Prostate chronic inflammation type IV and prostate cancer risk in patients undergoing first biopsy set:Results of a large cohort study
Antonio Benito Porcro*,Giovnni Novell Mtteo BlzrroGuido Mrtignoni,Mtteo Brunelli, Giovnni CccimniMri A.CerrutoWlter Artini
aUrologic Clinic,University Hospital,Ospedale Policlinico,Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata,Verona,Italy
bDepartment of Pathology,University Hospital,Ospedale Policlinico,Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata,Verona,Italy
Prostate chronic inflammation type IV and prostate cancer risk in patients undergoing first biopsy set:Results of a large cohort study
Antonio Benito Porcaroa,*,Giovanni Novellaa, Matteo Balzarroa,Guido Martignonib,Matteo Brunellib, Giovanni Cacciamania,Maria A.Cerrutoa,Walter Artibania
aUrologic Clinic,University Hospital,Ospedale Policlinico,Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata,Verona,Italy
bDepartment of Pathology,University Hospital,Ospedale Policlinico,Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata,Verona,Italy
Prostate;
Prostate cancer;
Prostate specific
antigen;
Prostate biopsy;
Chronic
inflammation;
Prostate volume;
Biopsy Gleason score
Objective:In prostate specimens,chronic inflammatory infiltrate(CII)type IV has been detected,but its association with prostate cancer(PCa)is controversial.The aim of the present study is to investigate on associations of CII with PCa detection in patients undergoing prostate first biopsy set.
Methods:Ultrasound transrectal-guided biopsies by the transperineal approach were retrospectively evaluated in 441 consecutive patients.The study excluded patients who were in active surveillance,prostate specific antigen(PSA)≥30 ng/mL,re-biopsies,incidental PCa after transurethral resection of the prostate(TURP),less than 14 cores or metastatic.Analysis of population and subpopulations(with or without PCa)was performed by statistical methods which included Mann-Whitney(U test),Kruskal-Wallis test,Chi-squared statistic,logistic regression.Multivariate logistic regression models predicting mean probability of PCa detection were established.
Results:PCa detection rate was 46.03%.Age,PSA,prostate volume(PV),prostate intraepithelial neoplasia(PIN)and CII were the significant independent predictors of PCa detection.PV (OR=0.934)and CII(OR=0.192)were both negative independent predictors.CII was a significant negative independent predictor in multivariate logistic regression models predicting the mean probability of PCa detection by age,PSA and PV.The inverse association of CII with PCa does not necessary mean protection because of PSA confounding.
Conclusion:In a population of patients undergoing prostate first biopsy set,CII was a strong negative independent predictor of PCa detection.CII type IV should be considered as an adjunctive parameter in re-biopsy or active surveillance protocols.
?2015 Editorial Office of Asian Journal of Urology.Production and hosting by Elsevier (Singapore)Pte Ltd.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http:// creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
1.Introduction
The concept of zonal anatomy is used to indicate origin and location of growing processes within the prostate[1].The two major diseases affecting the human prostate are benign prostate hyperplasia(BPH)and prostate cancer (PCa),and the former predominantly develops within the transition zone while the latter in the peripheral part of the gland.
The prostate gland may also undergo chronic inflammatory processes.The prostate is considered an immunocompetent organ and its environment is populated by inflammatory cells including T and B lymphocytes,macrophages and mast cells[2,3].The histology of proliferative inflammatory atrophy(PIA),which appears as simple atrophy or postatrophic hyperplasia,includes proliferative glandular epithelium and associates with inflammation[3]. It has been suggested that infiltrates and mediators of chronic inflammation might be involved in PCa carcinogenesis[4-12].Basic science has shown that chronic inflammation plays an important role in human carcinogenesis[2,3];indeed,development and progression of cancer might be related to reactive oxygen and nitrogen species developing in tissue microenvironment after related damage and regeneration[13-21].Experimental and epidemiologic studies show that estrogens might also have an independent role in chronic inflammation and PCa carcinogenesis[22-26].There are studies showing that chronic inflammation is the link between BPH and PCa [27,28].Because of the association of chronic inflammation with oxidative stress which is mediated by the cyclo-oxygenase(COX)gene pathway,it has been proposed that aspirin,which is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, might prevent PCa carcinogenesis by inhibiting COXs [29-31].However,the inflammatory infiltrate includes cells of both the innate(e.g.,monocytes and macrophages) and adaptive(B and T lymphocytes)immune system which is currently used for PCa immunotherapy strategies[5,32].
Clinically,the prostatitis syndromes have been classified in four categories by the National Institutes of Health(NIH) [33].The last category is named type IV and is diagnosed in patients who have no history of genitourinary tract pain complaints,but undergo prostate biopsy for evaluation of possible PCa because of increased serum prostate specific antigen(PSA)level,abnormal digital rectal exam(DRE)or both.The presence of chronic inflammatory infiltrate(CII) has been detected in prostate specimens and might be involved in the growing processes involving both PCa and BPH[34-37].However,the nature of the association of CII with PCa is a matter of controversy and still holds unsettled.
