Roles of Rap1 signaling in tumor cell migration and invasion
Yi-Lei Zhang, Ruo-Chen Wang, Ken Cheng, Brian Z. Ring, Li Su,Key Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics of Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 40074, China;Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 5075, China;Research Institute of Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Shenzhen, Shenzhen 5806, China
Roles of Rap1 signaling in tumor cell migration and invasion
Yi-Lei Zhang1, Ruo-Chen Wang1, Ken Cheng2, Brian Z. Ring1, Li Su1,31Key Laboratory of Molecular Biophysics of Ministry of Education, School of Life Science and Technology, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430074, China;2Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510275, China;3Research Institute of Huazhong University of Science and Technology in Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518063, China
Ras-associated protein-1 (Rap1), a small GTPase in the Ras-related protein family, is an important regulator of basic cellular functions (e.g., formation and control of cell adhesions and junctions), cellular migration, and polarization. Through its interaction with other proteins, Rap1 plays many roles during cell invasion and metastasis in different cancers. The basic function of Rap1 is straightforward; it acts as a switch during cellular signaling transduction and regulated by its binding to either guanosine triphosphate (GTP) or guanosine diphosphate (GDP). However, its remarkably diverse function is rendered by its interplay with a large number of distinct Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factors and Rap GTPase activating proteins. This review summarizes the mechanisms by which Rap1 signaling can regulate cell invasion and metastasis, focusing on its roles in integrin and cadherin regulation, Rho GTPase control, and matrix metalloproteinase expression.
Tumor; metastasis; Rap1; RapGEFs; RapGAPs
Introduction
Cell migration and tumor metastasis are responsible for up to 90% of cancer-associated mortality1. Ras-associated protein-1 (Rap1) plays important roles in the regulation of multiple key events in tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Rap1, a member of the 21-kilodalton Ras-like small GTPase family, can bind to either guanosine triphosphate (GDP) or guanosine diphosphate (GDP) and is modulated by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) and GTPase activating proteins (GAPs)2,3. Rap1 shares a high degree of sequence identity (53%) with Ras protein4and can revert the phenotype of K-Ras-transformed cells5. Consistent with this observation, overexpressed Rap1V12, a constitutively active form of Rap1 (Rap1GTP), inhibits lysophosphatidic acid (LPA)-induced Ras-dependent ERK activation6. However, Rap1 can also activate B-Raf and ERKs in a manner independent and distinct of Ras7. The many roles of Rap1 include its participation in regulation of integrin- and cadherin-mediated cell adhesion in response to various membrane receptors8and regulation of both the recycling,avidity, and affinity of integrins by modulating an inside-out activation process9-11. Rap1 activation may promote the formation of cadherin-mediated cell-cell contacts through inside-out regulation12or cell-cell contact-induced E-cadherin-mediated outside-in signaling13.
Regulation of Rap1 activity is primarily controlled by RapGEFs and GAPs (Figure 1). The dissociation rate of nucleotides from Rap1 is slow; however, GEFs accelerate this exchange reaction by several orders of magnitude14. Given that GEFs weaken the association between Rap1 and nucleotides, increases in GTP-bound forms over GDP-bound forms are caused by the higher intracellular concentration of GTP than GDP by approximately ten times15. GEFs contain a catalytic CDC25 homology domain and show selective activity for Rap1, although some GEFs can interact with other small G proteins16. This modulation of nucleotide binding of GEFs allows GEFs to respond to diverse stimuli, resulting in spatiotemporal regulation of Rap1. For example, RapGEFs, such as Epac1 and Epac2, are directly regulated by the secondary messenger cAMP, which controls local Epac-Rap1 signaling through its cellular distribution. Epac1 activation triggers the relocalization of Epac1 to the plasma membrane, activating membrane-localized Rap1 and enhancing integrin-mediated cell adhesion17. Another RapGEF, C3G, is regulated through post-translational modifications by Src and interacts with adaptor proteins of the Crk family upon activation of several receptors, includingplatelet-derived growth factor receptor and insulin receptor18-20. Rap1-bound GTP is efficiently hydrolyzed into GDP in the presence of RapGAPs, which accelerate the GTP hydrolysis reaction by several orders of magnitude.
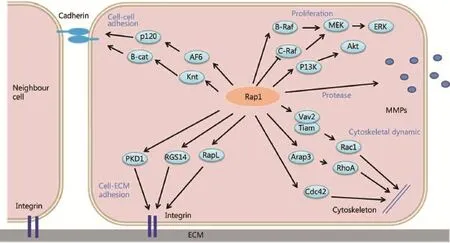
Figure 1 Mechanisms by which Rap1 signaling controls tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Rap1 signaling regulates integrin- or cadherinmediated cell adhesion, expression levels of proteases (e.g., matrix metalloproteinase), and cytoskeletal changes, which are linked to tumor cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis.
Two families of Rap1-specific GAPs exist: the Rap1GAP and SIPA1 families21. The mechanism through which all GAPs catalyze GTP hydrolysis primarily depends on the stabilization of the catalytic machinery of G protein through insertion of a catalytic side chain into the nucleotide-binding pocket, an arginine side chain for RasGAPs and asparagine side chain for RapGAPs22. Through differentially distributed subcellular features, such as protein-protein interactions and epigenetic modifications, RapGAPs target different Rap1-dependent signaling complexes and consequently perform distinct cellular functions. For example, Rap1GAP is recruited from the cytosol to the plasma membrane by its interaction with Gαz, which is activated by G protein coupled receptors23. E6 oncoprotein binds to SIPA1L1 (E6TP1) and targets it for degradation, resulting in deregulation of Rap1 activity24. In melanoma cells, Rap1GAP is downregulated via promoter methylation, promoting Rap1 activation, ERK phosphorylation, and cell proliferation and survival25.
