Health-promoting microbes in traditional Vietnamese fermented foods:A review
Nguyen La Anh
Food Industries Research Institute,301 Nguyen Trai Rd,Thanhxuan Distr.,Hanoi 100000,Viet Nam
Abstract Vietnam has a long history of numerous traditional fermented products that contain a range of microorganisms with favorable technological,preservative,and organoleptic properties for food processing as well as other functional properties.This review emphasizes the most common traditional Vietnamese fermented foods and their beneficial indigenous bacteria having health-promoting effects.
Keywords: Traditional fermented foods;Lactic acid bacteria(LAB);Microflora;Probiotic;Health effect
1.Introduction
Non-dairy fermented foods are popular in Asia;among these,nutritional and physiological properties of Koreankimchiare the most well characterized [1,2].Other fermented foods in Asia have been reviewed in terms of their processing technology and the role of lactic acid bacteria(LAB)in the organoleptic,preservative,and nutritive properties of these foods[3].However,data on Vietnamese traditional fermented foods are limited.Vietnam,located in Southeast Asia,is a tropical and highly populated country with a long history of numerous traditional fermented products.Unlike western countries,where commercially fermented foods are produced on a large scale using industrially produced starter cultures,in Vietnam,these foods are produced largely in the household or on small scale using methods that are passed down from one generation to another.Most traditional Vietnamese fermented products are artisanal and are closely related to the local natural microbiota,which makes them a pertinent source of beneficial indigenous microorganisms.
Studies on Vietnamese traditional fermented foods have mainly focused on their microbial biodiversity and technological and organoleptic properties such as lactic acid production,flavor development,and food preservation.Several recent studies have been performed on health benefits of microbes isolated from fermented foods; however,the available data are still sparse.This review summarizes data on traditional Vietnamese fermented foods to provide a detailed overview of their functional properties.
2.Discussion
2.1.Vietnamese traditional fermented foods
A list of the most popular Vietnamese fermented foods is given in Table 1.With respect to fermentation,traditional Vietnamese fermented foods are categorized into two groups: (i)food requiring short-term fermentation and (ii) food requiring long-term fermentation.Foods produced by short-term fermentation usually have a sour taste,are used for direct consumption or stored at 4–8°C,and have a short shelf life.Foods produced by long-term fermentation have high salt (sodium chloride)content to prevent pathogenic contamination.Similar to other Asian cuisines,raw materials used for preparing traditional Vietnamese fermented foods are usually non-dairy basedand inexpensive and contain various vegetables(e.g.,eggplant,radish,cabbage,bamboo shoot,bean sprout,leek,onion,and cucumber),fruits(e.g.,edible fiber of jackfruit,fig,and young mango),rice,fish,shrimp,and meat.Herbs and spices such as garlic,black or red pepper,green onion,and ginger,are often used as minor ingredients.Fermentation temperature largely depends on natural environment.It may also be controlled by leaving the food in the sun or in the shadow depending on the traditional procedure.LAB strains play an important role in the fermentation of many foods.Vietnam is a long-shaped country with different soil and climate conditions depending on the latitude.Therefore,traditional fermented foods may feature local produce or may be common throughout the country,with only slight modifications.These products are often consumed daily as appetizers or side dishes.
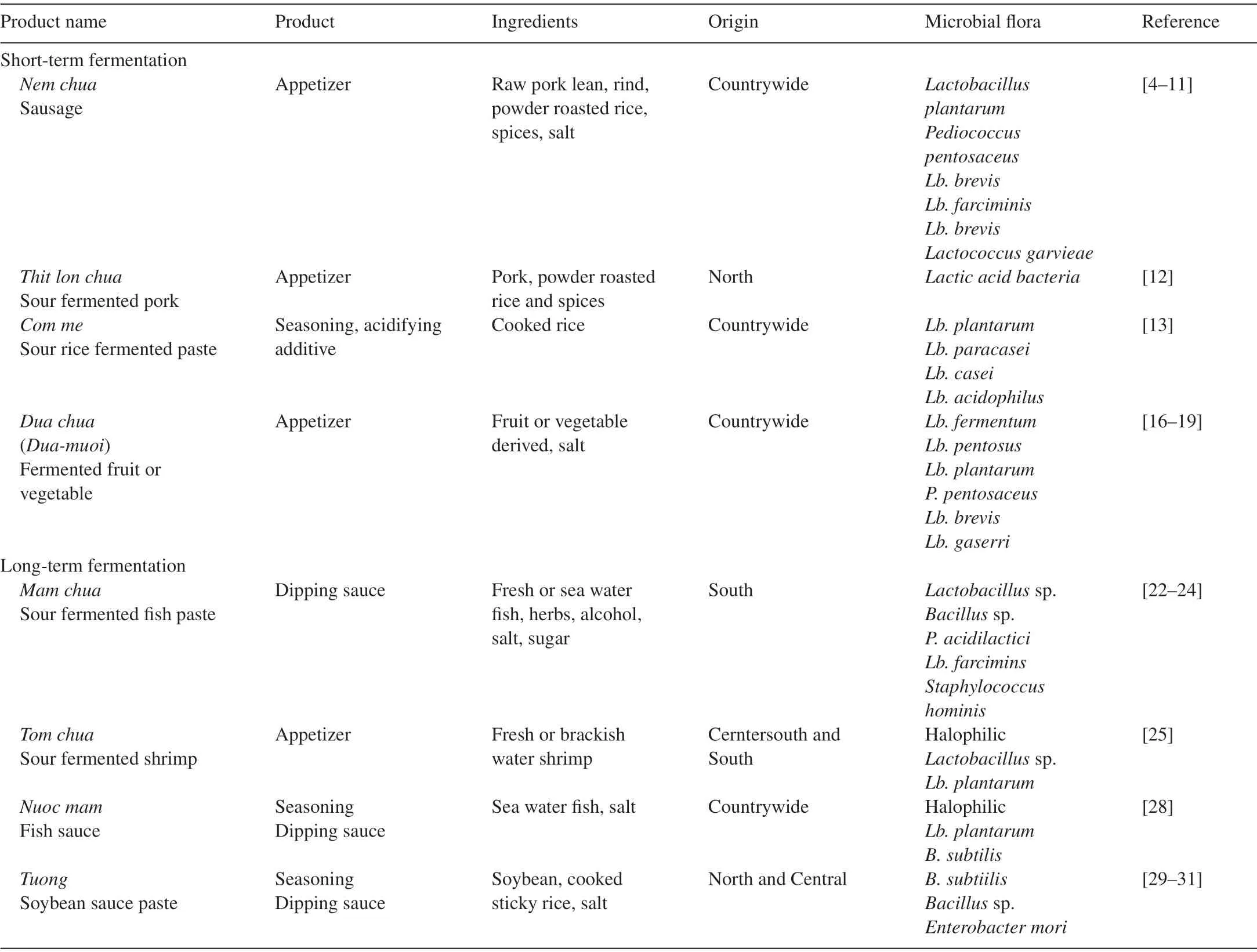
Table 1 Representative traditional fermented foods in Vietnam.
2.1.1.Nem chua
Nem chuais a fermented sausage product that is relatively well studied[4–6].Preparation ofNem chuais common in different parts of the country(Fig.1).The main ingredients ofNem chuainclude finely ground pork lean(95%protein),boiled and sliced pork rind (5% protein),powdered and roasted rice,salt(approximately 2%,w/w),and spices(pepper and garlic).Nem chuais prepared as follows:the ingredients are mixed according to the recipe and the mixture is then shaped into small cubes or cylinders,covered with some herbs such as pieces of guava or Ming aralias leaves and pieces of garlic or chilies(depending on local areas),wrapped in banana leaves by folding the two ends of the rolls tightly,and covered with a larger piece of banana leaf.This careful wrapping prevents air penetration into the mixture,thus creating a relatively anaerobic environment that favors the growth of LAB and makes the product sour and ripened after 1–2 days depending on the ambient temperature (20–37°C).Powdered and roasted rice used in the traditional method used of preparingNem chuaacts as a carbohydrate source for the growth of indigenous LAB and contributes to the sour taste.Manufacturers sometimes use a piece of fermentedNem chuaof a previous batch as a starter culture for producing a new batch.

Fig.1.Flow chart for preparing Nem chua.