The aim of the present study was to investigate on associations,if any,of CII with PCa detection in a population of patients who were referred to our institution for a first set biopsy because of suspected PCa.
2.Materials and methods
We retrospectively reviewed the records of 1260 patients who underwent transrectal ultrasound biopsy(TRUSB)at our institution from September 2010 to September 2014. Excluding criteria were as follows:(i)prostate re-biopsy, (ii)patients in active surveillance,(iii)PSA≥30 mg/dL,(iv) metastatic patients,(v)number of biopsy cores less than 14,(vi)incidental PCa after transurethral resection of the prostate(TURP)and(vii)painful rectal exam.After excluding criteria,indications of TRUSB included increased serum PSA levels,abnormal DRE with normal PSA,increased PSA and abnormal DRE(DRE+PSA),abnormal ultrasound imaging of the prostate with normal PSA.Abnormal DRE findings were as follows:diffusely hard prostate,discrete firm area,irregular contours or prominent lobe asymmetry. Family history of PCa(Fam PCa)and treatment with inhibitors of the enzyme 5-α reductase(5-ARI)were also investigated.Age(years)and body mass index(BMI,kg/m2) were calculated in each patient.PSA was measured by immuno-radiometric test(normal range:2-4 mg/dL).The volume of the prostate(PV)was measured by TRUS before performing biopsies.PV was determined by using the formula for an ellipsoid when viewed 3-dimensionally and the formula was transformed into volume(mL).The density of PSA(PSAD)was also computed.
In each biopsy core,the dedicated pathologists systematically assessed the following issues:(i)length,(ii) detection and grade of PCa according to the Gleason score system(biopsy Gleason score:BGS),(iii)length of biopsy core involved by PCa,(iv)prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia(PIN),(v)chronic inflammatory infiltrate(CII), (vi)glandular atrophy(GA)and(vii)atypical small acinar cell proliferation(ASAP).Chronic inflammation criteria, which have already been reported[9,10],included inflammatory cell infiltrate composed predominantly of lymphocytes associated with admixed plasma cells showing a periglandular distribution pattern.Sheets of neutrophils around and within the glands as well as aspects granulomatous prostatitis were the histopathology criteria which excluded a diagnosis of CII of the prostate.
According to biopsy outcome,the patient population was clustered in subpopulations with or without PCa. Summary statistics of population and subpopulations(with or without PCa)were calculated,and included means(SD) for continues variables as well as proportions(rates)forcategorical variables.The tests of Mann-Whitney(U test) and Kruskal-Wallis were used to compare continuous variables.The Chi-squared statistic was computed to test categorical variables.Covariates associating with PCa detection were investigated by logistic regression.PCa mean probability logistic regression models were computed after assessing independent predictive variables.All tests were two-sided,with a significance level of 0.05.
3.Results
After excluding criteria,441 patients were available for assessment.Prostate biopsy indications are depicted by Fig.1.As depicted in Fig.1,prostate biopsies were indicated because of increased serum PSA values(73.70%,325/ 441),abnormal DRE with normal PSA values(4.76%,21/ 441),both abnormal DRE and increased PSA(14.97%,66/ 441),abnormal prostate imaging with normal PSA values (6.58%,29/441).
As shown in Table 1,PCa was detected in 203 out of 441 patients(detection rate 46.03%).The PCa subpopulation,when compared to the group without PCa,showed to be significantly older with higher mean values of PSA;however,PV was significantly smaller and the corresponding density higher.When considering the variables relating to histopathology,CII,GA and PIN significantly were associated with PCa;moreover,the association was inverse in the first two(CII and GA)and direct in the latter(PIN).BMI, Fam PCa,5-ARI,abnormal DRE and ASAP did not show any significant association in the detection of PCa.Fig.2 shows the negative association of CII and PCa.
