Potential applications of artificial intelligence in colorectal polyps and cancer: Recent advances and prospects
Ke-Wei Wang, Ming Dong
Abstract Since the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) technology, it has been constantly studied and has achieved rapid development. The AI assistant system is expected to improve the quality of automatic polyp detection and classification. It could also help prevent endoscopists from missing polyps and make an accurate optical diagnosis. These functions provided by AI could result in a higher adenoma detection rate and decrease the cost of polypectomy for hyperplastic polyps. In addition, AI has good performance in the staging, diagnosis, and segmentation of colorectal cancer. This article provides an overview of recent research focusing on the application of AI in colorectal polyps and cancer and highlights the advances achieved.
Key Words: Artificial intelligence; Deep learning; Computer-assisted diagnosis; Colorectal polyps; Colorectal cancer
INTRODUCTION
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a wide-ranging branch of computer science concerned with building smart machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. AI technology has made great progress, mainly owing to the development of analytical methods such as support vector machines and deep learning. Through continuous learning from data and experience accumulation, the task processing ability of the machine is greatly enhanced. AI has been improved through algorithm learning and knowledge management. It has gradually been applied in imaging and pathological diagnosis, disease management, drug research and development[1], and promoting the development of genetics and molecular medicine. The research results of Theofilatoset al[2]confirm this view. In their research, AI was used to find new treatment methods through a protein interaction algorithm, which may become a new direction in the development of molecular medicine. AI systems that use deep learning have been utilized in images of lesions such as esophageal cancer, glaucoma, and skin cancer with good performance[3-5].
In recent years, the application of AI in the diagnosis and treatment of colorectal polyps and cancer has also increased[6-8]. In the field of gastroenterology, there has been considerable interest in utilizing AI as an adjunctive detection technique in endoscopy. AI provides the promise of increasing polyp detection and even optical polyp diagnosis, all requiring minimal training of the endoscopist. For instance, a fast detection algorithm named ResYOLO was pretrained with a large database of nonmedical images and then refined with images extracted from colonoscopic videos. Evaluated on 17574 frames from 18 endoscopic videos, the proposed method could find frames with polyps with an accuracy of 88.6%, recall of 71.6%, and a processing speed of 0.15 s per frame[6]. With the advent of deep learning algorithms and significant advances in computer capabilities, more and more AI assistance, some of which may be used in real time during colonoscopy, is now being implemented.
We searched for relevant literature in the MEDLINE and PubMed databases (2015–2020) using the following keywords: “deep learning,” “computer-assisted diagnosis,” “artificial intelligence,” “colorectal polyps,” and “colorectal cancer.” We only reviewed full journal articles published in English. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (1) Studies that associated AI with the detection and classification of colorectal polyps; and (2) Studies that associated AI with the diagnosis of colorectal cancer (CRC). This review highlights recent advances in the application of AI in colorectal polyps and cancer in the past 5 years (Figure 1).
AI IN COLORECTAL POLYPS
At present, colonoscopy is still the most important diagnostic method for colorectal polyps. It is estimated that the prevalence of precancerous polyps in the 50+ years old screening population will be more than 50%[9]. Adenoma is the most common precancerous polyp. The adenoma detection rate (ADR) is an indicator of the colonoscopist’s ability to detect adenomas. However, the ADR by colonoscopists varies from 7% to 53%[10]. Many studies have shown that endoscopists with a higher ADR in screening colonoscopy can more effectively protect patients from the subsequent risk of colon cancer[10,11]. Corleyet al[10]evaluated 314872 colonoscopies performed by 136 colonoscopists. The results showed that for every 1.0% increase in ADR, the risk of CRC was reduced by 3.0%. However, the rate of missed adenoma during colonoscopy is still high and estimated to be between 6% and 27%[12]. Thus, new techniques are required to increase the ADR during colonoscopy. In recent years, more and more scholars have investigated the application of AI in the diagnosis of colonic polyps[13-26]. All these studies/applications with detailed data are summarized in Tables 1 and 2.