Moreover, the diversity of cellular functions regulated by small G proteins is determined by the distinct downstream effectors of these proteins. The effectors of Rap1 include the adaptor proteins AF-6, RAPL, Ezrin, Rasip1, Radil, Krit1, RacGEFs (e. g. , Tiam1 and Vav2), and RhoGAPs, including RA-RhoGAP and Arap326-31, which contribute to the regulation of Rap1-dependent cellular functions, such as cell adhesion, junction, migration, and polarization. RAPL deficiency has been speculated to significantly reduce the ability of chemokine-stimulated lymphocytes to adhere to ICAM and migrate into peripheral lymph nodes and spleen26. AF-6 interacts with p120 catenin and inhibits E-cadherin endocytosis in a Rap1-dependent manner27, affecting E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion. Rasip1 mediates Rap1-induced cell spreading without affecting adhesion; it induces junctional tightening via interaction with Radil28. Concomitantly, Rap1 promotes translocation of Radil from cytoplasm to plasma membrane, and Radil overexpression increases cell adhesion29. Rap1 interacts with Tiam1 and Vav2 without affecting their catalytic activity but in turn activates Rac and CDC42, regulating cell polarization and movement30,31. Furthermore, the Rap1 effector B-Raf can mediate ERK activation, and regulation of PI3K/Akt by Rap1 is an important mechanism in the control of cell survival and proliferation32(Figure 1).
Tumor cell migration, invasion, and metastasis: roles of Rap1 signaling and its regulators
The diverse roles of Rap1 in the regulation of normal cell growth are translated into several distinct activities in tumorcell development. Rap1 demonstrates distinct actions during metastasis depending on the assay employed and cancer type studied (Table 1) based on standard assays used to determine the roles of Rap1 include overexpression of wild-type Rap1 or its active mutants (Rap1V12 or Rap1E63), the use of extracellular stimuli, such as HGF, TGFβ, EGF, or cAMP analogs, and the use of siRNAs and the pharmacological inhibitor GGTI-298, followed by assessment of the invasive capacity of tumor cells by means of scratch and Transwell assays in vitro or xenograft models in vivo. Active Rap1 inhibits tumor invasion and metastasis in bladder, lung, and brain33,34, whereas it has the opposite effect in melanoma, leukemia, breast cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC), pancreatic carcinoma, and non-small cell lung carcinoma35-40. Rap1 activation promotes the adhesion of lymphoma cells to endothelial cells and its subsequent transmigration into the hematopoietic system, through which lymphoma cells spread to distant organs39. Moreover, Rap1E63 contributes to the invasive ability of prostate cancer cells41, whereas Rap1V12 suppresses prostate cancer metastasis42. Additionally, both Rap1V12 and Rap1GAP impair the migratory and invasive abilities of melanoma cells39, whereas the two isoforms of Rap1, Rap1A, and Rap1B exert the opposite effect on cell motility in glioma43,44. These manifold phenotypes reflect the multiple signaling pathways that exist downstream of Rap1.
Similar to Rap1, which plays diverse roles in tumor metastasis, Rap1 regulators are pleiotropic (Table 2). Overexpression of the Rap1 activator DOCK4 suppresses invasion of mouse osteosarcoma cells45. Targeted shRNA-mediated EPAC1 inhibition reduces pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion46. Stable expression of a nondegradable mutant of RAPGEF2 in breast cancer cells blocks tumor invasion and metastasis47. Rap1GAP inhibits tumor cell invasion in pancreatic carcinoma, thyroid carcinoma, melanoma, renal carcinoma, and colon cancer48-50; however, increased expression of Rap1GAP induces cell invasion in leukemia51. High expression of SIPA1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis in prostate cancer, melanoma, and breast cancer52,53In colon cancer, downregulation of endogenous SIPA1 increases the invasive ability of cells54. This finding is inconsistent with the result for ovarian cancer, wherein C3G/Rap1 signaling promotes cell invasion, whereas Rap1GAP does not affect cell mobility55,56. Most of the studies included in Table 2 also assessed the role of Rap1 and the effect of GEFs and GAPs on tumor invasion and metastasis. Exceptions are the study on Rap1GAP in pancreatic carcinoma49and SIPA1 in melanoma and colorectal carcinoma52,54; these studies did not assess whether Rap1 is involved in the observed cellular changes.
Other potential functions of Rap1 GEFs and GAPs in addition to their regulatory role on Rap1 activity cannot be ruled out. A recent study demonstrated that nuclear SIPA1 could activate integrin β1 promoter and promote breast cancer cell invasion in a Rap1-independent manner53. Moreover, the opposite influences of Rap1GAP and SIPA1 on regulation of melanoma cell invasion imply that there exist multiple mechanisms through which Rap1GAPs can affect cell migration and invasion. Several independent investigations have shown that the Rap1 GEF PDZ-GEF2 promotes tumor cell invasion in colon cancer, whereas Rap1GAP and SIPA1 suppresses cancer cell invasion54,57. This finding suggests a potential central role of Rap1 signaling and Rap1 signaling partners in colorectal carcinoma metastasis, and that the function of the Rap1 signaling proteins in tumor metastasis is very complex and mediates the effect of a host of other cellular and tissue-specific factors. Dissemination of tumor cells from the original tumor mass involves a breakdown of cell-cell adhesion. Tumor cell migration is promoted by disruption of the extracellular matrix to form a proteolytic microtrack. Rap1 signaling participates in several processes that contribute to these events (Figure 2), as outlined below.
