Larvicidal activity of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus bacteria against Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus
Apichat Vitta, Punnawat Thimpoo, Wipanee Meesil, Thatcha Yimthin, Chamaiporn Fukruksa, Raxsina Polseela,2, Bandid Mangkit, Sarunporn Tandhavanant, Aunchalee Thanwisai,2
1Department of Microbiology and Parasitology, Faculty of Medical Science, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok, Thailand
2Centre of Excellence in Medical Biotechnology, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok, Thailand
3Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Faculty of Tropical Medicine, Mahidol University, Bangkok, Thailand
4Department of Veterinary Technology, Faculty of Veterinary Technology, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand
1. Introduction
Aedesmosquitoes are the main vectors of West Nile, chikungunya,and dengue viruses[1,2]. Recently the zika virus, with devastating effects, particularly for pregnant women, was proven to be transmitted to humans byAedes[3].Aedes aegypti(Ae. aegypti) andAedes albopictus(Ae. albopictus) are the main vectors of the dengue virus, causing dengue fever which has affected over 390 million people living in more than 100 countries[1,4]. At present, there are no specific treatments or vaccines for these viruses, and the best approach to prevent infection is avoidance of mosquito bites[3].Therefore, control adult and larvalAedesis an important measure to prevent the viral infection to human. Control methods for adult and larvalAedesspp. have been categorized as environmental,mechanical, chemical, genetic and biological controls[5]. Elimination of breeding sites ofAedesis a simple method and low cost to reduce the number of mosquitoes. Chemical controls (organochlorides,DDT; organophosphates, OP; pyrethroids) are the first method using in mosquito control. However, repeated use of these insecticides leads to development of insecticidal resistant mosquitoes and toxic to human.Aedeshave been reported to be resistant to DDT in worldwide. In addition, mosquitoes in several countries in Asia have been developed to resist pyrethroid[6]. Genetic control ofAedes(the sterile insect technique; rearing of insects carrying a dominant lethal allele) is a species specific method and most are in the laboratory conditions[7,8]. The genetic control methods need more consideration in cost, natural condition and environmental risk assessment[5].Control of larval mosquitoes is of low cost and can scope the certain source. Therefore, biological control of larval stage ofAedesis considered to be a potential measure to reduce number of mosquitoes leading to prevention and control of viral infection.
Biological control forAedesspp. using protozoa[9], copepods[10-12], plant extracts[13-15], fungi[16], bacteria and their toxins[17-20] are promoted as being ecologically friendly, which is important for human life.Bacillus thuringiensis(B. thuringiensis),entomopathogenic bacteria have potential for biological control ofAedesspp.[20,21]. This bacterium shows rapid killing of the mosquito larvae and has no cross-resistant with chemical insecticides[22].However,Aedesspp. can develop moderate resistant toBacillus thuringiensissubsp.israelensis(B. thuringiensissubsp.israelensis)[23]. Other bacteria commonly used for control of insects areXenorhabdusandPhotorhabduswhich are symbiotically associated with entomopathogenic nematodes. These bacteria have also been reported to have oral lethality toAe. aegyptilarvae[17,24].
XenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusare symbiotically associated with entomopathogenic nematodes which are Gram negative bacteria with the rod shape and peritichous flagella of the family Enterobacteriaceae. These bacteria produce several bioactive compounds with cytotoxic, antifungal, antibacterial, antiparasitic and insecticidal activities[25-31]. Isopropylstilbene and ethylstilbene produced byPhotorhabdus, and xenorhabdin and xenematide produced byXenorhabdus, have also shown insecticidal activity[32].Cell suspensions ofXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusand their toxins were lethal toAedeslarvae, and a previous study showed thatPhotorhabdusinsect-related protein fromPhotorhabdus asymbioticahad strong toxicity toAe. aegyptiandAe. albopictus[33]. More recently, suspensions ofPhotorhabdus luminescens(P. luminescens)andXenorhabdus nematophila(X. nematophila) were shown to kill between 42% and 83% ofAe. aegyptilarvae in laboratory conditions[24]. In addition,P. luminescensandX. nematophilasuspension mixed with Cry4Ba protein fromB. thuringiensissubsp.israelensisproduced a mortality rate up to 87% and 95% ofAe.aegypti[17]. These results suggest thatXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusspp. may be effective alternative agents for the biological control of mosquitoes. Some 30 species of these bacteria have been reported worldwide[34-37], but few species of these symbiotic bacteria have been tested to determine their efficacy in killing mosquito larvae.Xenorhabdus stockiae(X. stockiae) andPhotorhabdus luminescenssubsp.akhurstii(P. luminescenssubsp.akhurstii), the majority species found in Thailand, andXenorhabdus indica(X. indica), andPhotorhabdus luminescenssubsp.hainanensis(P. luminescenssubsp.hainanensis), also found in Thailand[38] suggested that these may be biological agents for controlling mosquito larvae, but the insecticidal or larvicidal activity of these symbiotic bacteria have never been tested againstAedeslarvae. During the survey of entomopathogenic nematodes and symbiotic bacteria in northeast of Thailand, we identified several isolates of these symbiotic bacteria includingX.stockiae,X. indica,P. luminescenssubsp.akhurstiiandP. luminescenssubsp.hainanensis. Therefore, the objective of this study was to evaluate the effect ofX. stockiae,X. indica,P. luminescenssubsp.akhurstiiandP. luminescenssubsp.hainanensisisolated from entomopathogenic nematodes in Thailand againstAe. aegyptiandAe.albopictuslarvae.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Bacterial isolates
XenorhabdusandPhotorhabduswere isolated from entomopathogenic nematodes collected from soil samples from northeast of Thailand. These bacteria were previously identified by the sequencing of a partial region of therecAgene. To identifyXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusinto species level, BLASTN analysis of the 588 bprecAgene was performed with cut-off at 97% identity. Two species ofXenorhabduswere identified asX.stockiaeisolate bNBP22.2_TH (Accession No. KY809323) andX. indicaisolate bKK26.2_TH (Accession No. KY809302). Two subspecies ofPhotorhabduswere identified asP. luminescenssubsp.akhurstiiisolate bMSK25.5_TH (Accession No. KY809375) andP.luminescenssubsp.hainanensisisolate bKK17.1_TH (Accession No.KY809363). These four entomopathogenic bacteria were used in bioassays.
2.2. Preparation of bacterial cell suspension
XenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusin LB broth with 20% glycerol were kept at -80 ℃ in our laboratory. Each bacterial isolate was grown on NBTA agar for 4 d and incubated at room temperature. To prepare a starter, a single colony was sub-cultured into 5 mL of 5YS medium containing 5% yeast extract (w/v), 0.5% NaCl (w/v), 0.05%K2HPO4(w/v), 0.05% NH2H2PO4(w/v), and 0.02% MgSO4·7H2O(w/v). The tube was then incubated in the dark for 24 h with shaking at 160 rpm. One mL of the starter was transferred into a 50 mL tube containing 39 mL of 5YS medium. The tubes were then incubated in the dark for 24 h with shaking at 160 rpm.
Escherichia coli(E. coli) ATCC?25922 that is used as the negative control was cultured on tryptone soy agar. The culturing process for theE. coliATCC?25922 was performed similarly to the preparation of theXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusbacteria.
To prepare bacterial cell suspension, the overnight cultures ofXenorhabdus,PhotorhabdusandE. coliATCC?25922 were then centrifuged at 10 000 rpm at room temperature for 20 min. The supernatants were discharged. The bacterial pellets were resuspended with sterile distilled water. The turbidity of bacterial suspension was adjusted to 1.0 with sterile distilled water at OD600nm by spectrophotometer. These bacterial suspensions were ready for using in bioassays.