The cell density of LAB is (9±1.3) (lg (CFU/g)) by the end of fermentation,which is quite high and lowers the pH of the final product to 4.64–4.77,which was required to keep the product at the acceptable microbiological safety [5].Microbiological analysis of 60 samples ofNem chuaobtained from different provinces across the country(Hanoi,Thanh Hoa,Hue,and Ho Chi Minh City) and prepared during different seasons (from March 2008 to May 2010) showed that LAB accounted for 80%–100% of the total aerobic bacteria count(TABC)in the samples.The dominant naturally occurring LAB species inNem chuaareLactobacillus plantarum(67.6%),Pediococcus pentosaceus(21.6%),Lactobacillus brevis(9.5%),andLactobacillus farciminis(1.3%)[6].A recent study analyzing the diversity of native LABstrains in 10 samples ofNem chuafrom Hanoi using (GTG)(5)-polymerase chain reaction (PCR)fingerprinting and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) showed high levels ofLb.farciminis(32.8%),Lb.plantarum(26.1%),Leuconostoc citreum(12.6%),Lactobacillus pentosus(8.4%),Lb.brevis(5.0%),P.pentosaceus(3.4%),andPediococcus acidilactici(2.5%)and low levels ofLeuconostoc fallax;Pediococcus stilesii;Weissella cibaria; and other species such asWeissella paramesenteroides,Lactobacillus rossiae,Lactobacillus paracasei,Lactobacillus acidipiscis,andLactococcus lactis(having less than 1%prevalence)[7].
Lb.plantarum,which is the most prevalent strain inNem chua,is used as a starter culture because of its acidic,sensorial[4–6,8],and biopreservative properties (associated with bacteriocin production)[8–10].Nem chuaobtained from the central Hue province had other bacteria such asBacillus amyloliquefaciensN1 that produces high levels of extracellular protease,which promotes the maturation ofNem chuaand provides it with a specific texture[11].
2.1.2.Thit lon chua
Thit lon chuais sour fermented pork,which is a traditional fermented food from the Phu Tho province in northwest Vietnam.For producingThit lon chua,pork is first grilled on charcoal;thinly sliced;mixed with roasted rice powder(20%),salt(approximately 1.5%),sugar(1%–3%),and spices;and fermented at an ambient temperature of approximately 30°C for 3–5 days.The final product has a specific flavor(sour and light sweet taste) and is yellow–brown in color and may be served with fig or guava leaves.The final product has a moisture content of 64%,protein content of 17%,lipid content of 11%,pH of approximately 5.0,and LAB density of 8.3(lg(CFU/g)).After storing for 4 days in refrigerator,the pH of the product decreases to 4.7 and LAB density is maintained at the same level.A study successfully usedLb.plantarumH1.40 isolated fromNem chuafor fermentingThit lon chua[12].
2.1.3.Com me
Com meis sour fermented paste made from overcooked wet rice fermented in clean and tightly closed containers for 7–10 days.Sometimes,the fermented product from a previous batch is added to the present batch to expedite the souring process.During fermentation,rice changes from the whole grain state to a macerated product and finally to a milky cream substance with a light sour aroma.After fermentation,the product is crushed and sieved.Com meis used as a souring agent during cooking and renders a meal a specific flavor and sour taste.Com mehas a pH of 2.9–3.5,moisture content of 71%–85%,total protein content of 0.27%–0.49%,carbohydrate content of 2.9%–5.8%,and fat content of 0.53%–2.6% depending on the rice variety used.Isolation of LAB from 28 samples ofCom mefrom six provinces along the Mekong river delta(South Vietnam)showed the presence ofLb.plantarum,Lb.paracasei,Lb.casei,andLb.acidophilus[13].
2.1.4.Dua chua
Dua chua(orDua muoi) is a common name for sour fermented fruit-or vegetable-derived foods.The traditional method for fruit/vegetable fermentation is simple and includes the following steps: vegetables are cleaned and dried (sometimes parched) and soaked in brine (2%–7% salt with some up to 3% sugar) for fermentation for 1–3 days in tight containers to achieve optimum acidity depending on the product type.Besides common vegetables that are used in many other countries,such as cabbage,cucumber,mustard greens (Brassica juncea),garlic,onion bulbs,Chinese scallion,andAllium chinense,people in Vietnam also ferment fruits and vegetables such as lotus root,eggplant,jackfruit,bamboo shoot,and raw mango.Fermented lotus root contains high vitamin C content in the range of 100–150 mg in 100 g product[14].Raw mangoes are fermented for 20 days by blanching in 0.5%CaCl2solution at 75°C for 90 s before soaking in a solution (1:1,w/v) containing 3% salt and 1.5%sucrose.After 4 days of fermentation,LAB concentration reaches approximately 1.75×107CFU/mL,with an acidity of 1.59%,which is equivalent to that of lactic acid[15].
Several studies have assessed the microbial biodiversity of fermented fruits and vegetables.The diversity of native LAB populations inDua muoi(fermented mustard and beet)andCa muoi(fermented eggplant) was investigated using recently validated techniques such as MALDI-TOF MS and phenylalanyl-tRNA synthase (pheS) sequence analysis.In all,881 LAB isolates were recovered from 21 samples and were identified asLb.fermentum(56.6%),Lb.pentosus(24.4%),andLb.plantarum(17.1%).Less abundant species includedP.pentosaceus(1.0%)andLb.brevis(0.5%).Species having less than 0.1%concentration includedLb.paracasei,Lb.pantheris,andP.acidilactici.Fermented mustard and beet preparation had the highest prevalence ofLb.fermentum,and fermented eggplant preparation had the highest prevalence ofLb.pentosus.In addition,genetic variability and strain dependency correlated with the type of fermented vegetable or the location of production was observed among the different predominant species.P.pentosaceuswas isolated only from fermented vegetable samples obtained from Hanoi,andLb.brevis,Lb.paracasei,Lb.pantheris,andP.acidilacticiwere isolated only from fermented vegetable preparation made in a particular household.Further,no members of the genusLeuconostocwere isolated[16].
Lb.fermentumHA6 isolated from fermented eggplant [17]andLb.gaserriHA4 isolated from fermented radish leaves[18]are important for their bioactive properties.A study addedLb.plantarumA17 as a starter culture(inoculum size,107CFU/mL)into a soaking solution of 6%salt and 2%sugar for mustard leaf fermentation and showed that this decreased the pH to lower than 4.5 and suppressedEscherichia coliinfection,thus producing a safe product[19].
2.1.5.Mam chua
Mam chuais a common name for sour fermented fish paste.Mam chuais made from different fish varieties using different methods.Chau Doc ward in southwest An Giang province(Mekong river delta)is well known forMam chuaproduction,with approximately 30 varieties being produced in this region.Of these,Mam ca locandMam chua ca sacare the most popular varieties.
Mam ca locis a sour fermented paste made from snakehead filet fishChanna maculata.It is prepared as follows:fish is mixed with salt(up to 20%,w/w)and powdered roasted rice(10%,w/w)and fermented for a long time.Finally,the product is seasoned by adding sugar.The final product is served as a side dish or used as an ingredient for preparing other meals[20].
Prolonging the fermentation period to approximately 60 days is the most important step.The level of protease in the supernatant increases slowly during the first 10 days,increases rapidly from 18 to 45 days,and decreases from 45 to 60 days.However,soluble protein content is not changed during this period[21].The content of organic acids increases from the day 1 to day 33–36.Further,the TABC in the supernatant increases slowly in the first 15 days and then rapidly from 15 to 30 days.In the macerated fish mass,TABC increases steadily from day 30 to day 45 and decreases slowly subsequently.A study isolated five halophytic bacterial strains fromMam ca locthat could withstand 17% salinity and produced protease.Of these,one strain belonged toLactobacillussp.and two strains belonged toBacillussp.,which showed high protease activity(1.18 tyrosine unit/mL)[22].
Mam chua ca sacis a sour fermented paste made from soft bone gourami fish(Trichogaster trichopterusandT.microlepis).It is prepared as follows:the fish is rinsed and its head and intestinal organs are removed but the fins are retained.The organs are soaked in water for 16 h,cleaned,drained,and parched for 6 h and are then mixed with sugar,anhydrous salt (approximately 10%),roasted rice powder,chili,garlic,and 5%vodka-like rice alcohol drink(v/w).The organs are then stored in covered jars for fermentation at 28–30°C for 20–30 days.The fish shape is retained but the skeleton becomes soft,thus making the product boneless.The final product has a sweet,sour,and salty flavor and is served directly as a side dish[23].A microbiological study reported that before fermentation,naturally occurring LAB strains(cell density,106–107CFU/g)were detected in theMam chua ca sacmixture.After fermentation,their density increased to 2.61×108to 1.14×109CFU/g.Some bacteria isolated fromMam chua ca sac,such asP.acidilacticiL1,Lb.farciminisL2 and L3,Staphylococcus hominisL4,produced amylases but only two strains,namely,P.acidilacticiL1 andLb.farciminisL2,produced proteases[24].
