Spatial distribution of heavy metals(Cu,Pb,Zn,and Cd) in sediments of a coastal wetlands in eastern Fujian,China
Lili Zhao?Weibin You?Haiqing Hu?Wei Hong?Xiaojuan LIAO?Shihong Xiao?Ren Wang?Jinbiao Cai?Xuncheng Fan?Yong Tan?Dongjin He
Spatial distribution of heavy metals(Cu,Pb,Zn,and Cd) in sediments of a coastal wetlands in eastern Fujian,China
Lili Zhao1?Weibin You1?Haiqing Hu2?Wei Hong1?Xiaojuan LIAO1?Shihong Xiao1?Ren Wang3?Jinbiao Cai4?Xuncheng Fan1?Yong Tan1?Dongjin He1
We investigated the spatial distribution (horizontal and vertical concentrations)of copper(Cu), lead(Pb),zinc(Zn),and cadmium(Cd)in five wetland types(mudflat,aquaculture wetland,water area,farmland wetland and mangrove)from three areas(Ningde,Fuding, and Xiapu),China.Cu concentrations in five wetland types descended in the order:farm wetland,mudflat,aquaculture, water area and mangrove.Pb concentrations decreased in the order:aquaculture,mangrove,farm wetland,mudflat, and water area.Zn content decreased in the order:farm wetland,water area,aquaculture,mudflat and mangrove, and Cd content decreased as follows:mangrove,aquaculture,waterarea,mudflat,and farm wetland.Comparison of the concentrations of the same heavy metals in different areas showed thatthe highest Cu(63.75 mg kg-1)and Zn (152.32 mg kg-1)concentrations occurred in Ningdecoastal wetlands;Pb(110.58 mg kg-1)and Cd (2.81 mg kg-1)contents were highest in Fuding wetlands, and the average contents ofallheavy metals were very low in Xiapu wetlands.Examination ofthe verticaldistribution showed thatthe Cu contentwas high in allmudflatlayers; Pb and Cd concentrations were highestin aquaculture and mangrove wetlands,respectively,and Zn content was highestin farm wetlands.The spatialdistribution of Cu and Zn contents for different areas decreased as follows: Ningde>Fuding>Xiapu,for Pb and Cd were most concentrated in Fuding coastalwetlands.Concentrations of Zn and Cu were highly correlated,while Zn and Cu were not significantly correlated with Pb.
Coastal wetland·Heavy metal·Spatial distribution·Eastern Fujian·Ningde City
Introduction
Coastal wetlands,the transitional zones between terrestrial and marine ecosystems,are highly dynamic and complex ecosystems(WERG 1999).They provide many important ecological,economic and social benefits,such as flood storage,weatherregulation,habitats forplants and animals, ecotourism,and study areas for scientific research(Wang et al.2011;McCready et al.2006).Because of their location,coastal wetlands are vulnerable to disturbance by both naturalfactors and human activities.In an era of rapid industrial and economic development,heavy metals from human activities accumulate in wetland sediments and are a majorthreatto the integrity ofcoastalwetlands(Batjargal et al.2010;Varol and Bulent 2012).For example,Cd,an impurity in phosphate rock,is mainly found in phosphate fertilizers.Cd is a significant pollutant in agricultural soilthroughout China as a result of agrochemical use.In addition,the electroplating industry,waste incineration, nonferrous metal production and domestic sewage discharge can cause Zn and Pb pollution in wetland sediments (Ao et al.2012;Xiao et al.2013).
Because of the variety of sources of heavy metals in coastal wetlands,there are diverse reasons for the variations in their distributions(Liu et al.2014).Bai et al. (2011b)reported that Pb,Cd,and Zn mainly originated from tidal seawater in the study of wetland soils along a tidal ditch of the Yellow River Estuary,China.Previous studies have shown that hydrodynamic conditions can affect the distribution of heavy metals in coastal wetland sediments and that concentrations of heavy metals tend to be low in strong hydrodynamic conditions(Liu etal.2012). Moreover,plantabsorption and accumulation also have an important influence on the distribution of heavy metals in the sediments,and different plant types may have a significant influence on heavy metals(Usman et al.2013). Heavy metal pollutants are well-known for their persistence;they also accumulate in organisms,which may eventually enter the human food chain,and resultin health problems(Aktar et al.2010;Hejabi et al.2011).As the pollutants in sediments from different wetland types and wetland areas may impact public health,study of the concentrations and spatialdistributions of heavy metals in different types of coastal wetlands in different areas is necessary to understand the potential risks.
In recent years,many studies investigated the distribution of heavy metals in Chinese coastal wetlands.These concentrated on the Yellow River Delta(Yu et al.2011), Hangzhou Bay,and the estuaries of the Yangtze(Dong et al.2010;Fang et al.2013)and Minjiang Rivers(Cai et al.2011).Eastern Fujian is in the northeast of Fujian Province and is the main provincialmariculture area.There are various types ofnaturalwetlands in this area,and while the mariculture industry has resulted in enormous economic and socialbenefits,there have inevitably been many negative effects on the surrounding wetland environment. To date there have been few studies on coastal wetlands in Eastern Fujian(He etal.2013;Liao etal.2013;Yan etal. 2013;You et al.2013),and information on the spatial distribution of heavy metals in differentwetland types has rarely been reported.Eastern Fujian has both mountainous and coastalresources,and is the northern distribution limit of the mangrove species Kandelia candel.Due to the effects of urbanization and human activities,the natural wetland area is shrinking and coastal wetlands are increasingly degraded(He et al.2012;Lin et al.2012).The objective of this study was to investigate concentrations and spatial distributions of heavy metals in wetland sediments of five typical wetland types(mudflat,aquaculture, water area,farm wetland and mangrove)in three areas (Ningde,Fuding and Xiapu)to improve understanding of contamination levels and to provide baseline information for protection of coastal wetlands in eastern Fujian.
