Chemotactic signaling and beyond: link between interleukin-16 and axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis
Chemotactic signaling and beyond: link between interleukin-16 and axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a progressive infl ammatory, and chronic demyelinating, neurodegenerative disease of central nervous system (CNS). Autoimmune responses to myelin and other CNS antigens mediated by cluster of diff erentiation 4 (CD4+) T cells are critical for initiation and progression of disease. Migration of autoimmune T cells from the peripheral lymph organs into CNS parenchyma leads to infl ammation, demyelination and damage of axonal cytoskeleton, which manifest in decreased impulse conduction velocity of motor and sensory nerves. Myelin and axonal pathology causes motor, sensory and autonomic nerve dysfunction, including optic nerve damage leading to double or distorted vision; paresis and paralysis of extremities, painful sensations, and bladder sphincter dysfunction, manifested as bladder incontinence. Gray matter pathology in cortical and subcortical regions, including cerebellum and hippocampus underlies cognitive and behavioral dysfunction consisting of memory defi cits, depression, and ataxic gait and tremor.
Multifaceted cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in autoimmune-mediated infl ammation, demyelination, and subsequent degeneration of axonal cytoskeleton as well as neuronal cell dysfunction and demise, have been researched in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). With the development of new EAE models, signifi cance of EAE in MS studies continues to be reexamined and the importance of similarity between two diseases to be highlighted (Skundric, 2005). This autoimmune experimental model is regularly used in development and preclinical testing of MS therapy aimed at treating or ameliorating autoimmune responses observed in MS, with an ultimate goal to cure or diminish tissue damage and support axonal regeneration and repair. Multiple sclerosis is a chronic, progressive, debilitating disease, which often takes a relapsing-remitting course. Relapses and remissions of disease correspond with reappearance and clearance of infl ammatory CD4+T cells in CNS, respectively as suggested from clinical analysis, MRI data, and histopathology (Giovannoni et al., 2001; Frischer et al., 2009). There is a relative lack of EAE models resembling clinical course, clinical fi ndings and histopathology of CNS infl ammatory infi ltration, demyelination and axonal degeneration, observed in relapsing remitting MS (RRMS). In search for regulatory mechanisms underlying autoimmune CD4+Th1 cell recirculation between CNS and peripheral lymph organs and re-infi ltration underlying EAE relapse, we investigated regulation of relapses in autoimmune responses induced by immunization with immunodominant epitope of myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein, a peptide p35–55 (MOG35–55). Studies of autoimmune responses to MOG in EAE are signifi cant for MS partly because MOG is highly conserved between mouse and humans and robust immune responses to MOG peptides, including MOG35–55by CD4+Th1 cells are found in patients with RRMS. Moreover, in parallel to eliciting autoimmune cellular responses, comprised of CD4+Th1 and Th17 cells, strong antibody responses to MOG are demonstrated in RRMS and other demyelinating diseases including aquaporin-4–(AQP4–) relapsing neuromyelitis optica (NMO) and other NMO-spectrum disease (NMOSD) (Reindl et al., 2013). In attempts to study EAE, which more closely resemble RRMS clinical course, we originally created a model of relapsing-remitting EAE in response to MOG35–55in (B6 × SJL) F1 (H-2b/s) mice. In these H-2b/shybrid mice, immunization with MOG35–55induces relapsing-remitting EAE in comparison to low or non-relapsing disease in parental B6 (H-2b) mice. Infi ltrating lesions in relapsing H-2b/smice were predominated by widespread CD4+T cell infi ltration, which was followed by lesser numbers of Mac-3+macrophages, followed by appreciable B220+B, and occasional CD8+T cells. Conversely, low-relapsing H-2bmice, exhibited more abundant Mac-3+macrophages compared to CD4+T cells and other cell types, in CNS infi ltrating lesions (Skundric, 2003). Histopathology of CNS lesions in relapsing H-2b/smice resembles human MS pathology of small infi ltrates, which are found scattered throughout brain parenchyma and extensive infi ltration in meninges. We observed an important similarity of specifi c pattern of demyelination in relapsing H-2b/smice, resembling MS lesion. Most pronounced decrease in levels of myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) in MS lesions, which was suggestive of oligodendrocyte dysfunction and/or damage was detected in CNS of relapsing H-2b/sbut not in H-2bmice. Preferential loss of MAG was unanticipated in lesions induced by autoimmune responses to a diff erent myelin protein, which was MOG35–55. Similar pattern of demyelination was reported in the MS lesion subtype III, where profound loss of MAG functions as a guide of a distal oligodendrogliopathy. Depletion of MAG correlated well with that of medium chain of neurofi lament (NF160) and sharp elevation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARPp85). Neurofilaments are the major type of intermediate fi laments in adult neurons, while a nuclear enzyme PARP regulates DNA repair. Profound depletion of MAG, decrease of NF160 axonal neurofi lament and sharp elevation of PARPp85 suggested axonal dysfunction and irreversible apoptosis, respectively and correlated with severe relapsing disease in H-2b/smice (Figure 1) (Skundric et al., 2008).