2.1.6.Tom chua
Tom chuais a sour fermented shrimp paste,which is a specialty of the central Hue province but is favored by consumers across the country.It is prepared as follows:shrimps are cleaned and their heads are removed.The shrimps are then mixed with steamed glutinous rice(50%–75%,w/w),salt(7.5%–12%,w/w),and spices(galingale,garlic,and chili)and are fermented.For large-scale production ofTom chua,the mixture of herbs and spices is fermented separately for 3–5 days before being added to the mixture of shrimp and steamed rice,which is fermented separately for 5–7 days.The raw product is fermented for 20–30 days at an ambient temperature of 30–35°C(Fig.2).Naturally occurring LAB ferment carbohydrate from steamed glutinous rice to produce lactic acid,rendering the product a smooth sour taste.During fermentation,proteins from raw shrimp are partially hydrolyzed,which allow easy digestion.Recently,researchers usedLb.plantarumstrains,which are halophilic and resistant to antimicrobial compounds in the spice extract,isolated from a previous batch ofTom chuaas a starter culture for large-scale fermentation.Compared to the traditional product,the product produced using the new method has higher microbiological safety and similar flavor[25].
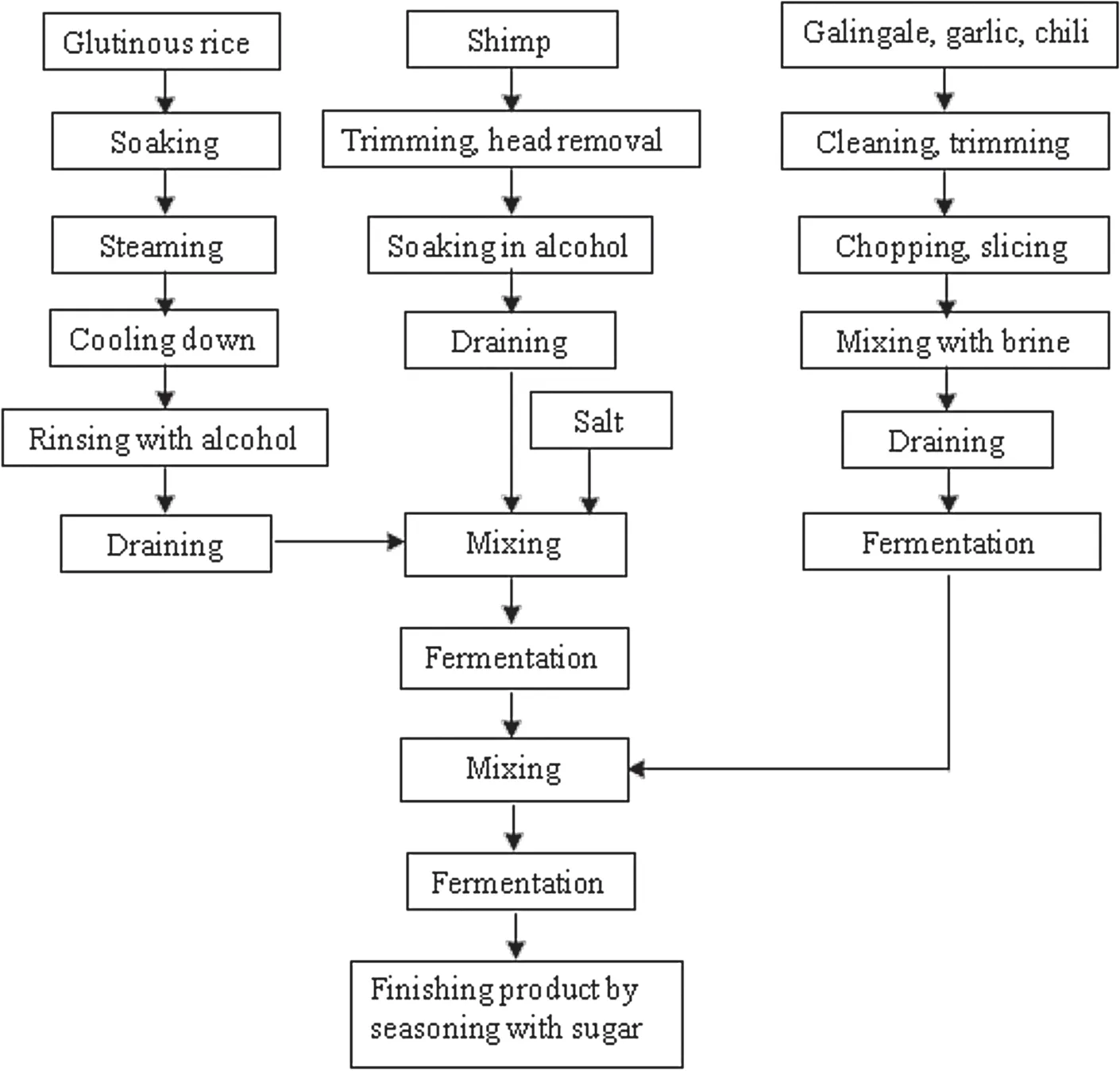
Fig.2.Flow chart for preparing Tom chua.
2.1.7.Nuoc mam
Nuoc mam(fish sauce) is one of few traditional products manufactured at a large-scale throughout the country,with an output of approximately 220 million l/year[26].The process for producingNuoc mamis presented in Fig.3 and includes the following steps:fish and salt are mixed at a ratio of 25%–33%(w/w)in a vessel made of wood,ceramic,or cement depending on the local custom.After maturation,extract is drained from the ripened fish mass,pomaced several times,and filtered to obtain a transparent liquid (the fish sauce).The extracts are mixed to obtain different grades of the product [27].The traditional method involves fermentation for 12–18 months.Nowadays,fermentation time is shortened to 6 months by addition of enzymes from external sources.Anchovy is the most commonly used fish for makingNuoc mam.Temperature for fermentation and hydrolysis is in the range of 35–50°C.Several microbial strains belonging to generaMicrococcus,Staphylococcus,andStreptococcus,andLactobacillushave been isolated fromNuoc mam.Nguyen et al.isolated halophilicLb.plantarumandB.subtilisthat not only produced protease but also produced volatile compounds such as butanoic acid 2-methyl and 1,3-propanediol that provided a typical flavor toNuoc mam[28].
2.1.8.Tuong
Tuong(soybean sauce paste) is a typical and popular traditional fermented food.The main raw materials for makingTuongare soybean (30%,w/v),glutinous rice (10%,w/v),salt (10%,w/v),and water.The production of soybean sauce is described in Fig.4.Briefly,steamed rice is incubated with a starter culture predominantly containingAspergillus oryzaeat approximately 30°C for 4–5 days.This serves as a multi-enzymatic matter,which hydrolyses ground,roasted soybean during the main fermentation and post-fermentation process.
Some studies have isolated bacteria duringTuongfermentation in addition to fungi.One of the most popularTuongisTuong ban(so called because of its production in the Ban-Yen-Nhan ward in north Hung Yen province).Bacterial count of someTuong bansamples was examined during soaking and after the fermentation.The TABC during the soaking stage increased gradually and reached 106CFU/mL.The frequency of proteaseproducing bacteria also increased from 18% to 20% in the beginning to 50%by the end of this stage.After the fermentation,only salt-tolerant strains survived,which decreased the TABC to 105CFU/mL.However,the frequency of protease-producing bacteria accounted for 98–100%of the TABC,and these bacteria belonged toBacillussp.Further 98% bacterial isolates detected after the fermentation had fibrinolytic activity [29].Compared with otherB.subtilisvar.natto strains which produced 1400–1800 fibrinolytic units(FU)/g,isolated from Natto Japan and Natto Taiwan,Bacillusstrains isolated fromTuongobtained from the Hung Yen province produced 540–1200 FU/g of dry soybean [30].Tuongfrom northern,central,and southern regions of Vietnam were also analyzed for bacteria having fibrinolytic activity.Six samples from these regions showed fibrinolytic activity ranging from 10.8 to 73.8 FU/g.Of these,the sample obtained from central Nghe An province showed the highest fibrinolytic activity of 73.8 FU/g.Bacterial strain isolated from this sample was identified asEnterobacter mori,which produced 1.14–1.49 FU/mL in the culture supernatant when grown in a medium containing shrimp shell powder,K2HPO4,and MgSO4·7H2O at 37°C for 24 h[31].
