Helicobacter pyloriand 17β-estradiol induce human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cell abnormal proliferation and oxidative DNA damage
Fei Ma, Yong Yang, Jian-Dong Wang, Zhi-Wei Quan and Di Zhou
Shanghai, China
Helicobacter pyloriand 17β-estradiol induce human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cell abnormal proliferation and oxidative DNA damage
Fei Ma, Yong Yang, Jian-Dong Wang, Zhi-Wei Quan and Di Zhou
Shanghai, China
BACKGROUND: Biliary cancers are more common in females, and previous studies have suggested thatHelicobacter pylori(H. pylori) exists in the biliary system. However, the effects ofH. pylori infection and estrogen on the biological behaviors of human biliary epithelium mucosa remain unknown.e present study aimed to clarify their effects on the proliferation, apoptosis, migration and oxidative DNA damage of a human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cell (HIBEC)linein vitro.
METHODS: HIBECs were co-cultured with 17β-estradiol(at 10-9mol/L, 10-7mol/L, and 10-5mol/L) andH. pylori(at MOI=0.5:1, 1:1, and 2:1) and continuously passaged until the 15th generation (approximately 45 days).en, the following assays were performed. HIBEC proliferation was measured using the CCK-8 assay, plate clone-formation assay and by determining Ki-67 expression with immunocytochemistry; cell apoptosis and migration were investigated using Annexin-V/PI and transwell assays, respectively; and reactive oxygen species (ROS) and 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG)production were detected by flow cytometry and immunofluorescence staining combined with confocal laser scanning microscopy, respectively.e results were the basis for evalu-ating the level of oxidative stress and the related DNA damage in HIBECs.
RESULTS: HIBECs maintained a normal morphology and vitality when treated with 17β-estradiol (at 10-9mol/L) andH. pylori(at MOI=0.5:1 and 1:1). 17β-estradiol at 10-7mol/L and 10-5mol/L andH. pyloriat MOI=2:1, by contrast, causedcell death. Compared with controls, HIBECs treated with 17β-estradiol (10-9mol/L) andH. pylori(MOI=1:1) had a higher up-regulation of proliferation, Ki-67 expression, clone formation, migration activity and the expression of ROS and 8-OHdG and exhibited a down-regulation of apoptosis.e above effects were further increased when 17β-estradiol andH.pyloriwere combined (P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:H. pyloriand 17β-estradiol, separately or in combination, promoted cell proliferation and suppressed apoptosis of HIBECsin vitro.e above phenomena might be related to oxidative stress and its subsequent DNA damage withH. pyloriand 17β-estradiol.
(Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2017;16:519-527)
H. pylori;
17β-estradiol;
biliary tract;
proliferation
Introduction
Histopathological studies have demonstrated that biliary cancer is based on long-term biliary mucosa chronic inflammation, including mononuclear cell infiltration, fibrosis, muscle layer thickening,hyperplasia, and metaplasia changes with gradual evolution into various premalignant and malignant lesions.[1]e pathogenesis of biliary tract inflammation and cancer has not been clear. However, bacterial infection in the biliary system might be a key factor in its pathogenesis.In 1996, Kawaguchi et al first discoveredHelicobacter pylori(H. pylori) in the gallbladder.[2]We previously performed the meta-analyses of the correlation betweenH.pyloriinfection in the biliary system and the occurrence of chronic cholecystitis and biliary carcinoma.[3,4]e results suggested that the correlation was not significant in European and American countries but significant in countries in South Asia, East Asia and South America.e conclusions were obtained through direct methods,such as Warthin-Starry staining of bacterial culture, and indirect methods of detectingH. pyloriand its specific components, such as 16S rRNA CagA, 26 kDa protein and IgG antibodies, and others, via PCR, ELISA, and immunohistochemistry in the biliary mucosa, bile, and gallstones, which is described in the included studies.e positive rate ofH. pyloriin gallbladder tissues detected by bacterial culture was 10%-20%.[3,4]Our previous research also supported this correlation betweenH. pyloriand gallbladder carcinoma. We further found that gallbladder mucosa withH. pyloriinfection had higher expression levels of the oxidative stress related molecules inducible nitric oxide synthase and reactive oxygen species (ROS).[5]Previous studies have thus far confirmed the statistical correlation betweenH. pyloriinfection and biliary inflammation or carcinogenesis, but there has been no further study on its mechanism.