To explore chemotactic mechanisms underlying a CD4+T cell predominated infl ammatory lesions in relapsing H-2b/smice, we investigated a T cell chemotactic factor, a cytokine interleukin (IL)-16 as likely candidate, though to our knowledge its relationship with MS and EAE had not been explored or suggested by others. A CD4 co-receptor specifi c ligand, IL-16, governs traffi cking and biological properties of CD4+T cells irrespective of cell activation state, through p56lck mediated signaling, which leads to the rearrangement of intracellular cytoskeleton. It was demonstrated that IL-16 induces preferential migration of CD4+Th1 compared to Th2 cells. A cytokine IL-16 controls key biological properties of CD4+T cells including cell activation, CD25 (IL-2Rα) expression, MHC class II molecule expression, co-stimulatory and inhibitory molecules expression, production of Th1, Th2 and immune modulatory cytokines and cooperation with antigen presenting cells (APC) including macrophages, dendritic cells (DC) and microglia, and communications with B and T cells, which are all of critical importance for the initiation and regulation of CD4+Th1 immune responses to myelin and other antigens. A cytokine IL-16 also regulates migration of a T regulatory (Treg) CD4+CD25+FOXP3+cells, expansion of CD4+CD25+T cells in long-term cultures propagated with IL-2, and de novo induction of FOXP-3 transcription. This cytokine modulates migration induced by chemokine receptor CCR5, which is expressed by activated cells including CD4+Th1 cells, through cross-receptor desensitization between CD4 and CCR5, which are structurally and functionally interrelated. It also modulates chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CXCR4 induced migration, which are all implicated in pathogenesis of MS. A very important feature of IL-16 lies in the fact that this is a shared molecule between the immune and nervous systems. In nervous system, IL-16 impacts on homeostatic properties of neuronal and synaptic functions. IL-16 is highly conserved across species including human and mouse. Post mitotic cerebellar granule neurons (CGN) and neurons in hippocampus contain neuronal IL-16 (NIL-16), splice variant of immune IL-16, and express CD4 molecule. In a CD4 dependent manner, IL-16 supports cultured CGN survival. Finally, IL-16 contains postsynaptic density/disc large/zona ocludens-1 (PDZ) domains, which makes this cytokine a scaff olding protein and enables important interaction with other proteins, DNA or RNA. Such interactions are signifi cant in pathogenesis of viral infection and malignant cell proliferation (Figure 2). PDZ domain related functions of IL-16bare great importance to complications of many disease-modifying therapies (DMT) of RRMS, which develop as a result of relative immune suppression or modulation. Those serious complications include increased susceptibility to viral infections and malignant cell transformation in DMT treated MS patients. Prospective IL-16 containing therapy would have unique potential to utilize PDZ domain mediated interactions in preventing common DMT complications in combination with DMT or as a single therapy. Neutralization of IL-16 was successful in treatment of MOG35–55induced relapsing-remitting EAE H-2b/smice. In this EAE therapy study, IL-16 specifi c antibody reversed paralysis, diminished CD4+T infi ltration, abrogated demyelination and axonal damage and supported re-myelination in relapsing EAE H-2b/smice. Administration of therapy as soon as onset of EAE occurred was pivotal for success of treatment. Repeated treatments at every relapsing episode had benefi cial protective eff ect (Skundric et al., 2005b).