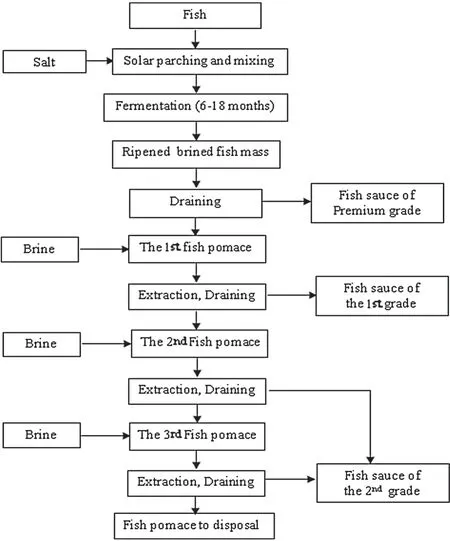
Fig.3.Flow chart for producing Nuoc mam.
Some other traditional fermented foods,namely,Mam Tom(salty shrimp paste),Com ruou(residue of fermented rice wort after alcohol distillation),Chao(tofu fermented using fungiActinomucor elegansandMucorsp.),and seasoned soybean sauce produced by fermentation withAspergillussp.are also popular.However,reports on these foods are scarce even though they are described in textbooks[32].
2.2.Traditional Vietnamese fermented foods as a source of health-promoting microbes
Traditional fermented foods are an important source of local microbes with important properties.In recent years,LAB present in sour fermented foods have been studied largely for their technological,sensorial[5,6],and biopreservative properties for food processing[8,10].Data are available on the health benefits of probiotic bacteria in animal feed;however,data on the health benefits of probiotic bacteria in humans are scarce in Vietnam.Probiotics are living microorganisms that are consumed as food or food supplements in sufficient quantities and that colonize a compartment of the host to exert health benefits [33].Criteria for the use of microbes as probiotics include the ability to tolerate the conditions in the gastrointestinal tract,adhere to the intestinal mucus,inhibit pathogenic microorganisms,and exert probiotic and other health-promoting effects[34].
Fig.4.Flow chart for producing Tuong.
2.2.1.Acid and bile stability
Survival in the human gastrointestinal tract is essential for any microorganism to be used as a probiotic.Acid tolerance is important for any microorganism that is selected for functioning in the gastrointestinal tract.Excretion of HCl in the stomach creates a low pH environment (pH ranging from as low as 0.9 to approximately 3.0) [35].A surveillance study reported the survival of LAB strains of Vietnamese origins isolated from traditional fermented foods,local yogurt products,and human products(breast milk and infant feces)in simulated gastric and small intestinal juices[36].In this study,0.2 mol/L glycine–HCl buffer(pH 2)was used for preparing simulated gastric juice to prevent the increase in pH after the addition of microbial suspensions.The time of exposure to gastric stress(0.3 g/L pepsin at pH 2.0)was 120 min and that for exposure to intestinal stress(0.1 g/L pancreatin and 0.3 g/L bile salts at pH 8.0)was 240 min at 37°Cin vitro.The gastrointestinal stress conditions allowed observation of the difference in viability of a number of strains;however,these conditions were harsher than those used in other studies.
Table 2 compares 181 LAB strains with respect to their survival ability.Of these,132 strains were isolated from traditional Vietnamese fermented foods,26 were isolated from local yogurt preparations,and 23 were isolated from breast milk and infant feces.The strains were grouped according to their survival rate.The remarkably stable strains were those that survived both artificial gastric and intestinal juices,with a decimal logarithmic decrease in viable cells from 0 to 3(lg(CFU/mL)).
Results presented in Table 2 indicate that 75 (41.4%)LAB strains were resistant to gastric stress,with less than 3(lg(CFU/mL))decrease in viable cells.Of these 75 strains,40,14,and 21 were isolated from traditional Vietnamese fermented foods,local yogurt products,and breast milk and infant feces,respectively.Further,50(27.6%)LAB strains were resistant to intestinal stress.Of these,30,7,and 13 were isolated from traditional Vietnamese fermented foods,local yogurt products,and breast milk and infant feces,respectively.Detailed characteristics of six potential probiotic strains isolated from Vietnamese traditional fermented foods were determined in this study.All these six strains survived the gastric and small intestinal stresses.Lb.plantarumNCDC3 isolated fromNem chuaobtained from Hanoi showed 1.32 and 0.36(lg(CFU/mL))decrease in viable cells andLb.brevisNCTH24 isolated fromNem chuaobtained from Thanh Hoa province showed 2.67 and 0.56(lg(CFU/mL))decrease in viable cells (Table 4).LAB strains isolated from traditional Vietnamese fermented foods tolerated gastrointestinal stress similar to other strains isolated from fermented milk or human products.However,isolation of 132 strains out of the total 181 LAB strains from traditional fermented foods indicates that these foods should be considered as accessible reservoirs of potential probiotics.
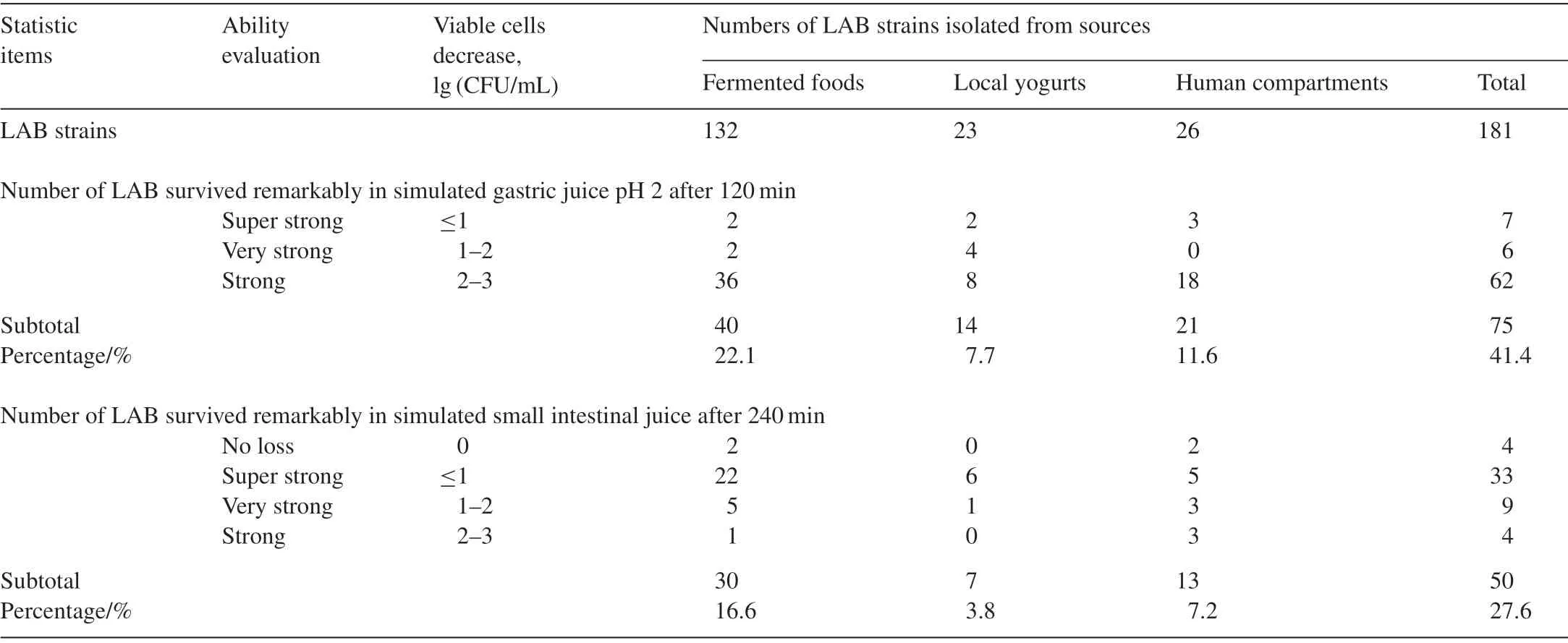
Table 2 In vitro stability of LAB strains of Vietnamese origin in acid and bile preparations.
Research on the ability of LAB to survive in simulated gut conditionsin vitrohas been reported in several other studies.Lb.fermentumHA6 showed no loss of viability when grown in simulated gastric juice at pH 3.0,slightly reduced viability to approximately 90% when grown at pH 2.5,and loss of viability when grown at pH 2.0; however,this strain showed nearly 80% viability when grown in small intestinal juice [17].Cell suspension ofca.108CFU/mL ofLb.gasseriHA4 retained atca.4(lg(CFU/mL)) in gastric juice at pH 2.0 and nearly 6(lg(CFU/mL))in small intestinal juice[18].