Materials and methods
Study area
Eastern Fujian(26°55′–27°20′N,119°55′–120°43′E) refers to Ningde City in Fujian Province;it is located near Fuzhou and Wenzhou in the northeast of Fujian Province. Eastern Fujian is one of the major mariculture areas in China.Ithas a coastline length of878 km,and accounts for nearly 36%of China’s marine fishery area.The total sea area is 46,000 km2,and comprises shallow sea and mudflat areas of 93,000 and 44,000 hm2,respectively.The coastal wetlands of Eastern Fujian are in the subtropicaltransition; the tides are strong,and the mean harbor tidal range is approximately 5 m or more,which is considered a very high tidal range.The total coastal wetland area of Eastern Fujian is 74 km2,and makes up 10.6%of the totalcoastal wetland area in Fujian Province;it includes mudflat, aquaculture,water areas,farm wetlands,and mangroves.It is rich in marine species,including Pseudosciaena crocea, Tegillarca granosa,Epinephelus sp.,Mycteroperca sp. (grouper)and Ensis sp.
Ningde comprises Jiaocheng,the Qiaodong economic development zone,the cities of Fu’an and Fuding,and Xiapu,Gutian,Zhouning,Shouning,Pingnan and Zherong counties.There are four main vegetation types in the wetland ecosystem in Eastern Fujian,viz.mangrove, coastal salt marsh,coastal psammophilous,and shallowwater wetland.The mangrove community is dominated by Kandelia candel,present both in large mangals and as scattered individuals.Coastal salt marsh vegetation is widely distributed and the common species include,among others,Spartina alterniflora,Phragmites australis,Suaeda australis,Typha angustifolia.The main coastal psammophilous species include Casuarina equisetifolia,Atriplex maximowicziana,and Teragonia teragonioides communities.Shallow-water wetland vegetation mainly includes Eichhornia crassipes,Alernantera philoxeroidis and Jussiaea repens communities.
Sample collection
Sampling locations were selected to reflect various levels of exposure to pollution.We chose sampling sites that included mudflats,aquaculture,water areas(water bodies, including shallow water and estuary water area),farm wetlands(paddy fields and irrigation canal system)and mangroves.These wetland types were distributed throughNingde,Fuding and Xiapu,and ten quadrats were sampled in each wetland type of the three areas in July 2011.Three sampling sites were distributed randomly across each quadrat measuring 20 m×30 m,and sediments were sampled at three depths of the sediment profile:surface (0–20 cm),intermediate(20–40 cm)and bottom (40–60 cm).The three samples from each layer were composited using the quartile method.A total of 450 sediments samples were collected from each wetland type of the three areas,and all samples were stored in polyethylene bags for transport and storage.All sediment samples were air-dried in the laboratory at room temperature.The air-dried sediment samples were then sieved through a 100 mesh to remove large debris,shells and roots,and were then stored in polyvinylchloride packages for later analysis.
Determination of heavy metals
For the analysis of total heavy metals,2 g of each sample were placed in a Teflon digestion vessel.Each sample was placed on a heating plate with a little water and 10 mL 37%HCl,and digested at 130°C for 1 h.Then,3 mL HNO3and 5 mL HF were added to the vesseland digested at 150°C for a further 2 h.Next,2 mL HClO4was added to the vesseland further digested at170°C for 2 h.When the solution was nearly dry,2 mL aqua regia(HCl/ HNO3=3:1)was added to the vessel and digested at 200°C until the supernatant was clear,and there were no further brownish-colored fumes.After digestion and cooling,the final solution was diluted to 50 mL.This digested solution was analyzed for Cu and Zn using flame atomic absorption spectrometry(Perkin Elmer 603);Pb and Cd were measured using graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry(Perkin Elmer Z/3030),following the National Standard Method.
Statistical analysis
The coefficientof variability(CV)is the bestdiscriminating factor for describing variability(Steel et al.1997).CVis a simple and useful statistical index for measuring the discrete dispersion(Wang 2007).We calculated CVusing the following equations:
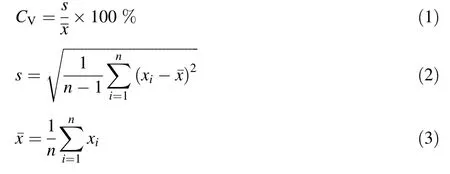
where s is standard deviation andˉx is the sample mean.
Data calculation and statistics were performed with SPSS 18.0 statistical software and Microsoft Excel.Shapiro–Wilk statistical tests were used to evaluate the normality of the data.The sediment data showed approximately normal distributions.Pearson correlation analysis was used to quantify relationships among heavy metals.