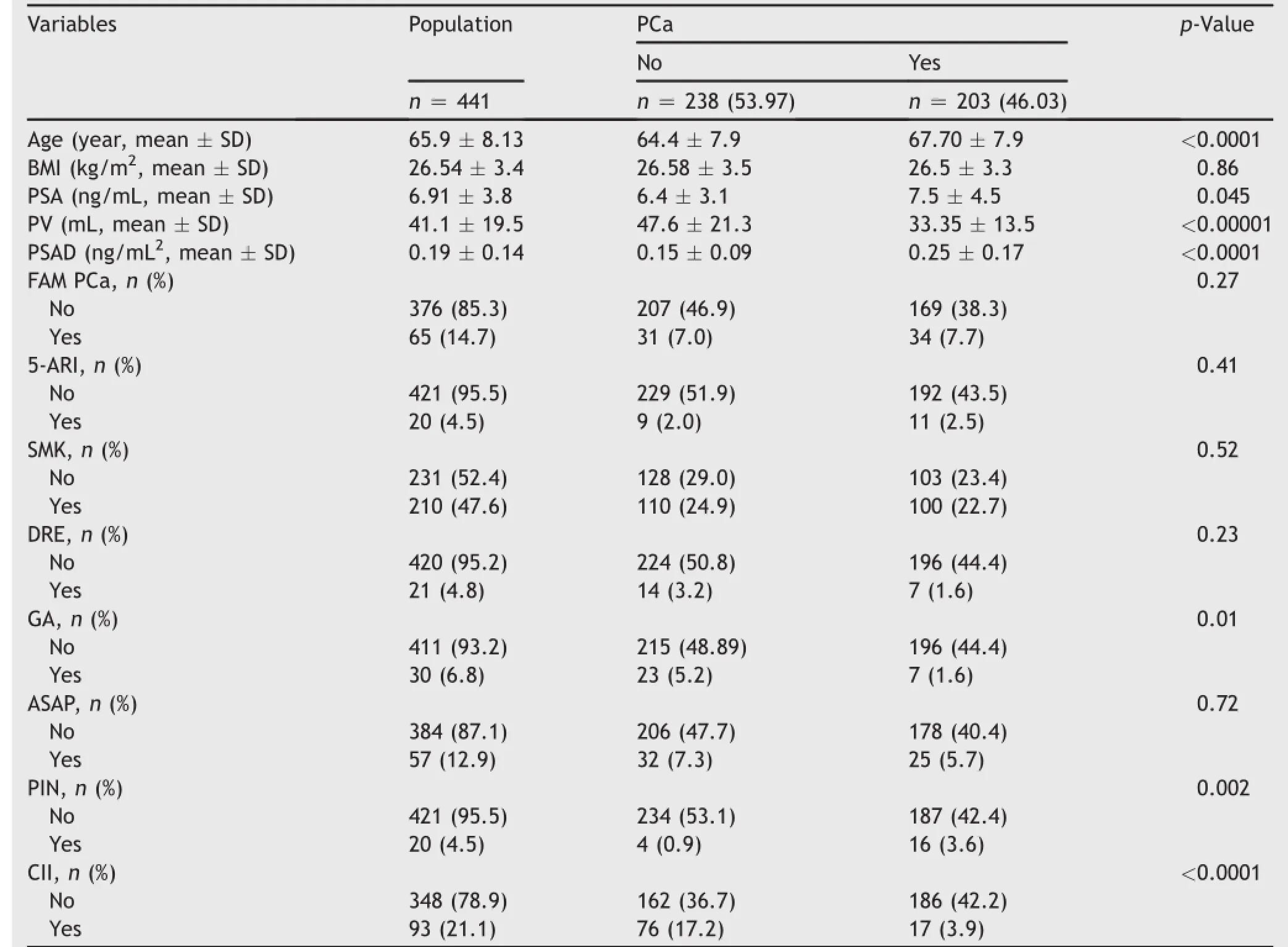
Table 1Statistics of the population and subpopulations of patients(with or without PCa)undergoing prostate biopsy.
Table 2 shows that the results of univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis of variables associating with PCa detection.Age,PSA,PV,CII and PIN were the significant independent predictive variables associating with PCa detection in the final multivariate logistic regression model.Moreover,the association was positive with age(OR=1.076),PSA(OR=1.200)and PIN (OR=3.875),and negative with CII(OR=0.192)and PV (OR=0.934).
Table 3 includes six multivariate logistic regression models which are all significant in predicting the mean probability of PCa detection.The models are stratified by the presence(+)or absence(-)of CII which might interact (models B,D,F)or not(models A,C,E)with the significant continuous variables including age(model A,B),PSA (models C,D)and PV(models E,F).Fig.3 depicts the curves stratified by CII of the six models which are reported in Table 3.As shown,the probability curves of models A,C,E have different intercepts but same slopes,while the curves of models B,D,F have different slopes but same intercepts. Interestingly,models A,B,C,D show that the mean probability of detecting PCa is decreased by the presence of CII and models E,F give evidence that the inverse risk of detecting PCa by PV is even more decreased when CII is present in the biopsy cores.