Although stability in acid and bile is an important factor,microorganisms having intermediate viability may still have impressive probiotic effects based on their other healthpromoting properties.
2.2.2.Intestinal adhesion
After transition through the stomach and the small intestine,probiotic bacteria adhere to the intestinal mucosa and colonize the intestinal tract,thus creating a gut barrier for performing their function,which is consistent with the probiotic selection criteria such as competitive exclusion,immunogenic effects,and other health effects.Intestinal adhesion is a prerequisite for colonization and thus an important criterion for probiotic evaluation.Suitable models for examining intestinal adhesion are based on monitoring adhesion to intestinal cell lines Caco-2 and HT-29 or binding to intestinal mucus preparations[37].
Lb.fermentumHA6 isolated fromDua muoi(fermented eggplants)adhered to the surface of human Caco-2 cells(Fig.5A)[17].Lb.gasseriHA4 also actively adhered to human Caco-2 cells but to a lower extent [18].Another study examining mucus adherence of probiotic strainsin vitrodetermined 20 potential probiotic strains with the highest ability to adhere to mucus-coated polystyrene surface of microtiter plates at a density of 107–108CFU/cm2.Of these,nine strains were isolated from traditional fermented foods,six from fermented milk,and five from breast milk and infant feces.The strains isolated from fermented foods belonged toLb.casei,Lb.fermentum,Lb.plantarum,andLb.brevis.A representative scanning electron microscopic image ofLb.brevisNCTH24 adhering to the mucus-coated polystyrene slide is shown in Fig.5B[36].
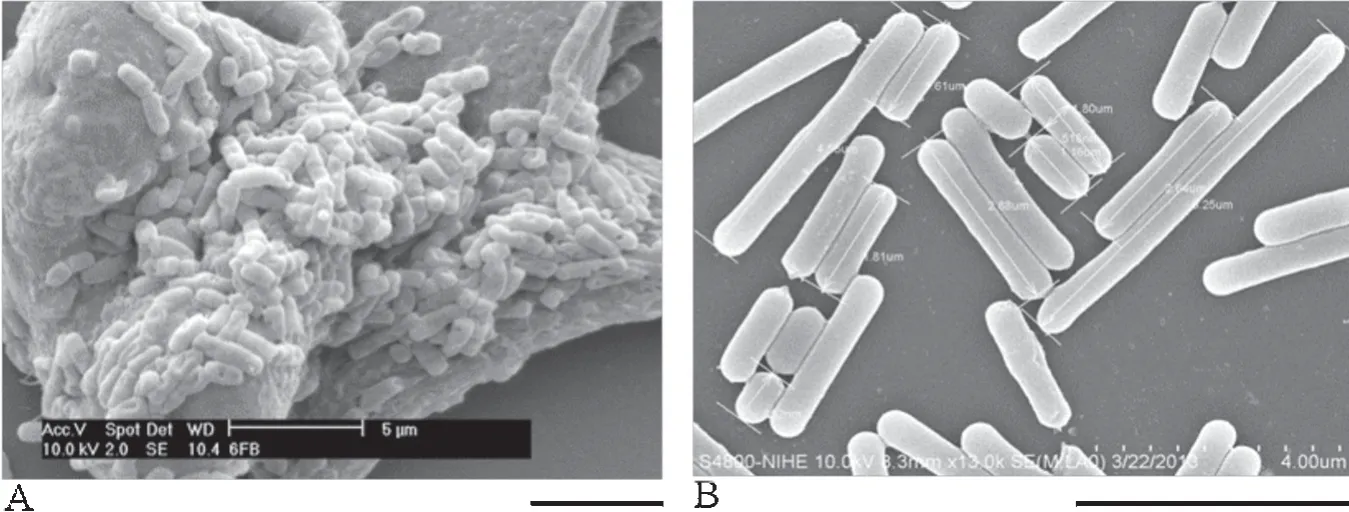
Fig.5.Monitoring of adhesion ability.(A)Lb.fermentum HA6 adhered to Caco-2 cells;scale bar=5 μm.Adapted from Ho and Adams[17].(B)Lb.brevis NCTH24 adhered to mucus-coated polystyrene slide;scale bar=4 μm.Adapted from Nguyen[36].
This study indicated that LAB isolated from fermented foods showed intestinal adhesion similar to strains isolated from human and dairy products,which are classically considered as probiotic sources for human use.
2.2.3.Antagonistic properties of pathogenic microbes
Probiotic microorganisms influence the composition of the gut microflora.They colonize the intestinal tract and exhibit protective properties by exerting antipathogenic effects based on competitive exclusion(for substrates and places of adhesion)and by inhibiting fermentation metabolites (organic acids and other antimicrobial compounds).They beneficially affect the host’s physiology and health by improving microbial balance in the intestinal tract.
Strong competitive exclusion of LAB toward pathogenic microbes has been observed in some studies [36].Four pathogenic bacteria,namely,B.cereusCNTP6089,Staphylococcus aureusCNTP6083,E.coliCNTP6078,andSalmonella entericasubsp.entericaATCC14028,were spread on DeMan,Rogosa,and Sharpe (MRS) agar in Petri dishes along with LAB strains.The dishes were incubated at 30°C for 3 days.Results showed that out of the 47 LAB strains,23 (48.9%) could exclude all the four pathogenic strains.Among these strains,12/20 (60.0%) were isolated from traditional Vietnamese fermented foods,4/10 (40.0%)were isolated from local yogurt products,and 7/17 (41.1%)were isolated from human products (Table 3 and Fig.6).The inhibitory effect of LAB strains may result from a combination of competition for metabolic substrates,growth suppression by organic acids,and bacteriocin secretion.
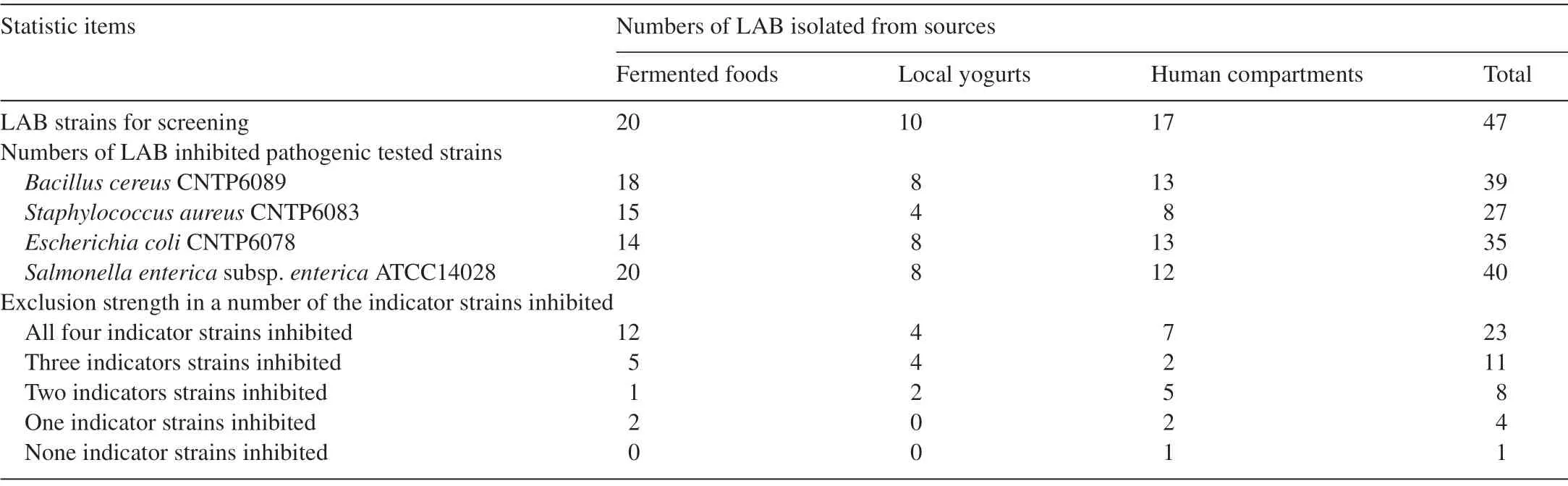
Table 3 Inhibitory effects of LAB strains isolated from Vietnamese fermented foods against four pathogenic strains.
Bacteriocin produced by some LAB strains inhibits closely related gram-positive bacteria.Several microbial strains producing bacteriocin have been isolated from traditional Vietnamese fermented foods such asNem chua.A study isolated bacteriocinproducingLb.plantarumNV23 fromNem chuaobtained from the Can Tho province located south of Mekong River delta[9].Bacteriocin produced byLb.plantarumNCDN4 isolated fromNem chuaobtained from the central costal Da Nang province was purified and characterized as a peptide of relatively large molecular weight between 14.3 and 20.1 kDa and belonged to bacteriocin class II[8].Lactococcus garvieae0-5 isolated fromNem chuaobtained from the northern province of Thanh Hoa produced class I bacteriocin having a MW of 2.5 kDa[10].