Estrogen, as a trans-activator factor and steroid hormone, is responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics.e target organs of estrogen include the reproductive system, skeletal system, lungs, central nervous system and digestive organs, among others. In recent years, increasing attention has been paid to the tumor-promoting effects of estrogen due to its ability to induce cell division and proliferation. Epidemiological studies have shown that gender is one of the most important risk factors for biliary tract cancer, and this cancer is twice as common in women as in men.[6,7]A few studies have suggested that the expression levels of estrogen receptor are related to the prognosis and malignancy of biliary tract malignant tumors.[8]However, what role does estrogen play in the development of malignant tumors of the biliary tract? Does the presence of estrogen induce the biliary epithelium to be more susceptible to other potential risk factors, such asH. pylori?
In the present study, we discuss the effects ofH. pyloriand estrogen individually or in combination on the biological behavior of biliary epithelial cellsin vitro, including proliferation, apoptosis, and migration.
Methods
H. pylori, reagents and cells
H. pyloristrains (Sydney Strain 1) were obtained from the Department of Microbiology, Shanghai Jiaotong University, School of Medicine. Aer they were inoculated on Brucella blood agar plates for culturing for 2-3 days in the micro aerobic incubation box,H. pyloricolonies were collected into an EP tube. Mixed with DMEM, the OD values ofH. pyloriwere detected by a UV analyzer.eH. pyloriconcentration was adjusted to 1×106CFU/ mL(1?660=1×108CFU/L) using a spectrophotometer.
Human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells (HIBECs,obtained from ScienCell, Product Code: 5200) were cultured in DMEM/F12 medium (10% fetal bovine serum and 90% medium). 17β-estradiol (Sigma, USA) was dissolved in ethanol and phenol red-free DMEM.
CCK-8 (Japanese Counterparts Chemistry) and anti-Ki-67 [B126.1] were used to evaluate cell proliferation.Anti-8 hydroxyguanosine (Abcam, USA) was used to detect DNA damage. Apoptosis was evaluated using an Annexin-V-FITC kit (Abcam, USA). 3, 3'-diaminobenzidine(DAB) color was purchased from Fuzhou Maixin Biotechnology (Fuzhou Maixin Biotechnology Development Co., Ltd, China).
Cell identification
Gram staining was used for the biochemical identif ication ofH. pylori. Slides were stained with gentian violet for 10 seconds and iodine solution for 10 seconds, followed by decolorizing for 20 seconds and yellow solution complex staining for 10 seconds aer elution.e urease assay was also used for the identification ofH. pylori.Samples, such as gastric mucosa, were scraped and analyzed by the urease kit to observe the color change of the reaction solution.
Warthin-Starry staining was used for the biochemical identification ofH. pylori. Samples were embedded with paraffin, and slides were generated. Aer deparaffinization and rehydration, the slides were stained with 1% silver nitrate solution at 43 ℃ for 30 minutes, and the color was developed for 15 minutes before the reaction was terminated.
Experimental groups
CCK-8 assay
Immunocytochemistry
Cells were cultured withH. pylorior 17β-estradiol at the indicated time points. Ki-67 expression was assessed by immunocytochemistry. Cells were incubated with 3%hydrogen peroxide in methanol to quench endogenous peroxidase.e sections were blocked for 30 minutes with 1% BSA and incubated with primary antibodies at 4 ℃ overnight. As negative controls, staining was performed in the absence of primary antibodies.e sections were then washed with PBS and incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies for one hour.e products were then visualized using a DAB staining kit(TIANGEN Biotech, Beijing, China) and counterstained in hematoxylin.