Results and discussion
Horizontal distribution patterns of heavy metals by wetland type
The coefficientof variability values of Cu,Pb,Zn,and Cd in surface sediments from each wetland type,together with concentrations of heavy metals,are presented in Table 1. CV(the coefficientofvariability)values ofheavy metals in mudflat wetlands decreased in the following order:Cd (47%)>Zn(39%)>Cu(38%)>Pb(27%),which indicates that Cd had the most uneven distribution,followed by Zn and Cu;Pb was distributed most evenly.The CV of heavy metals in aquaculture decreased in the order: Cd(81%)>Pb(57%)>Cu(36%)>Zn(31%),indicating that Cd and Pb had the most non-uniform distributions.The distributions of Cu and Zn in aquaculture and mudflat wetlands were similar.Zn and Cd had CV values of approximately 50%(48 and 56%,respectively)in water areas,and showed considerable variability,while Cu and Pb had the lowest CVs.CV values of Cu,Pb,and Cd were higher in mangroves,indicating uneven distributions. All four heavy metals had high CV values in farmland wetlands,indicating that Cu,Pb,Zn,and Cd were not evenly distributed.
Overall,the mean concentrations of 4 heavy metals in surface sediments decreased in the order:Zn>Pb>Cu>Cd.Cu concentrations were highest in farmland wetlands(59.27 mg kg-1),while Cu concentrations were lowest in mangrove wetlands(30.46 mg·kg-1).Zn concentrations decreased in the following order:farmland wetland>water area>aquaculture wetland>mangrove>mudflat.Cu and Zn concentrations were highestin farmland wetlands.This indicates thatcultivation history is also an important factor related to the accumulation of heavy metals in cultivated wetlands as reported earlier by Baietal.(Baietal.2010).These findings agree with those of(Zhang et al.2011)and(Bai et al.2011a),and suggest that Cu and Zn accumulation is probably due to fertilizer and pesticide use,in particular,applications of some unregulated agriculturalmaterials thatpromote accumulation ofheavy metals(Lopes etal.2011).Additionally,farmland in China is contaminated by heavy metals from atmospheric deposition(Zhang 2001).Previous studies haveshown that atmospheric inputs to agricultural systems can contribute significantly to Zn,Pb,and Cu loadings in agriculturalsoils(Gray etal.2003;Berthelsen etal.1995). The main atmospheric sources of heavy metals are waste incineration,traffic,and manufacturing processes,all of which are found throughoutthe study area.Pb decreased in the following order:aquaculture wetland>mangrove>farmland wetland>mudflat>water area.Pb concentrations were highest in aquaculture wetlands,suggesting that Pb was associated with inputs from aquaculture activities in wetland sediments.Of the four heavy metals,Cd concentrations were lowest,and decreased in the order:mangrove>aquaculture wetland>water area>mudflat>farmland wetland.Cd concentrations were highestin mangrove,reflecting the factthatmangrove plants had a greater ability to absorb Cd.(He et al.2013) Additionally,Cu and Zn concentrations were relatively low in mangrove,which may be associated with sampling season.We sampled in summer,the period of maximum aboveground biomass in wetlands.Even though they are heavy metals,Cu and Zn are also essential trace elements for plant growth and development(Pardo et al.2014;Alvarenga et al.2014),so the distribution of heavy metals may be affected by uptake by plants.Previous studies have shown that mangrove plants have strong absorption and accumulation ability for Cu and Zn,and the roots have higher accumulation,reflecting the physiological needs of plants.(Che 1999).
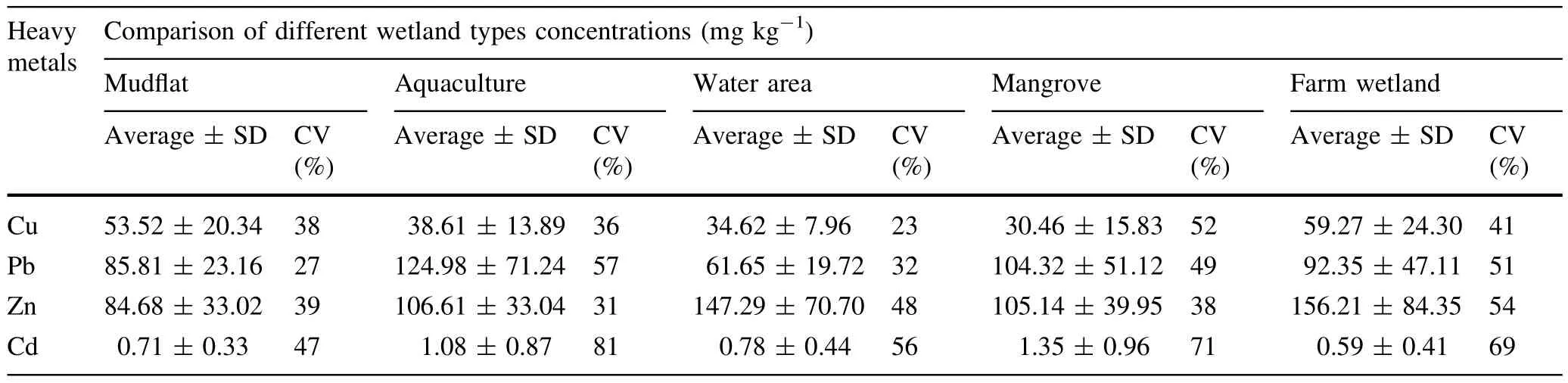
Table 1 Heavy metal concentrations and coefficients of variations in different wetland types of surface sediments in Eastern Fujian coastal wetlands

Table 2 Heavy metal concentrations and coefficients of variations in different area surface sediments in Eastern Fujian coastal wetlands
Horizontal distribution patterns of heavy metals by area
CV values of Cu,Pb,Zn,and Cd in surface sediments from different areas,together with concentrations of heavy metals,are presented in Table 2.Overall,from the three areas,Ningde had the highest concentrations of Cu (63.75 mg kg-1)and Zn(152.32 mg·kg-1),and Fuding wetland had the highest concentrations of Pb (110.58 mg kg-1)and Cd(2.81 mg kg-1).The 4 heavy metal contents were considerably lower at Xiapu when compared with other areas.CV values of Cu were similar at Fuding(51%)and Xiapu(46%)wetlands,and displayed higher degrees of discrete dispersion and uneven distribution.In contrast,Ningde had the lowest CV value for Cu(35%)and the distribution was relatively even.The CV value for Pb was low for all 3 areas,showing it was uniformly distributed.The CV for Zn in the Xiapu area was slightly higher than the CV values for Zn in either theNingde area or Fuding wetlands.The CV values for Cd were greater than 50%,and showed extensive variability and uneven distributions throughout Eastern Fujian.