Application of AI in colorectal polyp detection
AI is increasingly applied in gastrointestinal endoscopy, especially in the detection of colorectal polyps[27,28]. The ideal automatic detection tools for polyps should have a high sensitivity for polyp detection, a low rate of false positives, and a low latency so that polyps can be tracked and identified during real-time colonoscopy. Bowel preparation quality is an important factor affecting the accuracy of routine colonoscopy. Becqet al[29]evaluated the performance of a deep learning method for polyp detection during routine colonoscopy with variable bowel preparation quality and found that the deep learning method could effectively identify polyps bycolonoscopy, even in the setting of variable bowel preparation quality.

Table 1 Characteristics of studies on artificial intelligence in the detection and classification of colorectal polyps
In recent years, many studies have found that an AI system can remind the endoscopist in real time to avoid the omission of nonpolypoid lesions and other abnormalities during colonoscopy, which increases the ADR[30,31](Figure 2). However, this requires validation in large multicenter trials. In addition to conventional computer-assisted diagnosis (CAD), a convolutional neural network (CNN) system using AI has rapidly developed over the past 5 years[32]. A novel online and offline three-dimensional deep learning integration framework based on a three-dimensional fully convolutional network was proposed by Yuet al[33]. This framework can learn more representative spatiotemporal features from colonoscopy videos and has stronger recognition ability compared with previous methods such as twodimensional CNN or hand-crafted features[33]. Recently, a novel AI system (GI-Genius, Medtronic) was reported to have a sensitivity of 99.7% in the detection of colorectal polyps. The proportion of false positive frames found from colonoscopy was less than 1% of the total frames. Furthermore, the reaction time was shorter using this novel AI system compared with visual inspection by endoscopists in 82% of the cases[34]. Ameta-analysis including six studies of AI on polyp detection showed a pooled area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.90. The pooled sensitivity and specificity of AI for polyp detection were 95.0% and 88.0%, respectively[35].
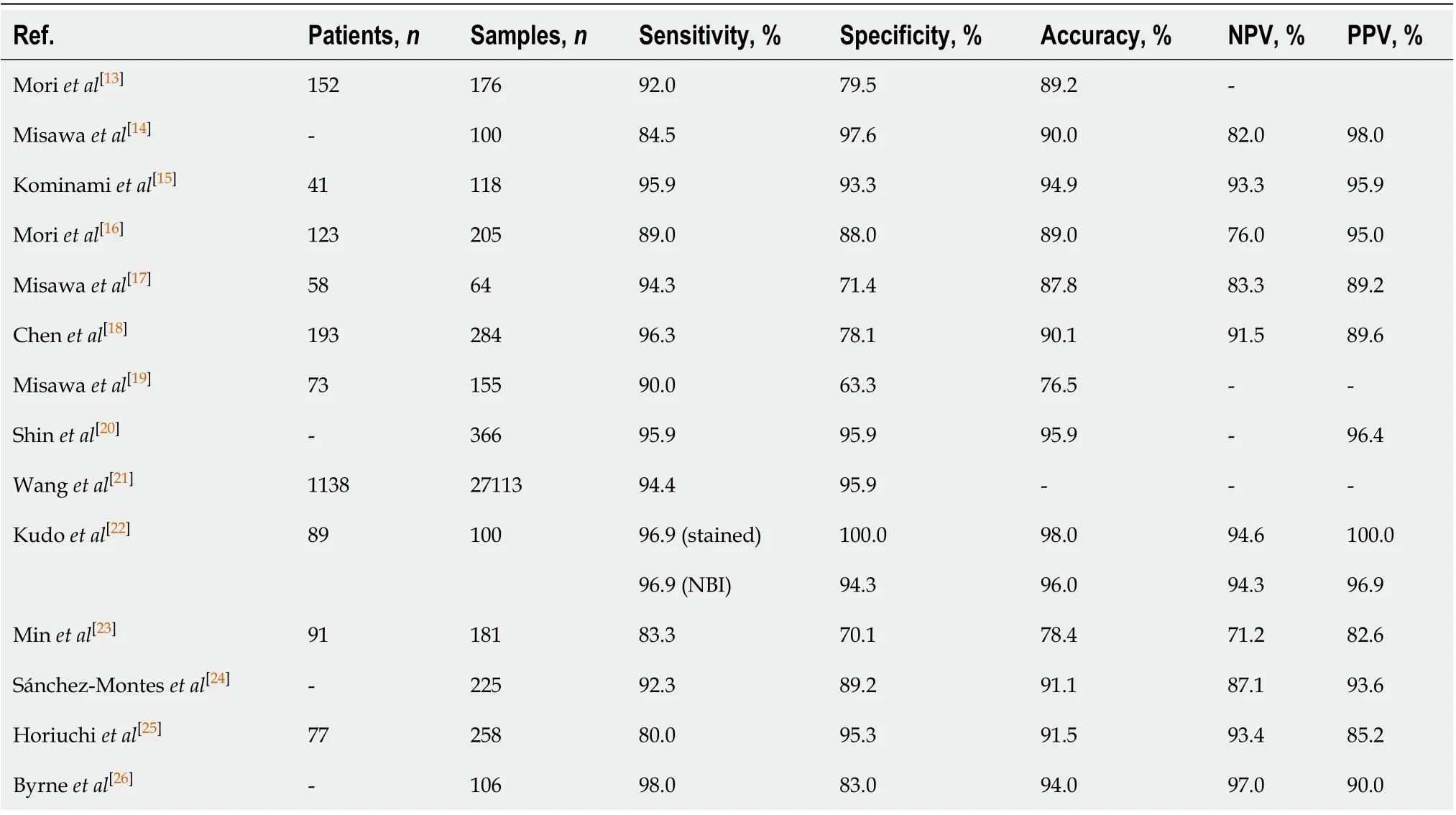
Table 2 Performance of artificial intelligence in the detection and classification of colorectal polyps
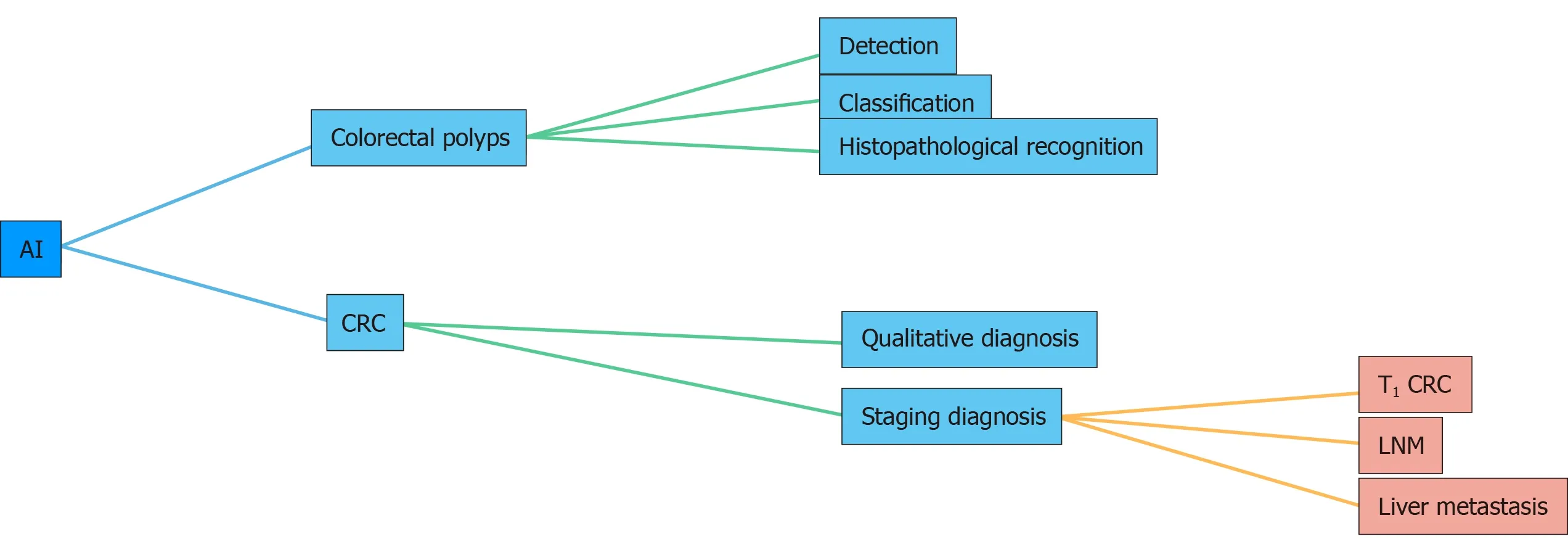
Figure 1 Applications of artificial intelligence in colorectal polyps and cancer. AI: Artificial intelligence; CRC: Colorectal cancer; LNM: Lymph node metastasis.
Wireless capsule endoscopy (WCE) is a noninvasive alternative to conventional endoscopes and is an essential tool for diagnostic inspection of the gastrointestinal tract. Due to large amounts of data captured by WCE, it takes a few hours for the doctor to make a diagnostic decision as the images need to be checked frame by frame. Therefore, an automatic CAD system is essential to assist physicians in analyzing and separating polyp images from whole data. For this purpose, Yuanet al[36]proposed a novel deep feature learning algorithm, named stacked sparse autoencoder with image manifold constraint, to identify polyps in the WCE images. The average accuracy of this algorithm for WCE images was 98.0%. Although this accuracy is high, it is far from perfect. The proposed algorithm did not perform well if inhomogeneous illuminations existed in the WCE images. Thus, there is still a lot of work to do to improve this method.

Figure 2 Workflow of the artificial intelligence system in endoscopy. The location and diagnostic probability of polyps can be marked on the screen in real time with an alarm. AI: Artificial intelligence.
Application of AI in colorectal polyp classification
In the preservation and incorporation of valuable endoscopic innovations of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommendation, endoscopists are required to receive intensive training on image-enhanced endoscopy to achieve a negative predictive value of > 90% in predicting the absence of adenomatous histology[37]. At present, many AI systems have reached the above standards. A total of 7680 colonic polyp images from 18 studies were included in a meta-analysis of polyp histology prediction utilizing an AI system. The pooled sensitivity in polyp histology prediction was 92.3%, and pooled specificity was 89.8%. The AUC of the AI in polyp histology prediction was 0.96[35]. When compared with visual inspection by endoscopists, the results of one study show that AI had similar precision (87.3%vs86.4%) but a higher recall rate (87.6%vs77.0%) and higher accuracy (85.9%vs74.3%)[38]. Sánchez-Monteset al[24]developed a CAD system that can help the identification of dysplastic lesions. This system includes three stages: (1) Image preprocessing; (2) Extraction of textons. They used three texton feature images (branching, tubularity, and contrast) generated from textons extracted from the input image; and (3) Characterization. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, negative predictive value, and positive predictive value were 92.3%, 89.2%, 91.1%, 87.1%, and 93.6%, respectively[24].
More and more studies have revealed that deep learning using CNNs is a good option for colonic polyp classification[39](Figure 3). Songet al[40]reported that the overall diagnostic accuracy of CAD using a deep learning model was 81.3%-82.4%, which was significantly higher than that of the trainees (63.8%-71.8%,P< 0.01) and comparable with that of experts (82.4%-87.3%)[40]. This result suggests that CAD using deep learning is helpful for trainees in diagnosing colorectal polyps. Similar results were also seen in the evaluation of diminutive (< 5 mm) colorectal polyps by a CNN model, which also significantly reduced the time of diagnosis by endoscopists (from 3.92 s to 3.37 s/polyp,P= 0.042)[41]. An optical diagnosis model based on CNN was specifically designed to identify hyperplastic/serrated and adenomatous polyps, and the performance of this model exceeded the threshold of preservation and incorporation of valuable endoscopic innovations for both “diagnose and leave” and “resect and discard” strategies independent of narrow-band imaging utilization[42]. With the development of AI systems, endoscopists may accurately predict the pathology of polyps less than 3 mm in diameter[43].
The above studies were all retrospective. In order to further verify the effectiveness of AI in recent years, more and more scholars have begun to carry out prospective research to examine the application of AI in the diagnosis of colorectal polyps[44-48]. Wanget al[46]conducted a nonblinded, prospective randomized controlled study from September 2017 to February 2018, which included the largest sample size to date. This prospective study enrolled 1058 patients including 522 randomized to colonoscopy with CAD and 536 randomized to standard colonoscopy. The results showed that the AI system significantly increased the ADR (29.1%vs20.3%,P< 0.001) and the mean number of adenomas per patient (0.53vs0.31,P< 0.001)[46]. In order to eliminate the operational bias in their nonblinded study and evaluate the effectiveness of the CAD system more rigorously, the authors performed a randomized, double-blind trial from September 2018 in a single center. The ADR was significantly higher in the CAD group than in the sham group (34%vs 28%,P= 0.03)[47].
