Factors infl uencing the spinal motoneurons in development
Stefan Wiese
Faculty for Biology and Biotechnology, Group for Molecular Cell Biology, Universitaetsstr. 150, Ruhr University Bochum, D-44801 Bochum, Germany
INVITED REVIEW
Factors infl uencing the spinal motoneurons in development
Stefan Wiese*
Faculty for Biology and Biotechnology, Group for Molecular Cell Biology, Universitaetsstr. 150, Ruhr University Bochum, D-44801 Bochum, Germany
The development of the spinal cord needs a concerted interaction of transcription factors activating diverse genes and signals from outside acting on the specifi cation of the diff erent cells. Signals have to act on the segments of the embryo as well as on the cranial-caudal axis and the dorso-ventral axis. Additionally the axons of the motoneurons have to cross the central nervous system barrier to connect to the periphery. Intensive anatomical studies have been followed by molecular characterization of the diff erent subsets of transcription factors that are expressed by cells of the developing spinal cord. Here, intensive studies for the most important appearing cells, the motoneurons, have resulted in a good knowledge on the expression patterns of these proteins. Nonetheless motoneurons are by far not the only important cells and the concert activity of all cells besides them is necessary for the correct function and integrity of motoneurons within the spinal cord. This article will briefl y summarize the diff erent aspects on spinal cord development and focuses on the diff erentiation as well as the functionalization of motoneurons.
axon; neurite; synapse muscle; extracellular matrix; transcription factors
Wiese S (2015) Factors infl uencing the spinal motoneurons in development. Neural Regen Res 10(11):1773-1776.
Introduction
dysfunctions for a longer time even makes it harder to start curing a disease as the loss of functional cells has started sometimes even years before. For example usually more than 50% of all motoneurons are already dysfunctional for a longer period before a patient comes to the clinic due to compensatory eff ects of the remaining functional cells in the spinal cord. Orphaned muscle cells are taken over by neighboring motoneurons as they send out new axonal side tribes to innervate these muscle fi bers. Knowledge on the development of the spinal motor circuits might help to understand and might even help fi nding cures against such degenerative diseases.
Early Steps in Spinal Cord in Development
The CNS epithelial cells of the neural tube are pseudo stratifi ed cells and perform symmetric cell divisions to increase the number of neural precursor cells (NPCs). These NPCs are generated at the anterior-posterior axis. Diff erent regional signals along the rostro-caudal axis start to instruct the positional identity of the cells defi ning forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain, and spinal cord.
Caudalization is induced by the vitamin A derivative retinoic acid (RA) followed by expression of Pax3 by neuroepithelial cells. Subsequently, mutant mice defi cient for retinaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (Raldh2) show severe alterations in hindbrain and spinal cord patterning. The second early molecule necessary for the specifi cation of the spinal cord is the fi broblast growth factor (FGF). Both FGF and RA form antagonizing gradients to determine the anterior hind-The development of the spinal cord plays a central role towards execution coordinated movements and of sensory inputs as well. Together with sensory inputs from the eye and ear in human they produce a movement output as a consequence of refl exes or higher brain cognitive functions. These circuits are mainly disturbed in motoneuron diseases like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) or in cases of lesions caused by accidents. The restauration of such disturbed motor output functions is the main goal for physicians and scientists all over the world. If we therefore take a closer look at the time cell diff erentiation and establishment of those motor circuits, this may help to restore the original function in disease.
Development of the Spinal Cord
The spinal cord as a central nervous system (CNS) structure builds up connections to the periphery of the body. Signals from diff erent brain regions are integrated to generate a movement. This includes muscle movement, breathing and rhythmic activities of muscle cells with a constant feed back to the higher brain regions. Disorders aff ecting the function of the motor system including ALS or SMA are characterized by the progressive inability not only to walk and move but also suff er from the increasing inability to breathe or speak. The complexity of dysfunctions aff ecting the motor system makes it unable to apply cures on single cell type level but rather needs a more systemic approach. The fact that the motor system has great abilities to compensatebrain and the posterior spinal cord along the rostro-caudal axis. Regionalization within the caudal part is performed by expression of the homeobox domain transcription factors (Hoxgenes) (Diez del Corral et al., 2003). These Hox transcription factors represent the concept for a neuronal subtype identity of the embryonic hindbrain and spinal cord (Wu et al., 2008).