Rap1 signaling regulates cell adhesion
Rap1 signaling regulates integrins and cadherins, which play important roles in cell adhesion to ECM and in cell-cell adhesion58. In lung cancer, cAMP-induced Epac-Rap activation suppresses TGFβ- and HGF-stimulated cell migration by enhancing cell-cell adhesion34. JAM-A drives breast cancer cell migration and adhesion through activation of Rap1 and integrin β1 and formation of a complex between JAM-A, AF-6, and PDZ-GEF236. Disrupting the balance in Rap1 activity in melanoma cells via expression of Rap1V12 or Rap1GAP impairs cell adhesion and migration via the FAK-and integrin-dependent pathways39. Given that both Rap1-specific GAPs Rap1GAP and SIPA1 inhibit cell adhesion to ECM, concluding that Rap1 plays a role in the regulation of cell adhesion is reasonable25,52. In prostate cancer cells, SIPA1 promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis at least partially by inhibiting Rap1-mediated cell adhesion to ECM42. Reduced cell-cell adhesion is required for individual cell dissemination and invasion at the leading edge of the tumor mass during epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and mesenchymal-migrating tumor cells require strong cell-to-ECM adhesion, whereas amoeboid movement does not58. In terms of the specific role of Rap1 in regulating integrin activation and integrin-mediated cell adhesion, Rap1 forms a complex containing talin combined with RIAM, which
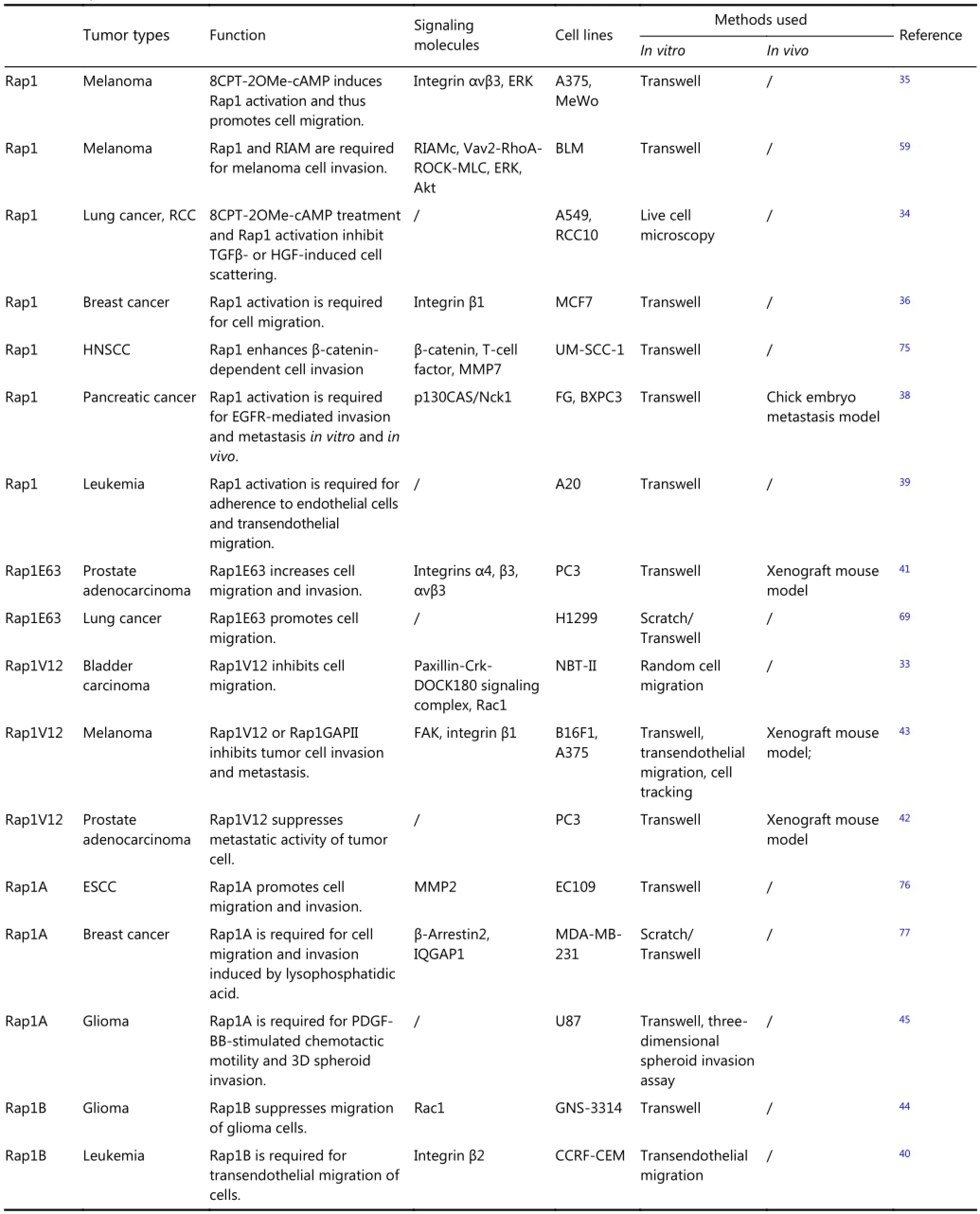
Table 1 Rap1 in tumor cell invasion and metastasis
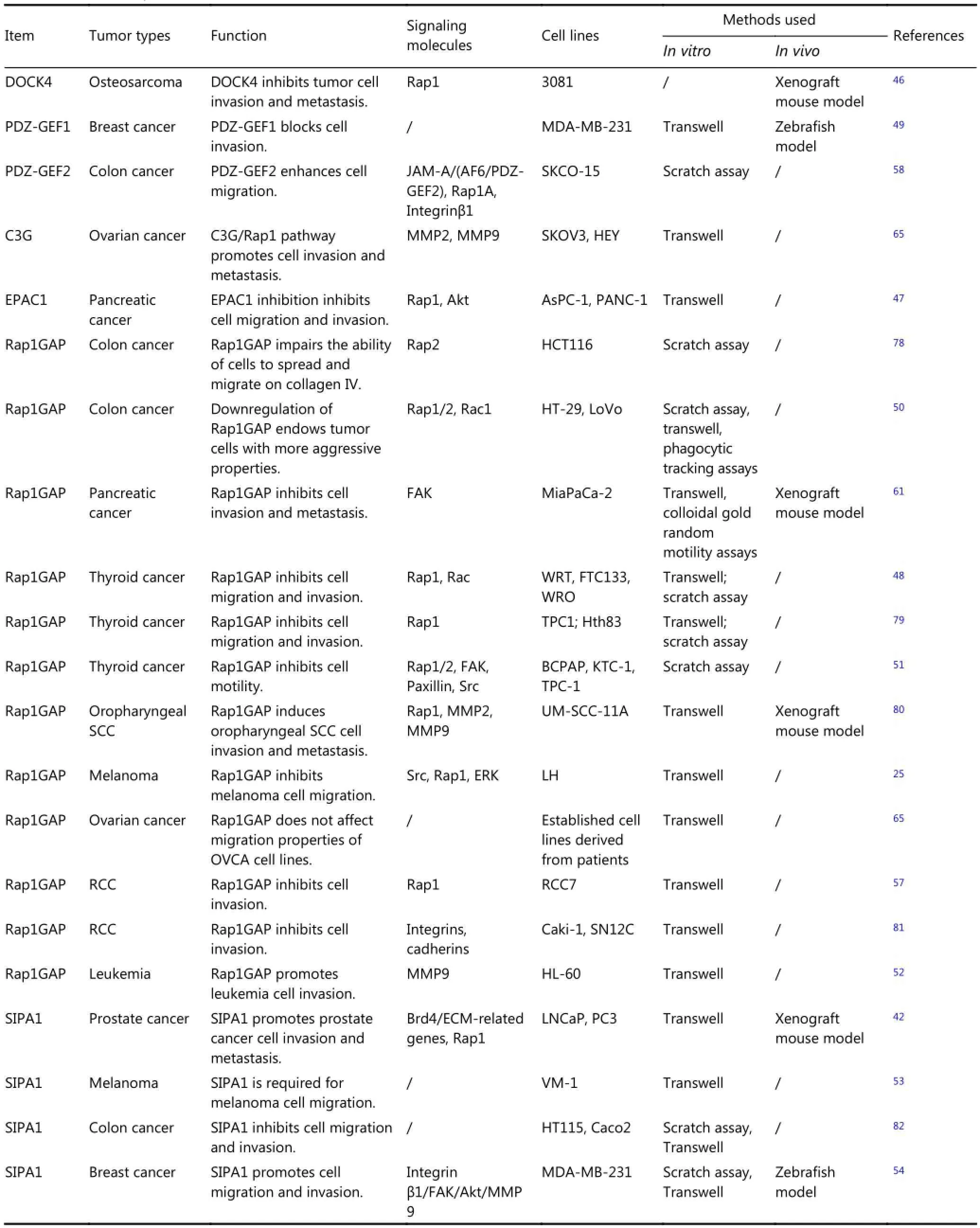
Table 2 Role of Rap1 GEFs and GAPs in tumor cell invasion and metastasis
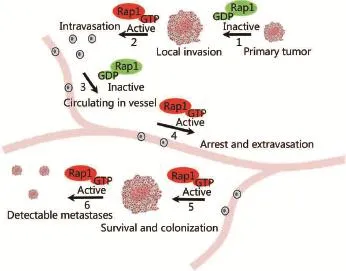
Figure 2 Dynamic change in Rap1 signaling during tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Dynamic change or cycling of Rap1 activity is required for invasive and metastatic behavior of tumor cells. For instance, while inactivation of Rap1-cadherin or integrin signaling is associated with reduced cell-cell adhesion or cell adhesion to extracellular matrix in one stage (steps 1 and 3), a separate step might entail increased Rap1 activity and cell adhesion (steps 2, 4, 5, and 6).
targets talin to integrin59. However, a complete description of the roles of Rap1 in mediating cell adhesion in tumor cell invasion and metastasis requires further clarification.
Rap1 signaling modulates expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