4.Discussion
In the present study,CII inversely and independently associated with PCa detection.An inverse association between CII and PCa has been reported by previous and recent studies[35-44];however,the subject has also been approached by other investigators who failed to detect any association at all[45-47].Although our findings suggest that the presence of CII decreases the probability of detecting PCa,the negative association of CII with PCa does not necessary mean causation.Trying to explain the reason of such negative association of CII with PCa detection is a hard task,however,as a theory,CII might protect from the different steps involving PCa genesis.Indeed,it is interesting to realize that recently anticancer vaccines and immunotherapies focus on empowering the immune system to overcome the tumor[48-50].Vaccine therapy or immunotherapies aim to stimulate the immune system and activate an appropriate immune-mediate response against malignant cells.The immune system consists of innate and adaptive components.The innate immune system encompasses phagocytic cells,natural killer cells,and cells that release inflammatory mediators.Macrophages and dendritic cells function as antigen presenting cells which serve as a bridge from innate to adaptive immunity.The adaptive arm of the immune system consists of B cells and Tcells.The Tcells are the most crucial component in mediating antitumor responses induced by cancer vaccines and immunotherapies. In the prostate microenvironment,CII might induce the liberation of tumor related antigens which stimulate the components of the immune system.Basic science studies are mandatory in order to assess the nature of the inflammatory infiltrate and its impact on the androgenic receptors gene in the prostate gland microenvironment.According to the improving evidence of PCa immunotherapy efficacy and the results of the present study,we propose,as illustrated in Fig.4,a schematic mechanistic diagram showing the potential cellular exchange of signaling pathways towards inflammation in PCa.Indeed,in early stages of PCa carcinogenesis,high grade PIN associates with disruption of the basement membrane which allows the cancer cell to migrate into the prostate microenvironment where they are attached by inflammatory cells with delivery of tumor antigens.Moreover,macrophages and dendritic cells expose the antigens to both helper(CD4+)and cytotoxic(CD8+)T lymphocytes which trigger a cytotoxic response against the cancer cells structuring the focus of high grade PIN.As a consequence,PCa carcinogenesis progression might be interrupted and the risk of PCa is reduced because of the activated immune system.
In the current study,it was shown that PV inversely associated with PCa.This finding confirms what has already been reported[51,52].Moreover,our study gives evidence how the mean probability of detecting PCa by PV may be decreased by the presence of CII.For example(see model E in Table 3 and Fig.1),the probability of detecting PCa of PV of 40 mL decreases by 60%-20%by the presence of CII (OR=0.113).
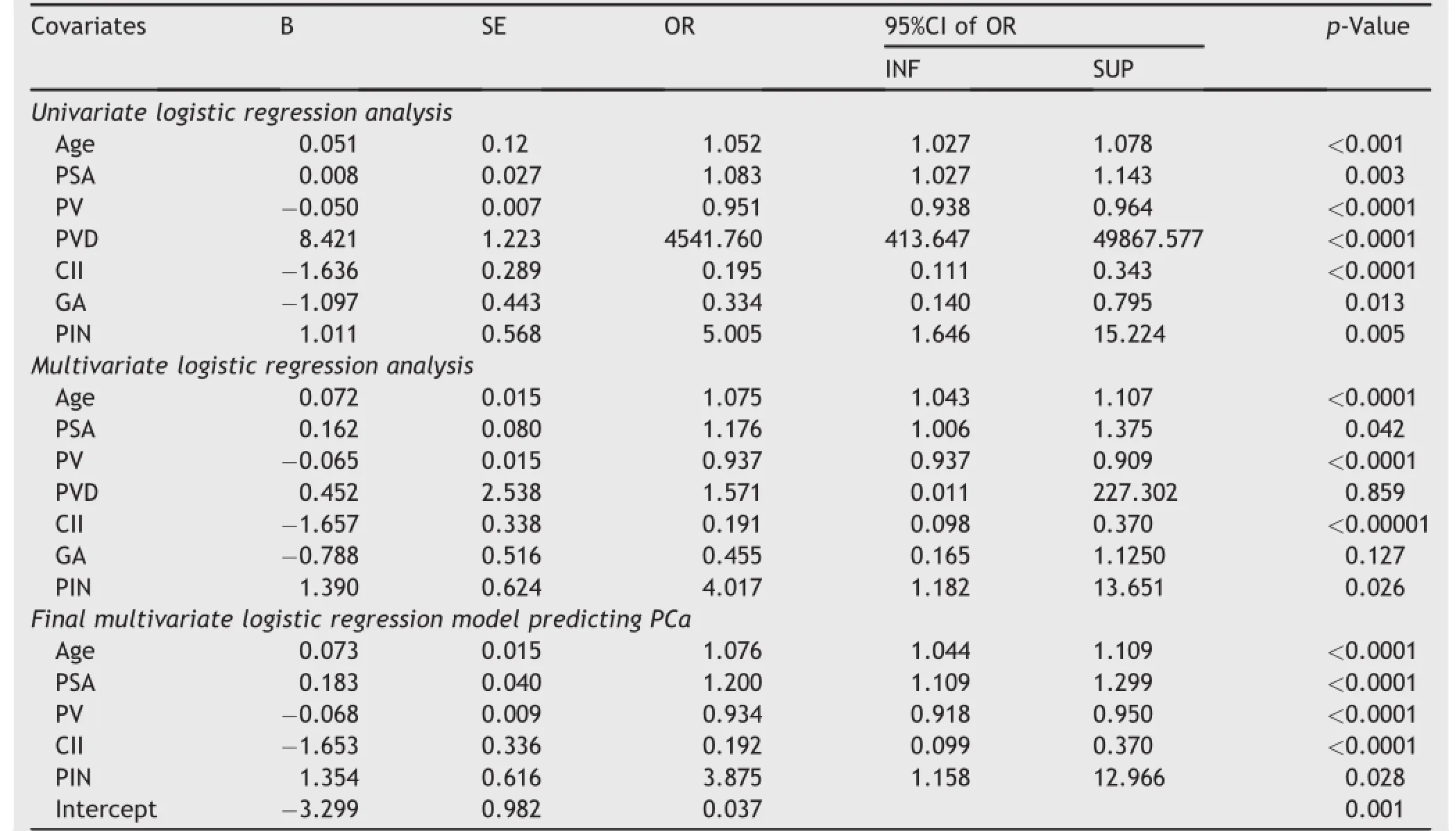
Table 2Logistic regression analysis of covariates associating with PCa detection(dependent variable)in patients who underwent TRUSB(n=441).