Warthin-Starry staining assay
To detectH. pyloriin tissue samples, Warthin-Starry staining was performed on paraffin slides for 57 cases of gallbladder carcinoma and 61 cases of bile duct cancer,which were obtained from Department of General Surgery, Xinhua Hospital from January 2012 to December 2014.e study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital, and signed informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Warthin-Starry staining was performed using a Warthin-Starry kit (Diagnostic BioSystems, Pleasanton, CA,USA). Gallbladder and bile duct mucosa tissues prepared to 4-μm paraffin sections were blocked for 1 hour at 60℃. Aer dewaxing and rehydration, the above sections were incubated at 56 ℃ in silver nitrate buffer for 1 hour,dipped in developer solution and then stained for 5 minutes. Finally, samples were dehydrated with 100% alcohol and cleared with xylene.H. pyloriwere identified as staining in buffy or a black color on a light-yellow background under an oil immersion lens (1000×).
Clone-formation assay
Annexin-V/PI staining assay for detecting HIBEC apoptosis
Cells were collected at the indicated time points.e single-cell suspension in buffer was prepared and incubated with Annexin-V-FITC and PI for 15 minutes.en,300 μL of buffer was added, and HIBEC apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry aer 1 hour.
Transwell assay
Cells were cultured withH. pylorior 17β-estradiol at the indicated time points.e bottom of the transwell upper chamber was coated with 0.2 g/mL Matrigel overnight, and cells co-cultured with the indicatedH. pylorior 17β-estradiol were seeded in the upper chamber at a concentration of 105.e lower chamber contained 600 μL of medium. Aer 48 hours, the cells were fixed with formaldehyde, and crystal violet staining was applied for 20 minutes before images were captured under a microscope.
Detection of 8-OHdG expression
Detection of ROS content in HIBECs
ROS content in HIBECs was analyzed by flow cytometry. Cells were inoculated in 6-well plates overnight and incubated for 30 minutes with 10 μL offluorescent probes (Vigorous, Beijing, China).e positive control group was treated with H2O2.
Statistical analysis
Categorical variables were evaluated using the Chisquare test, Mantel-Haenszel test or Fisher's exact probability test. Continuous variables were calculated as the mean±SD and analyzed by the Student'sttest. For abnormal distributions, the Mann-WhitneyUtest was used.SPSS 17.0.1 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for statistical analyses. A two-tailedPvalue <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
Results
H. pyloriidentification
Morphology changes of HIBECs aer co-incubation withH. pyloriand 17β-estradiol
HIBECs were observed under a light microscope 20 days aer co-culturing withH. pyloriand 17β-estradiol. We found that HIBECs without any intervention measures showed normal proliferation.e same results were observed inH. pyloriat MOI=0.5:1 or MOI=1:1,while most cells treated withH. pyloriat MOI=2:1 died,and their typical morphology disappeared. Morphological changes of HIBEC aer 45 days of co-culture withH.pyloriand 17β-estradiol were similar to 20 days. When treated with 17β-estradiol, significant death occurred at a concentration of 10-7mol/L, while cells maintained normal morphology and growth at a concentration of 10-9mol/L, which was close to the normal concentration of estrogen in the blood offemales. When HIBECs were treated withH. pyloriat MOI=1:1 in combination with 17β-estradiol at 10-9mol/L, the cells had higher proliferative activity. Aer 45 days of co-culturing HIBECs with 17β-estradiol andH. pyloriat MOI=0.5:1 or 1:1, the proliferative activity of HIBEC was similar to 20 days.erefore, we choseH. pyloriat MOI=1:1 and 17β-estradiol at 10-9mol/L for subsequent experiments (Fig. 2A).
Consistent with the observation of the morphology above, the CCK-8 assay showed that 17β-estradiol at a concentration of 10-9mol/L andH. pyloriat MOI=1:1 promoted HIBEC proliferation, and many HIBECs died with 10-7mol/L 17β-estradiol.e OD values of HIBECs co-cultured withH. pyloriand 17β-estradiol aer 45 days were similar to the results at 20 days (Fig. 2B).