During tumor invasion and metastasis, MMPs degrade ECM barriers, cleave and activate target proteins, and regulate cell adhesion. In HNSCCs, Rap1 promotes nuclear localization of β-catenin, which induces TCF-dependent MMP7 transcription, thereby contributing to tumor cell invasion37. Knockdown of C3G in ovarian cancer cells reduces MMP2 and MMP9 production and Rap1-GTP level56. However, in HNSCCs, overexpression of Rap1GAP increases the expression levels of MMP2 and MMP9 and the invasive capacity of cells, although the role of Rap1 in this process is unclear62. Overexpression of SIPA1 in prostate cancer cells reduces MMP12 expression42. By contrast, SIPA1 knockdown in breast cancer cells reduces MMP9 expression through the FAK/Akt pathway53.
Rap1 signaling controls Rho GTPase-mediated regulation of cytoskeletal dynamics
Several Rho family members function in actin cytoskeleton rearrangement and consequently in modulation of cell motility. Rap1 signaling can participate in motility regulation involving Rho family proteins, particularly Cdc42, Rac1, and RhoA. Rap1 associates with RacGEFs, such as Vav2 and Tiam1, to induce translocation of Vav2 and activates Rac1 to promote cell spreading30. Cdc42 activation by Rap1 increases the activity of cell polarization-related protein complex, which in turn activates Rac1 through Tiam1 and subsequently enhances cell polarization31. Moreover, Rap1 can interact with and activates Arap3, a RhoA GAP. During tumor metastasis, Rap1 increases the ability of melanoma cell to migrate via Vav2-dependent activation of the RhoA/ ROCK/MLC pathway60. In vitro overexpressed Rap1GAP inhibits Rap1, Rac1 activation, and thyroid tumor cell migration61. Additionally, Rap1's inhibitory effects on bladder cancer and glioma cell migration are intensified by reduced Rac1 activity33,43. Rap1 signaling can regulate Rhofamily protein activities either positively or negatively, causing a wide range of effects on tumor cell invasion and metastasis.
Rap1 signaling controls cell proliferation
Tumor cell growth can increase tumor volume and mass, contributing to invasion via physical pushing63. An inhibitory effect of Rap1 signaling-related molecules on cell proliferation and invasion has been repeatedly observed; for instance, DOCK4 inhibits osteosarcoma and Rap1GAP inhibits pancreatic cancer, thyroid carcinoma, and melanoma cells25,45,48,49. Additionally, SIPA1 drives both cell proliferation and invasion in melanoma cells52. SIPA1-induced expression exerts little effect on primary tumor mass in prostate cancer but significantly increases both tumor cell invasion and metastasis, suggesting that SIPA1 promotes metastasis through mechanisms other than proliferation42. SIPA1 knockdown impairs the invasive capacity of breast cancer cells while it enhances their proliferation53. Similarly, overexpression of Rap1V12 in melanoma cells increases tumor mass but inhibits tumor metastasis in vivo39. Moreover, Rap1GAP overexpression inhibits cell growth but induces MMP2- and MMP9-mediated oropharyngeal squamous carcinomas cell invasion51.