Vertical distribution patterns of heavy metals in different wetland types
The vertical distribution of heavy metals not only reflects deposition from different periods,but also records the migration of heavy metals in sediments(Jara-Marinietal. 2008;Bodin et al.2013).The heavy metal profile distributions differed by wetland type in Eastern Fujian.Cu contents were highest in mudflat,Pb contents were highest in aquaculture wetlands,Zn contents were highestin farm wetlands,and Cd contents were highest in mangrove wetlands(Fig.1).These results are consistent with the horizontaldistribution patterns ofheavy metals in different wetland types(except Cu).
With the exception of Cu,concentrations of heavy metals decreased with depth,from the surface sample to the bottom sample in mangrove.This indicates that most heavy metals accumulated in the surface of mangrove wetland sediments,and then moved downward after saturation.The vertical distribution of Cu was very different from that of the other metals in mangrove.Highest Cu contents were found in the surface sediments (0–20 cm),where the value was 30.46 mg kg-1;concentrations then decreased in the intermediate layer (20–40 cm),but increased again in the bottom layer(40-60 cm).The variation might be caused by natural factors such as tidal action or seasonal variation,or by human disturbance(Nobi et al.2010).Cu and Zn tended to increase from upper to lower layers in mudflats,which might indicate the primary geochemical conditions that control their distributions.(Ling etal.2010)With the exception of Zn,there was significant leaching and accumulation of all heavy metals in water areas because the high metal solubility in the flooded anaerobic conditions promoted downward leaching and accumulation.In contrast,heavy metal contents trended to decrease with depth in aquaculture and farm wetlands.
Vertical distribution patterns of heavy metals in different areas
Cu and Zn occurred at the three areas in the following order:Ningde>Fuding>Xiapu.Pb and Cd contents at Fuding were higher than at the other two areas(Fig.2). The verticaldistribution of Cu atXiapu firstincreased,then decreased;Cu decreased layer by layer at the other two areas.Of the three areas,Pb contents were highest at the Fuding coastal wetland,where contents decreased as depth increased.The Pb contents of sediments from Ningde were similarto,butslightly lowerthan,those atXiapu wetlands; contents were higher in the intermediate layer(20–40 cm) than in the other layers.Zn content was highest in the bottom layer(40–60 cm)at the Fuding wetlands;Zn decreased with depth at Xiapu and Ningde.Cd contents showed a decreasing trend with depth in the sediment profile at Fuding and Xiapu wetlands;Cd contents atNingde first increased,then decreased,such that the concentration atthe surface(0–20 cm)was higher than at the bottom(40–60 cm).