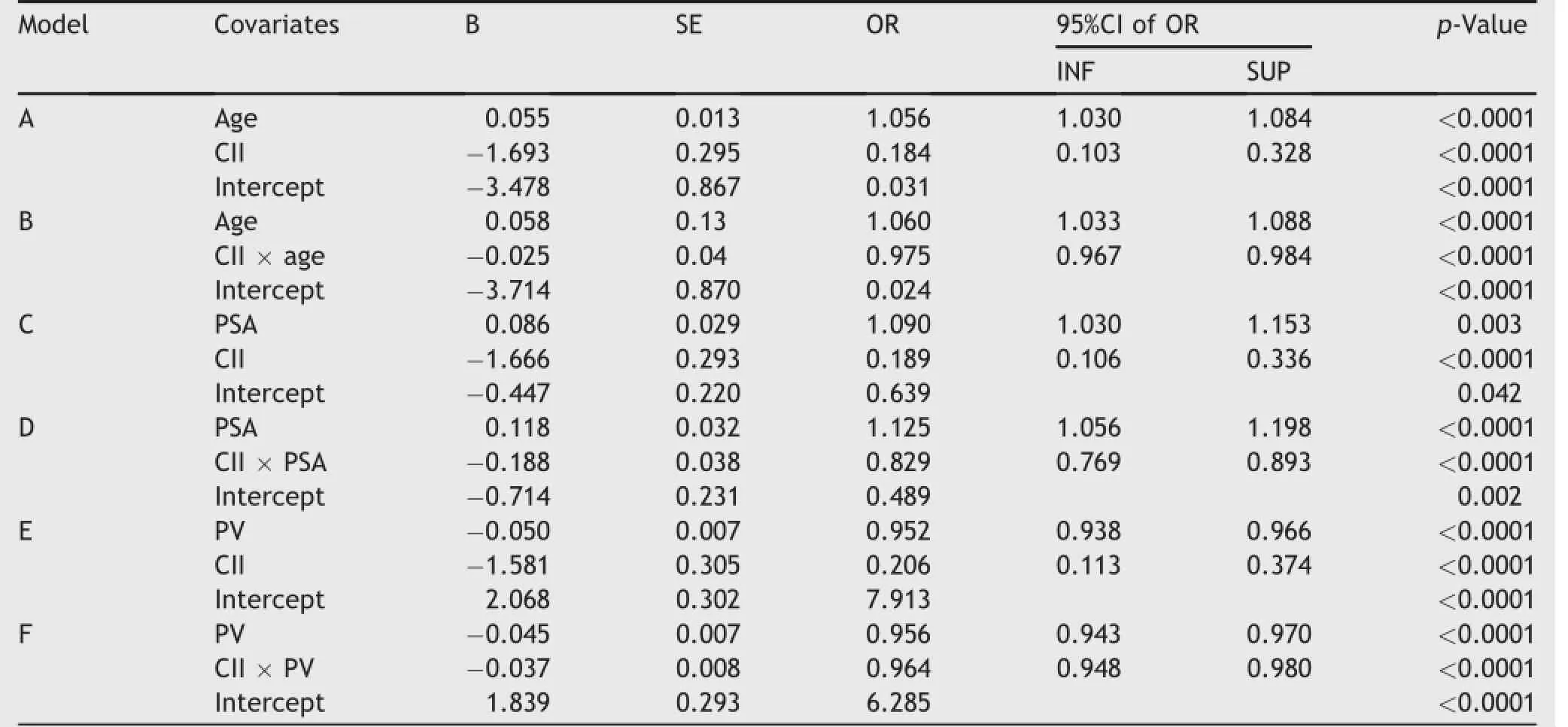
Table 3Multivariate logistic regression models predicting PCa in patients undergoing biopsy.