Regulation of Rap1 is dependent on tissue and subcellular-specific factors
Rap1 signaling can affect metastasis in different manners depending on tumor types (Table 3). Tissue-specific protein expression in different tumor types likely contributes to theregulation of Rap1 signaling, similar to the spatiotemporally regulated patterns of gene expression during tumor development64. Indeed, Rap1 has been implicated in the activation and inhibition of ERK pathway in different cell types21; cAMP-induced activation of Rap1 inhibits C-Rafinduced ERK activation65. However, in neuronal cells expressing B-Raf, activated Rap1 can directly bind to B-Raf and induces downstream ERK activation7,66. Additionally, over-activation or inactivation of Rap1 inhibits melanoma cell motility, suggesting that change in Rap1 activity is critical for the metastatic dissemination of melanoma cells39. The interaction of Rap1 signaling with tissue-specific factors may explain this considerably diverse functions of Rap1. For example, while basal level of Rap1-GTP maintains cell adhesion, insulin-like growth factor type I receptor transiently regulates Rap1 activity through C3G and Rap1GAP to promote cell movement67.
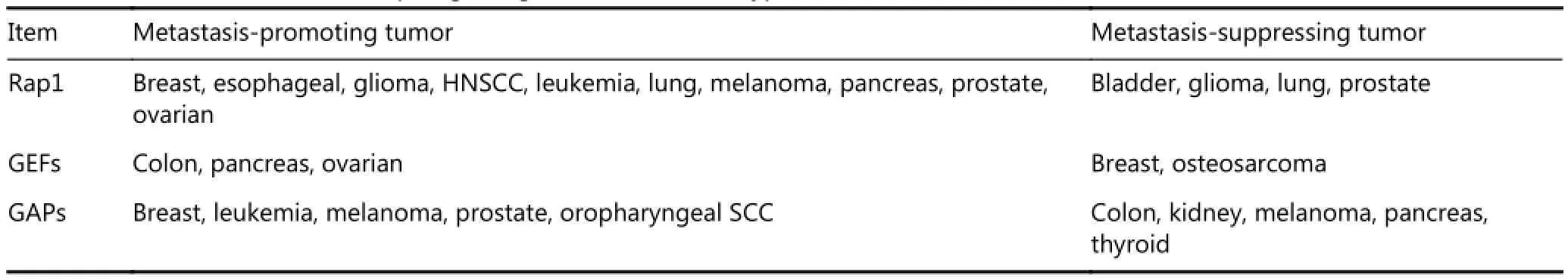
Table 3 Bidirectional effects of Rap1 signaling in different tumor types
Protein subcellular localization of Rap1 is vital to the specificity and diversity of its function68. Relatedly, tumor cell dissemination and invasion depends on the stability and activity of Rap1 (Figure 2). Rap1 phosphorylation prevents the membrane association of Rap1, resulting in cytosolic and nuclear accumulation and in subsequent decrease in Rap1-dependent cell adhesion69,70. In addition, Rap1 stabilizes βcatenin in the nucleus and enhances β-catenin-dependent transcription and invasion in HNSCC37,51. SIPA1, recruited by AF6 and co-localized with Rap1 at cell adhesion sites, inhibits endogenous Rap1GTP and integrin β1-mediated cell adhesion to fibronectin71. However, nuclear-localized SIPA1 activates the integrin β1 gene promoter and promotes cell invasion and adhesion (Figure 3)53.
Novel targets for the prevention of metastasis: insights from related studies on Rap1 signaling
Prevention or early detection of the initial dissemination of tumor cells and secondary spread of tumor is an important goal in research aiming to find better clinical therapies72. In a melanoma metastasis model, six distinct Rap1-regulating molecules were used to predict the aggressive capability of melanoma cells52. Several inhibitors of cell motility, such as metalloproteinase inhibitor73and the fascin inhibitor Migrastatin74, have been suggested to demonstrate clinical utility in preventing tumor cell dissemination and subsequent invasion and metastasis. However, formation of metastases often occurs prior to the diagnosis of cancer. The Rap1 signaling pathway offers many targets for novel clinical tools given that Rap1 affects not only cell polarity and cell adhesion but also cell proliferation and invasion. Treatmentwith the demethylating agent 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine induces Rap1GAP expression and reduces melanoma cell proliferation and survival25. In addition, treatment with 5-aza-deoxycytidine and/or the histone deacetylation inhibitor trichostatin A induces Rap1GAP expression in thyroid tumor cells, reducing cell invasion and proliferation48,75. Additional studies on these and other novel reagents targeting Rap1 signaling molecules are called for.
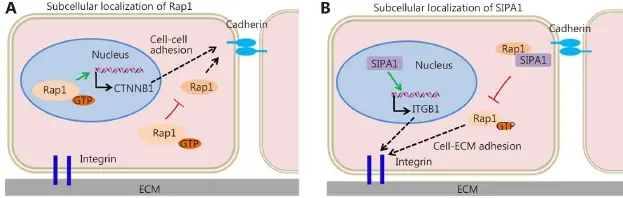
Figure 3 Subcellular localization of Rap1 and SIPA1 during tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Subcellular localization of Rap1 (A) and SIPA1 (B) contributes to their distinct functions within a cell.
Conclusions
Rap1 signaling plays several important roles in tumor cell invasion and metastasis. The full scope of its functions remains unknown; Rap1 can induce very distinct effects depending on the tissue in which Rap1 is expressed. Therefore, the specific functions and effects of Rap1 signaling on metastasis in different tumor types remains a subject of continuing research. Additionally, many proteins contribute to the diversity in the control of tumor invasion and metastasis by Rap1 signaling, and the full panoply of factors that work with Rap1 resulting in diverse control mechanisms is not yet fully elucidated. Future works employing high throughput screening strategies to identify new molecules contributing to Rap1 signaling and real-time monitoring of Rap1 signaling during tumor invasion and metastasis are needed to further define the roles of Rap1.
Acknowledgements
This study is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31271504 and 31471310) and the Shenzhen Science and Technology Innovation Committee, China (Grant No. JCYJ2013040 1144744187).
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
1.Valastyan S, Weinberg RA. Tumor metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell. 2011; 147: 275–92.
2.Gloerich M, Bos JL. Regulating rap small G-proteins in time and space. Trends Cell Biol. 2011; 21: 615–23.
3.Hattori M, Minato N. Rap1 GTPase: functions, regulation, and malignancy. J Biochem. 2003; 134: 479–84.
4.Caron E. Cellular functions of the Rap1 GTP-binding protein: a pattern emerges. J Cell Sci. 2003; 116: 435–40.