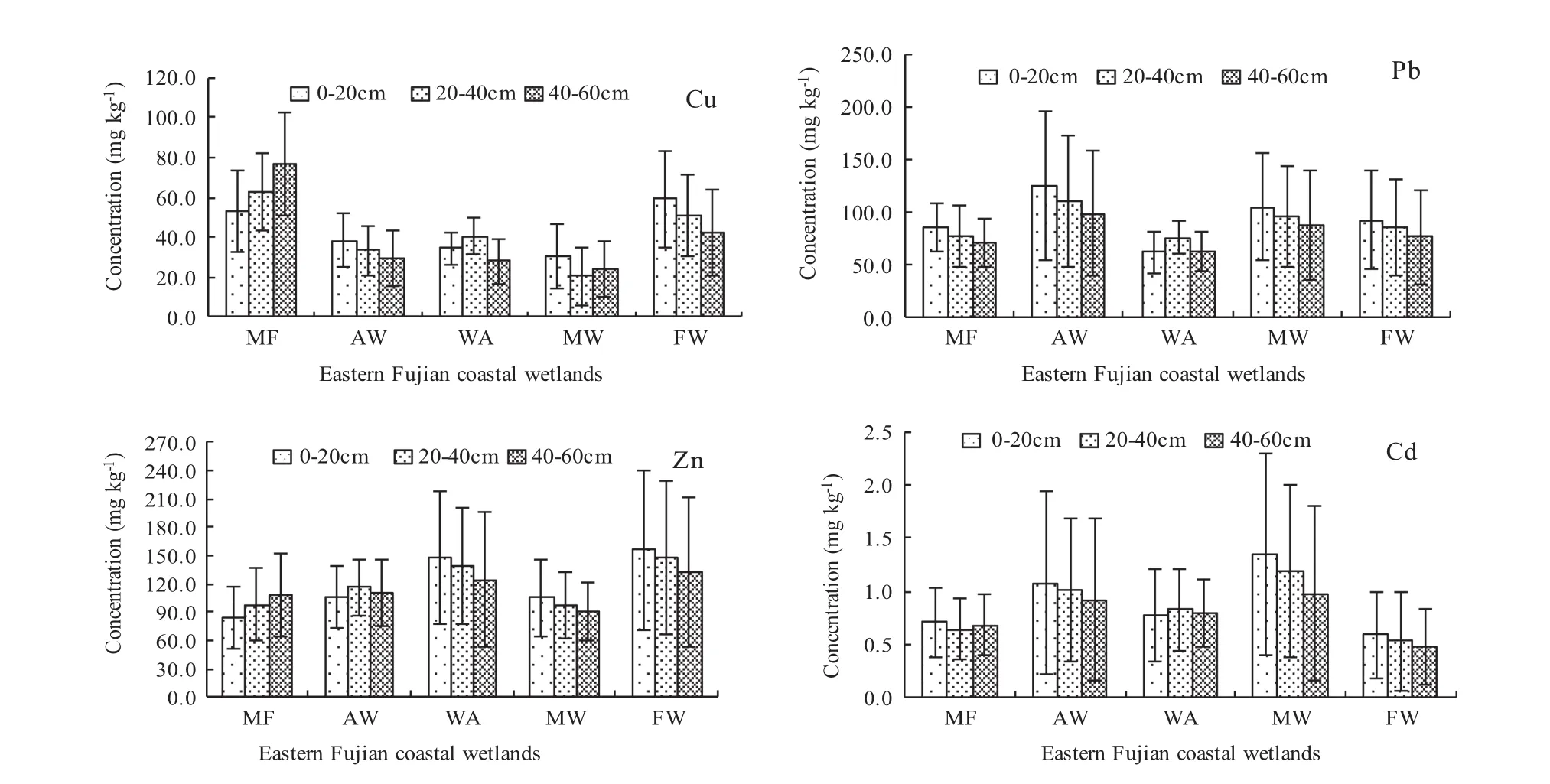
Fig.1 Heavy metals profile distribution in different wetland types of Eastern Fujian coastal wetlands.MF,AW,WA,MW and FW refer to mudflat,aquaculture wetland,water area,mangrove wetland and farmland wetland,respectively
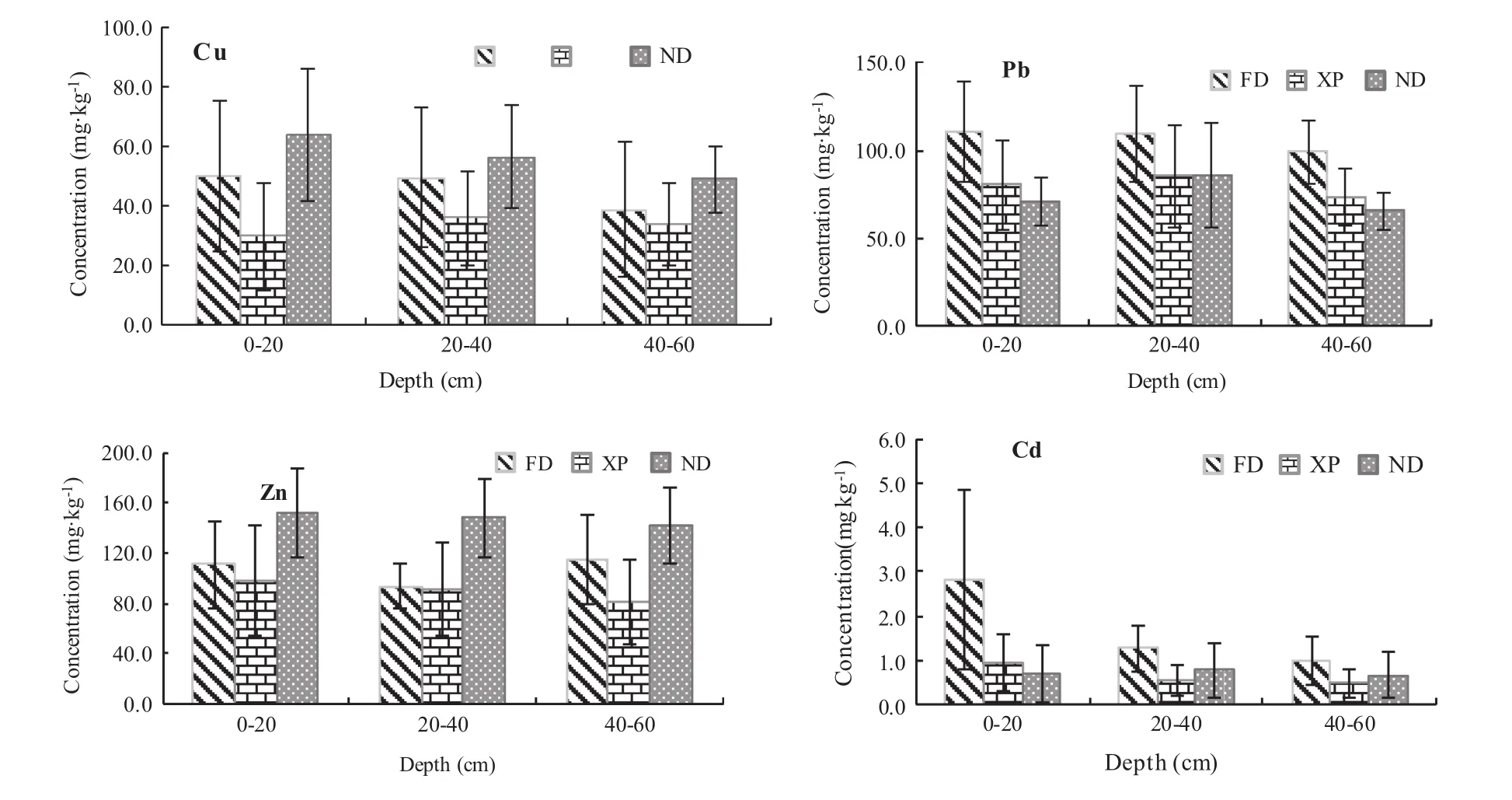
Fig.2 Heavy metals profile distribution in differentareas sediments of Eastern Fujian coastalwetlands.ND,FD and XP refer to Ningde,Fuding and Xiapu,respectively
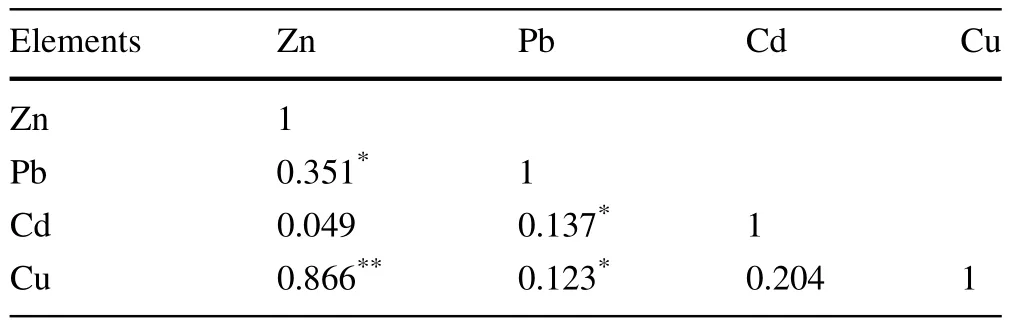
Table 3 Correlations among heavy metals in Eastern Fujian coastal wetlands
Relationships between heavy metals
Correlation analysis was used to examine whether heavy metals in Eastern Fujian coastal wetlands had the same sources(Table 3).Similar analyses were documented earlier(Ye et al.2013;Zhang et al.2013;Luo et al.2007; Gailey and Lloyd 1985).Zn and Cu were significantly correlated.The large amounts of pesticides and fertilizers—used to control plant diseases and to promote plant growth in agriculture—might have caused Zn and Cu accumulation in sediments.Zn and Pb were also correlated, indicating that the two metals could have a similar sources or distribution status.Cd was not significantly correlated with either Zn or Cu.]
Conclusions
We analyzed the spatial distribution of heavy metals(Cu, Pb,Zn,and Cd)in sediments from coastal wetland in Eastern Fujian.Mean concentrations of the 4 heavy metals in Eastern Fujian coastal wetlands decreased in the following order:Zn>Pb>Cu>Cd.Comparison of the distributions ofheavy metals atthree areas showed thatCu and Zn contents were highest at Ningde,Pb and Cd were highest at Fuding,and the mean concentrations of the 4 heavy metals were relatively low at Xiapu.Analysis of the vertical distributions showed that Cu contents were highest in the mudflats,Pb concentrations were highest in aquaculture,Cd contents were highest in mangroves,and Zn contents were highest in farm wetlands.The spatial distribution of Cu and Zn concentrations in the 3 areas were in the following order:Ningde>Fuding>Xiapu.Pb and Cd were most concentrated in Fuding coastal wetlands.We examined the spatial distribution and contents of heavy metals(Cu,Pb,Zn,and Cd)by site and depth in the sediments of Eastern Fujian,but we did not address the sources of heavy metals or transport mechanisms,both of which require further study.
