Step-by-step external fixation of unstable pelvis with separate anterior and posterior modules
Ivan Viktorovich Borozda, Nikolay Alexandrovich Ganzhurov, Alexander Alexandrovich Kapustyansky,Roman Valerievich Nikolaev, Kirill Sergeevich Golokhvast*Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Amur State Medical Academy, 95 Gorky Street, Blagoveshchensk, RussiaScientific Educational Centre of Nanotechnology, Far Eastern Federal University, 0 Pushkinskaya Street, Vladivostok, Russia
?
Step-by-step external fixation of unstable pelvis with separate anterior and posterior modules
Ivan Viktorovich Borozda1, Nikolay Alexandrovich Ganzhurov1, Alexander Alexandrovich Kapustyansky1,
Roman Valerievich Nikolaev1, Kirill Sergeevich Golokhvast2*1Department of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Amur State Medical Academy, 95 Gorky Street, Blagoveshchensk, Russia
2Scientific Educational Centre of Nanotechnology, Far Eastern Federal University, 10 Pushkinskaya Street, Vladivostok, Russia
Original article http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.11.002
Tel: +7 914 690 7603
Fax: +7 423 222 6451
E-mail: droopy@mail.ru
The study protocol was performed according to the Helsinki declaration and approved by Ethic Committee of the Amur State Medical Academy ( OT 26.10.2011). Informed written consent was obtained from Amur Regional Hospital with sign of all patients.
Peer review under responsibility of Hainan Medical University. The journal implements double-blind peer review practiced by specially invited international editorial board members.
2221-1691/Copyright?2016 Hainan Medical University. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V. This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
ARTICLE INFO
Article history:
Received 26 Aug 2015
Received in revised form 29 Sep, 2nd revised form 8 Oct 2015
Accepted 12 Nov 2015
Available online 10 Dec 2015
Keywords:
Unstable pelvic injuries
External fixation
Separate step-by-step reposition
Traumatology
ABSTRACT
Objective: To evaluate the treatment outcomes of patients with pelvic ring injury by applying step-by-step external pelvic fixation and circular external fixation device.
Methods: Atotalof28patientssufferingfromdisintegratedpelvicringinjuryareinvolved inthestudy.Fourteen patients(the treatmentgroup)underwentstep-by-stepexternalpelvic fixation by applying anterior (anti-shock) and posterior modules. For the rest 14 patients (theexperimentalgroup),theosteosynthesiswereconductedbymeansofacircularexternal fixation device. The long-term outcomes were evaluated in a year after the injury.
Results: The residual deformity of 5 (4–7) mm was observed in 10 patients (71.4%) from theexperimentalgroup.Inthetreatmentgroup,theresidualdeformitywasevidentonlyin4 (28.6%) cases being 2.5 (2–3) mm (P = 0.000319) on the average. The functional result (according to the Majeed scale) was statistically better in the treatment group (P = 0.000319). Nine (64.3%) and five (35.7%) patients in treatment group showed excellent and positive results, respectively. The excellent result was demonstrated by 3 patients (21.4%)ofthe experimental group,the positive outcomeswereobservedin 6 cases (42.9%) and the unsatisfactory one was displayed by 1 patient (7.1%) of the same group.
Conclusions: The modular approach applied is the advantage of the transosseous osteosynthesis allowing for a separate anterior (anti-shock)fixation and final posterior reposition of the pelvic ring preceded by the stabilization of vital functions. The above mentioned method gives an opportunity to increase the amount of techniques applied for the pelvic external fixation in polytrauma cases.
1. Introduction
In accordance with the national and foreign researchers, the rate of pelvic fractures in cases of polytrauma ranges from 20% to 52% [1–5]. In addition, pelvic ring discontinuity and destabilization caused by bone fractures and joint disruptions are observed in 80% cases of pelvic injuries [6–10]. Despite the success having been achieved in the polytrauma comprehensive treatment over the last 25 years, the lethality rate in cases of severe multisystem and multiple pelvic injuries still varies from 35% to 70% [11,12].
Multisystem and multiple pelvic injuries are observed in up to 90% cases being accompanied with traumatic shock, thus, aggravating the severity of a patient's condition. That is why life saving actions shall dominate during the first hour after the injury[13–18]. After the stabilization, the pelvic ring injury shall be treated as a long-standing trauma requiring a special subsequent treatment approach [19–21].
The time limits of final pelvic osteosynthesis directly depend on the efficiency of anti-shock treatment conducted in the acute traumatic disease period. Hence, the search of new emergencysurgical stabilization techniques to be applied in cases of unstable pelvic ring injuries are currently important[22–24].
The present study aimed to develop highly effective transosseous osteosynthesis techniques to achieve better treatment outcomes while treating unstable pelvic fractures.
2. Materials and methods
Treatment outcomes of 28 patients with unstable pelvic injuries caused by polytrauma and admitted to Amur Regional Clinical Hospital, Clinical Hospital of Yakutsk Medial Institute and Blagoveshchensk City Clinical Hospital in 2009–2013 were included in the present study.
As per the injury mode, the pelvic fractures were high-energy and closed. All the patients suffered from multisystem and multiple injuries [injury severity score (ISS)>17]. Twelve patients were diagnosed with cranium-brain trauma, 17 ones suffered from visceral injuries and skull bone fractures of different locations were observed in 20 cases. The most patients (n = 19) were taken to clinical hospitals during 24 h–2 weeks after the injury, and 5 patients were admitted to hospital in 3 h after the injury and the rest injured (4) were hospitalized more than 2 weeks after the trauma.
The injured people were divided into two groups with 14 patients in each. The patients having undergone step-by-step external fixation of unstable pelvis by applying separate anterior (anti-shock) and posterior modules were included into the treatment group. The circular external fixation devices were applied for conducting osteosynthesis in the experimental group. The classical procedures developed in Ural Scientific Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics named after VD Chaklin were followed while carrying out the surgical intervention [25]. In accordance with the procedures, the cut in pins inserted into the pelvic bones shall be fastened to the external support around the pelvic ring.
The groups were compared according to the basic parameters of gender, age, trauma mode and severity and patients' condition after admission (P>0.5).
Male patients prevailed among the patients: 8 (57.7%) men were presented in the treatment group, and 9 (64.3%) ones were included in the experimental group. The most injured patients were of a productive age being 21–50 years old. In compliance with the Association of Osteosynthesis (AO) fracture classification [21], all the patients suffered from unstable injuries accompanied with the discontinuity in the anterior and posterior areas and vertical dislocation (C type).
In all cases, the consent to the surgical intervention was obtained either from patients or from their relatives.

Table 1Osteosynthesis algorithm of unstable pelvic injuries [C type according to AO/Association for the Study of Internal Fixation (ASIF)].
When choosing an osteosynthesis method the tactical algorithm was used subject to pelvic ring injury type: 1) the directionof the pelvic parts dislocation (“open book”,“close book”and “crumpled book”types); 2) unilateral or bilateral injury; 3) the type of interior and posterior pelvic semi-ring injury (joint disruptions or fractures) (Table 1) [26].
Thus, in case of the external-rotational (and at the same time vertical) pelvic dislocation preceded by unilateral unstable pelvic injury of the“open book”type and the simultaneous sacral bone trauma of Denis III or Denis II types, the osteosynthesis of the anterior pelvic area shall be accomplished either with the application of an external fixation device or with a reparative plate, while the external fixation device with posterior module or a reparative plate shall be applied for the posterior pelvic area. In case of a sacral bone injury of Denis I type, the osteosynthesis of posterior pelvic area can be accomplished by means of a cannulated screw as injuries of the type bear no risk of intra-foraminal constriction injury to the sacral plexus roots.
The treatment group patients underwent two-stage curing (step-by-step strategy) in compliance with the transosseous osteosynthesis type elaborated by our team for treating unstable pelvic injuries[27]. Emergency stabilization applying the anterior (anti-shock) treatment module was conducted during the first stage (30 min–2 h after the patient's admission to hospital) [28]. After the vital functions have been restored, the pelvic osteosynthesis with transosseous posterior module was immediately accomplished aimed at reaching final reposition and reliable stabilization of fragments [29].
The devices and treatment modalities having been developed by our team differ from the widely known circular external fixation devices (Figures 1 and 2).
The posterior pelvic final reposition and fixation during the consolidation period are possible due to the posterior module. The precondition of the construction application is the continuity of posterior flank bones areas (spines) used for fixing the pins. At that, the latter shall not penetrate into the sacroiliac joint cavity, thus, making this device different from the most traditional ones for osteosynthesis.
The construction is made of the standard set of Ilizarov frame details being cost effective and more affordable as part of the compulsory health insurance program [30].
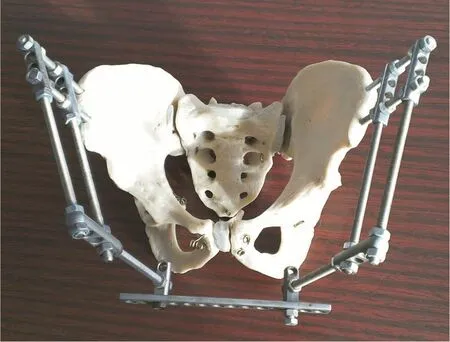
Figure 1. Anti-shock external pelvic fixation device (anterior module).
Posterior module osteosynthesis is accomplished in the lateral recumbent position on the stable pelvic side with the external frame of the posterior external fixation device module being put between the surgical table support bearings, thus, allowing for carrying out the required manipulations without any obstacles. Moreover, the external frame of the posterior module can be easily fixed to the surgical table for making an additional support during the unstable pelvic ring reposition (for lowering).

Figure 2. Transosseous module for the reposition and fixation of posterior pelvic areas (posterior module).1: Cut in cone-shaped nails of cervical type; 2: Holders with three plain and one front threaded holes; 3: Threaded nails; 4: Struts with holes; 5: Holders with one pierced hole and threaded shank; 6: Adjusting nuts.
Roentgenometry and the evaluation of average residual pelvic part dislocation index (Нav) offered by the Ural Scientific Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics[13]and the rating scale of functional treatment outcomes as per Majeed scale [31] were used to analyze the long-term treatment results in a year after the injury.
The anatomical outcome was considered positive if the posterior and anterior pelvic residual dislocation was less than 10 mm and 15 mm, respectively, pelvis joint asymmetry was below 10 mm and the pathological mobility of pelvic parts (Нav<11.7 mm) was absent; the result was considered satisfactory if the posterior and anterior pelvic dislocation was 10–19 mm and 15–29 mm correspondingly, pelvis joint asymmetry was 10–19 mm, and the pathological pelvic mobility was less than 5 mm (Нav<22.3 mm); the outcome was considered unsatisfactory if the posterior and anterior pelvic dislocation exceeded 20 mm and 30 mm correspondingly, the pelvis joint asymmetry was more than 20 mm regardless the pathological pelvic mobility (Нav<23.3 mm).
The software package Statistica Version 8.0 was applied for processing the statistical data. The accuracy of the average values was evaluated with the help of Wilcoxon signed-rank test (for the dependent samples) and Mann–Whitney U test (for the independent samples). Median center and interquartile range (25%; 75%) were figured out to estimate the sample values. The distinctions with P<0.05 were regarded statistically significant.
3. Results
After the treatment completion, the residual displacement of 5.5 mm was revealed in 10 patients (71.4%) from the experimental group having undergone surgical intervention by applying the circular external fixation device. At the same timethe residual deformation of 2.5 mm (P = 0.0039) was observed in 4 patients (28.6%) of the treatment group having been accomplished osteosynthesis by means of the external fixation device with separate modules. Thus, the anatomical treatment outcome reached by applying the offered techniques was verifiably better than the result obtained after using the circular external fixation device.
The functional treatment outcome was also better in the treatment group (Table 2). Only excellent and positive results were observed in the treatment group and the median value was 90 scores. As to the experimental group, the rate of satisfactory and unsatisfactory results was in 35.7% patients while the average value was 72 (P = 0.000319).

Table 2Functional treatment outcomes as per Majeed scale.
In our opinion, the distinguishing biomechanical properties are the reason for the better anatomical and functional treatment outcomes reached in cases when the above mentioned techniques were applied as against the cases which used the circular external fixation device. A separate reposition knot formed in the posterior pelvic area is based on two (instead of one) cut in pins (unlike the circular external fixation device), encouraging more localized efforts at the site of sacroiliac joint cavity fracture or disruption and assuring a more stable fixation in the long run. The use of the circular fixation device usually leads to redislocation affecting the overall anatomical outcome.
As to the functional outcome, it is a more subjective index not always fully conforming to the anatomical changes. Still, the two-module external fixation device is more convenient for the patients whose attitude towards it is more positive than to the circular one. Here are some case studies.
3.1. First case
A male patient of 26 year old was admitted to the Clinical Hospital of Yakutsk Medial Institute in 2 h after the injury caused by a car accident and being in the extremely critical condition. Systolic blood pressure was less than 80 mmHg; heart rate was 120 per minute; pulse was fine and scarcely perceptible. In the course of anti-shock treatment, the patient was examined in the Emergency and Anesthesia Department. The patient was diagnosed with closed left-side pubic arch fracture and right-side massa lateralis ossis sacri fracture (Figure 3a, b and c).
The patient had closed cranio-cerebral injury-mild brain contusion and subarachnoidal hemorrhage, and traumatic shock of Level III (ISS = 29). Right-side transforaminal sacral bone fracture was revealed after CT imaging. The anterior (antishock) module was used for the emergency pelvic stabilization and the posterior module was applied for conducting the scheduled osteosynthesis (Figure 4) in 10 days. The dislocations were removed and the pelvic ring shape was restored in the anterior and posterior areas. No neurological disorders were revealed. The short-term treatment outcomes are displayed on Figure 4. Rehabilitation was started in 24 h after the surgical intervention. On the sixth day, the patient was taught to walk with crutches. The device was removed in 8 weeks.
The patient got back to work in 12 weeks after the injury. The treatment outcome is considered positive.
Applying the elaborated method for treating patients with polytrauma during the acute traumatic disease period allows for suppressing hemorrhage and fixing pelvic bone fragments in order to avoid further trauma. At a later date, the above mentioned technique prevents from the forced hypodynamia and the associated complications, thus, improving the motoring conditions and life quality.
3.2. Second case
Sitting on a passenger seat, a 42 year old woman got an injury in a car accident caused by the frontal crash of two motor cars. The woman was squeezed in crush, some body parts were deformed and she lost consciousness at the moment of trauma.

Figure 3. Examination results of a patient (26 years old) after admission to hospital. X-ray picture of pelvis in frontal view (a) and caudal view (b); (c): CT image.
An ambulance team provided her with the first aid. Cramer's splints were applied for the shank and forearm immobilization, and pelvis immobilization was accomplished as per Volkovich method; narcotic analgesics were administered, and anti-shock solutions were infused in the peripheral veins. The patient was admitted to Murmansk City Hospital in an hour after the injury being in the extremely critical condition: systolic blood pressure 60 mmHg, coma I. Left-side transforaminal splintered sacral bone fracture and pubic articulation disruption with the vertical left-side pelvic instability were confirmed after CT imaging (Figure 5). The treatment procedures were carried out in the patient's room within the Emergency and Anesthesia Department including anti-shock infusion in 2 central veins andskeletal extension applied for stabilizing the injured extremity segments.

Figure 4. The 7th day after posterior module installation.

Figure 5. 3D CT imaging in a hour after the injury.