5.Kitayama H, Sugimoto Y, Matsuzaki T, Ikawa Y, Noda M. A rasrelated gene with transformation suppressor activity. Cell. 1989; 56: 77–84.
6.Cook SJ, Rubinfeld B, Albert I, McCormick F. RapV12 antagonizes Ras-dependent activation of ERK1 and ERK2 by LPA and EGF in Rat-1 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1993; 12: 3475–85.
7.Vossler MR, Yao H, York RD, Pan MG, Rim CS, Stork PJS. cAMP activates MAP kinase and Elk-1 through a B-Raf- and Rap1-dependent pathway. Cell. 1997; 89: 73–82.
8.Retta SF, Balzac F, Avolio M. Rap1: a turnabout for the crosstalk between cadherins and integrins. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006; 85: 283–93.
9.Bos JL, de Bruyn K, Enserink J, Kuiperij B, Rangarajan S, Rehmann H, et al. The role of Rap1 in integrin-mediated cell adhesion. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003; 31: 83–6.
10.Dustin ML, Bivona TG, Philips MR. Membranes as messengers in T cell adhesion signaling. Nat Immunol. 2004; 5: 363–72.
11.Lafuente EM, van Puijenbroek AAFL, Krause M, Carman CV, Freeman GJ, Berezovskaya A, et al. RIAM, an Ena/VASP and Profilin ligand, interacts with Rap1-GTP and mediates Rap1-induced adhesion. Dev Cell. 2004; 7: 585–95.
12.Pannekoek WJ, Kooistra MRH, Zwartkruis FJT, Bos JL. Cell-cell junction formation: the role of Rap1 and Rap1 guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009; 1788: 790–6.
13.Balzac F, Avolio M, Degani S, Kaverina I, Torti M, Silengo L, et al. E-cadherin endocytosis regulates the activity of Rap1: a traffic light GTPase at the crossroads between cadherin and integrin function. J Cell Sci. 2005; 118: 4765–83.
14.Vetter IR, Wittinghofer A. The guanine nucleotide-binding switch in three dimensions. Science. 2001; 294: 1299–304.
15.Boriack-Sjodin PA, Margarit SM, Bar-Sagi D, Kuriyan J. The structural basis of the activation of Ras by Sos. Nature. 1998; 394: 337–43.
16.Rebhun JF, Castro AF, Quilliam LA. Identification of Guanine Nucleotide Exchange Factors (GEFs) for the Rap1 GTPase: regulation of MR-GEF by M-RAS-GTP interaction. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275: 34901-8.
17.Ponsioen B, Gloerich M, Ritsma L, Rehmann H, Bos JL, Jalink K. Direct spatial control of Epac1 by cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol. 2009; 29: 2521–31.
18.Takahashi M, Rikitake Y, Nagamatsu Y, Hara T, Ikeda W, Hirata K, et al. Sequential activation of Rap1 and Rac1 small G proteins by PDGF locally at leading edges of NIH3T3 cells. Genes Cells. 2008; 13: 549–69.
19.Ohba Y, Ikuta K, Ogura A, Matsuda J, Mochizuki N, Nagashima K, et al. Requirement for C3G-dependent Rap1 activation for cell adhesion and embryogenesis. EMBO J. 2001; 20: 3333–41.
20.Chiang SH, Baumann CA, Kanzaki M, Thurmond DC, Watson RT, Neudauer CL, et al. Insulin-stimulated GLUT4 translocation requires the CAP-dependent activation of TC10. Nature. 2001; 410: 944–8.
21.Bos JL, de Rooij J, Reedquist KA. Rap1 signalling: adhering to new models. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2001; 2: 369–77.
22.Raaijmakers JH, Bos JL. Specificity in Ras and Rap signaling. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284: 10995–9.
23.Meng JW, Glick JL, Polakis P, Casey PJ. Functional interaction between Gαzand Rap1GAP suggests a novel form of cellular crosstalk. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274: 36663–9.
24.Gao QS, Srinivasan S, Boyer SN, Wazer DE, Band V. The E6 oncoproteins of high-risk papillomaviruses bind to a novel putative GAP protein, E6TP1, and target it for degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1999; 19: 733–44.
25.Zheng H, Gao L, Feng YF, Yuan LY, Zhao HB, Cornelius LA. Down-regulation of Rap1GAP via promoter hypermethylation promotes melanoma cell proliferation, survival, and migration. Cancer Res. 2009; 69: 449–57.
26.Katagiri K, Ohnishi N, Kabashima K, Iyoda T, Takeda N, Shinkai Y, et al. Crucial functions of the Rap1 effector molecule RAPL in lymphocyte and dendritic cell trafficking. Nat Immunol. 2004; 5: 1045–51.
27.Hoshino T, Sakisaka T, Baba T, Yamada T, Kimura T, Takai Y. Regulation of E-cadherin endocytosis by nectin through afadin, Rap1, and p120ctn. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280: 24095–103.
28.Post A, Pannekoek WJ, Ross SH, Verlaan I, Brouwer PM, Bos JL. Rasip1 mediates Rap1 regulation of Rho in endothelial barrier function through ArhGAP29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013; 110: 11427–32.
29.Liu LH, Aerbajinai W, Ahmed SM, Rodgers GP, Angers S, Parent CA. Radil controls neutrophil adhesion and motility through β2-integrin activation. Mol Biol Cell. 2012; 23: 4751–65.
30.Arthur WT, Quilliam LA, Cooper JA. Rap1 promotes cell spreading by localizing Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factors. J Cell Biol. 2004; 167: 111–22.
31.Gérard A, Mertens AEE, van der Kammen RA, Collard JG. The Par polarity complex regulates Rap1- and chemokine-induced T cell polarization. J Cell Biol. 2007; 176: 863–75.
32.Christian SL, Lee RL, McLeod SJ, Burgess AE, Li AHY, Dang-Lawson M, et al. Activation of the Rap GTPases in B lymphocytes modulates B cell antigen receptor-induced activation of Akt but has no effect on MAPK activation. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278: 41756–67.
33.Vallés AM, Beuvin M, Boyer B. Activation of Rac1 by paxillin-Crk-DOCK180 signaling complex is antagonized by Rap1 in migrating NBT- cells. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279: 44490–6.
