].In CD patients,a reduced GM diversity and lower bacterial load in inflamedvsnon-inflamed tissues was observed[8].In addition,several evidences report that the small bowel is responsible for the systemic tolerance towards microbes.A recent study revealed that the ileum harbors a distinctive niche of the GM that differs more from the colonic[9].This different GM composition could be attributed to the activation of distinctive immunological pathways.
In the present study,we used the multiplex gene assay[10,11]to analyze surgical specimens of CD patients with prevalent ileal localization.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patients
14 consecutive patients undergoing surgery for ileal CD aged 15 to 57 and hospitalized at the Surgery Unit of Azienda Ospedaliero-Universitaria Careggi,University of Florence,were recruited (Table 1).CD was diagnosed based on both histological and clinical/endoscopic criteria.Table 1 reports the clinical characteristics of the patients.
Peripheral blood samples from each patient were collected in EDTA tubes and genomic DNA was extracted using QIA-AMP DNA Blood Maxi Kit (Qiagen GmbH,Hilden,Germany).The main polymorphisms of the geneCard15/Nod2(R702W,G908R,and 1007fs) were analysed in each sample[12].
mRNA extraction and multiplex Gene Assay
Tissue samples were taken both from the tract affected by CD and from the apparently healthy and disease-free margins (internal controls).The surgical specimens were opened longitudinally.
All samples were stored in RNA later (Qiagen,Germany) before homogenization.Then each sample was weighed and the appropriate lysis solution was added to a final volume of 150 μL containing 50% Lysis Mixture (Thermo-Fisher,MA,United States) and 1 g/L proteinase.The mixture was agitated for 30 min at 65 °C to lyse the cells.The lysate was stored at -80 °C for later use.We used a microarray panel of 24 genes implicated in CD etiopathogenesis[10].We evaluated the expression of these genes in both non-inflamed and inflamed ileal biopsies.Table 2 indicates the panel of the examined genes,the number of Mendelian Inheritance in Man (MIM) (used as a reference),accession number and their corresponding encoded product and function.To improve the analysis of the results,the selected genes were divided into four groups according to their biological role:(1) Transport across epithelia:ABCB1,SLC40A1,SLC22A4,SLC22A5,HAMP;(2) Immune response:CCR6,IL-17F,IL-17A,MICA,MYD88,STAT3,IL-23R,JAK2,IFNG,NOD2;(3) Antimicrobial activity:HAMP,CAMP,LRRK2.DEFB4;and (4) Physiological activities:STAT3,ESR1,LRRK2,TNFSF15,CARD14,DLG5 BMP2 ATG16L1.
The messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) expression forCCR6,IL-17A,IL-17F,BMP2,TNFSF15,ABCB1,IL-23R,DEFB4,CARD14,STAT3,SLC40A1,JAK2,SLC22A5,ACTB,ATG16L1,CAMP,DLG5,ESR1,CARD15,MICA,MYD88,SLC22A4,IFN-γ,LRRK2,HAMP,ACTB(high expression housekeeping gene),HPTR1(low expression housekeeping gene) was measured using the QuantiGene?Plex assay (Thermo-Fisher,MA,United States).
A panel of oligonucleotide capture probes was covalently linked to carboxylated fluorescently encoded beads (Luminex,Bio-Rad,MA,United States).Each probe has a unique sequence of 15 bases.Each sample lysate diluted at 1:1 and 1:2 was mixed with the pooled capture beads in a round-bottom assay well and hybridized for 16 h at 54°C (final volume in each well was 100 μL).The assay mixture was moved to a MultiScreen?Filter Plate (Millipore,Billerica,MA,United States) and unboundmaterial was filter-washed from the wells by rinsing 3 times with wash buffer.The plate was hybridized with 100 μL/well of bDNA amplifier in Amplifier Diluent(Panomics,CA,United States) at 54 °C for 1 h.After the plate was filter- washed twice with wash buffer and incubated at 50 °C for 1 h with 100 μL/well of 5’-dT(Biotin)-conjugated label probe (Panomics,CA,United States) diluted in Label Probe Diluent(Panomics,CA,United States).After 2 washes,streptavidin-conjugated Rphycoerythrin diluted in SA-PE diluent (20 mmol/L Tris-HCl,400 mmol/L lithium chloride,1 mL/L Tween 20,1 mL/L bovine serum albumin,and 5 mL/L Micr-Oprotect) was added and the plate was shaken and incubated at room temperature for 30 min.We washed the beads to remove unbound SA-PE and then evaluated them with Bio-Plex?200 system (Bio-Rad,MA,United States).The SA-PE fluorescence measured from each bead was proportional to the number of mRNA transcripts captured by the beads.Expression of target-specific RNA molecules was calculated as the mean values from triplicate cultures and normalized againstActingene (high expression housekeeping gene).