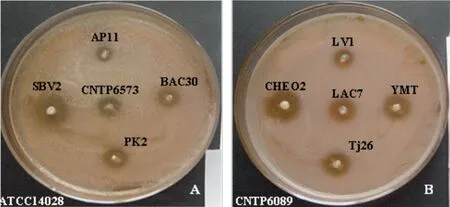
Fig.6.Inhibition potential of some probiotic LAB strains against pathogenic indicator strains.(A) Salmonella enterica subsp.enterica ATCC14028 and (B) B.cereus CNTP6089.
In another study,the potential probiotic strainLb.gasseriHA4 isolated fromDua chuashowed a broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against seven indicator bacterial strains,namely,Listeria monocytogenesATCC 7644,Pseudomonas aeruginosaATCC 27853,Yersinia enterocoliticaATCC 9650,E.coliO157:H7 VT-N NCTC 12900,S.aureusACM 4988,Salmonella typhimuriumATCC 14028,andEnterococci306 R.This was largely because of the acidity and the associated low pH,except forL.monocytogenesATCC 7644,which was inhibited because of a proteinaceous antibacterial compound that likely belonged to bacteriocin class IIa[18].
Antilisterial activity of LAB through competitive adhesion was also investigated.Lb.gasseriHA4 competitively decreased the adhesion of this food-borne pathogen to Caco-2 cells by more than 1(lg(CFU/mL)),with no significant difference inL.monocytogenescount whenLb.gasseriHA4 was added before,after,or at the same time withL.monocytogenes.In addition,active adhesion ofLb.gasseriHA4 to human epithelial cells suggested that this strain may inhibit pathogenic adhesion[18].
Antifungal activity of LAB was described based on several mechanisms such as synergistic activity of organic acids and pH [38] or pH-dependent antifungal proteins [39].Recently,a new antifungal compound 3,6-bis(2-methylpropyl)-2,5-piperazinedione(molecular mass,226 kDa)produced byLb.plantarumisolated from kimchi was identified [40].Several studies have reported the broad-spectrum antifungal activity of LAB strains isolated from Vietnamese fermented foods[17,18,41].Among 11 LAB strains tested,8 strains,including 5Lb.plantarumstrains HA2,HA3,HA5,HA8,and HA9 and 3Lb.fermentumstrains HA6,HA7,and HA10,showed a strong and broad inhibitory spectrum activity against 7 out of 11 indicator mold and yeast strains(Aspergillus terreus,A.fumigatus,A.niger,Absidia corymbifera,Paecilomyces lilacinus,Geotrichum candidum,Fusariumsp.,Scopulariopsis brevicaulis,Curvularia lunata,Penicilliumsp.,andCandida albicans) isolated from foods.Lb.fermentumHA7 showed the highest activity,with the inhibition of all the tested fungi and yeast to some extent.The fungusG.candidumwas the most resistant among the tested fungi and yeast and was inhibited by only strain HA7.A.nigerwas strongly inhibited by only two strains,namely,Lb.plantarumHA3 and HA9.S.brevicaulisandC.albicanswere the most sensitive test organisms because they were inhibited by all the 11 LAB strains[41].C.albicansis an opportunistic yeast causing dermatological diseases.Therefore,the potential of probiotic bacteria to inhibit the growth of fungi and yeast can not only improve the shelf life of food products but also help prevent candidosis.
Moreover,minor ingredients in herbs and spices (e.g.,garlic and ginger) used in preparing traditional fermented foods have antimicrobial activities against pathogenic microbes without any effect on LAB[25].Thus,the antipathogenic activity of traditional naturally fermented foods may result from a synergistic effect of fermented food-derived probiotic LAB and herbs and spices.
2.2.4.Antibiotic susceptibility
Bacteria show susceptibility,intermediate susceptibility,and resistance to different antibiotics.Bacteria show three types of resistance:natural(intrinsic or innate),acquired,and mutational.LAB strains are intrinsically resistant to many antibiotics.No particular safety concern is associated with LAB showing intrinsic resistance.Plasmid-associated antibiotic resistance,which occurs occasionally,may spread to other more harmful species and genera[42].
A survey of 44 potential probiotic LAB strains was performed to determine their antibiotic susceptibility[36].Of these,19 strains were isolated from traditionally fermented foods,15 were isolated from breast milk and infant feces,and 10 were isolated from local yogurt products.These strains were screened for resistance to 12 antibiotics,namely,cefoperazone,ceftriaxone,ceftazidime,gentamicin,penicillin,ofloxacin,azithromycin,erythromycin,chloramphenicol,streptomycin,polymyxin B,and clindamycin using the routine disk diffusion method.Chloramphenicol was the strongest antibiotic,which inhibited 40 strains,followed by erythromycin,which inhibited 32 strains.Streptomycin was the weakest antibiotic,with 43 tested strains showing resistance to it,followed by gentamicin,penicillin,and polymyxin B,with 42,40,and 37 strains,respectively,showing resistance to these antibiotics.These results showed that all the tested LAB strains were sensitive to at least one antibiotic and maximum to eight antibiotics.Two of the most resistant strains isolated from fermented foods were inhibited by only one antibiotic and one of the most sensitive strains was inhibited by seven antibiotics.Two of the most resistant strains isolated fromhuman products were inhibited by one antibiotic and one of the most sensitive strains was inhibited by eight antibiotics.Two of the most resistant strains isolated from yogurt were inhibited by one antibiotic and one of the most sensitive strains was inhibited by five antibiotics.
A summary of antibiotic susceptibility of the six potential probiotic strains isolated from traditional Vietnamese fermented foods is presented in Table 4.The most resistant strain wasLb.plantarumBAC52 isolated fromNem chuaobtained from the Thanh Hoa province,which was susceptible to chloramphenicol,moderately susceptible to erythromycin,and resistant to the remaining 10 antibiotics.The most susceptible strain wasLb.plantarumLV1 isolated fromCom ruouobtained from Lang-Van village in the Bac Giang province,which was susceptible to chloramphenicol,erythromycin,ceftriaxone,and ceftazidime;moderately susceptible to azithromycin; and resistant to the remaining eight antibiotics[36].
A recent study reported the use of whole genome sequencing for screening acquired antibiotic resistance genes in LAB strains that could be used in human nutrition[43].However,to the best of our knowledge,no study has determined the antibiotic susceptibility of LAB strains isolated from Vietnamese fermented foods using this technique.
2.2.5.Inhibition of human cancer cells in vitro
Indigenous microflora markedly affects the structure of the host intestinal mucus,its function,and the whole development of the immune system.Probiotic LAB strains can eliminate damage to the gut microenvironment,stimulate local and systemic immune responses,and maintain the integrity of the gut wall[44].
Majority ofin vitroandin vivostudies on the anticancer effects of probiotic LAB strains have been performed using colorectal cancer cells.In addition,some studies have investigated the effects of these bacteria on the repression of myeloma cell growth or inhibition of pancreatic,breast,bone,and liver cancer cell proliferation[45].Few studies have focused on the anticancer effects of LAB strains isolated from Vietnamese traditional fermented foods.A potential probiotic strainLb.fermentumHA6 was tested for its survival in simulated gastric and small intestinal juices,adhesion to colon epithelial cells,and ability to promote probiotic functionsin vitro.This strain inhibited the proliferation of four human cancer cell linesin vitro: 90% reduction in the proliferation of melanoma cell line MM200,60%reduction in the proliferation of breast cancer cell line MCF7 and prostate cancer cell line DU145,and 40%reduction in the proliferation of colon cancer cell line HT29.These results indicate the potential of these probiotic strains in preventing cancer[17].
2.2.6.Exorphin digestion
Exorphins are opioid-like and proline-rich peptides formed from partially digested foods that react with opiate receptors in the brain,thus causing digestive and neurological disorders.Because of the unique structure of proline,most microbial enzymes cannot hydrolyze exorphins by cleaving bonds in this amino acid.A recently study showed that some LAB strains produced X-prolyl dipeptidyl aminopeptidase(pepX;EC 3.4.14.5)that functions as an intracellular dipeptidase and digests dipeptide residues in proteins by hydrolyzing the peptide bond at the carboxyl end of the proline residue.
The pepX activity against exorphins has been mainly detected in dairy bacteria such asLb.caseiand in some casesLb.delbrueckiisubsp.bulgaricus,Lb.acidophilus,Propionibacterium shermanii,Lb.helveticus,andLb.curvatus.Recently,this activity was detected in LAB strains isolated from other fermented foods,such asLb.sakeiisolated from sausage andLb.sanfranciscensisisolated from sourdough[46].
Screening data of 47 LAB strains(19 from traditionally fermented foods,10 from local yogurt products,and 15 from breast milk and infant feces)showed that four strains produced pepX(Table 4).Of these,three strains belonged toLb.plantarumisolated formNem chuaand one strain belonged toLb.caseiisolated from the fecal specimen of a Vietnamese breast-fed infant[36].
Ho et al.screened 11 LAB strains isolated from Vietnamese naturally fermented foods and found that six strains ofLb.fermentum(HA6,HA7,HA10,and HA11),one strain ofLb.gasseri(HA4),and one strain ofLb.acidophilus(HA12)produced intracellular pepX that reduced gluten exorphin,beta-casomorphin,and dermorphin.PepX produced byLb.fermentumHA6 andLb.acidophilusHA12 showed complete digestion of the three peptides.PepX produced byLb.gasseriHA4 andLb.fermentumHA7 and HA11 reduced gluten exorphin and beta-casomorphin but showed less or no reduction of dermorphin.PepX produced byLb.fermentumHA10 changed the ratio of the three peptides in the mixture after digestion[47].
The pepX activity ofLb.fermentumHA6 was investigated in intact cells exposed and not exposed to simulated gastrointestinal juices.In both the conditions,Lb.fermentumHA6 demonstrated pepX activity.However,the activity decreased from 0.5 U/mL to 0.23 U/mL after 3 h of exposure to gastric juice at pH 2.5.Interestingly,pepX activity ofLb.fermentumHA6 exposed to simulated small intestinal juice for 3 h was better than its original activity (1.1 U/mLvs0.5 U/mL,respectively),suggesting that the application ofLb.fermentumHA6 as a probiotic agent could retain its metabolic activity.This may be due to the effects of bile salts in the small intestinal juice that have a detergentlike effect on microorganisms as a part of the gastrointestinal defense mechanism[48].The acid-adapted cells ofLb.fermentumHA6 showed specific pepX activity of 24.5 U/mg when grown in a mild acidic condition in MRS Broth (pH 4.0).The pepX activity of this strain was higher than that of control cells(17.8 U/mg),which were grown normally in batches.Thus,Lb.fermentumHA6 could be used for treating disorders caused by opioid peptides[49].
2.2.7.Production of gamma-aminobutyric acid
Gamma-aminobutyric acid(GABA)is a non-protein amino acid that is a major natural inhibitory neurotransmitter and calming agent.GABA is a bioactive constituent of fruits,vegetables,and cereals and is synthesized by some bacteria,yeast,and fungi.Probiotic LAB strains produce GABA by decarboxylating glutamic acid.These bacteria stabilize the digestive system by synthesizing GABAin situin the intestinal tract[50].
In all,181 LAB strains were screened and compared for their ability to synthesize GABA.Of these,132 strains were isolated from traditional fermented foods,26 were isolated from local yogurt products,and 23 were isolated from breast milk and infant feces.Of the 181 strains,13 (7.2%) produced GABA.Of these 13 strains,five strains were isolated from fermented foods,three strains were isolated from yogurt products,and five strains were isolated from breast milk.Remarkably,three GABA-producing strains were isolated fromNem chua,one was isolated fromDua chua,and one was isolated fromCom ruou.Of these five strains,four belonged toLb.plantarumand one belonged toLb.fermentum[36].Six out of 132 LAB strains isolated from traditional Vietnamese fermented foods(Table 4)were the most appropriate for probiotic use because they could survive in the gastrointestinal tract,with a decrease in the density of viable cells in the range of 0–3(lg(CFU/mL)),mucus adherence of 2.66×107to 1.48×108CFU/cm2,and high ability to compete with and exclude bacterial pathogens.In addition,three strains produced intracellular pepX and four strains produced GABA,indicating that these strains were as useful as the potential probiotic strains isolated from human products or fermented dairy foods,which are considered as the classical sources of probiotic bacteria[36,51].However,the strains isolated from Vietnamese traditional fermented foods were much superior to those isolated from fermented dairy products and human sources because of the availability and accessibility of sampling issue [36].Consumption of milk in Vietnam is only 14.8 l/person/year,which is very less than that in many other countries.Moreover,only 10.8%of this consumption is in the form of fermented dairy products,mainly yogurt[52],indicating that fermented milk products,which are commonly considered as a pertinent source of probiotics,are not available to all Vietnamese people every day.Therefore,Vietnamese people use traditional fermented foods daily,which serve a rich source of beneficial native microbes that exert a range of health-promoting effects.
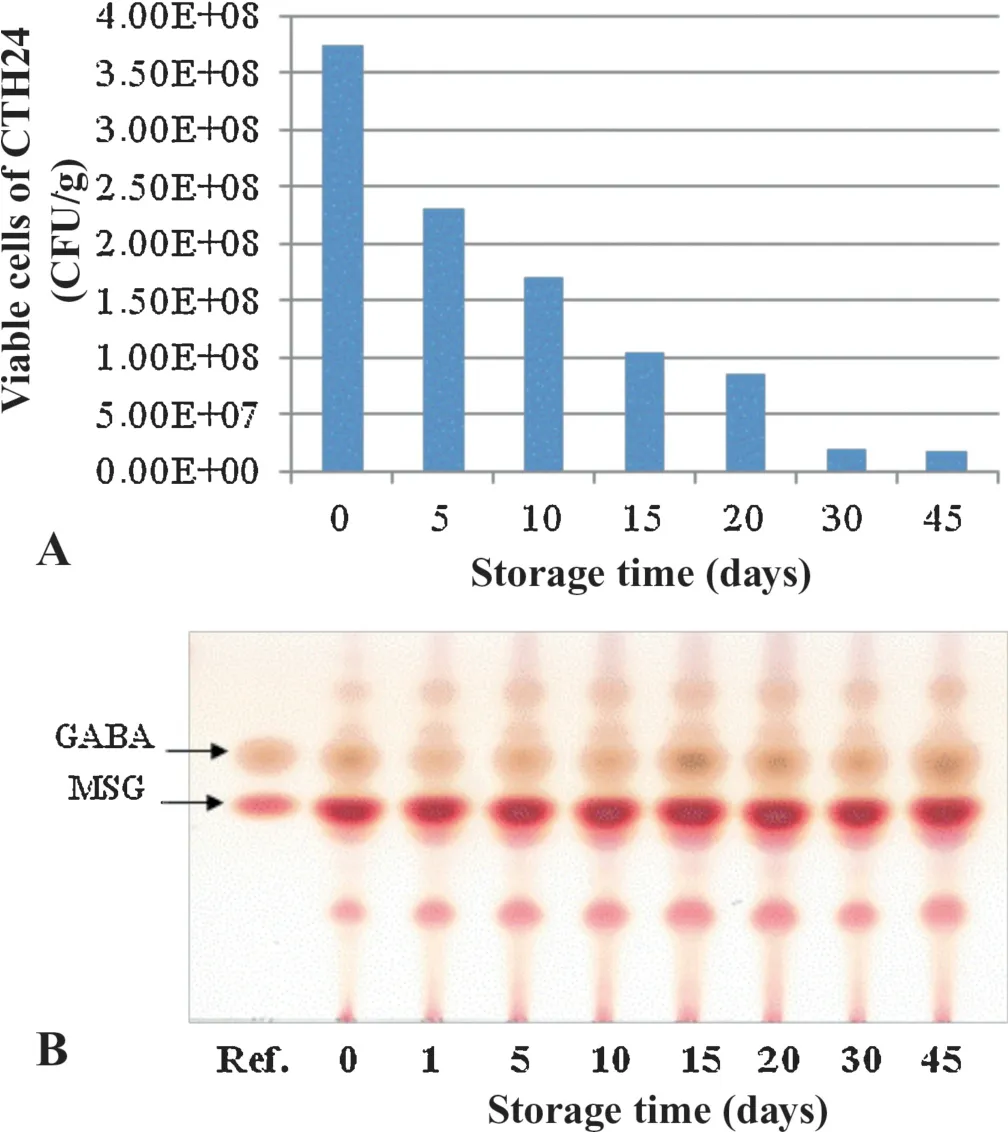
Fig.7.Stability of Lb.brevis NCTH24 in bioyogurt stored at 4°C for 45 days.(A)Time-dependent changes of the viable cell number;(B)GABA production ability:Ref.:Reference sample of GABA and MSG.The numbers on the bottom line correspond to the date of storage of Lb.brevis NCTH24 isolated from the produced bioyogurt.