PSA selection for prostate biopsy may pose a potential bias because its increments also associate with CII[53-55]. Interestingly,our investigation gives new evidence when dealing with this controversial subject.Indeed,as shown in Table 3 and Fig.1(model C and D),for a PSA of 10 ng/mL the mean probability of detecting PCa is decreased by 60%-20%by CII;moreover,when PSA interacts with CII(interaction,model D),two completely different probability curve risks of PCa are depicted.Indeed,the probability risk curve elevates(positive slope)as PSA increases when CII is absent;however,the curve declines(negative slope)when PSA interacts with CII.
There are limits in our study.First,it was single center, but the sample size was enough large.Second,we measured PV by means of TRUS and not by prostatectomy specimens;however,TRUS is widely used and is considered and effective technique.Finally,the inverse association of chronic inflammation with PCa might be confounded by PSA.Indeed,PSA may elevate by both inflammation and cancer;hence,if biopsies are performed in cases with increased PSA,some patients will have cancer and others CII[53-55].Patients with inflammation may undergo biopsy procedures more frequently than men without inflammation because of potential higher PSA levels.As a result,men with CII will automatically be less likely to have cancer and vice versa.
In a patient population undergoing first biopsy after prostate assessment,CII of the prostate type IV inversely and independently associated with a reduced risk of PCa. In multivariate logistic mean probability models,CII was an independent prognostic factor which lowered the risk of PCa detection.As a consequence,CII of the prostatetype IV might have drawbacks for approaching and managing prostate diseases.Furthermore,the role of chronic inflammation in PCa carcinogenesis remains a controversial issue which needs further clinical and basic research. In the future,it might be interesting to include in clinical practice other diagnostic elements such as new biomarkers(prostate health index,phi or PCa antigen 3, pca3)and/or multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging in order to investigate the possibility of differentiating the inflammatory infiltrates from high grade PIN or PCa.
CII type IV should be considered as an adjunctive parameter in re-biopsy or active surveillance protocols.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
[1]Selman A.The McNeal prostate:a review.Urology 2011;78: 1224-8.
[2]De Marzo AM,Platz EA,Sutcliffe S,Xu J,Gro¨nberg H, Drake CG,et al.Inflammation in prostate carcinogenesis.Nat Rev Cancer 2007;7:256-69.
[3]Sfanos KS,De Marzo AM.Prostate cancer and inflammation: the evidence.Histopathology 2012;60:199-215.
[4]Bardia A,Platz EA,Yegnasubramanian S,De Marzo AM, Nelson WG.Anti-inflammatory drugs,antioxidants,and prostate cancer prevention.Curr Opin Pharmacol 2009;9:419-26.
[5]Drake CG.Prostate cancer as a model for tumour immunotherapy.Nat Rev Immunol 2010;10:580-93.
[6]Caruso C,Balistreri CR,Candore G,Carruba G,Colonna-Romano G,Di Bona D,et al.Polymorphisms of proinflammatory genes and prostate cancer risk:a pharmacogenomic approach.Cancer Immunol Immunother 2009;58: 1919-33.
[7]Klein EA,Silverman R.Inflammation,infection,and prostate cancer.Curr Opin Urol 2008;18:315-9.
[8]Nelson WG,De Marzo AM,Isaacs WB.Prostate cancer.N Engl J Med 2003;349:366-81.
[9]Shook SJ,Beuten J,Torkko KC,Johnson-Pais TL,Troyer DA, Thompson IM,et al.Association of RNASEL variants with prostate cancer risk in Hispanic Caucasians and African Americans.Clin Cancer Res 2007;13:5959-64.
[10]Wagenlehner FM,Elkahwaji JE,Algaba F,Bjerklund-Johansen T,Naber KG,Hartung R,et al.The role of inflammation and infection in the pathogenesis of prostatecarcinoma.BJU Int 2007;100:733-7.
[11]Nelson JE,Harris RE.Inverse association of prostate cancer and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs(NSAIDs):results of a case-control study.Oncol Rep 2000;7:169-70.
[12]Montironi R,Mazzucchelli R,Pomante R,Thompson D,Duval da Silva V,Vaught L,et al.Immunohistochemical expression of pi class glutathione S-transferase in the basal cell layer of benign prostate tissue following chronic treatment with finasteride.J Clin Pathol 1999;52:350-4.
[13]Coussens LM,Werb Z.Inflammation and cancer.Nature 2002; 420:860-7.
[14]Mantovani A,Allavena P,Sica A,Balkwill F.Cancer related inflammation.Nature 2008;464:436-44.
[15]Lin X,Asgari K,Putzi MJ,Gage WR,Yu X,Cornblatt BS,et al. Reversal of GSTP1 CpG island hypermethylation and reactivation of pi-class glutathione S-transferase(GSTP1)expression in human prostate cancer cells by treatment with procainamide.Cancer Res 2001;61:8611-6.
[16]Fujita K,Ewing CM,Getzenberg RH,Parsons JK,Isaacs WB, Pavlovich CP.Monocyte chemotactic protein-1(MCP-1/CCL2) is associated with prostatic growth dysregulation and benign prostatic hyperplasia.Prostate 2010;70:473-81.