2.3. Mosquito strains
Ae. aegyptiandAe. albopictuseggs were purchased from the Taxonomy and Reference Museum of the Department of Medical Sciences at the National Institute of Health of Thailand, Ministry of Public Health, Thailand. The filter papers containing the dried eggs of eachAedesspecies were placed in separate plastic containers containing dechlorinated water to allow theAedeslarvae to hatch.Larvae at the late third and early fourth instar were then selected out and feed with minced pet food.
2.4. Bioassay
Four different isolates of symbiotic bacteria (X. stockiaebNBP22.2_TH,X. indicabKK26.2_TH,P. luminescenssubsp.akhurstiibMSK25.5_TH andP. luminescenssubsp.hainanensisbKK17.1_TH)were tested as a larvicide againstAe. aegyptiandAe. albopictus. The efficacy ofXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdussuspensions against late third to fourth early instar larvae of bothAe. aegyptiandAe. albopictuswas evaluated under laboratory conditions. In each bioassay, ten larvae were placed in 100 μL of water in a well in a 24-well plate(COSTAR?, USA). Two mL of each bacterial suspension (107-108CFU/mL) was added to the well. Distilled water and suspension ofE. coliATCC?25922 were used as the negative control. The bioassay was designed to test two groups, the ‘fed group’ which wasAedeslarvae fed with minced pet food during exposure to bacterial suspension and the ‘unfed group’ which was not fed during the experiment. All bioassays were conducted in triplicate on different dates. The mortality of theAedeslarvae was monitored at 24, 48, 72 and 96 h exposure to the bacterial suspensions. The dead larvae were determined when no movement was detected when teasing with fine sterile toothpick.
2.5. Data analysis
Mortality ofAedeslarvae after exposure to the bacteria suspension with the comparison with the control groups was analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis test using SPSS version 17.0.P-value < 0.05 was considered as significant differences. The mortality of theAedeslarvae from both the fed and unfed groups was statistically analyzed by Mann-Whitney test.
3. Result
BothAe. aegyptiandAe. albopictus(late 3rd to early 4th instars larvae) were susceptible to all isolates ofXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusbacteria. The mortality of the larvae began to die at 24 h after exposure to the bacterial suspension. In the fed group, a cell suspension ofX. stockiae(bNBP22.2_TH) demonstrated the highest toxicity toAe. aegyptilarvae (99% mortality) at 72 h after exposure.In the unfed group,X. stockiae(bNBP22.2_TH) showed the highest pathogenic effect onAe. aegyptilarvae, with 87% mortality at 96 h after exposure. Significant mortality among all bacterial isolates and negative controls (distilled water andE. coliATCC?25922) was observed at each time in the unfed group, although at a low rate of mortality (Table 1). However, the mortality rate of both the fed and unfed groups byAe. aegyptiwas not significantly different among the four bacterial isolates.
Table 2 shows the mortality rate ofAe. albopictuslarvae after exposure to cell suspension ofXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdus.X.indica(bKK26.2_TH) was highest toxic toAe. albopictusat 96 h in both fed (82%) and unfed (96%) condition. This bacterial isolate seemed to be fast pathogens toAe. albopictushaving kill 84% of 24 h. Mortality rate at each time among bacterial isolates and controls was significantly different in both fed and unfed conditions.
Mortality rate ofAe. aegyptiat each time between fed and unfed groups was not significant different. Significant mortality between fed and unfed groups ofAe. albopictuslarvae after exposure toX. indica(bKK26.2_TH) andP. luminescenssubsp.hainanensis(bKK17.1_TH) was observed at 24 h.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we demonstrate the alternative bacterial agent for controlAedesspp., a main vector for important virus infection in man. BothAedesspp. are susceptible toX. stockiae(bNBP22.2_TH)X. indica(bKK26.2_TH)P. luminescenssubsp.akhurstii(bMSK25.5_TH) andP. luminescenssubsp.hainanensis(bKK17.1_TH). It seems that the symbiotic bacteria of genusXenorhabdusandPhotorhabduscause superior mortality ofAedes.X. stockiae, asymbiotic bacterium that is found to be associated withSteinernema websteri, have been used for acaricidal and antibacterial activity[39,40].X. indicaproduces several bioactive compounds including taxlllaids A-G which has weakly effect onPlasmodium falciparum[41]. In addition, metalloprotease purified fromX. indicashowed insecticidal activity againstHelicoverpa armigera[42].P. luminescenssubsp.akhurstiiandP. luminescenssubsp.hainanensisshowed less effective againstAedes aegypti[43]. To our knowledge, it is reported for the first time that four symbiotic bacteria [P. luminescenssubsp.akhurstii(bMSK25.5_TH),P. luminescenssubsp.hainanensis(bKK17.1_TH),X. stockiae(bNBP22.2_TH) andX. indica(bKK26.2_TH) in the present study are symbiotic bacteria for oral pathogenicity againstAe. albopictus.