Aktar MW,Paramasivam M,Ganguly M,Purkait S,Sengupta D (2010)Assessment and occurrence of various heavy metals insurface water of ganga river around kolkata:a study for toxicity and ecological impact.Environ Monit Assess 160(1–4):207–213
Alvarenga P,de Varennes A,Cunha-Queda AC(2014)The effectof composttreatments and a plant cover with agrostis tenuis on the immobilization/mobilization of trace elements in a mine-contaminated soil.Int J Phytorem 16(2):138–154
Ao L,Shan BQ,Zhang H,Tang WZ(2012)Heavy metals distribution and risk assessment of sediments in the riverine wetland of sanmenxia reservoir.Huanjing Kexue 33(4):1176–1181
BaiJH,CuiBS,Yang ZF,Xu XF,Ding QY,Gao HF(2010)Heavy metal contamination of cultivated wetland soils along a typical plateau lake from southwest China.Environ Earth Sci59(8):1781–1788
Bai JH,Huang LB,Yan DH,Wang QG,Gao HF,Xiao R,Huang C (2011a)Contamination characteristics of heavy metals in wetland soils along a tidal ditch of the yellow river estuary, China.Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 25(5):671–676
Bai JH,Xiao R,Cui BS,Zhang KJ,Wang QG,Liu XH,Gao HF, Huang LB(2011b)Assessment:of heavy metal pollution in wetland soils from the young and old reclaimed regions in the Pearl River estuary,south China.Environ Pollut159(3):817–824
Batjargal T,Otgonjargal E,Baek K,Yang JS(2010)Assessment of metals contamination of soils in ulaanbaatar,mongolia.JHazard Mater 184(1–3):872–876
Berthelsen B,Steinnes E,Solberg W(1995)Heavy metal concentrations in plants in relation to atmospheric heavy metal deposition.J Environ Qual 24(5):1018–1026
Bodin N,N’Gom-Ka R,Ka S,Thiaw O,De Morais LT,Le Loc’H F, Rozuel-Chartier E,Auger D,Chiffoleau J(2013)Assessmentof trace metal contamination in mangrove ecosystems from senegal,west africa.Chemosphere 90(2):150–157
Cai HY,Zeng LF,Fang MZ,Ge HL,Ye YZ,Zeng CS(2011) Distribution features and assessment of heavy metal in Tajiaozhou wetland of Minjiang estuary.Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Natural Science Edition) 40(3):285–289(In Chinese)
Che RGO(1999)Concentration of 7 heavy metals in sediments and mangrove rootsamples from maipo,hong kong.Mar Pollut Bull 39(1–12):269–279
Dong AG,Zhai SK,Yu ZH,Han DM(2010)Evaluation on potential ecological risk of the heavy metals in the surface sediments of the Changjiang(Yangtze)estuary and its adjacent coastal area. Marine Sciences 34(3):69–75(In Chinese)
Fang M,Wu YJ,Liu H,Jia Y,Zhang Y,Wang XT,Wu MH,Zhang CL(2013)Distribution,sources and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of the Yangtze River estuary.Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae 33(2):563–569(In Chinese)
Gailey FA,Lloyd OL(1985)Grass and surface soils as monitors of atmospheric metal pollution in central scotland.Water Air Soil Pollut 24(1):1–18
Gray CW,McLaren RG,Roberts A(2003)Atmospheric accessions of heavy metals to some new zealand pastoral soils.Sci Total Environ 305(1–3):105–115
He DJ,Zheng KJ,Wang R,Zhang DQ,CaiJB,LiXJ,Wang QB,You W,You HM(2012)Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals(Zn,Cd,Cu)in different originated Kandelia candel mangrove stands in Eastern Fujian Province.Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University(Natural Science Edition) 41(2):187–192(In Chinese)
He DJ,You WB,Wang R,Xiao SH(2013)Spatial distribution of heavy metals in sediments from Kandelia candelbetween natural forest and plantation in the north marginal region of natural mangrove wetlands,China.Chinese Journal of Applied& Environmental Biology 19(6):945–951(In Chinese)
Hejabi AT,Basavarajappa HT,Karbassi AR,Monavari SM(2011) Heavy metal pollution in water and sediments in the Kabini river,karnataka,india.Environ Monit Assess 182(1–4):1–13
Jara-Marini ME,Soto-Jimenez MF,Paez-Osuna F(2008)Trace metals accumulation patterns in a mangrove lagoon ecosystem, mazatlan harbor,southeast gulf of california.J Environ Sci Health A 43(9):995–1005
Liao XJ,He DJ,Wang R,Cai JB,Su SC,Zhang ZR,Xiao SH,Chen ZW,Huang P(2013)Distribution pattern of soilorganic carbon contents in the coastal wetlands in Eastern Fujian.Wetland Science 11(2):192–197(In Chinese)
Lin L,He DJ,Wang R,Cai JB,Hong W,You WB,Liao XJ,Su SC, Zhang ZR,Chen ZW,Huang P(2012)Research on landscape classification and pattern feature of coastal wetland in East Fujian Province.Journal of Southwest Forestry College 32(2):62–67(In Chinese)
Ling M,Liu RH,Wang Y,Tang AK,Yu P,Luo XX(2010)The spatial distribution of heavy metals in the soil of tamarix chinensis forest farm in yellow river delta wetland and its ecologicalsignificance.Trans Oceanol Limnol31(04):41–46(In Chinese)
Liu ZJ,Li PY,Zhang XL,Li P,Zhu LH(2012)Regionaldistribution and ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in surface sediments from coastal wetlands of the Yellow River Delta. Huan Jing Ke Xue 33(4):1182–1188(In Chinese)
Liu MX,Yang YY,Yun XY,Zhang MM,Li QX,Wang J(2014) Distribution and ecological assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of the east lake,China.Ecotoxicology 23(1):92–101
Lopes C,Herva M,Franco-Uria A,Roca E(2011)Inventory ofheavy metalcontentin organic waste applied as fertilizerin agriculture: evaluating the risk of transfer into the food chain.Environ Sci Pollut Res 18(6):918–939
Luo W,Wang T,Lu Y,Giesy JP,Shi Y,Zheng Y,Xing Y,Wu G (2007)Landscape ecology of the guanting reservoir,beijing, China:multivariate and geostatisticalanalyses ofmetals in soils. Environ Pollut 146(2):567–576
McCready S,Birch GF,Long ER(2006)Metallic and organic contaminants in sediments of sydney harbour,australia and vicinity—a chemical dataset for evaluating sediment quality guidelines.Environ Int 32(4):455–465
Nobi EP,Dilipan E,Thangaradjou T,Sivakumar K,Kannan L(2010) Geochemical and geo-statistical assessment of heavy metal concentration in the sediments of differentcoastalecosystems of andaman islands,India.Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 87(2):253–264
Pardo T,Martinez-Fernandez D,Clemente R,Walker DJ,Bernal MP (2014)The use of olive-millwaste compostto promote the plant vegetation cover in a trace-element-contaminated soil.Environ Sci Pollut Res 21(2):1029–1038
Steel RGD,Torrie JH,Dickey DA(1997)Principles and procedures of statistics:a biometrical approach.McGraw-Hill,New York, p 666
Usman ARA,Alkredaa RS,Al-Wabel MI(2013)Heavy metal contamination in sediments and mangroves from the coastof red sea:Avicenna marina as potential metal bioaccumulator.Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 97(1):263–270
Varol M,Bulent S(2012)Assessment of nutrient and heavy metal contamination in surface water and sediments of the upper tigris river,turkey.Catena 92:1–10
Wang WS(2007)Coefficient of variability–a simple and useful statistical index for measuring the discrete dispersion.Popular statistics 06:41–42(In Chinese)
Wang YX,Cheng S,Ju HB,Zhang HQ,Jiang D,Zhuang DF(2011) Evaluating sustainability of wetland system:a case study in east Dongting lake area.China.African Journal of Agricultural Research 6(28):6167–6176
WERG(Wetland Ecosystems Research Group)(1999)Wetland functional analysis research program.College Hill Press,London,pp 8–10
Xiao R,Bai JH,Huang LB,Zhang HG,Cui BS,Liu XH(2013) Distribution and pollution,toxicity and risk assessmentof heavy metals in sediments from urban and rural rivers of the Pearl River delta in southern China.Ecotoxicology 22(10):1564–1575
Yan JY,He DJ,LiXJ,Wang R,Cai JB,You WB,Su SC,Zhang ZR, Xiao SH(2013)Comparative studies on the carbon storage between the Kandelia candel natural forests and plantations in north mangrove forests of China.Chin J Trop Crops 34(7):1395–1401(In Chinese)
Ye HX,Zang SY,Zhang LJ,Zhang YH(2013)Distribution and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of zhalong wetland.Environ Sci 34(4):1333–1339 (In Chinese)
You WB,Lin L,He DJ,Wang R,Cai JB,Wang P,Zhang ZR,Xiao SH,Zheng XY(2013)Dynamic assessment on ecological vulnerability of coastal wetlands in eastern Fujian Province. J Fujian Agric For Univ(Nat Sci Ed)42(6):15–21(In Chinese)
Yu JB,Dong HF,Wang HB,Chen XB,Xie WJ,Mao PL,Gao YJ, Shan K,Chen JC,Ma XM(2011)Spatial distribution characteristics of metals in New-born coastal wetlands in the Yellow River Delta.Wetl Sci 09(4):297–304(In Chinese)
Zhang NM(2001)Effects of air settlement on heavy metal accumulation in soil.Soil Environ Sci 10(02):91–93(In Chinese)
Zhang QW,Yang ZL,Luo LG,Zhang AP(2011)Distribution of nutrients and heavy metals concentration in sedimentprofiles of a wetland in Ningxia Irrigation Area.J Soil Water Conserv 25(1):74–80(In Chinese)
Zhang PY,Qin MZ,Yan JH,Yang L,Li J,Sun C,Chen L(2013) Spatial variation of soil heavy metals in the beach of lower yellow river:a case study in kaifeng section.Geogr Res 32(3):421–430(In Chinese)
29 March 2014/Accepted:30 June 2014/Published online:28 April 2015
?Northeast Forestry University and Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2015
Projectfunding:This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Grant No.31370624),Key Financing Project of Fujian Provincial Department of Science and Technology (2009N0009).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Corresponding editor:Zhu Hong
?Dongjin He fjhdj1009@126.com
1Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, Fuzhou 350002,Fujian,People’s Republic of China
2Northeast Forestry University,Harbin 150040,Heilongjiang, People’s Republic of China
3Forestry Bureau of Fuding,Fujian 350002, People’s Republic of China
4Forestry Bureau of Xiapu,Xiapu 355100, People’s Republic of China
 Journal of Forestry Research2015年3期
Journal of Forestry Research2015年3期
- Journal of Forestry Research的其它文章
- Axial variations in anatomical properties and basic density of Eucalypturograndis hybrid(Eucalyptus grandis×E.urophylla) clones
- Nest site characteristics and nest loss of Marsh Grassbird at Zhalong National Nature Reserve,China
- Variations in electrical impedance and phase angle among seedlings of Pinus densata and parental species in Pinus tabuliformis habitat environment
- Optimization of corn-stalk skin flake-wood shaving composite technology
- Characterization of ploidy levels in Chrysanthemum L.by flow cytometry
- Effects of salinity on the nail-holding power of dimension lumber used in light-frame wood building