Table1 Clinical characteristics of patients with ileal Crohn’s disease
Polymorphism analysis
A standard non-enzymatic method,using the QIA-AMP?DNA Blood Maxi Kit(Qiagen GmbH,Hilden,Germany) was used to extract Genomic DNA from peripheral blood leucocytes of all CD patients and healthy controls.In addition,DNA samples from 70 healthy Caucasian subjects (140 alleles) were analysed as controls.Three exon of theCARD15/NOD2gene (Exon 4,Exon 8,Exon 11),were amplified by PCR using pairs of primers derived from the published sequence of the gene(available upon request).Each exon is associated with the three main singlenucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (R702W-C2104T;G908R-G2722C;1007fs-3020insC).These three main variants,associated with susceptibility to CD,represented 32%,18%,and 31%,respectively,of the total CD mutations[13-15].
The BigDye?Terminator Cycle Sequencing kit (Applied Biosystems,CA,United States) was used to perform direct sequencing of PCR amplified products (SNPs rs87950,rs127951,and rs137955) of theCARD15/NOD2gene.The samples were analysed in an ABI Prism?310 genetic analyzer (Applied Biosystems,CA,United States).The of the sequences were confirmed with the analysis of newly-amplified fragments and the sequencing of both DNA strands.
Statistical analysis
SSPS software vers.10 (SPSS Inc.,IL,United States) was used to perform the statistical analysis.All comparisons of genes mRNA expression in tissues (non-inflamed and inflamed areas) were performed by non-parametric assay (Mann-Whitney test,Wilcoxon test).Data are reported as mean and ranges unless otherwise stated.APvalue < 0.05 was accepted as statistically significant.Furthermore,to better characterize the different clinical CD phenotypes,we compared the results regarding theCARD15,CCR6,interferon gamma,andIL-17Agenes to colonic CD patients previously examined for these same genes.

Table2 Panel of the 24 genes investigated

MIM:Mendelian Inheritance in Man.1:Transport across epithelia;2:Immune response;3:Antimicrobial activity;4:Different physiological activities.
Histological analysis
Once removed,tissue samples were rinsed in 0.1 M,pH 7.0 cacodylate buffer,the same used in prefixation and further steps of histological preparation.Samples were then placed in Karnovsky (1965)[16],aldehyde solution,and after 3 h prefixation (4°C),underwent prolonged washing in the buffer.Surgery specimens were reduced into approximately 20 mm3fragments that were post-fixed (1 h 30 min,4°C) with 1% OsO4 in cacodylate.These specimens were washed in the buffer,dehydrated in graded ethanol series,soaked in propylene oxide,and embedded in Epon 812.Flat blocks were obtained after polymerization,which were reduced into semi-thin sections (1.5μm thick),using an 8800 ULTROTOME III LKB equipped with glass knives.Semi-thin sections were stained with borax buffered 1% toluidine blue,and observed with a LEITZ DMRB,in order to collect LM digital images (JPG) for structural analysis.Subsequent ultrastructural observations were carried out on ultrathin sections,obtained with an ULTROTOME NOVA LKB,using a DIATOME diamond knife.Ultrathin sections with gold yellow to silver gray interference colour were selected and collected on uncoated 200-300 mesh copper grids to be electron-dense stained with a hydroalcoholic saturated solution (25 mg/mL) of uranyl acetate,followed by alkaline lead citrate (2 mg/mL).These sections where finally observed (80 KV) with a PHILIPS 201 TEM (BIO,UNIFI),and analogic images were collected,which were later acquired and stored as digital TIFF files using a DIMAGE SCAN DUAL (MINOLTA).
RESULTS
Expression of CD susceptibility genes in the inflamed ileum tissue
The simultaneous expression of 24 genes involved in the pathogenesis of CD was studied in surgical specimens from 14 CD patients with ileal localization of disease.The expression of genes in inflamed ileal mucosa was compared to that of noninflamed ileal sites collected from the same patient.We observed a significant increase in mRNA levels of twelve genes compared to internal control (Figure 1).
Figure1 shows that genes related to innate immune response (NOD2,ATG16L1,DEFB4),and to adaptive immune response (CCR6,IL17A,IL17F,IL23R,IFN-γ) were significantly increased in inflamed mucosa of CD patients compared with noninflamed sites.Moreover,the levels of mRNA for genes involved in physiological functions of epithelial cells,such asJAK2,TNFSF15,andSLC22A4were higher in inflamed mucosa compared to non-inflamed mucosa and the differences in expression reached statistical significance.
Detection of CARD15 polymorphism
DNA samples obtained from peripheral blood were sequenced to investigate the presence of polymorphisms ofCARD15/NOD2gene.The results of this analysis showed that four patients (28.5%) included in this study are carriers of at least one of the polymorphisms investigated,suggesting that genetic factors might contribute to the dysregulated expression ofCARD15/NOD2gene[17-19].

Figure1 Quantitative evaluation of gene expression using multiplex gene assay in surgical ileum specimens of CD patients.
Morphological analysis
In order to observe the morphology of inflamed tissue samples,light microscopy(LM) and TEM micrographs were obtained.Both gut wall and Lieberkühn crypts retain usual features in both lining epithelium andlamina propria.Epithelial cells consist of constitutive enterocytes along with goblet mucocytes,whereas the underlying connective tissue contains large amounts of cells with wide morphological variety (Figure 2).Goblet cells are involved in impressive secretory processes,releasing a moderately opaque product into cryptal and gut lumen through gaps between enterocytes apices (Figure 3).As a consistent pattern,the lamina propria contains granulocytes and plasma cells.
DISCUSSION
Among the numerous genes that have been studied so far with respect to CD,strong and replicated associations have been identified withNOD2,IL23R,andATG16L1genes[20].Environmental factors like smoking,low-fiber and,high-carbohydrate diet,altered GM,and medications such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs interact with genetic background and induce abnormal inflammation and dysregulation of the immune response.Clinical symptomatology relates to such dysregulation.
The clinical course of CD is conditioned by several parameters such as disease location,extra-intestinal manifestation,and age at onset[21].Strictures and fistulas are more frequent in patients with ileal disease,whereas Crohn's colitis remains uncomplicated for many years.On the whole,almost 80% of patients with CD require intestinal surgery,with a permanent stoma required by almost 10%.The presence of selected mutations in theNOD2gene (see,e.g.,605956.0001-605956.0003) (IBD1;266600) has been associated with susceptibility to ileum-localized CD[22];patients homozygous for the 1007fs mutation had an early disease onset with long-segment ileal stenoses and entero-enteral fistulas;they frequently needed surgical intervention and had a high risk of recurrence[23,24].BesideNOD2gene,huge genome-wide linkageanalyses and meta-analyses have described several CD susceptibility regions including IBD5 locus,DLG5,and autophagy- related 16-like 1 (ATG16L1) gene,JAK2,STAT3 interleukin-23 receptor (IL23R),SLC22A4 and SLC22A5 TNFSF15[14].
In this paper,we evaluated the expression of 24 genes that were associated to CD susceptibility[10].mRNA was extracted from gut specimens obtained from patients with CD ileal localization of CD,undergoing surgery.We used a multiplex gene assay which directly quantifies the mRNA amounts without need of reverse transcription and gives a detailed picture of the inflammation process for each patient[11].The same technique was used to quantify gene expression in colonic mucosa from surgical specimens or endoscopic bioptic fragments obtained by CD patients with predominant colonic (L2) location[10].
The analysis revealed a clear activation of immune-adaptive Th17 response in association with a Th1 response in inflamed mucosa of patients undergoing surgery suggesting a dysregulated and very aggressive immune-inflammatory response.