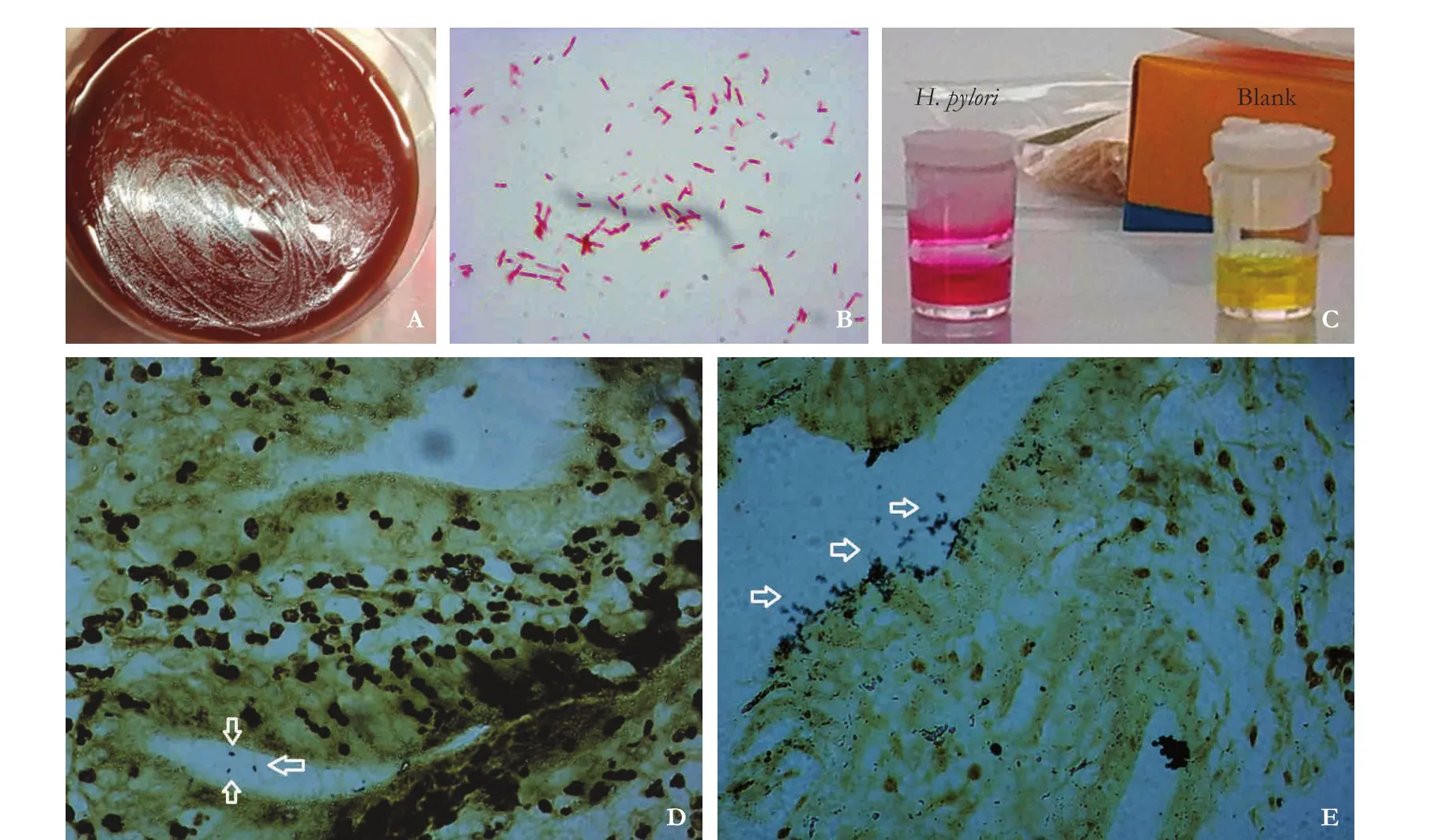
Fig. 1.H. pyloriidentification. Morphologies ofH. pyloricolonies (A). Gram staining ofH. pylori(B, original magnification ×1000).Result of the rapid urease test ofH. pylori(C). Warthin-Starry staining ofH. pylori(arrows) in gallbladder cancer (D) and biliary duct cancer (E) tissues was observed under a light microscope at 1000× magnification.
H. pyloriat MOI=1:1 and 17β-estradiol at 10-9mol/L enhance the migration ability of HIBEC
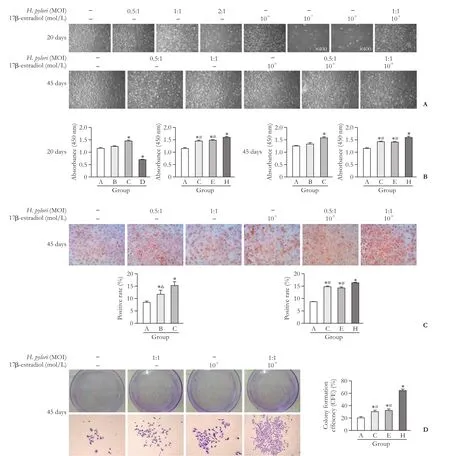
Fig. 2.Morphologies of HIBECs co-cultured withH. pyloriand 17β-estradiol (A, original magnification ×100).e results of CCK-8 assay (B). Ki-67 expression was detected by immunocytochemistry (C, original magnification ×100). HIBECs were cultured in medium(group A) or medium withH. pyloriand 17-β estradiol for 45 days (D, original magnification ×100). *:P<0.05, compared with group A;#:P<0.05, compared with group H; △:P<0.05, compared with group C.
H. pyloriat MOI=1:1 and 17β-estradiol at 10-9mol/L inhibit HIBEC apoptosis
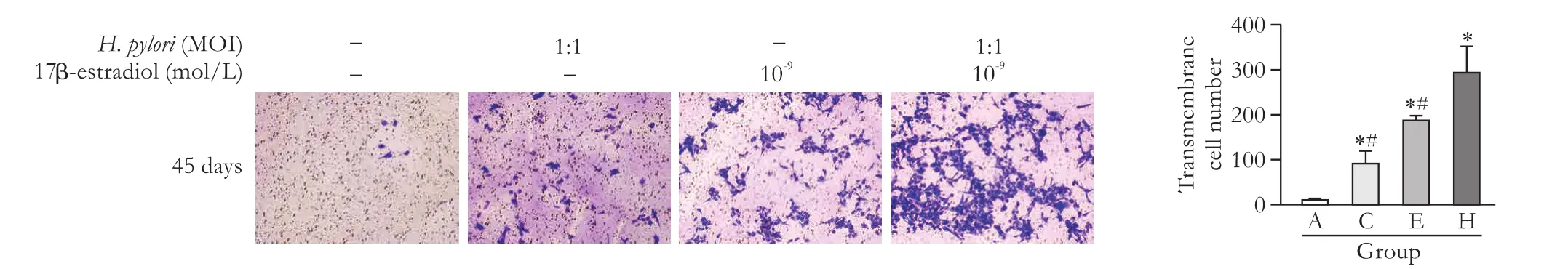
Fig. 3.Results of the transwell assay for detecting the migration ability of HIBECs aer 45 days of incubation (original magnification ×100).*:P<0.05, compared with group A; #:P<0.05, compared with group H.
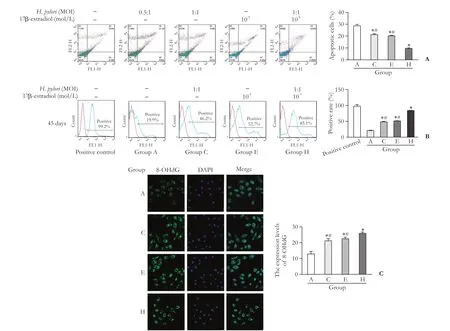
Fig. 4.Results of the Annexin-V/PI assay of HIBECs, immunofluorescence staining of 8-OHdG and flow cytometry detection of ROS in HIBECs. Results of the Annexin-V/PI assay of HIBECs aer 45 days of co-culture withH. pyloriand treatment with 17β-estradiol(A). ROS expression in HIBECs aer 45 days of co-culture withH. pyloriand treatment with 17β-estradiol (B). 8-OHdG expression in HIBECs aer 45 days of co-culture withH. pyloriand treatment with 17β-estradiol (C). *:P<0.05, compared with controls; #:P<0.05,compared with group H.