2.3.Application of LAB isolated from fermented foods as potential probiotics in food processing
Food-based probiotics may have more favorable technological and sensorial properties than those obtained from human products,thus rendering food products as a reliable source of probiotics.Food-based probiotics can control the growth of pathogenic microorganisms without the use of expensive treatments and packaging and provide desirable organoleptic qualities to food.
Therefore,several studies have used the potential probiotic and fermented food-derived LAB strains to improve the quality and assure the safety of processed foods produced using traditional or novel techniques.
Lb.plantarumVKL33 was successfully applied as a starter culture for producingNem chuaandDua chua[6].Some studies have used bacteriocin-producingLb.plantarumNCDN4 forNem chuaandTom chuaproduction [8,53] and the potential probioticLb.plantarumA17 for producing fermented mustard leaves[19].
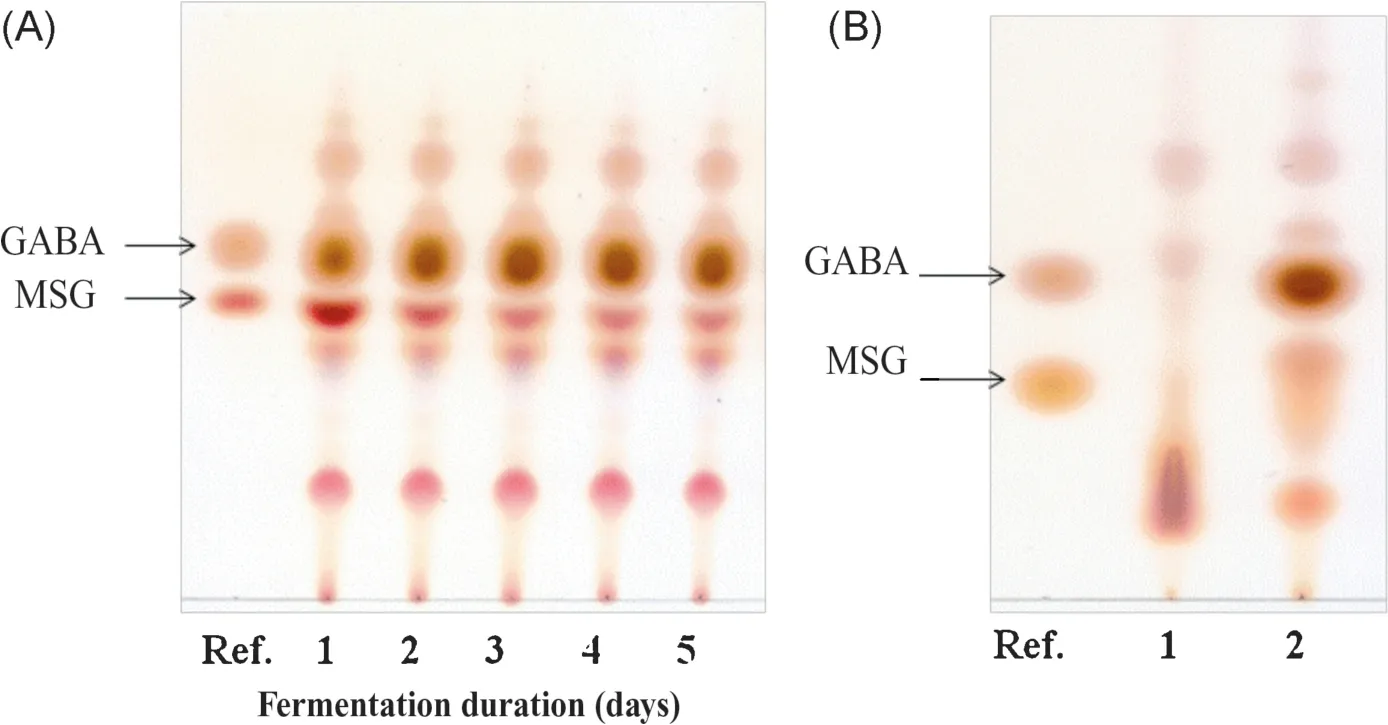
Fig.8.Fermentation of medium partially constituted of rice bran extract and 10 g/L MSG.(A)Changes in MSG and GABA levels during 5-day fermentation.(B)Comparison of the samples: sample 1,rice bran extract without fermentation; sample 2,medium partially constituted of rice bran extract and 10 g/L MSG after fermentation.
Several food-processing techniques have been developed on the concept of probiotic foods,which contain probiotic biomass of at least 106CFU/g during its shelf life,according to the Codex standard for fermented milks(2003).Lb.fermentumHA6 is not affected by less than 1% polyphenol solution that is used for producing probiotic milk containing 0.025% green tea extract(which contains 95% polyphenol).Lb.fermentumHA6 is stable for probiotic use because when the probiotic milk enriched with green tea extract was treated with simulated gastric juice(pH 2.5) and small intestinal fluid,the survival ofLb.fermentumHA6 did not change significantly(95.8%and almost 100%survival in simulated gastric acid juice and small intestinal fluid,respectively)[54].However,addition ofLb.fermentumHA6 at a density of 108CFU/mL to carrot juice changed its organoleptic properties,indicating that it does not have suitable sensory requirements[55].Nguyen et al.appliedLb.acidophilustoCentellajuice at a density of 107CFU/mL(pH 4.93)and observed that the number of viable cells remained at 106CFU/mL and the pH decreased to 4.53 after 35 days[56].
Soy yogurt was prepared usingLb.fermentumDC5,Lb.plantarumN5,andP.acidilacticiTC2 isolated from traditionally fermented foods obtained from the central Hue province as a seed culture(106CFU/mL)for fermentation at 43°C after 9 h.The resultant product was firm,smooth,and homogenous(structure),with good gel structure and pH ranging from 4.47 to 4.54.Further,0.7–1% coconut extract and 10% sugar was added to the soymilk to increase its sensory qualities[57].
The potential probiotic strainLb.brevisNCTH24 isolated fromNem chuathat produced GABA was used for bioyogurt production.The process involved the following steps:milk was fermented with a commercial starter culture and then added withLb.brevisNCTH24 to achieve a cell density of 3.75×108CFU/g in the final product.After 45 days of storage at 4°C,the organoleptic properties of the obtained yogurt remained unchanged.The yogurt had smooth structure,a balance of sweet and sour taste,and pleasant flavor.The cell density ofLb.brevisNCTH24 in the final product was 1.75×107CFU/mL,and these cells could produce GABA when grown in the MRS medium supplemented with 10 g/L monosodium glutamate(MSG;Fig.7)[58].
Another study used the potential probiotic strainLb.plantarumNCDC3 isolated fromNem chuaobtained from Hanoi for fermenting a medium partially constituted with rice bran extract and 10 g/L MSG.The strain showed sufficient GABA production,with 6.49 g/L GABA produced after 3 days,thus indicating a very high biotransformation rate(Fig.8).The fermented suspension may be used directly as a probiotic beverage as well as a semi-final product or an ingredient to be mixed with other raw materials for producing GABA-enriched foods[59].
Application of appropriate and safe microorganisms isolated from Vietnamese traditional fermented foods in food processing depends on LAB strains isolated from these foods and their health benefits.
3.Conclusion
Traditional Vietnamese fermented foods are an abundant source of probiotic and useful microorganisms and constitute an important part of daily nourishment.According to the probiotic selection criteria,microbes isolated from fermented foods may be more efficacious to some extent than those isolated from human or dairy sources.LAB strains play important roles in many traditional fermented foods produced in Vietnam.However,probiotic functions of LAB strains isolated from non-dairy fermented foods in Vietnam have not been investigated intensively.Therefore,more studies should be performed on microbiota isolated from various traditional Vietnamese fermented foods to explore their health benefits.Moreover,these probiotic microbes should be considered for developing innovative foods and food supplements.
- 食品科學(xué)與人類健康(英文)的其它文章
- About the Beijing Academy of Food Sciences
- Functional properties,phenolic constituents and antioxidant potential of industrial apple pomace for utilization as active food ingredient
- Antioxidants,anti-proliferative,anti-inflammatory,anti-diabetic and anti-microbial effects of isolated compounds from Swertia corymbosa(Grieb.)Wight ex C.B.Clark–An in vitro approach
- Methanol extracts of Brachystegia eurycoma and Detarium microcarpum seeds flours inhibit some key enzymes linked to the pathology and complications of type 2 diabetes in vitro
- Chemistry and health beneficial effects of oolong tea and theasinensins
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS