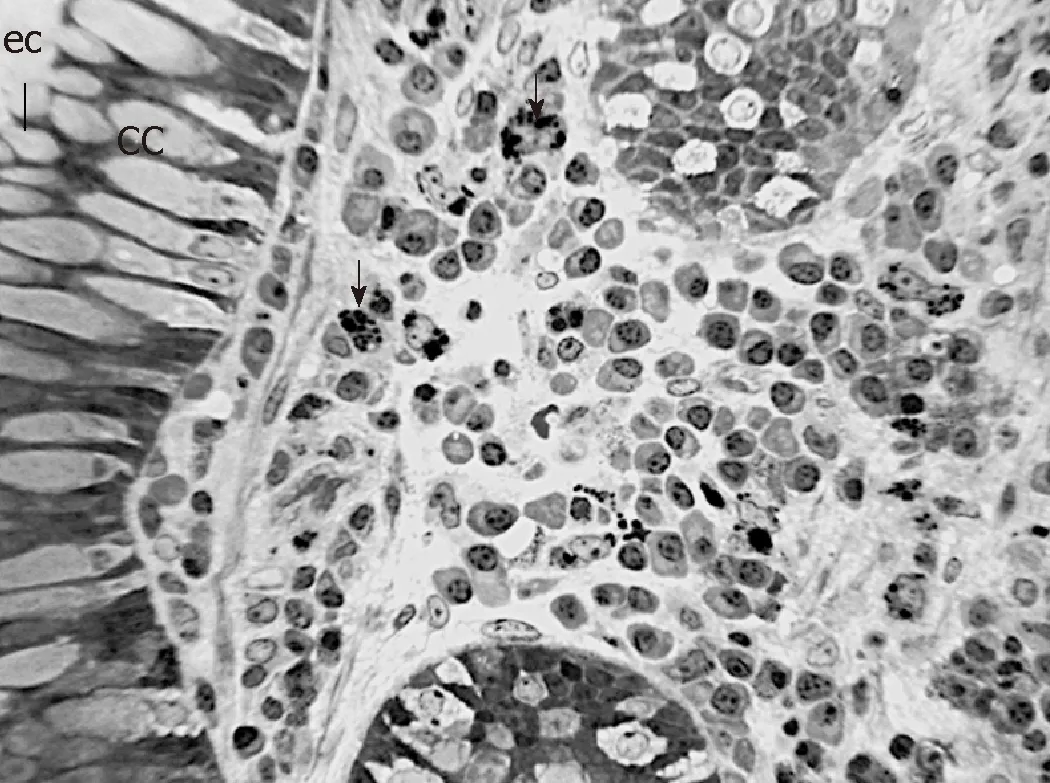
Figure2 Representative Light microscope (LM) of the lamina propria between Lieberkühn crypts in inflamed ileal tissue of CD patient number 7b.
Here gene expression analysis of inflamed ileal mucosa revealed an increased expression of genes involved in adaptive immune response compared to noninflamed tissue.In particular,we found a significant increase ofIL17AandIL17F,IL 23RandCCR6gene expression suggesting an activation of a Th17 adaptive response[25,26]similar to that found in gut mucosa of patients with colonic localization.According with this hypothesis,three additional genes involved in Th17 differentiation asJAK2,STAT3andTNFSF15[27,28]were found to be overexpressed in inflamed ileal mucosa of CD patients compared to non- inflamed sites.Furthermore,as we expected,the expression of the antimicrobial peptides as defensin (DEFB4)[29]and Hepcidin 6 (HAMP)[30]were significantly increased in inflamed mucosa of CD patients compared with non-inflamed sites,suggesting the overwhelming stimulation of epithelial cells by commensal GM.Indeed,while the human β-defensin (HBD) 1 is constitutively expressed,other genes,like HBD2 (gene name DEFB4),show pathogen and/or inflammation dependent upregulation[31]while also being inducible by probiotic bacteria[32].Conversely,HAMP transcription mediates the effects of host defence and inflammation.Shanmugamet al.provided persuasive evidence in support of an important role for the GM composition in influencing hepcidin expression during intestinal inflammation in mouse models of colitis[33].