Oxidative stress was detected when HIBECs were cultured and passaged until the 15th generation at 45 days. ROS levels were significantly increased compared with those of the first generation. Compared with the control group, aer 45 days, more ROS were produced in HIBECs incubated withH. pyloriat MOI=1:1 or 17β-estrogen at 10-9mol/L. Consistent with previous results,H. pyloriat MOI=1:1 in combination with 17β-estradiol at 10-9mol/L stimulated the production of ROS. Together, the above results supported the relationship between DNA damage and ROS levels, which enhanced the anti-apoptosis phenotype of HIBECs (Fig. 4B).e average fluorescence intensity of 8-OHdG was significantly increased in HIBECs cultured withH. pyloriat MOI=1:1 or 17β-estradiol at 10-9mol/L compared with that in the control group. Moreover, treatment with bothH. pyloriat MOI=1:1 and 17β-estradiol at 10-9mol/L further enhanced 8-OHdG expression (Fig. 4C).
Discussion
In this study, we investigated the effects ofH. pyloriand 17β-estradiol on the biological behavior of HIBECsin vitro. According to the protocol reported by Yu et al,[9]we initially used three MOIs ofH. pylorito identify the ideal concentration that could induce behavior changes in HIBECs. Our results showed that the cell proliferation and invasion abilities of HIBECs were significantly up-regulated, while apoptosis was inhibited aer co-culture withH. pyloriat MOI=1:1 or 17β-estradiol (10-9mol/L) for 45 days. Moreover, when treated with bothH. pyloriand 17β-estradiol, the changes were more obvious. In addition, we found that DNA damage occurred in HIBECs aer treatment withH. pyloriand 17-estradiol, which might be related to oxidative stress.
In addition to the above preliminary cell biological behavior changes, aer co-culture withH. pylori, increased expression of oxidative stress reaction-related products, including ROS and 8-OHdG, were observed in HIBECs by flow cytometry and fluorescent staining assay through laser scanning confocal microscope, respectively.Notably, ROS and 8-OHdG are oen closely related to cell carcinogenesis.
ROS are various types of metabolites from aerobic cells, defined as O2-, produced from intracellular O2that accepted electrons through the electron transfer chain and further biochemical reactions. Peroxide, oxygen ions and oxygen free radicals are major members of ROS.ROS is a “double-edged sword” in the biochemical reaction of cells. As a “second messenger”, a physiological dose of ROS plays a critical role in the signal transduction process of cells, which is important for maintaining the balance of cell proliferation and apoptosis. However,because ROS can move freely through the cell membrane, excessive ROS lead to oxidative stress damage,which is followed by cytoplasm damage, DNA rupture,protein destruction and cell death.[11]When cellular ROS levels are increased, normal cells can reduce damage through the protective effects of active enzymes, such as dismutase (superoxide, SOD).[12,13]A number of small molecular substances, such as vitamins, uric acid, glutathione, melatonin, alpha lipoic acid, carotenoids, trace elements copper, zinc, selenium and other metal substances, also have antioxidant effects.[14-17]However, when endogenous or exogenous stimuli, such as long-lasting ionizing radiation or toxic substances, exceed the antioxidant scavenging effect of the cell, damage induced by oxidative stress occurs and persists. At present, the most intensive studies focusing on the relationship betweenH.pyloriand ROS are in the field of gastric cancer, and two potential mechanisms have been proposed.e first theory is thatH. pylorican induce chronic inflammation of normal gastric cancer cells, which is followed by releasing tumor necrosis factors, interferons and inflammatory cytokines and interleukins that stimulate intracellular ROS generation, inhibit the reduction of endogenous glutathione (reduced glutathione, GSH) expression and result in DNA damage.[18]e second theory, proposed by Nagata et al,[19]is that in addition to secondary ROS production,H. pylorican secrete ROS and induce gastric mucosal damage. In our study, we found that compared with the control group, HIBECs cultured withH. pyloriat MOI=1:1 for 45 days had a significantly increased level of ROS (48.70%±1.61% vs 20.93%±0.84%,P=0.000), suggesting thatH. pyloricould also promote oxidative stress in the biliary epithelium of HIBECin vitro.