[17]Ko¨nig JE,Senge T,Allhoff EP,Ko¨nig W.Analysis of the inflammatory network in benign prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer.Prostate 2004;58:121-9.
[18]Barbisan F,Mazzucchelli R,Santinelli A,Lopez-Beltran A, Cheng L,Scarpelli M,et al.Overexpression of ELAV-like protein HuR is associated with increased COX-2 expression in atrophy,high-grade prostaticintraepithelial neoplasia,and incidental prostate cancer in cystoprostatectomies.Eur Urol 2009;56:105-12.
[19]Palapattu GS,Sutcliffe S,Bastian PJ,Platz EA,De Marzo AM, Isaacs WB,et al.Prostate carcinogenesis and inflammation: emerging insights.Carcinogenesis 2005;26:1170-81.
[20]Stock D,Groome PA,Siemens DR.Inflammation and prostate cancer:a future target for prevention and therapy?Urol Clin North Am 2008;35:117-30.
[21]Di Silverio F,Bosman C,Salvatori M,Albanesi L,Proietti Pannunzi L,Ciccariello M,et al.Combination therapy with rofecoxib and finasteride in the treatment of men with lower urinary tract symptoms(LUTS)and benign prostatic hyperplasia(BPH).Eur Urol 2005;47:72-9.
[22]Coffey DS.Similarities of prostate and breast cancer:evolution,diet,and estrogens.Urology 2001;57(4 Suppl.1):31-8.
[23]Rohrmann S,Nelson WG,Rifai N,Brown TR,Dobs A, Kanarek N,et al.Serum estrogen,but not testosterone,levels differ between black and white men in a nationally representative sample of Americans.J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2007; 92:2519-25.
[24]Deroo BJ,Korach KS.Estrogen receptors and human disease. Clin Invest 2006;116:561-70.
[25]Bosland MC.Sex steroids and prostate carcinogenesis:integrated,multifactorial working hypothesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci 2006;1089:168-76.
[26]Prins GS,Korach KS.The role of estrogens and estrogen receptors in normal prostate growth and disease.Steroids 2008; 73:233-44.
[27]Hsing AW,Sakoda LC,Chua Jr S.Obesity,metabolic syndrome, and prostate cancer.Am J Clin Nutr 2007;86:s843-57.
[28]Murphy C,McGurk M,Pettigrew J,Santinelli A,Mazzucchelli R, Johnston PG,et al.Nonapical and cytoplasmic expression of interleukin-8,CXCR1,and CXCR2 correlates with cell proliferation and microvessel density in prostate cancer.Clin Cancer Res 2005;11:4117-27.
[29]Jacobs EJ,Rodriguez C,Mondul AM,Connell CJ,Henley SJ, Calle EE,et al.A large cohort study of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and prostate cancer incidence.J Natl Cancer Inst 2005;97(13):975-80.
[30]Pruthi RS,Derksen JE,Moore D.A pilot study of use of the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib in recurrent prostate cancer after definitive radiation therapy or radical prostatectomy.BJU Int 2004;93:275-8.
[31]Di Silverio F,Sciarra A,Gentile V.Etoricoxib and intermittent androgen deprivation therapy in patients with biochemical progression after radical prostatectomy.Urology 2008;71: 947-51.
[32]Kantoff PW,Higano CS,Shore ND,Berger ER,Small EJ, Penson DF,et al.IMPACT Study Investigators.Sipuleucel-T immunotherapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer.N Engl J Med 2010;363:411-22.
[33]Krieger JN,Nyberg Jr L,Nickel JC.NIH consensus definition and classification of prostatitis.JAMA 1999;282:263-7.
[34]De Marzo AM,Marchi VL,Epstein JI,Nelson WG.Proliferative inflammatory atrophy of the prostate:implications for prostatic carcinogenesis.Am J Pathol 1999;155:1985-92.
[35]Blumenfeld W,Tucci S,Marayan P.Incidental lymphocytic prostatitis.Selective involvement with non malignant glands. Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16:975-81.
[36]De Nunzio C,Kramer G,Marberger M,Montironi R,Nelson W, Schro¨der F,et al.The controversial relationship between benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer:the role of inflammation.Eur Urol 2011;60:106-17.
[37]Gandaglia G,Briganti A,Gontero P,Mondaini N,Novara G, Salonia A,et al.The role of chronic inflammation in the pathogenesis and progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).BJU Int 2013;112:432-41.
[38]Porcaro AB,Novella G,Molinari A,Terrin A,Minja A,De Marco V,et al.Prostate volume index and chronic inflammation of the prostate type IV with respect to the risk of prostate cancer.Urol Int 2015;94:270-85.
[39]Porcaro AB,Rubilotta E,Petrozziello A,Ghimenton C, Migliorini F,Zecchini Antoniolli S,et al.Chronic inflammation of the prostate type IV with respect to risk of prostate cancer. Arch Ital Urol Androl 2014;86:208-11.
[40]Gerstenbluth RE,Seftel AD,Maclennan GT,Rao RN,Corty EW, Ferguson K,et al.Distribution of chronic prostatitis in radical prostatectomy specimens with up-regulation of bcl-2 in areas of inflammation.J Urol 2002;167:2267-70.
[41]Irani J,Goujon JM,Ragni E,Peyrat L,Hubert J,Saint F, et al.High-grade inflammation in prostate as a prognostic factor for biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy.Pathologist Multi Center Study Group.Urology 1999; 54:467-72.
[42]Karakiewicz PI,Benayoun S,Be′gin LR,Duclos A,Valiquette L, McCormack M,et al.Chronic inflammation is negatively associated with prostate cancer and high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia on needle biopsy.Int J Clin Pract 2007;61:425-30.
[43]Moreira DM,Nickel JC,Gerber L,Muller RL,Andriole GL, Castro-Santamaria R,et al.Baseline prostate inflammation is associated with a reduced risk of prostate cancer in men undergoing repeat prostate biopsy:results from the REDUCE study.Cancer 2014;120:190-6.
[44]Zhang W,Sesterhenn IA,Connelly RR,MostofiFK,Moul JW. Inflammatory infiltrate(prostatitis)in whole mounted radical prostatectomy specimens from black and white patients is not an etiology for radical difference in prostate specific antigen. J Urol 2000;163:131-6.
[45]Roberts RO,Bergstralh EJ,Bass SE,Lieber M,Jacobsen SJ. Prostatitis as a risk factor for prostate cancer.Epidemiology 2004;15:93-9.
[46]Davidsson S,Fiorentino M,Andre′n O,Fang F,Mucci LA, Varenhorst E,et al.Inflammation,focal atrophic lesions,and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia with respect to risk of lethal prostate cancer.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2010; 20:2280-7.
[47]Engelhardt PF,Brustmann H,Seklehner S,Riedl CR.Chronic asymptomatic inflammation of the prostate type IV and carcinoma of the prostate:is there a correlation?Scand J Urol 2013;47:230-5.
[48]Hammerstrom AE,Cauley DH,Atkinson BJ,Sharma P.Cancer Immunotherapy:sipuleucel-T and beyond.Pharmacotherapy 2011;31:813-28.
[49]Brennen WN,Denmeade SR,Isaacs JT.Mesenchymal stem cells as a vector for the inflammatory prostate microenvironment.Endocr Relat Cancer 2013;20:R269-90.
[50]Nguyen DP,Li J,Tewari AK.Inflammation and prostate cancer: the role of interleukin 6(IL-6).BJU Int 2014;113:986-92.
[51]Roobol MJ,Schroder FH,Hugosson J,Jones JS,Kattan MW, Klein EA,et al.Importance of prostate volume in the European Randomised Study of Screening for Prostate Cancer (ERSPC)risk calculators:results from the prostate biopsy collaborative group.World J Urol 2012;30:149-55.
[52]Al-Azab R,Toi A,Lockwood G,Kulkarni GS,Fleshner N.Prostate volume is strongest predictor of cancer diagnosis at transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy with prostatespecific antigen values between 2.0 and 9.0 ng/mL.Urology 2007;69:103-7.
[53]Hoekx L,Jeuris W,Van Marck E,Wyndaele JJ.Elevated serum prostate specific antigen(PSA)related to asymptomatic prostatic inflammation.Acta Urol Bel 1998;66: 1-2.
[54]Sindhwani P,Wilson CM.Prostatitis and serum prostatespecific antigen.Curr Urol Rep 2005;6:306-12.
[55]Hochreiter WW.The issue of elevated prostate cancer evaluation in men with elevated prostate-specific antigen and chronic prostatitis.Andrologia 2008;40:130-3.
Received 2 May 2015;received in revised form 2 July 2015;accepted 18 August 2015
Available online 25 September 2015
*Corresponding author.
E-mail address:drporcaro@yahoo.com(A.B.Porcaro).
Peer review under responsibility of Shanghai Medical Association and SMMU.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajur.2015.08.007
2214-3882/?2015 Editorial Office of Asian Journal of Urology.Production and hosting by Elsevier(Singapore)Pte Ltd.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Journal of Urology2015年4期
Asian Journal of Urology2015年4期
- Asian Journal of Urology的其它文章
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
- Ureteral stent technology:Drug-eluting stents and stent coatings
- Stellate scar sign of renal cell carcinoma
- Laparoscopic ureterolysis with simultaneous ureteroscopy and percutaneous nephroscopy for treating complex ureteral obstruction after failed endoscopic intervention:A technical report
- Implication of ultrasound bladder parameters on treatment response in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia under medical management
- Does the presence of a percutaneous renal access influence fluoroscopy time during percutaneous nephrolithotomy?