As the position of the pathogenic tissue may condition not only the clinical course of the disease but also the probability to require surgery,we also compared with the same methodology (Quantigene 2.0) the expression of selected genes (IFN-γ,CCR6,IL17A,NOD2) involved in immune responses in inflamed mucosa with predominant ileal location with the one previously studied[10]in inflamed mucosa with colonic location.mRNA expression for IFN-γ γ and for the chemokine CCR6 appeared significantly higher in ileal site compared to colonic site (ileal CD = 2.7 ± 1.5;colonic CD = 0.2 ± 0.06;P= 0.01).The mRNA for IL-17 and NOD2 appeared to be expressed at higher levels in ileal site compared to colonic site,even if the difference is not statistically significant (P≥ 0.05).The significant differences in the expression levels ofIFN-γ gene (higher expression in specimens from patients with ileal localization compared to patients with colonic localization) may suggest an increased damage of the ileal mucosa due to the simultaneous presence of Th1 and Th17 effector cells and/or the shift of Th17 cells to Th1 effectors functionally more aggressive than Th17 unshifted cells[34,35].
Furthermore,according to a worse clinical course of patient with ileal localization of CD compared with patient with colonic localization[36],the increased expression of IL17 and NOD2 in mucosal fragments from patients with ileal CD compared to patients with colonic CD is in agreement with the NOD2 -dependent regulation of immunity in mouse intestinal tract[37].We suppose that the above differences between the two gut tracts (ileal and colonic) may be due to the Paneth cells at the bottom of the crypts of Lieberkühn in the small intestine,which produce antimicrobial peptides and hinder commensal GM and pathogenic bacteria to penetrate gut mucosa.Initially described as innate immune cells producing antimicrobial products,Paneth cells have recently been suggested to constitute a cardinal component of the intestinal stem cell niche.In fact,Paneth cells contribute to controlling the luminal flora as well as repairing the intestinal barrier following an insult.Genomic alterations that impede the Paneth cell compartment functionality can potentially increase the propensity to develop CD[38].
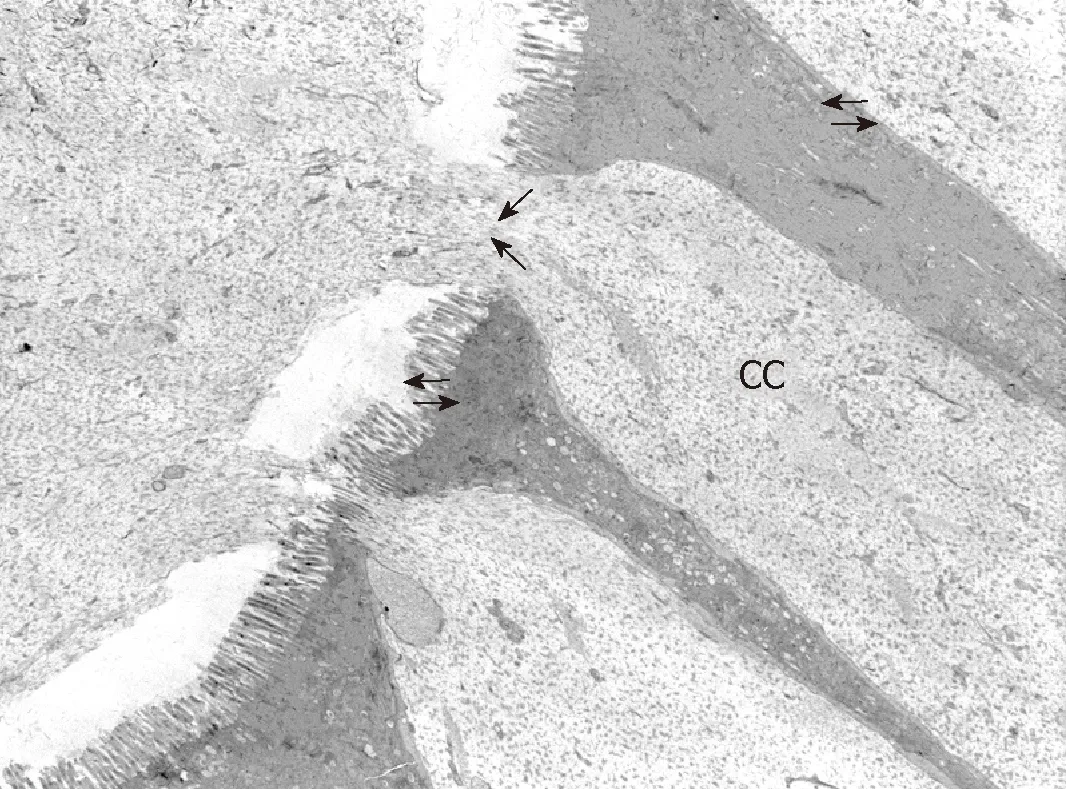
Figure3 Representative TEM micrograph of Lieberkühn crypt wall and lumen that contains mucous product released (large arrows) by goblet cells (CC) in inflamed ileal tissue CD patient number 7b.