Most investigations regarding the role of estrogen in the occurrence of biliary diseases have focused on their effect on the induction of gallstone formation.[23,24]Although a few clinical studies have demonstrated that estrogen and its receptors might be related to the prognosis of biliary tract cancer, no cellular or molecular biological mechanisms have been reported. Moreover, the sample sizes in prior studies were too small, and their results require further confirmation. In the present study, we found that using estrogen (17β-estradiol) at a concentration close to physiological levels in females (10-9mol/L)could induce HIBEC proliferation, invasion, and oxidative DNA damage while inhibiting apoptosis. Notably,17β-estradiol also had a synergistic effect of strengtheningH. pylorieffects on the above abnormal biological behaviors.ese findings were consistent with the epidemiological characteristics of biliary tract malignancies.
In conclusion,H. pyloriand 17β-estradiol, individually or together, promote HIBEC proliferation, inhibit their apoptosis, and induce a degree of invasivenessin vitro.ese findings might be related to oxidative stress and subsequent DNA damage in HIBECs. Furtherin vivomechanism studies should be performed to verify the above findings.
Contributors:MF and YY performed the research, wrote the first draand contributed equally to this article. All authors contributed to the design and interpretation of the study. ZD is the guarantor.
Funding:is study was supported by grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81401932).
Ethical approval:is study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Xinhua Hospital (XHEC-F-2014-006).
Competing interest:No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
1 Liczko J, Stawski T, Zaba M, Kurek J, Sabat D, Wyrobiec G, et al. Tissue factor and tissue factor pathway inhibitor in chronically inflamed gallbladder mucosa. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014:403639.
2 Kawaguchi M, Saito T, Ohno H, Midorikawa S, Sanji T, Handa Y, et al. Bacteria closely resembling Helicobacter pylori detected immunohistologically and genetically in resected gallbladder mucosa. J Gastroenterol 1996;31:294-298.
3 Zhou D, Wang JD, Weng MZ, Zhang Y, Wang XF, Gong W, et al. Infections of Helicobacter spp. in the biliary system are associated with biliary tract cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013;25:447-454.
4 Zhou D, Zhang Y, Gong W, Mohamed SO, Ogbomo H, Wang X, et al. Are Helicobacter pylori and other Helicobacter species infection associated with human biliary lithiasis? A meta-analysis. PLoS One 2011;6:e27390.
5 Zhou D, Guan WB, Wang JD, Zhang Y, Gong W, Quan ZW. A comparative study of clinicopathological features between chronic cholecystitis patients with and without Helicobacter pylori infection in gallbladder mucosa. PLoS One 2013;8:e70265.
6 Hundal R, Shaffer EA. Gallbladder cancer: epidemiology and outcome. Clin Epidemiol 2014;6:99-109.
7 Srivastava A, Sharma KL, Srivastava N, Misra S, Mittal B. Significant role of estrogen and progesterone receptor sequence variants in gallbladder cancer predisposition: a multi-analytical strategy. PLoS One 2012;7:e40162.
8 Saranga Bharathi R, Singh R, Gupta R, Verma GR, Kalra N,Kiran K, et al. Female sex hormone receptors in gallbladder cancer. J Gastrointest Cancer 2015;46:143-148.
9 Yu XW, Xu Y, Gong YH, Qian X, Yuan Y. Helicobacter pylori induces malignant transformation of gastric epithelial cells in vitro. APMIS 2011;119:187-197.
10 Burkitt MD, Duckworth CA, Williams JM, Pritchard DM. Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric pathology: insights from in vivo and ex vivo models. Dis Model Mech 2017;10:89-104.
11 Chokshi K, Pancha I, Ghosh A, Mishra S. Nitrogen starva-tion-induced cellular crosstalk of ROS-scavenging antioxidants and phytohormone enhanced the biofuel potential of green microalga Acutodesmus dimorphus. Biotechnol Biofuels 2017;10:60.
12 Riaz L, Mahmood T, Coyne MS, Khalid A, Rashid A, Hayat MT, et al. Physiological and antioxidant response of wheat(Triticum aestivum) seedlings to fluoroquinolone antibiotics.Chemosphere 2017;177:250-257.
13 Tsai MH, Lee CW, Hsu LF, Li SY, Chiang YC, Lee MH, et al.CO-releasing molecules CORM2 attenuates angiotensin II-induced human aortic smooth muscle cell migration through inhibition of ROS/IL-6 generation and matrix metalloproteinases-9 expression. Redox Biol 2017;12:377-388.
14 Kapil A, Singh JP, Kaur T, Singh B, Singh AP. Involvement of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in vitamin D-mediated protection against acute kidney injury in rats. J Surg Res 2013;185:774-783.
15 Garlet TR, Parisotto EB, de Medeiros Gda S, Pereira LC,Moreira EA, Dalmarco EM, et al. Systemic oxidative stress in children and teenagers with Down syndrome. Life Sci 2013;93:558-563.
16 Schrag M, Mueller C, Zabel M, Croon A, Kirsch WM, Ghribi O, et al. Oxidative stress in blood in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: a meta-analysis. Neurobiol Dis 2013;59:100-110.
17 Awadallah S. Protein antioxidants in thalassemia. Adv Clin Chem 2013;60:85-128.
18 Obst B, Wagner S, Sewing KF, Beil W. Helicobacter pylori causes DNA damage in gastric epithelial cells. Carcinogenesis 2000;21:1111-1115.
19 Nagata K, Yu H, Nishikawa M, Kashiba M, Nakamura A,Sato EF, et al. Helicobacter pylori generates superoxide radicals and modulates nitric oxide metabolism. J Biol Chem 1998;273:14071-14073.
20 Wu LL, Chiou CC, Chang PY, Wu JT. Urinary 8-OHdG: a marker of oxidative stress to DNA and a risk factor for cancer,atherosclerosis and diabetics. Clin Chim Acta 2004;339:1-9.
21 Goldin RD, Roa JC. Gallbladder cancer: a morphological and molecular update. Histopathology 2009;55:218-229.
22 Kanthan R, Senger JL, Ahmed S, Kanthan SC. Gallbladder cancer in the 21st century. J Oncol 2015;2015:967472.
23 de Bari O, Wang TY, Liu M, Portincasa P, Wang DQ. Estrogen induces two distinct cholesterol crystallization pathways by activating ERα and GPR30 in female mice. J Lipid Res 2015;56:1691-1700.
24 de Bari O, Wang HH, Portincasa P, Liu M, Wang DQ.e deletion of the estrogen receptor α gene reduces susceptibility to estrogen-induced cholesterol cholelithiasis in female mice.Biochim Biophys Acta 2015;1852:2161-2169.
November 30, 2016
Accepted after revision June 23, 2017
AuthorAffiliations:Department of Oncology (Ma F) and Department of General Surgery (Yang Y, Wang JD, Quan ZW and Zhou D), Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University, School of Medicine, Shanghai 200092,China
Di Zhou, MD, Department of General Surgery,Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University, School of Medicine, 1665 Kongjiang Road, Yangpu District, Shanghai 200092, China (Tel: +86-21-25077905; Fax: +86-21-65795173; Email: m13918070485@163.com)
? 2017, Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. All rights reserved.
10.1016/S1499-3872(17)60038-9
Published online June 30, 2017.
 Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International2017年5期
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International2017年5期
- Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International的其它文章
- Letters to the Editor
- The “Colonial Wig” pancreaticojejunostomy:zero leaks with a novel technique for reconstruction after pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Risk factors and managements of hemorrhage associated with pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Tailored pancreatic reconstruction after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a single-center experience of 892 cases
- Prospective comparison of prophylactic antibiotic use between intravenous moxifloxacin and ceftriaxone for high-risk patients with post-ERCP cholangitis
- Comparative study of the effects of terlipressin versus splenectomy on liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats
