A new species of the genus Amolops (Amphibia: Ranidae) from southeastern Tibet, China
Ke JIANG, Kai WANG,2, Fang YAN, Jiang XIE, Da-Hu ZOU4,, Wu-Lin LIU, Jian-Ping JIANG, Cheng LI, Jing CHE,*
1State Key Laboratory of Genetic Resources and Evolution, Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming Yunnan 650223, China2Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History and Department of Biology, University of Oklahoma, Norman OK 73072-7029, U.S.A.3North China Electric Power University Science and Technology College, Baoding Hebei 071051, China4Tibet University, Lhasa Tibet 850000, China5Institute of Forestry Survey, Plan and Research of Xizang Autonomous Region, Lhasa Tibet 850000, China6Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu Sichuan 610041, China7Imaging Biodiversity Expedition, Beijing 100107, China
?
A new species of the genus Amolops (Amphibia: Ranidae) from southeastern Tibet, China
Ke JIANG1, Kai WANG1,2, Fang YAN1, Jiang XIE3, Da-Hu ZOU4,1, Wu-Lin LIU5, Jian-Ping JIANG6, Cheng LI7, Jing CHE1,*
1State Key Laboratory of Genetic Resources and Evolution, Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming Yunnan 650223, China
2Sam Noble Oklahoma Museum of Natural History and Department of Biology, University of Oklahoma, Norman OK 73072-7029, U.S.A.3North China Electric Power University Science and Technology College, Baoding Hebei 071051, China
4Tibet University, Lhasa Tibet 850000, China
5Institute of Forestry Survey, Plan and Research of Xizang Autonomous Region, Lhasa Tibet 850000, China
6Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu Sichuan 610041, China
7Imaging Biodiversity Expedition, Beijing 100107, China
Received: 20 October 2015; Accepted: 18 December 2015
Foundation items: This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2014FY210200 and 2011FY120200), the Animal Branch of the Germplasm Bank of Wild Species of Chinese Academy of Sciences (the Large Research Infrastructure Funding), and partially supported by the project “National Second Survey of Wild-animals in Xizang Autonomous Region of China”
ABSTRACT
A new species of the genus Amolops Cope, 1865 is described from Nyingchi, southeastern Tibet, China, based on morphological and molecular data. The new species, Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. is assigned to the Amolops monticola group based on its skin smooth, dorsolateral fold distinct, lateral side of head black, upper lip stripe white extending to the shoulder. Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. is distinguished from all other species of Amolops by the following combination of characters: (1) medium body size, SVL 48.5-58.3 mm in males, and 57.6-70.7 mm in females; (2) tympanum distinct, slightly larger than one third of the eye diameter; (3) a small tooth-like projection on anteromedial edge of mandible; (4) the absence of white spine on dorsal surface of body; (5) the presence of circummarginal groove on all fingers; (6) the presence of vomerine teeth; (7) background coloration of dorsal surface brown, lateral body gray with yellow; (8) the presence of transverse bands on the dorsal limbs; (9) the presence of nuptial pad on the first finger in males; (10) the absence of vocal sac in males. Taxonomic status of the populations that were previously identified to A. monticola from Tibet is also discussed.
Keywords:Amolops monticola group; Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov.; DNA barcoding; Tibet
INTRODUCTION
The cascade frogs of the genus Amolops Cope, 1865 inhabits rocky, fast-running streams and small rivers. Currently, the genus contains 49 recognized species (Frost, 2015), distributing from Nepal eastwards to southern China, and southeastwards to Malaysia. Previous phylogenetic studies of the genus Amolops all supported the monophyly of this genus (Cai et al., 2007; Matsui et al., 2006; Stuart, 2008). Based on morphological data, both Fei et al. (2005) and Stuart et al. (2010) recognized the A. monticola group.1
Firstly described by Fei et al. (2005) based on morphological character and later confirmed by phylogenetic data, the A. monticola group includes species that possess smooth skin, lateral side of head dark, with a light-colored upper lip-stripe extending to the shoulder, and distinct dorsolateral folds (Stuart et al., 2010). Currently, the A. monticola species group includes 14 species distributed in southern China, southern and southeastern Asia (Stuart et al., 2010; Frost, 2015). Six species of the A. monticola group are known in China, four of which are found in Tibet, including A. aniqiaoensis Dong, Rao and Lü, 2005, A. chayuensis Sun, Luo, Sun and Zhang, 2013, A. gerbillus (Annandale, 1912), and A. monticola (Anderson, 1871) (Fei et al., 2009b; Sun et al., 2013).
During our herpetological surveys in southeastern Tibet in July 2012, April 2014 and May 2015, a total of 23 specimens of Amolops were collected from two localities of Nyingchi (=Linzhi) Prefecture. These specimens are referred to the A. monticolagroup based on morphological and molecular data, and they cannot be assigned to any known congeners. Therefore, we describe it as a new species. Taxonomic status of the populations from Tibet that were previously identified to A. monticola is also discussed.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sampling
A total of 23 individuals of new species were collected from southeastern Tibet, China, including 13 adults and five subadults from Medog (=Motuo), and five adults from Mainling (=Milin). Following euthanasia, all specimens were fixed in 10% formalin solution after sampling of liver tissues (in 95% ethanol), and transferred to 75% ethanol after fieldwork. All specimens were designated as the type series.
Morphological analysis
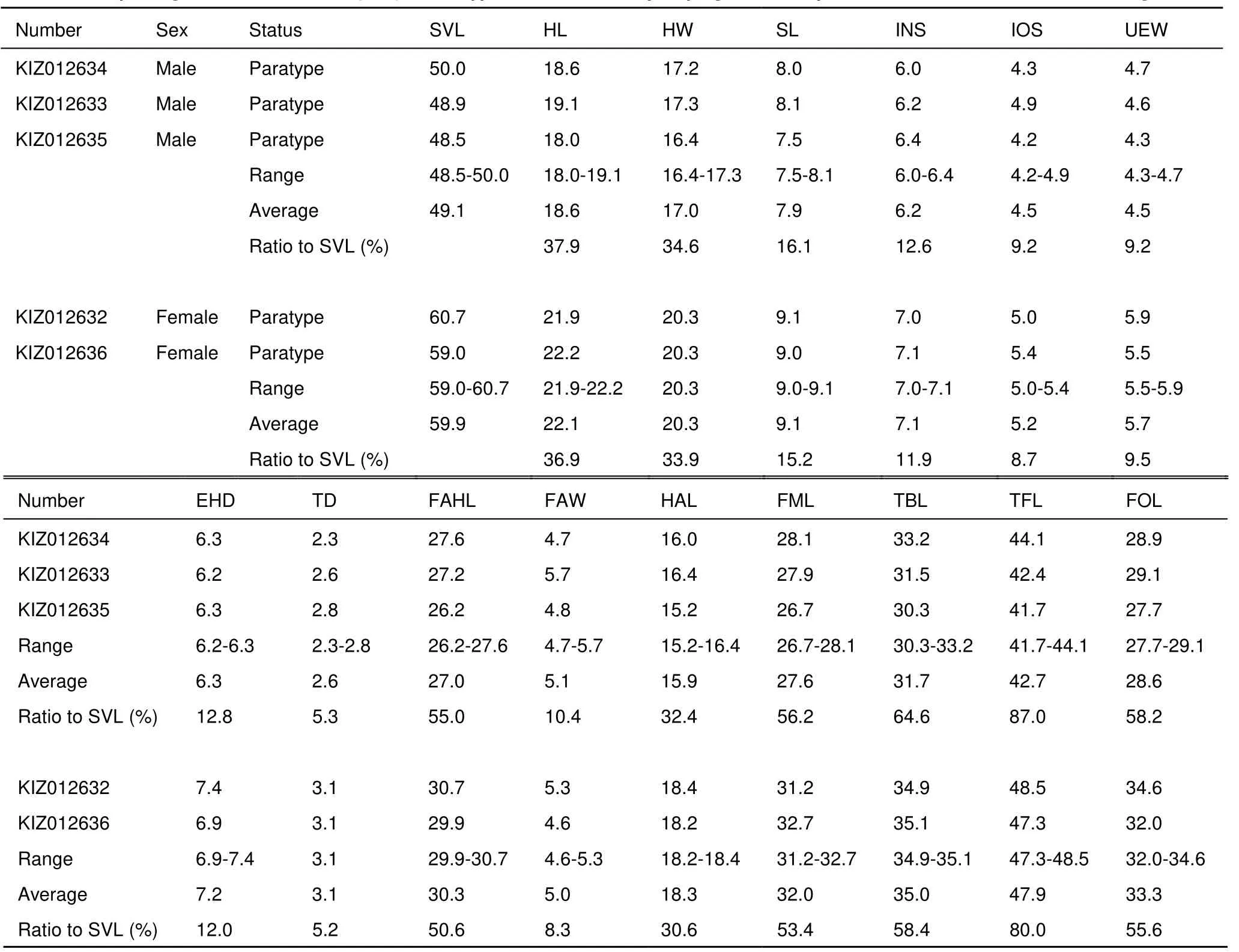
All the 18 adult specimens of new species were measured, and five other species were examined (Appendix). All measurements were carried out with slide calipers to the nearest 0.1 mm. Morphological characters used and their measurement methods followed Fei et al. (2009a), webbing formula followed Savage & Heyer (1997). The morphological characters and their abbreviations as: SVL, snout-vent length; HL, head length; HW, head width; SL, snout length; INS, internarial distance; IOS, interorbital distance; EHD, eye horizontal diameter; UEW, maximum width of upper eyelid; TD, tympanum diameter; FAHL, forearm and hand length; FAW, maximum width of forearm; HAL, hand length; FML, femur (thigh) length; TBL, tibia (shank) length; TFL, length of tarsus and foot; FOL, foot length.
Morphological data of congeners were obtained from vouchered specimens (Appendix) as well as from literatures (Anderson, 1871; Fei et al., 2009b; Liu et al., 2000). The following museum abbreviations were used: CIB-Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chengdu, China. KIZ-Kunming Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, China.
Molecular analysis
The genome DNA of four individuals of the new species of Amolops (KIZ 016415 and 016416 from Medog, 012632 and 012633 from Mainling) and other three known species from Tibet, China (A. aniqiaoensis, A. chayuensis and A. medogensis, in Table 1) was extracted from liver tissues with a standard three-step phenol-chloroform extraction method (Sambrook et al., 1989). A 600 base pair DNA barcoding sequence of mitochondrial gene cytochrome oxidase subunit I (COI) was sequenced using primers Chmf4 and Chmr4 (Che et al., 2012). Protocols for PCR and sequencing followed Che et al. (2012). All newly generated sequences were deposited in GenBank (Table 1). The COI sequences of the available 14 species of the genus Amolops and seven outgroup species were downloaded from GenBank (Table 1).
All dataset were aligned and edited using MEGA 5 (Tamura et al., 2011). For each codon position, the best model of nucleotide substitution was calculated in Modeltest v1.0.1 (Posada, 1998). Bayesian inference (BI) was used to generate a phylogenetic relationship using MrBayes 3.1.2 (Ronquist & Huelsenbeck, 2003). With different four runs, the Markov chains were estimated for 10 million generations, and every 100 generations were sampled. The pairwise comparisons for genetic distance among species was calculated using MEGA 5 with Kimura 2-parameter model (Che et al., 2012).
RESULTS
Genetic analysis
Our results show that all Amolops species used in the current study form a monophyletic group using BI analysis. Given the limited genetic data used, our results did not provide enough resolution regarding phylogenetic relationships among different species groups of the genus Amolops. However, the data does support all four individuals of the new species as distinct mitochondrial lineage with high support values. The lineage of new species is clustered with A. bellulus (Yunnan, China), A. mengyangens (Yunnan, China) and A. aniqiaoensis (Tibet, China) (Figure 1). For Amolops species used in our study, the average genetic distance between congeners is between 3.7% and 26.3% (Table 2), while the new species possesses a 5.5% genetic divergence from its sister species A. bellulus.
Morphological comparison
Our morphological comparisons support that the new species of Amolops as a member of the A. monticola group, because the new species possesses diagnostic characters of the species group, including light lip stripes and distinct dorsolateral folds. However, the new species differ from all congeners of the A. monticola species group by distinct coloration, the presence of circummarginal grooves on all fingers, presence of vomerine teeth, absence of white spine on the dorsal surfaces of head and body, and absence of vocal sacs in males.
Taxonomic conclusion
Because morphological and phylogenetic data support that the Nyingchi population of Amolops represent a distinct and independent evolutionary lineage and concordance among independent evidence confirms species status (Hou et al., 2014; Wu & Murphy, 2015), we describe it herein as a new species.
Taxonomic account
Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. Jiang, Wang, Xie, Jiang, and Che (Figure 2-3)
Holotype: KIZ 016432 (Figure 2), an adult male, from Gedang (N29.43871°, E95.66502°, elevation 1 887 m), Medog, Nyingchi Prefecture, Tibet, PR China, collected by Ke JIANG on 02 May 2015, and deposited in KIZ.
Allotype: KIZ 016418, an adult female, specimen shares the same locality and collection information as the holotype.
Paratypes: two adult males, KIZ 016415 and KIZ 016433, and nine adult females KIZ 016416-17, KIZ016419-24, KIZ 016435, all share the same locality and date as the holotype, collected by Ke JIANG, Fang YAN and Da-Hu ZOU. Three adult males, KIZ 012633-35, and two adult females, KIZ 012632 and KIZ 012646, from Zhibai (N29.62078°, E94.93358°; elevation 2 941 m), Paizhen, Mainling (=Milin), Nyingchi Prefecture, Tibet, PR China, collected by Ke JIANG, Kai WANG and Jiang XIE on 05 July 2012. Above specimens are deposited in KIZ. Five sub-adults, CIB 0140506-10, collected by Jian-Ping JIANG and Wu-Lin LIU from the same locality as the holotype on 24 April 2014, and deposited in CIB.

Table 1 Information of samples used in molecular analysis

Figure 1 Bayesian inference tree based on barcoding COI data of the Tibetan congeners of the genus Amolops and selected outgroups
Diagnosis: According to morphological character for the Amolops monticola group by Stuart et al. (2010), Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. is placed in the Amolops monticola group by following diagnosis: (1) skin smooth; (2) dorsolateral fold distinct; (3) lateral side of head black, upper lip stripe white extending to the shoulder.
Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. is further distinguished from all other congeners in the Amolops monticola group by the following combination of characters: (1) medium body size, SVL 48.5-58.3 mm in males, and 57.6-70.7 mm in females; (2) tympanum distinct, slightly larger than one third of the eye diameter; (3) a small tooth-like projection on anteromedial edge of mandible; (4) the absence of white spine on dorsal surface of body; (5) the presence of circummarginal groove present on all fingers; (6) the presence of vomerine teeth; (7) background coloration of dorsal surface brown, lateral body gray with yellow; (8) the presence of transverse bands on dorsal limbs; (9) the presence of nuptial pad on the first finger in males; (10) the absence of vocal sac in males.
Description of the holotype: Body size moderate, SVL 58.3 mm, slightly compressed vertically. Head slightly longer than wide (HL/HW=1.05); snout projecting forward and depressed, somewhat pointed at tip; nostril lateral, closer to eye than tip of snout; canthus rostralis distinct, slightly constricted behind nostrils; loreal region concave and oblique; eye relatively large (EHD/HL=0.40); interorbital distance same as width of upper eyelid; tympanum distinct, about one third of eye diameter (THD/EHD=0.34), tympanic rim not elevated; ridge of upper lip distinct. Vomerine teeth weakly developed, on two short oblique between choanae; tongue pyriform, deeply notched posteriorly, free for approximately two third of its length; a small tooth-like projection on anteromedial edge of mandible; vocal sac and vocal sac opening absent.
Fore-limb robust; tips of all four fingers expended into discs, disc on finger III approximately equal to diameter of tympanum; circummarginal grooves present on tips of all fingers, relatively feeble on first finger; relative finger length: I Hind limb slender, tibiotarsalis beyond the snout when adpressed, heels overlap when flexed and held perpendicular to body. Tips of all five toes expanded into discs, width of toe IV disc less than finger III disc; relative toe length: I Dorsal and lateral head and body smooth, except few indistinct tubercles present on temporal head and above vent; supratympanic fold indistinct; dorsolateral fold distinct, from rear of upper eyelid to near vent; ventral surfaces smooth except lightly flat tubercles on basal ventral surface of thigh; one low rictal gland, continuous with upper lip. Coloration of holotype in life: Dorsal surfaces of the head and body and lateral surfaces of the snout are flesh ocher. Coloration is much lighter along the upper margins of the dorsolateral fold. Small black spots are randomly scattered on the dorsal surfaces of the head and body. A white lip-stripe is present from the tip of the snout to the anterior joint of the shoulder on each side. The upper one fourth of the iris is golden yellow with small brown spots, while the remaining lower part of the iris is reddish brown. The tympanic region is dusky brown, with some lime-green mottling patterns of pigmentations scattered. A black stripe runs from the tip of snout to the anterior corner of the eye along the lower edge of canthus rostralis, and the stripe continues from the posterior corner of the eye along the dorsolateral fold to the pelvis. Lateral surfaces of the body are gray with olive yellow, scattered with some darker mottling. Dorsal surfaces of the limbs are rufous, darker on the hind limbs. Lateral surfaces of the hind limbs are trogon yellow, and the coloration is more obvious closer to the bases of the limbs. Irregular black, transverse bands are observed on the dorsal surfaces of limbs, and the bands are much more distinct on the hind limbs. Dark marbled patterns of pigmentation are observed on the dorsal surfaces of the fingers and toes. The throat and chest are pinkish white, with blackish vermiculate patterns of pigmentation. Abdominal region is offwhite, and faded dark gray blotches of pigmentation are observed on the anterior part of the region. The ventral surfaces of the forelimbs are light orange yellow. The ventral surfaces of the thigh and shank are pinkish-yellow and light orange yellow respectively. Figure 2 Different views of the male holotype (KIZ 016432) of Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. in life (Photos by Ke JIANG) Coloration of holotype in preservative: Dorsal surfaces of the head and body are dark gray, with scattered small, indistinct, black mottling. The upper margins of the dorsolateral fold are light gray. Lateral surfaces of the body are dusky brown. The throat, chest, abdominal region, the ventral surfaces of the fore limbs, and the ventral surfaces of the shank and feet are white, while the ventral surfaces of the thigh are yellowish. The iris becomes uniform gray in preservative. Variation: Measurements of type series are summarized in Table 3 and Table 4. Sexually dimorphism is observed. Males have distinct nuptial pads (v.s. absence in females) and have thick, robust forearms (v.s. thin and slender in females). In addition to the morphometric variations, differences of coloration are also observed among the type specimens. In two adult male specimens (KIZ 012634 and KIZ 016433), both black and light gray mottling patterns are observed on the dorsal surfaces of the head and body, while other three adult males specimens (KIZ 012633, KIZ 012635, and KIZ 016415) do not possess any mottling pattern on the dorsal surfaces of the head and body. Similar difference of coloration is also observed among the 12 adult females: KIZ 016435 and 016423 have dark gray spots only, KIZ 016418 and 016421 has light gray spots only, KIZ 016417, 016424, and 016422 have both light and black mottling patterns, and KIZ 016419, 016420, 016416, and 016434 have no mottling pattern at all. Figure 3 Different views of the female paratopotypes in life, from Medog (KIZ016434) (Photos by Ke JIANG and Kai WANG) Comparison: In the Amolops monticola group, Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. is most morphological similar to A. aniqiaoensis, A. bellulus, A. chayuensis, A. chunganensis, and A. monticola. But the new species could be distinguished from the four species except for A. bellulus by the absence of vocal sac in male (v.s. presence), and further differs from A. aniqiaoensis by the absence of white spine on dorsum (v.s.presence of both sexes) and the distinct transverse bands on dorsal limbs (v.s.absent or indistinct), differs from A. chayuensis by coloration of dorsum (light brown or yellowish brown v.s. green), differs from A. chunganensis by the smooth nuptial pad (v.s.the presence of tubercles on nuptial pad). Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. differs from A. bellulus by the presence of circummarginal groove on all fingers (v.s. absence of first finger) and different color of posterior and lower flank (gray with yellow v.s. bluish green to olive green) and iris (upper one fourth golden yellow, lower part red brown v.s.upper half golden yellow, lower half dark brown) in life; Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. differs from A. gerbillus by the distinct tympanum (v.s. indistinct), and difference of dorsal coloration (light brown or yellowish brown v.s. dark gray with light spots). Etymology: The species name “nyingchiensis” is the Latin form of name of Nyingchi Prefecture, which includes the two localities of the new species. According to the Latin name, we suggest the English common name as “Nyingchi cascade frog”, and the Chinese common name as “Lin Zhi Tuan Wa” (林芝湍蛙). Ecological notes The new species, A. nyinchiensis is found in the small to medium sized, fast flowing streams near mixed forest at relative high elevation (Figure 4). At the type locality (Gedang), the stream is much faster, and has rocky shores, while at the other locality (Zhibai) the stream is slower, and the shores are covered by vegetation and not rocky. Such distinct microhabitats suggest a wide ecological niche of the new species. In Gedang, only the new species was observed, and in Zhibai, one amphibian species, Nanorana parkeri (Stejneger, 1927) was co-distributed with the new species, and one reptile species Pseudoxenodon macrops (Blyth, 1854) was also observed. Reproductive season of the new species is unknown. The type species of the A. monticola group, A. monticola, was described based on a single female specimen from Darjeeling, northeast India (Anderson, 1871). Later, Boulenger (1920)redescribed the species and added a single topotypic male specimen in the description, which possesses a pair of external vocal sacs. However, since no additional descriptions or phylogenetic studies of the topotypic A. monticola have been published ever since, the diagnosis of the species is limited, and the species boundary of A. monticola remained unclear. Yet based on available information from the description of topotypes by Boulenger (1920), our new species can still be diagnosed from the true A. monticola by the absence of vocal sacs in males. Table 3 Morphological measurements (mm) of the type series of Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. from Gelin, Medog Table 4 Morphological measurements (mm) of the type series of Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. from Zhibai, Paizhen, Mainling Within Tibet, although A. monticola is recorded from several localities (Bom [=Bomi], Medog, Zayü [=Chayu], and Cona [=Cuona]) in Nyingchi Prefecture and Shannan Prefecture (Fei et al., 1977; Hu, 1987; Li et al., 2010), only one study provided information of vouchered specimens and their descriptions, and the vouchered specimens did not include any adult male (Hu, 1987). Given the lack of comparable information of the true A. monticola and the lack of male specimens of Amolops from Tibet, Hu (1987) temporarily identified those above specimens as A. monticola, and clearly stated that further studies are needed to clarify the taxonomic status of these Tibetan Amolops. Our examinations of Hu’s (1987) specimens of A. monticola from Medog (one adult female, CIB 35332) shows that the specimens differ from the original description of A. monticola by the presence of white spine on dorsum (v.s. absence) and the absence of distinct transverse bands on dorsal limbs (v.s. presence), but resemble to A. aniqiaoensis by above two diagnoses. Therefore, the record of A. monticola from Medog in Hu (1987) is a misidentification of A. aniqiaoensis and should be replaced by the latter. For the remaining specimens in Hu’s (1987) description of A. monticola from Bom, Zayü, and Cona (tadpole only), we cannot assign their taxonomic statuses with confidence due to the conservative morphology of females, the lack of malespecimens, and the lack of comparable materials of the true A. monticola. We recommend that future studies should collect and compare additional specimens from Bom, Zayü, and Cona of Tibet and topotypic A. monticola from India to clarify the taxonomic status of these Tibetan Amolops populations. Figure 4 Habitat of Amolops nyingchiensis sp. nov. at Gelin, Medog (A) and Zhibai, Mainling (B), Tibet, China (Photos by Ke JIANG and Kai WANG) We thank to the volunteers, Mr. Tao LIANG, Mr. Duan YOU, Mr. Ya-Di HUANG and Mr. Ya-Qiang SUN, who helped with fieldwork in Tibet, Prof. Yue-Zhao WANG (CIB), Prof. Yue-Ying CHEN (CIB) and Prof. Sheng-Quan LI (CIB) for kindly letting us examine specimens under their care. Anderson J. 1871. A list of the reptilian accession to the Indian Museum, Calcutta from 1865 to 1870, with a description of some new species. Journal of the Asiatic Society of Bengal, 40: 12-39. Boulenger GA. 1920. A monograph of the South Asian, Papuan, Melanesian and Australian frogs of the genus Rana. Records of the Indian Museum, 20: 1-226. Cai HX, Che J, Pang JF, Zhao EM, Zhang YP. 2007. Paraphyly of Chinese Amolops (Anura, Ranidae) and phylogenetic position of the rare Chinese frog, Amolops tormotus. Zootaxa, 1531: 49-55. Che J, Chen HM, Yang JX, Jin JQ, Jiang K, Yang ZY, Murphy RW, Zhang YP 2012. Universal COI primers for DNA barcoding amphibians. Molecular Ecology Resources, 12 (2): 247-258. Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ. 2009a. Fauna Sinica, Amphibia. Vol. 2. Beijing: Science Press, 1-957. (in Chinese) Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Huang YZ. 2009b. Fauna Sinica, Amphibia. Vol. 3. Beijing: Science Press, 959-1847. (in Chinese) Fei L, Hu SQ, Ye CY, Wu GF. 1977. A survey of amphibians in Xizang (Tibet). Acta Zoologica Sinica, 23 (1): 54-63. (in Chinese) Fei L, Ye CY, Huang YZ. 2005. An illustrated key to Chinese amphibians. Chengdu: Sichuan Publishing Group, 1-340. (in Chinese) Frost DR. 2015. Amphibian Species of the World: an Online Reference. Version 6.0 (Nov 26, 2015). Electronic Database accessible at http: // research.amnh.org/herpetology/amphibia/index.html. American Museum of Natural History, New York, USA. Hou M, Wu YK, Yang KL, Zheng S, Yuan ZY, Li PP. 2014. A missing geographic link in the distribution of the genus Echinotriton (Caudata: Salamandridae) with description of a new species from southern China. Zootaxa, 3895: 89-102. Hu SQ. 1987. Amphibia-Reptilia of Xizang. Beijing: Science Press, 1-153. (in Chinese) Li PP, Zhao EM, Dong BJ. 2010. Amphibians and Reptiles of Tibet. Beijing: Science Press, 1–251. (in Chinese) Liu WZ, Yang DT, Ferraris C, Matsui M. 2000. Amolops bellulus: A new species of stream-breeding frog from western Yunnan, China (Anura: Ranidae). Copeia, 2000 (2): 535-541. Matsui M, Shimada T, Liu WZ, Maryati M, Khonsue W, Orlov N. 2006. Phylogenetic relationships of Oriental torrent frogs in the genus Amolops and its allies (Amphibia, Anura, Ranidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 38 (3): 659-666. Posada D, Crandall KA. 1998. MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics, 14 (9): 817-818. Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP. 2003. MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics, 19 (12): 1572-1574. Sambrook J, Fritsch E, Maniatis T. 1989. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual (2nd edition). New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. Savage JM, Heyer WR. 1997. Digital webbing formulae for anurans: a refinement. Herpetological Review, 28 (3): 131. Stuart BL. 2008. The phylogenetic problem of Huia (Amphibia: Ranidae). Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution, 46 (1): 49-60. Stuart BL, Bain RH, Phimmachak S, Spence K. 2010. Phylogenetic systematics of the Amolops monticola group (Amphibia: Ranidae), with description of a new species from northwestern Laos. Herpetologica, 66 (1): 52-66. Sun GZ, Luo WX, Sun HY, Zhang GY. 2013. A new species of cascade frog from Tibet: China-Amolops chayuensis. Forestry Construction, 5 (1): 14-16. (in Chinese) Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G. 2011. MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28 (10): 2731-2739. Wu YK, Murphy RW. 2015. Concordant species delimitation from multiple independent evidence: A case study with the Pachytriton brevipes complex (Caudata: Salamandridae). Molecular Phylogenetic and Evolution, 92: 108-117. The following specimens were examined: Amolops aniqiaoensis (n=6): KIZ 011138-39 (2♂♂), KIZ 011136-37, KIZ011158 (3♀♀), CIB35332 (1♀), Medog, Tibet. Amolops chayuensis (n=19): KIZ 014016, KIZ 014019-21, KIZ 014028-34 (12♂♂), KIZ 014017-18, KIZ 014022-26 (7♀♀), Baxoi, Tibet. Amolops chunganensis (n=1): CIB 33536 (1♂), Chong’an, Fujian. Amolops medogensis (n=5): KIZ 06634 (1♂), KIZ 06635-37 (3♀♀), KIZ 016438 (1♀), Medog, Tibet. Amolops cf. monticola (by Hu, 1987) (n=2): CIB 35331 (1♀), Zayü, Tibet, CIB 35333 (1♀), Bom, Tibet. DOI:10.13918/j.issn.2095-8137.2016.1.31 *Corresponding author, E-mail: chej@mail.kiz.ac.cn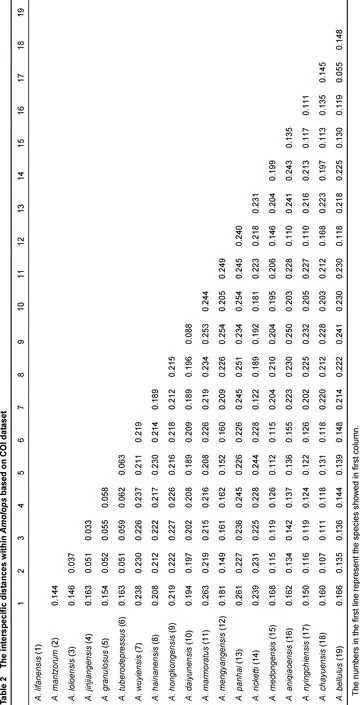


DISCUSSION


ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
REFERENCES
APPENDIX