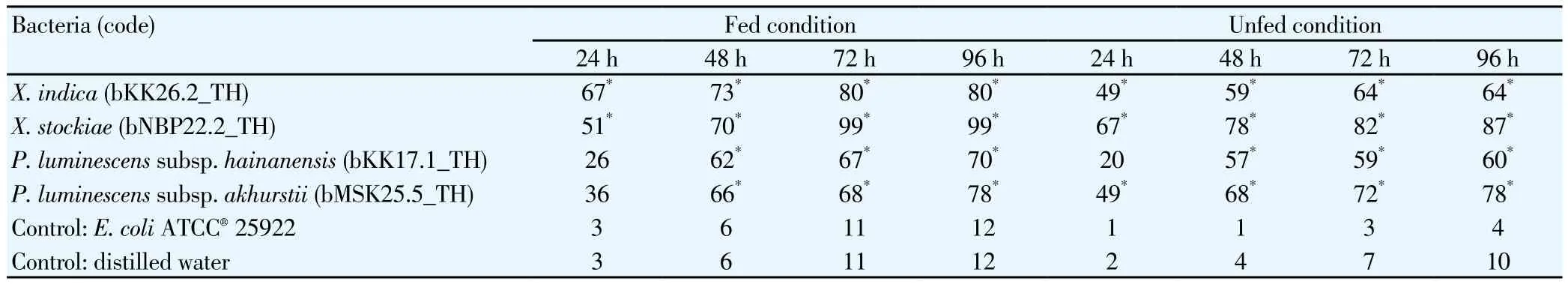
Table 1 Mortality rate of Ae. aegypti larvae after exposure to cell suspension of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus in fed and unfed conditions in laboratory.

Table 2 Mortality rate of Ae. albopictus larvae after exposure to cell suspension of Xenorhabdus and Photorhabdus in fed and unfed conditions in laboratory.
Ae. aegyptiandAe. albopictus, both serious transmitting vectors of West Nile, chikungunya, dengue and zika viruses to humans, are globally distributed[1,4]. Although several control methods against these vectors have been attempted to stop the transmission of viral infections, the numbers of human case has not declined, especially dengue infection[44]. Biological controls of the vectors are an alternative measure to reduce human-mosquito contact. Our study demonstrated larvicidal activity ofX. stockiae(bNBP22.2_TH),X.indica(bKK26.2_TH),P. luminescenssubsp.akhurstii(bMSK25.5_TH) andP. luminescenssubsp.hainanensis(bKK17.1_TH) againstAe. aegyptiandAe. albopictus. Both vectors were susceptible toXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusbacteria by oral ingestion. This may be due to the bacteria producing insecticidal compounds including isopropylstilbene, ethylstilbene, xenorhabdin and xenematide[32].To support this scenario,Photorhabdusinsect-related protein fromPhotorhabdus asymbioticashowed strong toxicity toAe. aegyptiandAe. albopictus[33]. In addition, a suspension ofPhotorhabdus luminescenssubsp.laumondiiTT01 DSM15139 andX. nematophilaATCC?19061 showed orally lethality toAe. aegyptilarvae in laboratory conditions[24].P. luminescensandX. nematophilasuspension mixed with Cry4Ba protein fromB. thuringiensissubsp.israelensisenhanced the mortality rate ofAe. aegyptiup to 87%and 95%, respectively[17]. Recently,X. nematophilamixed withB. thuringiensissubsp.israelensiswas observed to enhance the toxicity toAe. albopictusandCulex pipiens pallens[18]. In addition,Xenorhabdus ehlersiiisolated fromSteinernema scarabaeishowed good potential efficacy in killingAe. aegyptiwith 100% mortality[43].In our study, we confirmed the oral toxicity ofXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusagainstAe. aegyptiandAe. albopictus. However, it remains unknown as to the mechanism of killing effect of these bacteria onAedesspp.
XenorhabdusandPhotorhabdushave orally toxicity toAedesspp.,but mortality rates vary. It is possible that the different pathogenicity from each bacterial species or isolates produces different amounts and kinds of bioactive compounds. Phurealipid derivatives, the inhibitor of juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase in insects, were produced by different isolates ofP. luminescenssubsp.akhurstii[45,46].In addition, the virulence ofXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusvaried among insect species is related to foraging behavior[47]. This suggests that the virulent factors ofXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusrequire further study for more deeply understanding.
We demonstrate the potential of entomopathogenic bacteria,X.stockiae,X. indica,P. luminescenssubsp.akhurstiiandP. luminescenssubsp.hainanensis, for the control of arbovirus vectors,Ae. aegyptiandAe. albopictus, by oral ingestion. This study confirms thatXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdushave orally toxicity againstAedeslarvae and provides further information relevant to the biological control of mosquito larvae. Further studies on identification and isolation of purified useful bioactive compounds to control both larval and adult mosquitoes, and their mechanisms of killing mosquitoes, are suggested.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Higher Education Research Promotion, The Commission on Higher Education, Thailand (Grant No. R2558A008) and Naresuan University (Grant No. R2557B013).We would like to thank Miss Chutima Sarai and Miss Ponsuwan Aeiwong for their assistance with the laboratory technique. Many thanks were extended to Mr. Roy Morien of the Naresuan University Language Centre for his editing assistance and advice on English expression in this document.
[1] Benelli G, Mehlhorn H. Declining malaria, rising of dengue and Zika virus: insights for mosquito vector control.Parasitol Res2016; 115(5):1747-1754.
[2] Gebre Y, Forbes N, Gebre T. Zika virus infection, transmission, associated neurological disorders and birth abnormalities: A review of progress in research, priorities and knowledge gaps.Asian Pac J Trop Biomed2016;6(10): 815-824.
[3] World Health Organization.Zika virus.Fact sheet2016a. [Online]Available from: http://www. who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/zika/en/.[Accessed on 27th December, 2016].
[4] Bhatt S, Gething PW, Brady OJ, Messina JP, Farlow AW, Moyes CL, et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue.Nature2013; 496(7446):504-507.
[5] Baldacchino F, Caputo B, Chandre F, Drago A, della Torre A, Montarsi F, et al. Control methods against invasiveAedesmosquitoes in Europe: a review.Pest Manag Sci2015; 71(11): 1471-1485.
[6] Naqqash MN, Gokce A, Bakhsh A, Salim M. Insecticide resistance and its molecular basis in urban insect pests.Parasitol Res2016; 115(4): 1363-1373.
[7] Bellini R, Medici A, Puggioli A, Balestrino F, Carrieri M. Pilot field trials withAedes albopictusirradiated sterile males in Italian urban areas.J Med Entomol2013; 50(2): 317-325.
[8] Winskill P, Harris AF, Morgan SA, Stevenson J, Raduan N, Alphey L, et al. Genetic control ofAedes aegypti: data-driven modelling to assess the effect of releasing different life stages and the potential for long-term suppression.Parasit Vectors2014; 7: 68.
[9] Otta DA, Rott MB, Carlesso AM, da Silva OS. Prevalence ofAcanthamoebaspp. (Sarcomastigophora: Acanthamoebidae) in wild populations ofAedes aegypti(Diptera: Culicidae).Parasitol Res2012;111(5): 2017-2022.
[10] Russell BM, Muir LE, Weinstein P, Kay BH. Surveillance of the mosquitoAedes aegyptiand its biocontrol with the copepodMesocyclops aspericornisin Australian wells and gold mines.Med Vet Entomol1996;10(2): 155-160.
[11] Mahesh Kumar P, Murugan K, Kovendan K, Panneerselvam C, Prasanna Kumar K, Amerasan D, et al. Mosquitocidal activity ofSolanum xanthocarpumfruit extract andcopepodMesocyclops thermocyclopoidesfor the control of dengue vectorAedes aegypti.Parasitol Res2012; 111(2):609-618.
[12] Veronesi R, Carrieri M, Maccagnani B, Maini S, Bellini R.Macrocyclops albidus(Copepoda: cyclopidae) for the biocontrol ofAedes albopictusandCulex pipiensin Italy.J Am Mosq Control Assoc2015; 31(1): 32-43.
[13] Zuharah WF, Ahbirami R, Dieng H, Thiagaletchumi M, Fadzly N.Evaluation of sublethal effects ofIpomoea cairicaLinn. extract on life history traits of dengue vectors.Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo2016; 58:44.
[14] Zuharah WF, Yousaf A. Assessment ofGluta renghasL. andMangifera indicaL. (Sapindales: Anacardiaceae) extracts on the sublethal effects of dengue vector.J Asia Pac Entomol2016; 19(4): 1043-1051.
[15] Francine TN, Cabral BNP, Anatole PC, Bruno MM, Pauline N,Jeanne NY. Larvicidal activities of hydro-ethanolic extracts of three Cameroonian medicinal plants againstAedes albopictus.Asian Pac J Trop Biomed2016; 6(11): 931-936.
[16] Carolino AT, Paula AR, Silva CP, Butt TM, Samuels RI. Monitoring persistence of the entomopathogenic fungusMetarhizium anisopliaeunder simulated field conditions with the aim of controlling adultAedes aegypti(Diptera: Culicidae).Parasit Vectors2014; 7: 198.
[17] Park Y. Entomopathogenic bacterium,Xenorhabdus nematophilaandPhotorhabdus luminescens, enhancesBacillus thuringiensisCry4Ba toxicity against yellow fever mosquito,Aedes aegypti(Diptera: Culicidae).J Asia Pac Entomol2015; 18(3): 459-463.
[18] Park Y, Kyo Jung J, Kim Y. A mixture ofBacillus thuringiensissubsp.israelensiswithXenorhabdus nematophila-cultured broth enhances toxicity against mosquitoesAedes albopictusandCulex pipiens pallens(Diptera:Culicidae).J Econ Entomol2016; 109(3): 1086-1093.
[19] Setha T, Chantha N, Benjamin S, Socheat D. Bacterial larvicide,Bacillus thuringiensisisraelensisstrain AM 65-52 water dispersible granule formulation impacts both dengue vector,Aedes aegypti(L.) population density and disease transmission in Cambodia.PLoS Negl Trop Dis2016;10(9): e0004973. doi:10.1371/ journal.pntd. 0004973.
[20] Mohiddin A, Lasim AM, Zuharah WF. Susceptibility ofAedes albopictusfrom dengue outbreak areas to temephos andBacillus thuringiensissubsp.israelensis.Asian Pac J Trop Biomed2016; 6: 295-300.
[21] Gama ZP, Nakagoshi N, Suharjono, Setyowati F. Toxicity studies for indigenousBacillus thuringiensisisolates from Malang city, East Java onAedes aegyptilarvae.Asian Pac J Trop Biomed2013; 3(2): 111-117.
[22] Marcombe S, Darriet F, Agnew P, Etienne M, Yp-Tcha MM, Yébakima A, et al. Field efficacy of new larvicide products for control of multiresistantAedes aegyptipopulations in Martinique (French West Indies).Am J Trop Med Hyg2011; 84(1): 118-126.
[23] Tetreau G, Stalinski R, David JP, Després L. Monitoring resistance toBacillus thuringiensissubsp.israelensisin the field by performing bioassays with each Cry toxin separately.Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz2013;108(7): 894-900.
[24] da Silva OS, Prado GR, da Silva JL, Silva CE, da Costa M, Heermann R.Oral toxicity ofPhotorhabdus luminescensandXenorhabdus nematophila(Enterobacteriaceae) againstAedes aegypti(Diptera: Culicidae).Parasitol Res2013; 112(8): 2891-2896.
[25] Fang XL, Li ZZ, Wang YH, Zhang X.In vitroandin vivoantimicrobial activity ofXenorhabdus bovieniiYL002 againstPhytophthora capsiciandBotrytis cinerea.J Appl Microbiol2011; 111(1): 145-154.
[26] Hu X, Liu Z, Li Y, Ding X, Xia L, Hu S. PirB-Cry2Aa hybrid protein exhibits enhanced insecticidal activity againstSpodoptera exigualarvae.J Invertebr Pathol2014; 120: 40-42.
[27] Li Y, Hu X, Zhang X, Liu Z, Ding X, Xia L, et al.Photorhabdus luminescensPirAB-fusion protein exhibits both cytotoxicity and insecticidal activity.FEMS Microbiol Lett2014; 356(1): 23-31.
[28] Grundmann F, Kaiser M, Schiell M, Batzer A, Kurz M, Thanwisai A, et al. Antiparasitic chaiyaphumines from entomopathogenicXenorhabdussp. PB61.4.J Nat Prod2014; 77(4): 779-783.
[29] Bock CH, Shapiro-Ilan DI, Wedge DE, Cantrell CL. Identification of the antifungal compound, trans-cinnamic acid, produced byPhotorhabdus luminescens, a potential biopesticide against pecan scab.J Pest Sci2014;87(1): 155-162.
[30] Ullah I, Khan AL, Ali L, Khan AR, Waqas M, Hussain J, et al.Benzaldehyde as an insecticidal, antimicrobial, and antioxidant compound produced byPhotorhabdus temperataM1021.J Microbiol2015; 53(2): 127-133.
[31] Shi D, An R, Zhang W, Zhang G, Yu Z. Stilbene derivatives fromPhotorhabdus temperataSN259 and their antifungal activities against phytopathogenic fungi.J Agric Food Chem2017; 65(1): 60-65.
[32] Bode HB. Entomopathogenic bacteria as a source of secondary metabolites.Curr Opin Chem Biol2009; 13(2): 224-230.
[33] Ahantarig A, Chantawat N, Waterfield NR, Ffrench-Constant R,Kittayapong P. PirAB toxin fromPhotorhabdus asymbioticaas a larvicide against dengue vectors.Appl Environ Microbiol2009; 75(1): 4627-4629.
[34] Ferreira T, van Reenen CA, Endo A, Spr?er C, Malan AP, Dicks LM.Description ofXenorhabdus khoisanaesp. nov., the symbiont of the entomopathogenic nematodeSteinernema khoisanae.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol2013; 63(9): 3220-3224.
[35] Ferreira T, van Reenen CA, Pages S, Tailliez P, Malan AP, Dicks LM.Photorhabdus luminescenssubsp.noenieputensissubsp. nov., a symbiotic bacterium associated with a novelHeterorhabditisspecies related toHeterorhabditis indica.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol2013; 63(5): 1853-1858.
[36] Ferreira T, van Reenen CA, Endo A, Tailliez P, Pagès S, Spr?er C, et al.Photorhabdus heterorhabditissp. nov., a symbiont of the entomopathogenic nematodeHeterorhabditis zealandica.Int J Syst EvolMicrobiol2014; 64(5): 1540-1545.
[37] Tailliez P, Laroui C, Ginibre N, Paule A, Pages S, Boemare N. Phylogeny ofPhotorhabdusandXenorhabdusbased on universally conserved protein-coding sequences and implications for the taxonomy of these two genera. Proposal of new taxa:X. vietnamensissp. nov.,P. luminescenssubsp.caribbeanensissubsp. nov.,P. luminescenssubsp.hainanensissubsp. nov.,P. temperatasubsp.khaniisubsp. nov.,P. temperatasubsp.tasmaniensissubsp. nov., and the reclassification ofP. luminescenssubsp.thracensisasP. temperatasubsp.thracensiscomb. nov.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol2010; 60(8): 1921-1937.
[38] Thanwisai A, Tandhavanant S, Saiprom N, Waterfield NR, Ke Long P,Bode HB, et al. Diversity ofXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusspp. and their symbiotic entomopathogenic nematodes from Thailand.PLoS One2012; 7(9): e43835. doi: 10.1371/journal. pone. 0043835.
[39] Bussaman P, Sa-Uth C, Rattanasena P, Chandrapatya A. Acaricidal activities of whole cell suspension, cell-free supernatant, and crude cell extract ofXenorhabdus stockiaeagainst mushroom mite (Luciaphorussp.).J Zhejiang Univ Sci B2012; 13(4): 261-266.
[40] Bussaman P, Rattanasena P. Additional property ofXenorhabdus stockiaefor inhibiting cow mastitis-causing bacteria.Biosci Biotech Res Asia2016;13(4): 1871-1878.
[41] Kronenwerth M, Bozhüyük KA, Kahnt AS, Steinhilber D, Gaudriault S,Kaiser M, et al. Characterisation of taxlllaids A-G; natural products fromXenorhabdus indica.Chemistry2014; 20(52): 17478-17487.
[42] Pranaw K, Singh S, Dutta D, Singh N, Sharma G, Ganguly S, et al.Extracellular novel metalloprotease fromXenorhabdus indicaand its potential as an insecticidal agent.J Microbiol Biotechnol2013; 23(11):1536-1543.
[43] Fukruksa C, Yimthin T, Suwannaroj M, Muangpat P, Tandhavanant S, Thanwisai A, et al. Isolation and identification ofXenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusbacteria associated with entomopathogenic nematodes and their larvicidal activity againstAedes aegypti.Parasit Vect2017; 10(1):440.
[44] World Health Organization.Dengue and severe dengue.Fact sheet2016b.[Online]Available from: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs117/en/. [Accessed on 28th December, 2016].
[45] Nollmann FI, Heinrich AK, Brachmann AO, Morisseau C, Mukherjee K, Casanova-Torres áM., et al. APhotorhabdusnatural product inhibits insect juvenile hormone epoxide hydrolase.Chembiochem2015; 16(5):766-771.
[46] Muangpat P, Yooyangket T, Fukruksa C, Suwannaroj M, Yimthin T,Sitthisak S, et al. Screening of the antimicrobial activity against drug resistant bacteria ofPhotorhabdusandXenorhabdusassociated with entomopathogenic nematodes from Mae Wong National Park, Thailand.Front Microbiol2017; 8: 1142.
[47] Owuama CI. Entomopathogenic symbiotic bacteria,XenorhabdusandPhotorhabdusof nematodes.World J Microbiol Biotechnol2001; 17(5):505-515.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2018年1期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2018年1期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- A comprehensive review on anti-diabetic property of rice bran
- Ethnobotanical survey of antimalarial plants in Awash-Fentale District of Afar Region of Ethiopia and in vivo evaluation of selected ones against Plasmodium berghei
- Larvicidal activity of Neem oil and three plant essential oils from Senegal against Chrysodeixis chalcites (Esper, 1789)
- Protective effect of ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) against neurotoxicity induced by aluminum chloride in rats
- Oxidative stress mitigation, kinetics of carbohydrate-enzymes inhibition and cytotoxic effects of flavonoids-rich leaf extract of Gazania krebsiana (Less.): An in vitro evaluation
- Identification of commonly regulated genes in HPV18- and HPV16-infected cervical cancer cells treated with the curcumin analogue 1,5-bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4-pentadiene-3-one