Figure 1 Concordant depletion of myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) levels with reduction of axonal fi lament medium chain (neurofilament (NF160)) in relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) (B6 x SJL) F1 mice.Upper – Profound depletion of MAG levels in relapsing H-2b/smice. Dissimilar regulation of relative levels of MAG was observed between H-2band H-2b/smice throughout EAE. Levels of MAG in spinal cord of EAE mice were measured by western blot. Representative blot of 3–4 similar experiments shows: acute – H-2b/s(13 dpi, grade 4.5), H-2b(16 dpi, grade 4); relapse – H-2b/s(21 dpi, grade 3.5, 1strelapse), H-2b(27 dpi, grade 2, 1strelapse); and chronic-sustained – H-2b/s(72 dpi, grade 2.5). Compared to levels in control and in H-2bmice, H-2b/smice markedly reduced their relative levels of MAG during acute and chronic period. Most profound depletion of MAG was found in relapsing H-2b/smice.Lower – Distinctive reduction of NF160 levels in central nervous system in relapsing H-2b/scompared to H-2bmice. Relative levels of medium chain of axonal fi lament (NF160) were signifi cantly depleted in mice with relapsing and chronic disease. Relative levels of NF160 were measured similarly as levels of MAG (upper). Most profound drop in NF160 levels was observed in relapsing H-2b/smice.
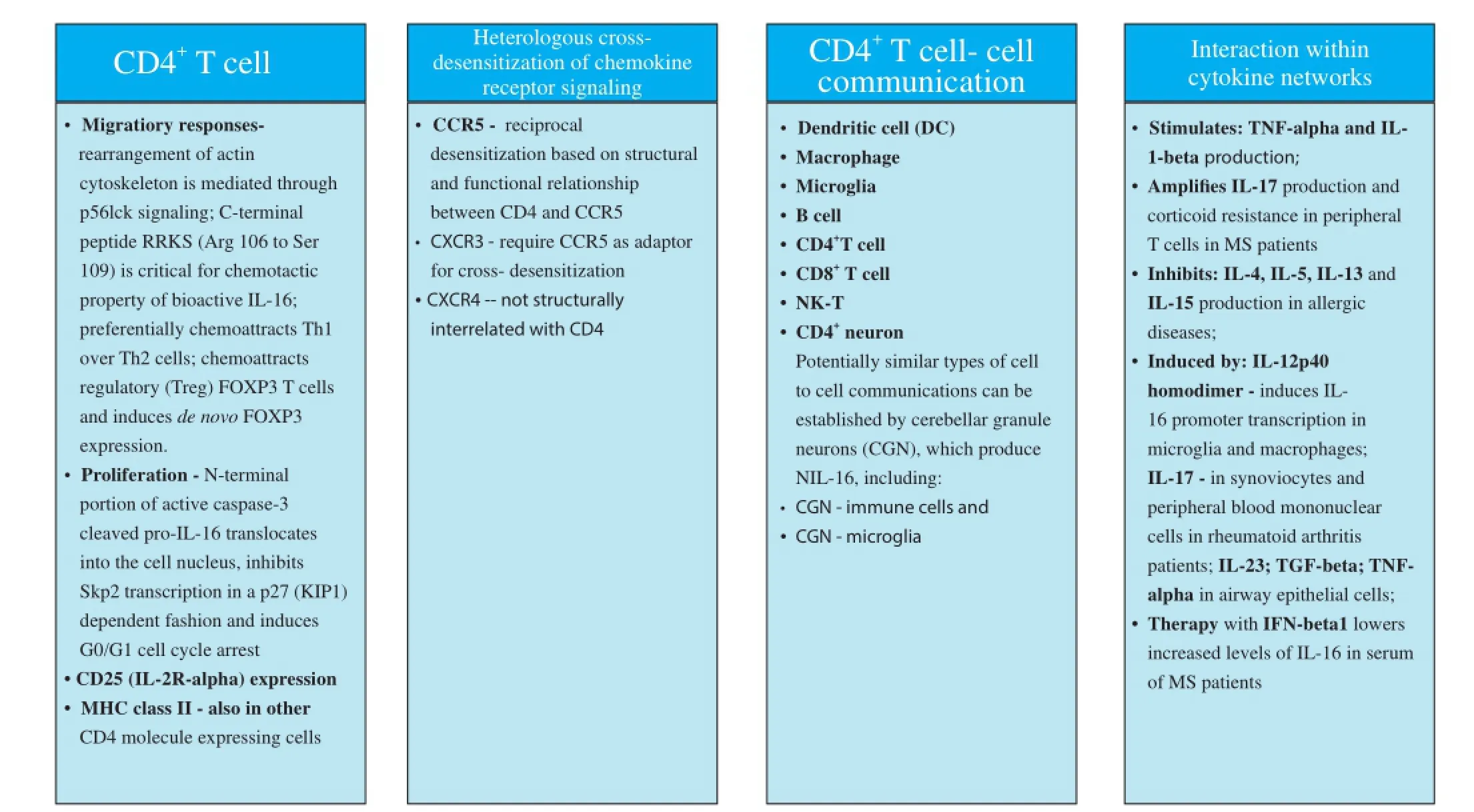
Figure 2 Interleukin 16 (IL-16) - cluster of diff erentiation 4 (CD4) receptor specifi c signaling pathway controls major biological properties.
In relapsing-remitting MOG35–55induced EAE in (B6 x SJL) F1 (H-2b/s) mice, intra-CNS production of IL-16 correlates with extensive CD4+T cell infi ltration, increased levels of active caspase-3, accompanied by phosphorylation of axonal cytoskeleton, which all peak during relapses and in chronic progressive disease. IL-16 and CD4 were co-precipitated from CNS of relapsing H-2b/smice. EAE data suggest active caspase-3 mediated release of bioactive IL-16 from infi ltrating CD4+T cells, which supports progression of local infl ammation by specifi cally enhancing traffi cking of additional CD4+T cells (Skundric et al., 2005a).
Concomitant studies of RRMS lesions and corresponding MOG35–55induced relapsing EAE in (B6 x SJL) F1 (H-2b/s) mice, revealed similar regulation and potentially roles of IL-16 in regulation of relapsing disease. IL-16 was abundantly present in CD3+, CD4+T cells, followed by CD20+B, CD8+T, CD83+dendritic cells and to some extent in Mac-1+microglia. Often, IL-16 located to CD4+T cell cytoplasm, sometimes in the cell nucleus, or polarized on the membrane towards connecting, adjoining mononuclear cells.
Similarly to data from relapsing EAE, in RRMS CNS lesions the majority of CD4+IL-16+cells were T-bet+and active caspase-3+. Increased levels of bioactive IL-16 correlated with levels of active caspase-3, T-bet, Stat-1 (Tyr701), and neurofilaments of axonal cytoskeleton [NF (M+H) P], which suggested a role for IL-16 in regulation of CD4+Th1 infl ammation and damage of axonal cytoskeleton, respectively.
In RRMS similarly to EAE relapse, peak levels of IL-16 and active caspase-3 correlated with CD4+T cell infi ltration and was found in lesions. Apart from lesions, bioactive IL-16 was located in normal appearing white matter (NAWM) and normal appearing grey matter (NAGM) in RRMS brain and spinal cord. In the MS brain, highest levels of IL-16 were detected in chronic lesions, followed by subacute and acute. Conversely, in spinal cord, acute lesions contained highest levels of IL-16. More robust increase of IL-16 was noted in spinal cord compared to brain NAWM. Sharp increase of pro-IL-16 was found in NAGM in RRMS brain (Skundric et al., 2006). Data propose regional diff erences in IL-16 regulation in CNS lesions between brain and spinal cord and a role of bioactive and pro-IL-16 in pathology of NAWM and NAGM in RRMS. Corresponding to our fi ndings of elevated IL-16 levels in situ, raised levels of IL-16 were detected in serum of MS patients. Following IFN-β1a therapy, IL-16 serum levels decreased. Authors suggested that IL-16 may serve as a biomarker for MS responses to IFN-β1a therapy (Nischwitz et al., 2014).
Results from RRMS and corresponding data from MOG35–55induced relapsing EAE in H-2b/smice suggest a role of IL-16 in neuron-immune cell communications in gray matter lesions including cerebellum and hippocampus, and in adjacent NAGM and NAWM. Grey matter lesions underlie cognitive deficits observed in MS (Howell et al., 2014). Emerging role of IL-16 in immune regulation of relapsing EAE and RRMS, which is supported by experimental data concordant with MS clinical and histopathological evidence, underscores potential of IL-16 for development of more specifi cally targeted, a CD4+Th1 cell selective therapies for RRMS and possibly other progressive infl ammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Delineating mechanisms responsible for selective enhancement of migration specifi c for CD4+T cell subsets is critical for better understanding and subsequent therapy of MS and other chronic infl ammatory and demyelinating diseases. Broader, greater insights into a mechanisms of IL-16 in regulation of other chronic and progressive infl ammatory, demyelinating and neurodegenerative diseases holds promise for development of new therapeutic approaches aimed at protection of neurons and repair of axonal function. A MOG35–55induced relapsing-remitting EAE in H-2b/smice enables insights into local regulation of pathology of myelin forming cells in CNS, oligodendrocytes, especially in studies aimed at understanding how to overcome inhibitory signals of re-myelination in CNS and help in developing therapies to foster re-myelination. This EAE model may be also employed in studies of oligodendroglial damage, which occurs as result of metabolic, vascular, or toxic insults (Skundric et al., 2015).