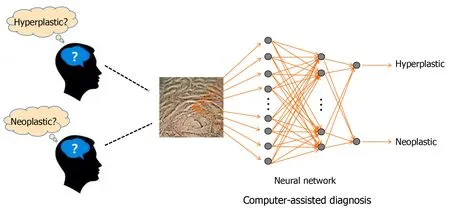
Figure 3 Deep learning using deep neural network for colonic polyp classification.
Application of AI in colorectal polyp histopathological recognition
Histopathological characterization of colorectal polyps is still the gold standard for diagnosis of polyps. It is critical for determining future endoscopic resection or regular follow-up in patients. However, this characterization is a challenging task and suffers significant intra- and interobserver variability. Thus, an automatic image analysis AI system that can help pathologists to identify different types of colorectal polyps accurately is necessary. In recent years, many scholars have begun to probe into this area[49-51]. Korbaret al[50]proposed an AI system based on a deep neural network model to identify the types of colorectal polyps on whole slide, hematoxylin and eosinstained images. The results of this system showed a precision of 89.7%, F1 score of 88.8%, recall of 88.3%, and accuracy of 93.0%[50]. In another study, a deep learning model was proposed to recognize four different stages of cancerous tissue development, including normal mucosa, early preneoplastic lesion, adenoma, and cancer. An overall accuracy of > 95% was achieved[51].
AI IN CRC
CRC usually begins with a benign tumor, initially in the form of polyps, which will develop into cancer over time. It is the third most common cancer and second most common cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide[52]. The number of patients with new onset CRC is approximately 12 million a year with 600000 deaths[53]. The high mortality and poor prognosis of CRC make this disease a huge threat to the social economy and people’s health. Early diagnosis and treatment patients with CRC have always been the focus of clinical work. The systematic research in application of AI in the diagnosis of CRC is still lacking. However, with the continuous development of AI and more applications in the field of medicine, it has now emerged in the diagnosis of CRC.
Application of AI in the qualitative diagnosis of CRC
The diagnosis of colorectal tumors can be divided into qualitative diagnosis and staging diagnosis. Qualitative diagnosis refers to colonoscopy and pathological biopsy to determine the presence of colorectal tumors. Colonoscopy has been an effective tool in the early detection of neoplastic lesions. Although magnifying endoscopy[54], narrow-band imaging[55], endocytoscopy[56], and confocal laser endomicroscopy[57]have a higher accuracy, the results are operator dependent. It is difficult to train all endoscopists to perform all methods well. Thus, a CAD system for endocytoscopy was developed to solve this problem. Takedaet al[58]carried out a study to evaluate the diagnostic ability of a CAD system for endocytoscopy for invasive CRC. In this study, a CAD system for endocytoscopy analyzed endocytoscopy images that are based on the information from texture analysis and nuclei. All 296 features (288 from texture analysis, 8 from nuclei) are used as the data for evaluating endocytoscopy images. A support vector machine analyzed these features and classified the images into three histological groups: Invasive cancer, adenoma, and non-neoplasm. The sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, negative predictive value, and positive predictive value were 89.4%, 98.9%, 94.1%, 90.1%, and 98.8%, respectively[58]. This technology is expected to bridge the gap in diagnosis quality for endoscopists at different levels. Histopathological diagnosis can be made by pathologists based on images of tissues obtained from a colonoscopic biopsy. Recently, many scholars have begun to explore the application of AI in identifying histopathological images of CRC[59,60]. Yoonet al[60]evaluated the performance of the CNN model in histologic diagnosis. The results for sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 95.10%, 92.76%, and 93.48%, respectively. The CNN model correctly classified 294 of 309 normal images and 667 of 719 tumor images[60].
Application of AI in the staging diagnosis of CRC
AI is also used in the staging diagnosis of CRC. Computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and other imaging techniques are commonly used to stage CRC. Itoet al[60]used CNN to assist in the diagnosis of cT1b CRC. With CNN learning, the sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 67.5%, 89.0%, and 81.2%, respectively, and the AUC was 0.871[61]. Whether additional surgery is required after endoscopic resection of T1CRC is currently based on international guidelines. A recent study reported that an AI model predicted positivity or negativity for lymph node metastasis by analyzing 45 clinicopathological factors of T1CRC. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 100%, 66%, and 69%, respectively, which were higher compared to the current guidelines[62]. These results suggested that AI may help to reduce unnecessary additional surgery after endoscopic resection of T1CRC. MRI is the best method for confirming the diagnosis of pelvic lymph node metastasis before surgery. Radiologists make diagnostic decisions usually based on their subjective experience. Thus, this diagnosis lacks accuracy and objectivity. To address this problem, a faster regionbased CNN was trained to read pelvic MRI images and to make diagnoses with an AUC of 0.912. The diagnosis time in one case by faster region-based CNN was 20 s, which was much shorter than that (600 s) for the radiologists’ diagnoses[63,64]. These results suggest that the faster region-based CNN enables an accurate and rapid diagnosis of CRC lymph node metastasis.
Liver is another common metastatic site of CRC. Therefore, screening of CRC patients with a high risk of liver metastasis is very important for individualized surveillance. One hundred and fifty-two tumor features extracted from computed tomography imaging and six clinical factors were used to develop a new noninvasive AI model for this task. The hybrid model, which combined relevant imaging features and clinical variables, improved accuracy of both training (90.63%) and validation (85.50%) sets with an AUC of (0.96; 0.87)[65].
Colorectal tumor segmentation is an important step in the analysis and diagnosis of CRC. However, the manual delineation of tumors is a time-consuming procedure and requires a high level of expertise. Thus, many deep learning models for automatic localization and segmentation of rectal cancers on MRI images have been proposed with high accuracy in recent years[66,67]. These AI systems can save radiologists a lot of time, but more randomized controlled studies are required to verify the stability of the results.
FUTURE PROSPECTS
Although the results from previous studies appear to be promising, supporting evidence of AI systems applied in colonoscopy is still lacking as most studies were designed retrospectively. Due to the retrospective nature of most studies and the potential selection bias involved, further prospective double-blinded clinical trials are required to confirm the role of AI-assisted colonoscopy in clinical practice. We suggest the following for further research: (1) A prospective evaluation with real-time use of AI is required; (2) In order for the proposed method to have practical value in clinical trials, further testing with a large number of pathologically proved data sets is very important to verify the effectiveness and stability of the proposed classification method; (3) A study in an international, multicenter setting should be conducted to ensure the reproducibility and stability of the results; and (4) The efficacy of AI should be evaluated in all types of colorectal lesions. Other important types of lesions such as sessile serrated lesions, ulcerative colitis, or colitis-associated cancer should be also investigated as targets of an AI system. In addition, the establishment of a clinical AI system requires the use of a large amount of clinical data from patients. Compared with research in other directions, the application of medical data also involves protection of patient privacy and ethical issues. Once the information is leaked, it may cause unpredictable consequences. Therefore, the safe management of medical data should also be a key issue. When these problems are appropriately addressed, AI can be used clinically for colorectal diseases.
CONCLUSION
AI is an exciting new field in colorectal diseases. AI technologies such as deep learning can speed up the processing of large amounts of imaging or clinical data, allowing machines to assist physicians in many important tasks such as colorectal polyp detection and classification as well as qualitative and staging diagnosis of CRC. In order to utilize AI wisely, clinicians should strive to understand the feasibility of AI and mitigate its drawbacks.
 World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年34期
World Journal of Gastroenterology2020年34期
- World Journal of Gastroenterology的其它文章
- Peliosis hepatis complicated by portal hypertension following renal transplantation
- Endoscopy-based Kyoto classification score of gastritis related to pathological topography of neutrophil activity
- Golgi protein-73: A biomarker for assessing cirrhosis and prognosis of liver disease patients
- Arachidyl amido cholanoic acid improves liver glucose and lipid homeostasis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis via AMPK and mTOR regulation
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for Budd-Chiari syndrome: A comprehensive review
- Mixed epithelial endocrine neoplasms of the colon and rectum – An evolution over time: A systematic review