Clinical diagnosis for the patients included car accident polytrauma: unstable pelvic injury (C type); the primary open dislocation-fracture of right ankle bone; closed right-side splintered displaced fracture of radial bone distal epiphyseal cartilage; brain contusion of low severity level; coma of I level and traumatic shock of III level (ISS = 34).
The stabilization of arterial blood pressure (110/80 mmHg) was followed by the pelvic fixation applying anti-shock pelvis bandage. In 8 h after hospitalization the patient was admitted to Amur Regional Clinical Hospital in Blagoveshchensk by the air medical helicopter being accompanied by a doctor. The flight time lasted for 1.5 h.
The subsequent treatment was provided in the Emergency and Anesthesia Department of the Amur Regional Clinical Hospital. In the course of anti-shock therapy, the external fixation device with the anterior module was used to fix the pelvic fragments under the general endotracheal anesthesia 30 min after admission (Figure 6). The right forearm was fixed with a plaster bar and the fenestrated plaster cast was used to fix the left shank. The wound cleaning was performed.
Pelvic osteosynthesis applying the external fixation device with posterior module was conducted in 10 days after the injury. At the same time the shank injury necrectomy was performed along with the osteosynthesis of left ankle joint applying the external fixation device and the osteosynthesis of right forearm was accomplished applying the Ilizarov frame. Rehabilitation exercises with the gradual increase of motion range in the unfixed joints and the training of walking skills were carried out during the postoperative period.

Figure 6. 3D CT imaging of pelvis made after anterior fixation.
Control CT and clinical test preceded the removal of the external fixation device under intravenous anesthesia in 75 days after the surgical intervention.
Temporary incapacity lasted for 8 months. The long-term treatment outcome (in a year) was evaluated as a positive one.
If the situation so requires, the step-by-step application of module of transosseous constructions can be combined with the external fixation of posterior pelvic areas preceded by the removal of rough dislocations in the external fixation device (Figure 7).
The stabilization of posterior pelvic areas applying the relevant module allows for its combination with the external osteosynthesis of acetabulum and anterior pelvic ring areas.
3.3. Third case
An ambulance team delivered a female patient of 18 years old to the injure care centre of II level in 30 min after injury being the result of a vehicle accident.
The following diagnosis was set after admission: splintered fracture of right flank bone wing and shaft, high double column fracture of right acetabulum, bilateral fracture of pubic and sciatic bones, ileum mesenterium disruption and hemoperitoneum, with traumatic shock of III level (ISS = 41).

Figure 7. X-ray picture of pelvis. The combination of external fixation device and screw stabilization of the sacroiliac joint.
Anti-shock therapy was combined with emergency laparotomy. Conservative therapy including skeletal extension was not efficient. In 7 days, the patient was admitted to the injury care centre of I level (Amur Regional Clinical Hospital in Blagoveshchensk). CT imaging was performed after admission (Figure 8).

Figure 8. 3D CT imaging of pelvis in frontal (a) and caudal (b) view.
A scheduled surgical intervention was carried out on the 9th day after the injury for accomplishing osteosynthesis applying a ring-supported external fixation device of 3/4 of the thigh circumference and traction-closed continuous reposition of acetabulum (Figure 9).
Rehabilitation was started on the 2nd day after the surgery. On the 10th day, the patient was taught to walk with crutches. The device was removed in 9 weeks, control CT was made in 8 weeks after the device removal (Figure 10).
The emerged adhesive small bowel obstruction required one more surgical intervention. The patient continued her studies in 20 weeks after the injury. The treatment result was evaluated as positive.
3.4. Fourth case
A 17-year-old female patient got a polytrauma caused by the fall from a 4-storey building. The first aid was provided by an ambulance team.

Figure 9. CT imaging after osteosynthesis.

Figure 10. 3D CT imaging of pelvis in frontal (a) and caudal (b) view in 8 weeks after the removal of fixation device.
The patient was taken to the waiting room of the Amur Regional Children's Clinical Hospital in 30 min after the injury.Her condition was extremely critical: systolic blood pressure was 70 mmHg and coma of I level.
Diagnosis of the patient included catatrauma: closed polyfocal pelvic and left-side acetabulum fracture with the iliac dislocation of left thigh; ruptured spleen and hemoperitoneum; brain contusion of low severity level; coma of I level and traumatic shock of III level (ISS = 38).
In the course of anti-shock treatment, the patient was examined and underwent an urgent surgical intervention.
The pelvis X-ray picture displayed the fracture of anterior column and posterior acetabulum with left thigh dislocation (Figure 11a). Laparotomy, reinfusion, splenectomy, closed reduction of femoral head and pelvis osteosynthesis by applying anterior (anti-shock) module and extension beyond the left thigh were applied. The X-ray picture of pelvis after external device fixation with anterior frame for pelvis and thigh was shown in Figure 11b.

Figure 11. X-ray picture of pelvis before (a) and after (b) external device fixation with anterior frame for pelvis and thigh.
External acetabulum osteosynthesis applying screws was accomplished in 10 days. The external fixation was prolonged (Figure 12).
The external fixation device was removed in 6 weeks and the rehabilitation treatment course was carried out. A partial load on the left leg was permitted in 3 months after the surgery, and a complete load was allowed in 6 months.

Figure 12. The patient in the course of physical therapy on the 5th day after surgery.
Temporary incapacity lasted for 8 months. The long-term treatment outcome was evaluated in a year (Figure 13) and regarded as positive.

Figure 13. The same patient. Functional treatment outcome in an year after the injury.
4. Discussion
Transosseous osteosynthesis of unstable pelvic injury allows for a separate step-by-step reposition of the anterior and posterior pelvic semi-rings by applying two separate transosseous modules which assures low-traumatic reposition and the stabilization of pelvic fragments by means of reducing weight of external fixation device[28].
The application of two pins, as against one, inserted into the posterior spines of flank bones excludes rotation and provides an opportunity to use the uninjured pelvic part as a reliable support for reposition and fixation. The above mentioned technique can be applied upon condition that the posterior areas of flank bones (the places of pin insertion) are either uninjured or unilateral injured. In such a situation, there is no need to use a massive external frame surrounding a patient's body and entailing considerable inconveniences as against the circular external fixation device upgrading the quality of patients' lives during the treatment period [29,30].
The application of the uninjured pelvic ring as a locating support (the missing external frame segment) serves as the biomechanical point for applying separate transosseous modules as there is no sense to treat the uninjured pelvic ring area with an additional external support.
Separate reposition of posterior areas is highly efficient especially if applied during a two-week period after the injury. At the same time, in clinical cases when more than 2–3 weeks passed after the injury and the time for the appropriate single-step reposition was lost, the posterior and anterior modules of the offered external fixation device can be combined, thus, switching to the gradual reposition by applying a circular frame device and following the method elaborated in the VD Chaklin Ural Scientific Research Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics.
The offered step-by-step treatment (in the acute period) of traumatic disease caused by polytrauma provides an opportunity to suppress hemorrhage and avoid the second hit brought about by a massive surgical intervention. In the longer term, it prevents from the forced hypodynamia and associated complications.
The module approach of the external fixation device allows for gradual addition of posterior module to an anterior one (preceded by the stabilization of vital functions) and the final reposition of both anterior and posterior pelvic areas.
Clinical conditions (wounds and abrasions, traumatic soft tissue detachment, bedsores, burns and the danger of constriction injury of lumbar plexus nerve roots caused by traumas of Denis II and III types) requiring external fixation of posterior pelvic areas are the invariable indications for applying the above mentioned procedure.
In case of old and long-term unfixed injuries or the step-bystep correction of fixed deformities, the transformation of the module of circular external fixation device allows for the gradual stabilization and reposition of pelvic ring fragments.
The stabilization of posterior pelvic areas by applying the relevant module provides an opportunity to combine it with the external osteosynthesis of acetabulum and anterior pelvic ring areas as well as to apply external fixation of posterior pelvic areas (if necessary) having removed rough dislocations in the external fixation device.
The described osteosynthesis techniques serve as a reliable and low-cost alternative for the existing external (two stage) methods and for osteosynthesis accomplished by means of the circular external fixation device. It also increases the amount of metal constructions that may be used for curing patients suffering from the isolated, multisystem and multiple pelvic injuries [29].
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
References
[1] Stelmakh KK, Myakotina LI. Comparative biomechanical assessment of the functional outcomes of treatment in patients with pelvic bone fractures. Russ J Biomech 2000; 4(3): 80-5.
[2] Bondarenko AV, Smazniev KV. [Transosseous osteosynthesis in rehabilitation of patients with pelvic and acetabular injuries in polytrauma]. Vestnik travmatologii i ortopedii im. N.N. Priorova 2006; 4: 18-24. Russian.
[3] Dyatlov MM. [Complex pelvic injuries. What to do]? Gomel: Gomel State Medical University; 2006. Russian.
[4] Seliverstov PA, Shapkin JG, Akramov IE. [The structure analysis politrauma and a plural trauma of the oporno-impellent device]. Bull Med Online Conf 2013; 3(8): 1053. Russian.
[5] Langford JR, Burgess AR, Liporace FA, Haidukewych GJ. Pelvic fractures: part 1. Evaluation, classification, and resuscitation. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 2013; 21(8): 448-57.
[6] Lazarev AF, Kostenko YS. [Big problems of small pelvis]. Vestnik travmatologii i ortopedii im. N.N. Priorova 2007; 4: 83-7. Russian.
[7] Kazantsev AB, Dubrov VE, Putiatin SM, Gnitiev ME, Li EA. Operative treatment in patients with unstable pelvic ring lesions. Eur J Trauma 2006; 32(Suppl 1): 293.
[8] Bagnenko SE, Kashanskiy YB, Rzaev RS, Kucheev IO. [Anatomical and clinical substantiation of treatment technique of pelvic injuries with its disrupted ring]. Traumatol Orthop Russ 2009; 2(52): 46-52. Russian.
[9] Shlamovitz GZ, Mower WR, Bergman J, Chuang KR, Crisp J, Hardy D, et al. How (un)useful is the pelvic ring stability examination in diagnosing mechanically unstable pelvic fractures in blunt trauma patients? J Trauma 2009; 66(3): 815-20.
[10] Ricci WM, Mamczak C, Tynan M, Streubel P, Gardner M. Pelvic inlet and outlet radiographs redefined. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2010; 92: 1947-53.
[11] Gur’ev SO, Maksimenko MA. [Clinical and anatomical characteristics of patients with pelvic trauma due to road accident]. Trauma 2013; 14(1): 13-5. Russian.
[12] Tscherny H, Regel G. Care of the polytraumatised patient. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1996; 78(5): 840-52.
[13] Shlykov IL, Kuznetsova NL. [Curative and diagnostic algorithms in patients with unstable pelvic fracture]. Saratov J Med Sci Res 2010; 6(1): 159-63. Russian.
[14] Kalinkin OG. [The results of long-term experience in treating victims with severe pelvic injuries in acute and early periods of traumatic disease]. Trauma 2013; 14(3): 80-4. Russian.
[15] Gardner MJ, Osgood G, Molnar R, Chip Routt ML Jr. Percutaneous pelvic fixation using working portals in a circumferential pelvic antishock sheet. J Orthop Trauma 2009; 23(9): 668-74.
[16] Borozda IV, Danilov MA, Golokhvast KS. Treatment of patients with acromioclavicular joint injuries (Rockwood II-VI) with modeled Kirschner wire and cortical screw. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2015; 5(7): 579-84.
[17] Karadimas EJ, Nicolson T, Kakagia DD, Matthews SJ, Richards PJ, Giannoudis PV. Angiographic embolization of pelvic ring injuries. Treatment algorithm and review of the literature. Int Orthop 2011; 35(9): 1381-90.
[18] G¨ansslen A, Hildebrand F, Pohlemann T. Management of hemodynamic unstable patients“in extremis”with pelvic ring fractures. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech 2012; 79(3): 193-202.
[19] Pavi'c R, Margeti'c P. Emergency treatment for clinically unstable patients with pelvic fracture and haemorrhage. Coll Antropol 2012; 36(4): 1445-52.
[20] Gilfanov SI, Danilyak VV, Vedeneeev YM, Emelin MA, Vrzhesinsky VV.[Fixationofposteriorpelvicringinunstablepelvic fractures]. Traumatol Orthop Russ 2009; 2(52): 53-8. Russian.
[21] Tile M, Helfet DL, Kellam J. Fractures of the pelvis and acetabulum. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2003.
[22] Shapovalov VM, Gumanenko EK, Dulaev AK, Tanin VN. [Surgical stabilization of pelvic injuries in wounded and victims]. Saint-Petersburg: MORSAR AV; 2000. Russian.
[23] Eastridge ВJ, Starr A, Minei JP, O'Keefe GE, Scalea TM. The importance of fracture patterning using therapeutic decision-making in patients with hemorrhagic shock and pelvic ring disruptions. J Trauma 2002; 53(3): 446-50.
[24] Smith WR, Ziran BH, Morgan SJ. Fractures of the pelvis and acetabulum. New York: Informa Healthcare; 2007.
[25] Suzuki T, Smith WR, Hak DJ, Stahel PF, Baron AJ, Gillani SA, et al. Combined injuries of the pelvis and acetabulum: nature of a devastating dyad. J Orthop Trauma 2010; 24(5): 303-8.
[26] Runkov AV. [Transosseous osteosynthesis of the pelvis and acetabulum: methodological recommendations]. Ekaterinburg: Ekaterinburg Publishing house of the Ural University; 2000. Russian.
[27] Borozda IV, Nikolaev RV, Slastin SS. [Osteosynthesis algorithm of unstable pelvic injuries (C type according to AO/ASIF classification)]. Patent of the Russian Federation No. 1837. 2012. Russian.
[28] Borozda IV, Kanivets DV, Slastin SS, Ganzhurov NA. [Transosseous osteosynthesis of unstable pelvic injuries]. Patent of the Russian Federation No. 2457805. 2012. Russian.
[29] Borozda IV, Bushmanov AV, Ganzhurov NA, Kapustyansky AA, Farkhutdinova SV. [Antishock apparatus for pelvis external fixation]. Patent of Russian Federation No. 2014120563. 2014. Russian.
[30] Borozda IV, Kanivets DV, Nikolaev RV, Ganzhurov NA, Slastin SS. [Transessous module for the reposition and fixation of posterior pelvic areas]. Patent of Russian Federation No. 2014122102. 2014. Russian.
[31] Majeed SA. Grading the outcome of pelvic fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1989; 71(2): 304-6.
*Corresponding author:Kirill Sergeevich Golokhvast, Scientific Educational Center of Nanotechnology, Far Eastern Federal University, 10 Pushkinskaya Street, Vladivostok, Russia.
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2016年2期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2016年2期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Inhibitory actions of Pseuderanthemum palatiferum (Nees) Radlk. leaf ethanolic extract and its phytochemicals against carbohydrate-digesting enzymes
- Feasibility of using melatonin as a new treatment agent for Ebola virus infection: A gene ontology study
- Prevalence of refractive errors among primary school children in a tropical area, Southeastern Iran
- Inhibitory effect of gold nanoparticles conjugated with interferon gamma and methionine on breast cancer cell line
- Evaluation of imatinib mesylate (Gleevec) on KAI1/CD82 gene expression in breast cancer MCF-7 cells using quantitative real-time PCR
- Anti-hyperglycemic effects of aqueous Lenzites betulina extracts from the Philippines on the blood glucose levels of the ICR mice (Mus musculus)