34.Lyle KS, Raaijmakers JH, Bruinsma W, Bos JL, de Rooij J. cAMP-induced Epac-Rap activation inhibits epithelial cell migration by modulating focal adhesion and leading edge dynamics. Cell Signal. 2008; 20: 1104–16.
35.Gao L, Feng YF, Bowers R, Becker-Hapak M, Gardner J, Council L, et al. Ras-associated protein-1 regulates extracellular signalregulated kinase activation and migration in melanoma cells: two processes important to melanoma tumorigenesis and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2006; 66: 7880–8.
36.McSherry EA, Brennan K, Hudson L, Hill AD, Hopkins AM. Breast cancer cell migration is regulated through junctional adhesion molecule-A-mediated activation of Rap1 GTPase. Breast Cancer Res. 2011; 13: R31.
37.Goto M, Mitra RS, Liu M, Lee J, Henson BS, Carey T, et al. Rap1 stabilizes β-catenin and enhances β-catenin-dependent transcription and invasion in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Clin Cancer Res. 2010; 16: 65–76.
38.Huang M, Anand S, Murphy EA, Desgrosellier JS, Stupack DG, Shattil SJ, et al. EGFR-dependent pancreatic carcinoma cell metastasis through Rap1 activation. Oncogene. 2012; 31: 2783–93.
39.Lin KBL, Tan P, Freeman SA, Lam M, McNagny KM, Gold MR. The Rap GTPases regulate the migration, invasiveness and in vivo dissemination of B-cell lymphomas. Oncogene. 2010; 29: 608–15.
40.Infante E, Heasman SJ, Ridley AJ. Statins inhibit T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell adhesion and migration through Rap1b. J Leukoc Biol. 2011; 89: 577–86.
41.Bailey CL, Kelly P, Casey PJ. Activation of Rap1 promotes prostate cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2009; 69: 4962–8.
42.Shimizu Y, Hamazaki Y, Hattori M, DoiK, Terada N, Kobayashi T, et al. SPA-1 controls the invasion and metastasis of human prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011; 102: 828–36.
43.Malchinkhuu E, Sato K, Maehama T, Ishiuchi S, Yoshimoto Y, Mogi C, et al. Role of Rap1B and tumor suppressor PTEN in the negative regulation of lysophosphatidic acid--induced migration by isoproterenol in glioma cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2009; 20: 5156–65.
44.Barrett A, Evans IM, Frolov A, Britton G, Pellet-Many C, Yamaji M, et al. A crucial role for DOK1 in PDGF-BB-stimulated glioma cell invasion through p130Cas and Rap1 signalling. J Cell Sci. 2014; 127: 2647–58.
45.Yajnik V, Paulding C, Sordella R, McClatchey AI, Saito M, Wahrer DCR, et al. DOCK4, a GTPase activator, is disrupted during tumorigenesis. Cell. 2003; 112: 673–84.
46.Almahariq M, Tsalkova T, Mei FC, Chen HJ, Zhou J, Sastry SK, et al. A novel EPAC-specific inhibitor suppresses pancreatic cancer cell migration and invasion. Mol Pharmacol. 2013; 83: 122–8.
47.Magliozzi R, Low TY, Weijts BGMW, Cheng TH, Spanjaard E, Mohammed S, et al. Control of epithelial cell migration and invasion by the IKKβ- and CK1α-mediated degradation of RAPGEF2. Dev Cell. 2013; 27: 574–85.
48.Zuo H, Gandhi M, Edreira MM, Hochbaum D, Nimgaonkar VL, Zhang P, et al. Downregulation of Rap1GAP through epigenetic silencing and loss of heterozygosity promotes invasion and progression of thyroid tumors. Cancer Res. 2010; 70: 1389–97.
49.Zhang LZ, Chenwei L, Mahmood R, van Golen K, Greenson J, Li GY, et al. Identification of a putative tumor suppressor gene Rap1GAP in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2006; 66: 898–906.
50.Kim WJ, Gersey Z, Daaka Y. Rap1GAP regulates renal cell carcinoma invasion. Cancer Lett. 2012; 320: 65–71.
51.Mitra RS, Goto M, Lee JS, Maldonado D, Taylor JMG, Pan QT, et al. Rap1GAP promotes invasion via induction of matrix metalloproteinase 9 secretion, which is associated with poor survival in low N-stage squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2008; 68: 3959–69.
52.Mathieu V, Pirker C, Schmidt WM, Spiegl-Kreinecker S, L?tsch D, Heffeter P, et al. Aggressiveness of human melanoma xenograft models is promoted by aneuploidy-driven gene expression deregulation. Oncotarget. 2012; 3: 399–413.
53.Zhang Y, Gong Y, Hu D, Zhu P, Wang N, Zhang Q, et al. Nuclear SIPA1 activates integrin β1 promoter and promotes invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2015; 34: 1451–62.
54.Ji K, Ye L, Toms AM, Hargest R, Martin TA, Ruge F, et al. Expression of signal-induced proliferation-associated gene 1 (SIPA1), a RapGTPase-activating protein, is increased in colorectal cancer and has diverse effects on functions of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2012; 9: 321–7.
55.Ho SM, Lau KM, Mok SC, Syed V. Profiling follicle stimulating hormone-induced gene expression changes in normal and malignant human ovarian surface epithelial cells. Oncogene. 2003; 22: 4243–56.
56.Che YL, Luo SJ, Li G, Cheng M, Gao YM, Li XM, et al. The C3G/Rap1 pathway promotes secretion of MMP-2 and MMP-9 and is involved in serous ovarian cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2015; 359: 241–9.
57.Vuchak LA, Tsygankova OM, Meinkoth JL. Rap1GAP impairs cellmatrix adhesion in the absence of effects on cell-cell adhesion. Cell Adh Migr. 2011; 5: 323–31.
58.Kooistra MRH, Dubé N, Bos JL. Rap1: a key regulator in cell-cell junction formation. J Cell Sci. 2007; 120: 17–22.
59.Han J, Lim CJ, Watanabe N, Soriani A, Ratnikov B, Calderwood DA, et al. Reconstructing and deconstructing agonistinduced activation of integrin αbβ3. Curr Biol. 2006; 16: 1796–806.