As a consistent trait,cryptal globlet cells produce large amounts of mucus that performs the double role of barrier and holder of antimicrobial products.The microscopic anatomy analysis aims to provide some details that illustrate phenotypic features:the large cell variety in thelamina propriaincludes immune lines that represent a further defense tool.Although these morphological traits are not directly related to specific gene outputs,they illustrate the tissue responses to key gene deregulation.
As a pilot study,our study presents a low number of subjects investigated which may have influenced the statistical power of the results.To confirm these results,studies with a larger number of patients are needed.In addition,gene expression was evaluated with Multiplex Gene Assay only.This method directly quantifies the mRNA amounts without need of reverse transcription and gives a detailed picture of the metabolic processes for each patient but it should be validated by comparisons with additional techniques to evaluate gene expression.
One of the main purposes of our research is therefore to identify new molecules involved in metabolic pathways that could potentially represent new biological drugs to identify the appropriate therapy in relation to the clinical phenotype of the CD patient.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
The interplay of environmental,genetic and microbial elements influences the etiopathogenesis of Crohn’s disease (CD).Differences in the clinical course of CD have recently been reported in patients with ileal or colonic localization of the inflammatory process.
Research motivation
Aim of this study was to define biochemical and histological differences in intestinal biopsies from patients with ileal or colonic localization of Crohn disease in order to identify new assays which can be useful for planning individual therapeutic strategies
Research objectives
Main objective of the current research was to investigate the expression of genes involved in immune-inflammatory pathways in gut mucosa from patients with ileal or colonic localization of CD and to correlate the results of gene expression with those obtained through a classical morphological analysis of surgical biopsies.
Research methods
A Multiplex Gene Assay was used to assess the simultaneous expression of 24 genes related to immune-inflammatory process and to CD pathogenesis.Structural and ultrastructural features of gut samples were also evaluated through Light microscopy (LM) and Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) techniques.
Research results
We observed a strong activation of genes involved in TH-1- and TH-17 immune response in patients with ileal localization of CD compared to patients with colonic localization.In addition,the expression of genes for antimicrobial peptides as DEFB4 and HAMP was found highly stimulated in ileal mucosa from CD patients suggesting a possible interference with microbial commensals at this site.
Research conclusions
Our results indicate that patients with ileal localization of CD have a stronger activation of TH-1 and TH-17 immune-inflammatory responses compared with patients with colonic localization of the disease thus defining a clear subclinical phenotype of CD.
Research perspectives
These results may suggest that therapeutic strategies with biological drugs in CD patients can be differentiated depending on the location of the disease
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank Dr.Michele Tanturli for the statistical support,Dr.Giulia Ricciardi for additional manuscript revision,and all the patients who participated to this study,
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2019年17期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2019年17期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Brachiocephalic artery stenting through the carotid artery:A case report and review of the literature
- An extremely rare pedunculated lipoma of the hypopharynx:A case report
- Calcifying fibrous tumor of the mediastinum:A case report
- Wilson disease associated with immune thrombocytopenia:A case report and review of the literature
- Carcinoma ex pleomorphic adenoma of the trachea:A case report
- Cause of postprandial vomiting - a giant retroperitoneal ganglioneuroma enclosing large blood vessels:A case report