Dusanka S. Skundric*
Department of Immunology and Microbiology, School of Medicine, Wayne State University, Detroit, MI, USA
*Correspondence to: Dusanka S. Skundric, Ph.D., Skundric@wayne.edu.
Accepted: 2015-07-20
orcid: 0000-0002-9711-5343 (Dusanka S. Skundric)
Frischer JM, Bramow S, Dal-Bianco A, Lucchinetti CF, Rauschka H, Schmidbauer M, Laursen H, Sorensen PS, Lassmann H (2009) The relation between infl ammation and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis brains. Brain 132:1175-1189.
Giovannoni G, Miller DH, Losseff NA, Sailer M, Lewellyn-Smith N, Thompson AJ, Thompson EJ (2001) Serum infl ammatory markers and clinical/ MRI markers of disease progression in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 248:487-495.
Howell OW, Schulz-Trieglaff EK, Carassiti D, Gentleman SM, Nicholas R, Roncaroli F, Reynolds R (2014) Extensive grey matter pathology in the cerebellum in multiple sclerosis is linked to infl ammation in the subarachnoid space. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol doi: 10.1111/nan.12199.
Nischwitz S, Faber H, S?mann PG, Domingues HS, Krishnamoorthy G, Knop M, Mü ller-Arnowski F, Yassouridis A, Weber F (2014) Interferon β-1a reduces increased interleukin-16 levels in multiple sclerosis patients. Acta Neurol Scand 130:46-52.
Reindl M, Pauli F, Rostasy K and Berger T (2013) The spectrum of MOG antibody associated demyelinating diseases. Nat Rev Neurol 9:455-461.
Skundric DS (2005) Experimental models of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: Current concepts and perspective. Curr Neurovasc Res 2:349-362.
Skundric DS, Zhou W, Cruikshank WW, Dai R (2005a) Increased levels of bioactive IL-16 correlate with disease activity during relapsing experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). J Autoimmun 25:206-214.
Skundric DS, Cai J, Cruikshank WW, Gveric D (2006) Production of IL-16 correlates with CD4+Th1 infl ammation and phosphorylation of axonal cytoskeleton in multiple sclerosis lesions. J Neuroinfl ammation 3:13.
Skundric DS, Zakarian VL, Dai R, Zhou W (2008) Autoimmune-induced preferential depletion of myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) is genetically regulated in relapsing EAE (B6 x SJL) F1 mice. Mol Neurodegener 3:7.
Skundric DS, Zakarian V, Dai R, Lisak R, James J (2003) Distinct immune regulation of the response to H-2brestricted epitope of MOG causes relapsing-remitting EAE in H-2b/smice. J Neuroimmunol 136:34-45.
Skundric DS, Cruikshank WW, Montgomery PC, Lisak RP, Tse HY (2015) Emerging role of IL-16 in cytokine-mediated regulation of multiple sclerosis. Cytokine doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2015.01.005.
Skundric DS, Dai R, Zakarian VL, Bessert D, Skoff RP, Cruikshank WW, Kurjakovic Z (2005b) Anti-IL-16 therapy reduces CD4+T-cell infi ltration and improves paralysis and histopathology of relapsing EAE. J Neurosci Res 79:680-693.
10.4103/1673-5374.165294 http://www.nrronline.org/
Skundric DS (2015) Chemotactic signaling and beyond: link between interleukin-16 and axonal degeneration in multiple sclerosis. Neural Regen Res 10(11):1762-1763.
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- The role of the Rho/ROCK signaling pathway in inhibiting axonal regeneration in the central nervous system
- Targeting brain microvascular endothelial cells: a therapeutic approach to neuroprotection against stroke
- Severe bilateral anterior cingulum injury in patients with mild traumatic brain injury
- Injury of corticoreticular pathway and corticospinal tract caused by ventriculoperitoneal shunting
- Susceptibility weighted imaging in the evaluation of hemorrhagic dif use axonal injury
- Mechanical properties of nerve roots and rami radiculares isolated from fresh pig spinal cords