60.Hernández-Varas P, Coló GP, Bartolomé RA, Paterson A, Medra?o-Fernández I, Arellano-Sánchez N, et al. Rap1-GTP-interacting adaptor molecule (RIAM) protein controls invasion and growth of melanoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286: 18492–504.
61.Tsygankova OM, Prendergast GV, Puttaswamy K, Wang Y, Feldman MD, Wang HB, et al. Downregulation of Rap1GAP contributes to Ras transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 2007; 27: 6647–58.
62.Mitra RS, Zhang ZC, Henson BS, Kurnit DM, Carey TE, D'Silva NJ. Rap1A and rap1B ras-family proteins are prominently expressed in the nucleus of squamous carcinomas: nuclear translocation of GTP-bound active form. Oncogene. 2003; 22: 6243–56.
63.Friedl P, Alexander S. Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: plasticity and reciprocity. Cell. 2011; 147: 992–1009.
64.Levine M. Transcriptional enhancers in animal development and evolution. Curr Biol. 2010; 20: R754–63.
65.Zwartkruis FJT, Wolthuis RMF, Nabben NMJM, Franke B, Bos JL. Extracellular signal-regulated activation of Rap1 fails to interfere in Ras effector signalling. EMBO J. 1998; 17: 5905–12.
66.Grewal SS, Horgan AM, York RD, Withers GS, Banker GA, Stork PJS. Neuronal calcium activates a Rap1 and B-Raf signaling pathway via the cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275: 3722–8.
67.Guvakova MA, Lee WSY, Furstenau DK, Prabakaran I, Li DC, Hung R, et al. The small GTPase Rap1 promotes cell movement rather than stabilizes adhesion in epithelial cells responding to insulin-like growth factor I. Biochem J. 2014; 463: 257–70.
68.Butler GS, Overall CM. Proteomic identification of multitasking proteins in unexpected locations complicates drug targeting. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009; 8: 935–48.
69.Takahashi M, Dillon TJ, Liu C, Kariya Y, Wang ZP, Stork PJS. Protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation of Rap1 regulates its membrane localization and cell migration. J Biol Chem. 2013; 288: 27712–23.
70.Ntantie E, Gonyo P, Lorimer EL, Hauser AD, Schuld N, McAllister D, et al. An adenosine-mediated signaling pathway suppresses prenylation of the GTPase Rap1B and promotes cell scattering. Sci Signal. 2013; 6: ra39.
71.Su L, Hattori M, Moriyama M, Murata N, Harazaki M, Kaibuchi K, et al. AF-6 controls integrin-mediated cell adhesion by regulating Rap1 activation through the specific recruitment of Rap1GTP and SPA-1. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278: 15232–8.
72.Wells A, Grahovac J, Wheeler S, Ma B, Lauffenburger D. Targeting tumor cell motility as a strategy against invasion and metastasis. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013; 34: 283–9.
73.Kessenbrock K, Plaks V, Werb Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell. 2010; 141: 52–67.
74.Chen L, Yang SY, Jakoncic J, Zhang JJ, Huang XY. Migrastatin analogues target fascin to block tumour metastasis. Nature. 2010; 464: 1062–6.
75.Dong X, Korch C, Meinkoth JL. Histone deacetylase inhibitors upregulate Rap1GAP and inhibit Rap activity in thyroid tumor cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2011; 18: 301-10.
76.Wang K, Li J, Guo H, Xu XQ, Xiong G, Guan XY, et al. MiR-196a binding-site SNP regulates RAP1A expression contributing to esophageal squamous cell carcinoma risk and metastasis. Carcinogenesis. 2012; 33: 2147–54.
77.Alemayehu M, Dragan M, Pape C, Siddiqui I, Sacks DB, Di Guglielmo GM, et al. β-Arrestin2 regulates lysophosphatidic acidinduced human breast tumor cell migration and invasion via Rap1 and IQGAP1. PloS One. 2013; 8: e56174.
78.Tsygankova OM, Wang HB, Meinkoth JL. Tumor cell migration and invasion are enhanced by depletion of Rap1 GTPase-activating protein (Rap1GAP). J Biol Chem. 2013; 288: 24636–46.
79.Wu JJ, Zhang YS, Frilot N, Kim JI, Kim WJ, Daaka Y. Prostaglandin E2regulates renal cell carcinoma invasion through the EP4 receptor-Rap GTPase signal transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286: 33954–62.
80.Qiu TT, Qi XF, Cen JN, Chen ZX. Rap1GAP alters leukemia cell differentiation, apoptosis and invasion in vitro. Oncol Rep. 2012; 28: 622–8.
81.Dong XY, Tang WX, Stopenski S, Brose MS, Korch C, Meinkoth JL. RAP1GAP inhibits cytoskeletal remodeling and motility in thyroid cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2012; 19: 575–88.
82.Severson EA, Lee WY, Capaldo CT, Nusrat A, Parkos CA. Junctional adhesion molecule A interacts with Afadin and PDZGEF2 to activate Rap1A, regulate β1 integrin levels, and enhance cell migration. Mol Biol Cell. 2009; 20: 1916–25.
Cite this article as:Zhang Y, Wang R, Cheng K, Ring BZ, Su L. Roles of Rap1 signaling in tumor cell migration and invasion. Cancer Biol Med. 2017; 14: 90-9. doi: 10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2016.0086
Brian Z. Ring and Li Su
E-mail: bzring@gmail.com and lisu@hust.edu.cn
Received October 24, 2016; accepted December 7, 2016. Available at www.cancerbiomed.org
Copyright ? 2017 by Cancer Biology & Medicine
 Cancer Biology & Medicine2017年1期
Cancer Biology & Medicine2017年1期
- Cancer Biology & Medicine的其它文章
- Erratum to Bcl-2 expression is a poor predictor for hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis of andropause-age patients
- Metformin prevents hormonal and metabolic disturbances and 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon carcinogenesis in non-diabetic rats
- Truth telling for patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Henan, China
- Estimation of lung cancer burden in Australia, the Philippines, and Singapore: an evaluation of disability adjusted life years
- A pilot study of radiologic measures of abdominal adiposity: weighty contributors to early pancreatic carcinogenesis worth evaluating?
- Association of genotypes of rs671 within ALDH2 with risk for gastric cardia adenocarcinoma in the Chinese Han population in high- and low-incidence areas