Generation of the Dorso-ventral Patterning in the Spinal Cord
While FGFs and RA defi ne the cellular identity for the rostro-caudal axis, cellular identities along the dorso-ventral axis of the developing hindbrain and spinal cord are defi ned by members of the bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and of the wingless/Int-1 (Wnt) family, secreted from the roof plate cells. The respective antagonizing signal comes from the notochord and later on from the fl oor plate cells which secrete Sonic hedgehog (Shh) as a ventralization signal for the spinal cord cells (Dessaud et al., 2008). Diff erent concentrations of Shh form diff erent neural progenitor regions in the ventral part. The resulting progenitor cells, as well as the resulting cells from these progenitor pools are characterized by a specifi c expression patterning of homeodomain transcription factors. Consequently, mutations in Patched 1 or Smoothened, both being receptor parts of the Shh pathway, induce severe patterning defects during embryogenesis. This homeodomain transcription factor concept has been considered as the essential mechanism for specifi cation of neuronal and the latter glial subtype identities. Defi nition of cells might be in general performed by the transcription factor code but it does not clarify the way towards a specialized cell type. Such signals have to be positioned outside the cells and therefore the extracellular matrix most probably plays a pivotal role in this process.
For example, heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) are found in almost all mammalian cells. They are on cell surfaces (glypicans, syndecans) and in the extracellular space (perlecan, collagen type XVIII or agrin). They are composed of a core protein with covalent O-linked heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycan side chains. HSPGs can interact with cytokines, growth factors and other extracellular matrix molecules. The FGF2 and FGF4, the Wnt and the Notch signaling pathways have been reported to be affi nity- and position-dependent on the presence of HSPGs. The matrix binds and places these factors to the optimal positions and thereby enhances specifi city and availability of these factors (Androutsellis-Theotokis et al., 2006).
Additionally, neuroepithelial cells start their diff erentiation into neurons, by changing their 6-O-sulfation profi le and their HS chain length. These modifi cations coincide with a switch from FGF2 to FGF1 signaling. Alterations in N-sulfation, 3-O-sulfation and 6-Osulfation have been detected during stem cell diff erentiation. The elimination of sulfation during in vitro neural stem cell diff erentiation changes the relative proportion of early neurons generated from the stem cell pool and appears to block the further diff erentiation of these post-mitotic cells. HSPGs have to pass the Golgi apparatus as their side chains are sulfated by a subset of (sulfotransferase) enzymes (Karus et al., 2012; Karus et al., 2013). Future research will have to focus not only on the transcription factor code but rather on the matrix and their specifi c discrete changes infl uencing position, diff erentiation and the total number of cells.
Organization of Motoneuron Subtypes and Motor Columns
More motoneurons than necessary are generated during embryonic development to serve the needs for adulthood. The excess in cells is reduced fi rst due to the limited amount of trophic support and second by electric activity and connectivity to the target cells, the skeletal muscle. The motoneuron subtypes are well organized along the rostro-caudal and dorso-ventral axis in the spinal cord sorted by function and innervation targets. Neurons innervating the same target are together in a column (Jessell, 2000) (see also Figure 1). For example the motoneurons of mediomedial column present throughout the spinal cord innervate the axial trunk muscles while the lateral motor column (LMC), which is positioned in the brachial and lumbal part of the spinal cord innervates the skeletal muscles of the limbs and thereby regulates fi ne motor skills (Bonanomi and Pfaff , 2010).
Three motoneuron subtypes exist in the motor columns, the α-, β-, and γ-motoneurons. The α-and γ-motoneurons can be distinguished by morphology and projection patterning. The large multipolar α-motoneurons innervate the extrafusal skeletal musculature receiving input from the proprioceptive sensory aff erent neurons. Up to 30% of all motoneurons are smaller γ-motoneurons controlling the intrafusal muscle fi bers in the muscle spindles. They modulate the response of the muscle spindle in accordance to the muscle extension and receive no direct input from proprioceptive sensory aff erents. γ-Motoneurons express the spindle-derived glial-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) for their survival during the early postnatal period. Experiments with conditional transgenic knock out mice also indicated that β- and possibly also α-motoneurons in part depend on factors generated from the muscle spindle. The skeleto-fusi motoneurons (β-motoneurons) project both on the skeletal muscle and the muscle spindle. They can only hardly be distinguished from the α-motoneurons and only little is known about their specifi c properties (Kanning et al., 2010).
Apart from the terminal diff erentiation and positioning of the motoneuron cell bodies within the motor columns the growth of axons combined with correct targeting is critical for the latter function of the body.
Mechanisms of Axonal Pathfi nding to the Target Muscle
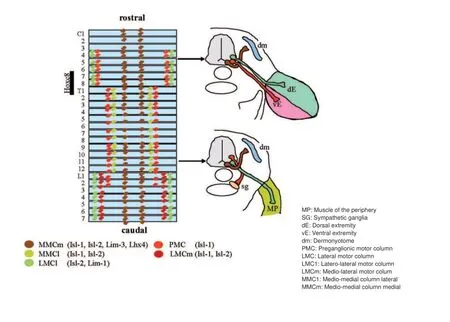
Figure 1 Segmentation and motoneuron connection during spinal cord development in mice.
Axon growth is not a random outgrowth process but needs a directed navigation. The direction is determined at the site of the growth cone. The pathfi nder structures are capable of recognizing diff erent signals from their surrounding and subsequently react to them. R.W. Sperry postulated in 1963 his chemo-affinity theory, by which the axons find their target cells according to the receptors in the growth cone so that they can recognize the guiding molecules along their way (Sperry, 1963). Nowadays we know that axonal growth is not exclusively dependent on guidance molecules but also depends on molecules on the cell surface, diff usible trophic factors, electric activity and last not least extracellular matrix molecules (Faissner, 1997; Klausmeyer et al., 2011). Diff usible factors can infl uence growth behavior and survival of neurons over long distances. Basically, diff usible factors and linked signals can act attractively or repulsively on the growing axon and the composition of the receptors on a growth cone determines the chemo-attractively or chemo-repulsively behavior.
The combination of attraction and repulsion reveals that the growing axon fi nds the exit point from the spinal cord to target the muscle tissue. The mechanisms that allow the exit from the neural tube are not fully understood. Specialized neural crest cells, the “Boundary Cap Cells” (BCs), make sure that the motor axons pass the neuroepithelium while the cell bodies stay in the neural tube. When they are not present, this leads to emigration of the cell bodies along the growing axons. Therefore the BCs not only influence the correct axon growth but rather take over responsibility for the resting behavior of the cell bodies of motoneurons. In contrast, the dorsal root ganglionic neurons behave totally diff erent. When taken into culture these neurons start fasciculating as soon as they connect to each other. This behavior is not known from motoneurons when taken into culture. The interaction of the BCs and the growing motor axons is performed by semaphorins and their receptors Neuropilin 2 (Nrp2) and/or Plexin-A2. The protein family of semaphorins includes membrane bound and soluble proteins and represents one of the largest protein families involved in axonal pathfi nding.
The metametric segmental patterning of the spinal nerves correlates with the typical segmentation including a repetitive rostro-caudal growth patterning and projection through the anterior part of the somites. This is induced bythe repulsive signals of the posterior part of the sklerotom. Inhibiting factors are the Peanut Agglutinin (PNA)-Binding glycoprotein and Semaphorin 3F (Sema3F). Positioning of motoneuron cell bodies is mainly mediated by signals from the Slit and Robo family. The Slits prevent migration of the motoneurons towards the ventral fl oor plate and thereby help them to stay in their correct columns. In contrast, the Netrin/DCC (deleted in colorectal cancer) system attracts spinal motoneurons. The more dorsally positioned interneurons are subdivided in the dI1 to dI6 interneurons. The correct positioning and function of interneurons is important for coordination and gait. Here, the Eph/ephrins and Netrin/DCC act as important mediators. Eff ects were observed in knock out mice and could show for developing commissural interneurons aberrant midline axon guidance capabilities while the missing dI6 interneuron marker Dmrt3 (Double sex/Male-abnormal-3 Related Transcription factor) results in divergent gait patterning (Vallstedt and Kullander, 2013).
Growing spinal motoneurons have to pass embryonic connective tissue on their way. Guidance is performed by chemo-attractive and -repulsive signals. While the axons of the medio-medial motor column (MMC) target to the dorsal trunk musculature, axons of the lateral motor column (LMC) project ventrally towards the limb musculature. Fibroblast growth factor has been identifi ed as a chemotrophic factor for targeting the MMC motoneuron axons. It is secreted by the dermomyotome. Repulsive signals originate from the dorsal root ganglionic cells (DRGs) and the ventral mesenchyme by receptor tyrosine kinases EphA3 and EphA4 and their respective ligand EphrinA. EphA3/EphA4 double mutants display a misguided axon growth as they cannot react to the repulsive signals of EphrinA. As a consequence the growing motor axons of the MMC artifi cially target the DRGs. Motor axons of the LMC grow ventrally to the limb musculature as they express other receptors compared to the motoneurons of the MMC. They do not react to the repulsive signals which prevent growth of the MMC motor axons into the limbs. The limb target tissue provides cell adhesion molecules of the Immunglobulin superfamily like L1 and the neuronal cell adhesion molecule NCAM. If this direct cell to cell interaction is inhibited it results in a stronger fasciculation and a wrong projection pattern.
The concerted activity of soluble factors, membranebound factors, receptors on the cell surface and fi nally electric activity of the target cell establish the correct connection to the muscle cells. Experiments have shown that even on the level of already reduced axon numbers on the muscle so that one fi ber is innervated by only one axon of a motoneuron there is still possible substantial alteration. This is mainly due to the fact that the initially made synapses have diff erent stabilities. Experiments have shown that synapses at the skeletal muscle can be discriminated into fast synapsing (FaSyn) and slow synapsing (DeSyn) terminals. Treatment of younger mice with α-bungarotoxin resulted in selective and permanent denervation of the DeSyn synapses when applied before 3 months of age. Interestingly the actual more stable FaSyn synapses appear more vulnerable in a mouse model for spinal muscular atrophy (Murray et al., 2008).
Androutsellis-Theotokis A, Leker RR, Soldner F, Hoeppner DJ, Ravin R, Poser SW, Rueger MA, Bae SK, Kittappa R, McKay RD (2006) Notch signalling regulates stem cell numbers in vitro and in vivo. Nature 442:823-826.
Bonanomi D, Pfaff SL (2010) Motor axon pathfinding. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2:a001735.
Dessaud E, McMahon AP, Briscoe J (2008) Pattern formation in the vertebrate neural tube: a sonic hedgehog morphogen-regulated transcriptional network. Development 135:2489-2503.
Diez del Corral R, Olivera-Martinez I, Goriely A, Gale E, Maden M, Storey K (2003) Opposing FGF and retinoid pathways control ventral neural pattern, neuronal diff erentiation, and segmentation during body axis extension. Neuron 40:65-79.
Faissner A (1997) The tenascin gene family in axon growth and guidance. Cell Tissue Res 290:331-341.
Jessell TM (2000) Neuronal specifi cation in the spinal cord: inductive signals and transcriptional codes. Nat Rev Genet 1:20-29.
Kanning KC, Kaplan A, Henderson CE (2010) Motor neuron diversity in development and disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 33:409-440.
Karus M, Hennen E, Safi na D, Klausmeyer A, Wiese S, Faissner A (2013) Diff erential expression of micro-heterogeneous lewisX-type glycans in the stem cell compartment of the developing mouse spinal cord. Neurochem Res 38:1285-1294.
Karus M, Samtleben S, Busse C, Tsai T, Dietzel ID, Faissner A, Wiese S (2012) Normal sulfation levels regulate spinal cord neural precursor cell proliferation and diff erentiation. Neural Dev 7:20.
Klausmeyer A, Conrad R, Faissner A, Wiese S (2011) Infl uence of glial-derived matrix molecules, especially chondroitin sulfates, on neurite growth and survival of cultured mouse embryonic motoneurons. J Neurosci Res 89:127-141.
Murray LM, Comley LH, Thomson D, Parkinson N, Talbot K, Gillingwater TH (2008) Selective vulnerability of motor neurons and dissociation of pre- and post-synaptic pathology at the neuromuscular junction in mouse models of spinal muscular atrophy. Hum Mol Genet 17:949-962.
Sperry RW (1963) Chemoaffi nity in the orderly growth of nerve fi ber patterns and connections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 50:703-710.
Tiret L, Le Mouellic H, Maury M, Brulet P (1998) Increased apoptosis of motoneurons and altered somatotopic maps in the brachial spinal cord of Hoxc-8-defi cient mice. Development 125:279-291.
Vallstedt A, Kullander K (2013) Dorsally derived spinal interneurons in locomotor circuits. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1279:32-42.
Wu Y, Wang G, Scott SA, Capecchi MR (2008) Hoxc10 and Hoxd10 regulate mouse columnar, divisional and motor pool identity of lumbar motoneurons. Development 135:171-182.
*Correspondence to: Stefan Wiese, Ph.D., stefan.wiese@rub.de.
orcid: 0000-0002-3203-5289 (Stefan Wiese)
10.4103/1673-5374.169639 http://www.nrronline.org/
Accepted: 2015-09-29
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- The role of the Rho/ROCK signaling pathway in inhibiting axonal regeneration in the central nervous system
- Targeting brain microvascular endothelial cells: a therapeutic approach to neuroprotection against stroke
- Severe bilateral anterior cingulum injury in patients with mild traumatic brain injury
- Injury of corticoreticular pathway and corticospinal tract caused by ventriculoperitoneal shunting
- Susceptibility weighted imaging in the evaluation of hemorrhagic dif use axonal injury
- Mechanical properties of nerve roots and rami radiculares isolated from fresh pig spinal cords

