Improving Acacia auriculiformis seedlings using microbial inoculant (Beneficial Microorganisms)
Bayezid M. Khan ? M.K. Hossain ? M.A.U. Mridha
Introduction
Akashmoni (Acacia auriculiformis A Cunn. ex Benth.), is a moderate-sized, evergreen, multipurpose tree under the family Leguminosae (Mimosoideae), which is native to the Savannas of Papua New Guinea, islands of the Torres Straight, and the northern areas of Australia (Luna 1996). It is an attractive fast-growing tree, planted primarily for fuel-wood production and erosion control but also as an ornamental, timber, shade bearer, and source of pulp and tannin in many tropical countries of the world (Girijashankar 2011). The species is very useful for the rehabilitation of degraded lands because of its rapid growth, ability to fix nitrogen and tolerance for a range of soil conditions: infertile, acid, alkaline, saline, moderately dry, and seasonally waterlogged (Hossain et al. 1997; Azad et al. 2011; Girijashankar 2011). The plant has already been proven successful for afforestation, reforestation and agroforestry programs in Bangladesh for its growth, short rotation, non-palatability to grazing animals, and ability to thrive in poor soil (Hossain et al. 1994; Azad et al. 2011).
To fulfill the high demand, many organizations are producing akashmoni seedlings in the nursery in Bangladesh to supply those in the plantation programs. Because the plants are grown in unfavorable soil conditions, beneficial soil microorganisms can play a significant role in early establishment and better growth of the inoculated seedlings under field conditions.
The microbial inoculant in this study, with the commercial name “Effective Microorganisms” or EM, was developed at the University of Ryukyus, Okinawa, Japan, in the early 1980s by a distinguished professor of horticulture, Dr. Teruo Higa (Kyan et al. 1999). The main species comprising EM are lactic acid bacteria (Rhodopseudomonas spp.), photosynthetic bacteria (Lactobacillus spp., Streptococcus spp.), yeast (Saccharomyces spp., Candida spp.), Actinomycetes (Streptomyces spp.) and beneficial fungi (Aspergillus spp., Penicillium spp.). The microorganisms are added into the inoculant in the manufacturing process and can survive in the inoculant liquid at pH 3.5 or below.
The density of most of the above mentioned microbes is in the range of 1 × 106to 1 × 108mL-1(Xu 2000). EM can be applied as inoculant to increase the microbial diversity of soils. It has been used with considerable success to improve soil quality and yield of crops, particularly in nature farming and organic farming systems (Xu 2000). Inoculation of EM culture can improve photosynthesis and fruit yield (Xu 2000; Wang et al. 2000). Although A. auriculiformis is used for wide range of purposes and even planted intensively in the field, the initial growth potential under the influences of microbial inoculant was not studied. Therefore, the aim of this study was to observe the effectiveness of EM inoculant on seed germination and the seedling growth of akashmoni and also to find out the best concentration of EM solution for ensuring maximum seedling development in the nursery.
Materials and methods
Collection of seeds and soils
The experiment was carried out in the nursery of the Institute of Forestry and Environmental Sciences; University of Chittagong, Bangladesh (lies approximately at the intersection of 91°50′E and 22°30′N). The seeds of A. auriculiformis were collected from the seed orchard division of Bangladesh Forest Research Institute (BFRI) where the source of seed had a mother tree of 20 years old. The soils collected from the degraded hills of the University Campus was sieved well (<3 mm) and mixed thoroughly with decomposed cow dung in a ratio of 3:1. The brown hill soils (Rashid 1991), are sandy loam to sandy clay loam, moderately to strongly acid and poorly fertile with pH <5.5, organic matter <2.0%, CEC <10 me per 100 g, BSP <40% (Osman et al. 2001). The polybags of 15 cm ×10 cm in size were filled with the prepared mixture and a thin layer of coconut husk was added to each bag as a top layer to reduce evaporation and to supply a source of organic matter.
Treatment design
There were seven treatments including control and 25 replications for each treatment. For control purposes, seeds were sown in polybags with no added EM but only water. To test the treatment options, seeds were sown with 0.1%, 0.5%, 1%, 2%, 5% and 10% concentrations of EM solution. The 50-mL solution of EM was mixed with the soils before one week of sowing the seeds and another 50-mL was applied one week after sowing the seeds. Five seeds were sown in an individual polybag to observe the influence of EM on germination on nursery conditions (temperature, 28°C; humidity, 75%). After completing germination, only one seedling (the best one) per polybag was maintained to observe the growth parameter and nodulation status of the seedlings. Partial shade and covering were provided using polythene on the nursery roof to protect the seedlings from strong sunlight and rain.
Growth measurement
Germination was recorded daily from the date of seed sowing and continuing up to the last germination. The seedlings were allowed to grow altogether for five months from the time of seed sowing. After five months, five representative seedlings from each treatment were selected for measuring growth parameters. The recorded parameters included, shoot and root lengths, collar diameter, phyllode number, fresh shoot and root weights, dry shoot and root weights, and nodulation status. For recording dry weights, shoots and roots were oven dried at 75oC for 48 h. Vigor index, volume index, and quality index were calculated according to Abdulbaki and Anderson (1973) and Dickson et al. (1960) respectively. Sturdiness was obtained by dividing shoot length (cm) with collar diameter (cm) of each seedling.
Measurement of pigment contents
The pigment contents (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoid) were determined from the fresh leaves (Phyllode) of seedlings in different treatments (Wettstein 1957; Khan 2012). Ten leaf discs were cut with a cork borer (inside diameter of 5 mm), weighed immediately after cutting, and dipped in 100% acetone in 5 mL in test tube with stopper. After 24 h of incubation, the supernatant-colored solution from the top was decanted carefully into a 25-mL volumetric flask. The leaf discs were then crushed with a blunt glass rod gently and 5 mL fresh acetone was added to the test tube and left for 15 min. Then the supernatant-colored solution from the top was again decanted to the same volumetric flask very carefully, avoiding the fragmented plant tissues. The process was repeated until the leaf fragments became colorless. Finally, the volume was made up to 25 mL with fresh acetone and the measurement was taken immediately after preparation of the solution. The measurement of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoid were made at 662 nm, 644 nm, and 440.5 nm respectively, with a spectrophotometer (Spectronic-20). The pigment contents in the extract were calculated by following the formula in Wettstein (1957).
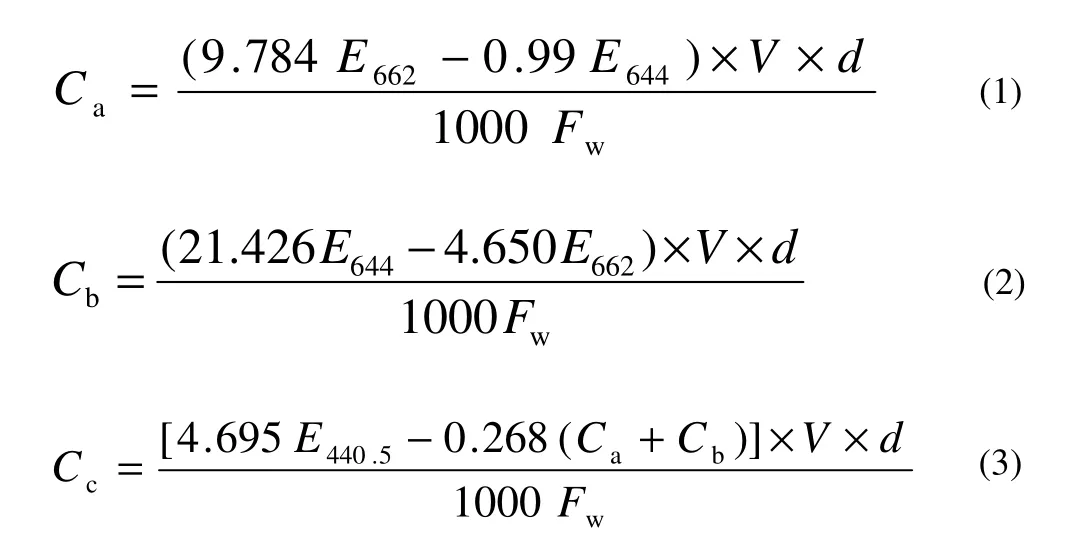
where, Cais the chlorophyll a (mg·L-1), Cbthe chlorophyll b (mg·L-1), CCthe carotenoid (mg·L-1), V the total volume (25 mL); d the dilution factor, FWthe fresh weight of leaf disc (g), and E is the absorbance at a particular wavelength (440.5, 644 and 662 nm).
All data were analyzed statistically using the computer software package, SPSS (Version 20, SPSS Incorporation, Chicago, USA). Possible significant variations among the treatments were explored by Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (DMRT). Means were separated by MS Excel (MS Office 2010). Graphs were prepared in Sigma plot (Version 12).
Results and discussion
The highest seed germination (72%) was observed in 2% EM, while the lowest (55%) was found in the control treatment. Both the highest shoot and root lengths (30.6 cm and 31.2 cm, respectively) were recorded in 2% EM solution and were significantly (p <0.05) different from control (Table 1 and Fig. 1). Collar diameter was maximum (4.53 mm) in 2% EM and was significantly (p <0.05) different from the control and 0.1%, 0.5%, and 10% EM solutions. Seedlings treated with EM had more phyllode compared to the control (Table 1).
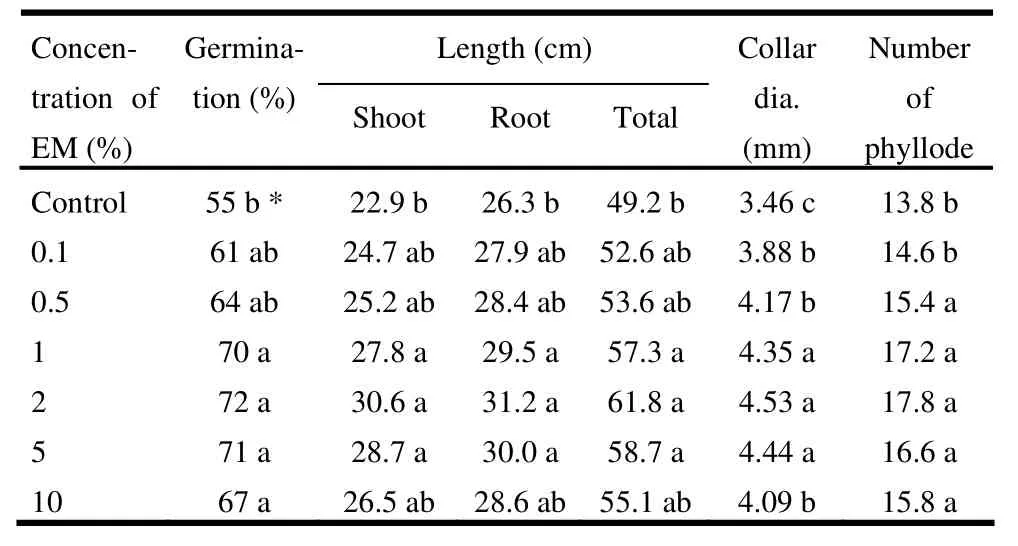
Table 1: Effect of microbial inoculant (EM) on germination rate, shoot and root lengths, collar diameter and phyllode number of Acacia auriculiformis in the nursery
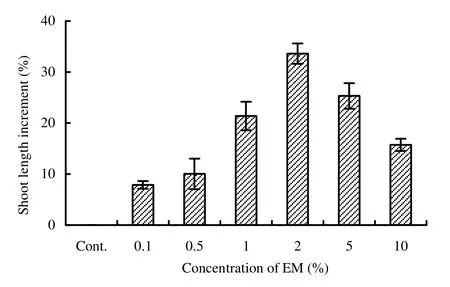
Fig. 1: Effect of microbial inoculant (EM) on shoot length increased to decreased (%) with respect to control in Acacia auriculiformis
Both fresh and dry shoot weights were maximum (8.66 g and 2.99 g, respectively) in 2% EM, whereas both fresh and dry root weights were maximum (2.56 g and 1.23 g, respectively) in 5% EM solution and were significantly (p <0.05) different from that of control (Table 2). Though maximum vigor index, volume index and sturdiness (4450, 628 and 67.5, respectively) were found in 2% EM solution (Table 2 and Fig. 2) but the maximum quality index (0.455) was found in 5% EM treatment (Fig. 3). The total dry weight increment was highest in 2% EM treatment, followed by 5% and 1% EM. Increased biomass production (shoot and root weights) in the treated seedlings might be due to the better root development. Such promotion might also be due to the biological active substances in EM (Lim et al. 1999), such as IAA and gibberellins, which improve plant growth and are produced by Rhodopseudomonas spp., Lactobacillus spp., Saccharomyces spp. and Aspergillus spp. (Chowdhury et al. 1994).

Fig. 2: Effect of microbial inoculant (EM) on sturdiness of Acacia auriculiformis
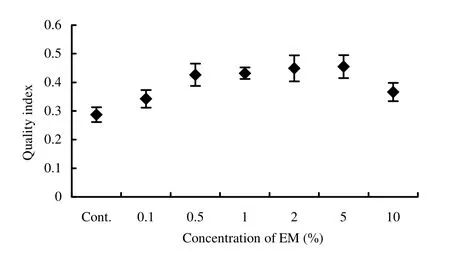
Fig. 3: Effect of microbial inoculant (EM) on quality index of Acacia auriculiformis
Microbial inoculants are being applied in Japan, United States, France, China, Brazil, Thailand and many other countries of the world. Application of EM solution can play a role in enhancing germination, growth, and yield of various agricultural crops and vegetables (Shin et al. 1995; Vongprachanch 1995; Zacharia 1995; Iwaishi 2000). EM solution with organic fertilizer and other chemicals is also reported to enhance germination, growth, and yield of different grains (Ahmed et al. 1995; Anuar et al. 1995; Xu 2000).
But the influence of EM on the forest crops has not been studied widely (Khan et al. 2005, 2006, 2011). From this study, it has been observed that soil amended with different concentrations of EM can also improve the seedling growth of forest crops. Khan et al. (2006, 2011) and Khan (2012) also reported enhanced seed germination rate and seedling growth, with the application of low concentrations of EM. However, as the concentration of EM increased, seed germination and seedling growth was depressed, which may be due to the perniciousness of higher concentration of EM (Khan 2012).

Table 2: Effect of microbial inoculant (EM) on fresh and dry weights of shoot and root, vigor index and volume index of Acacia auriculiformis
The nodule number was highest (68) in the 0.5% EM solution, followed by 65 in 0.1% EM and 61 in control treatment. It was lowest (43) in 10% EM solution (Table 3). Both fresh and dry nodule weights were maximum (1.08 g and 0.36 g, respectively), at 0.5% EM and lowest (0.62 g and 0.21 g, respectively), were in 10% EM solution. The rate of nodule increment was positive in case of 0.1% and 0.5% EM, while negative for all other treatments compared to the control (Fig. 4). The nodule dry weight increment rate was positive in 0.1%, 0.5%, and 1% EM while negative for all other treatments, with respect to control (Table 3). These results support the finding of Thach et al. (1999), that the number of nodules in soybean roots was not significant due to application of higher EM concentrations.
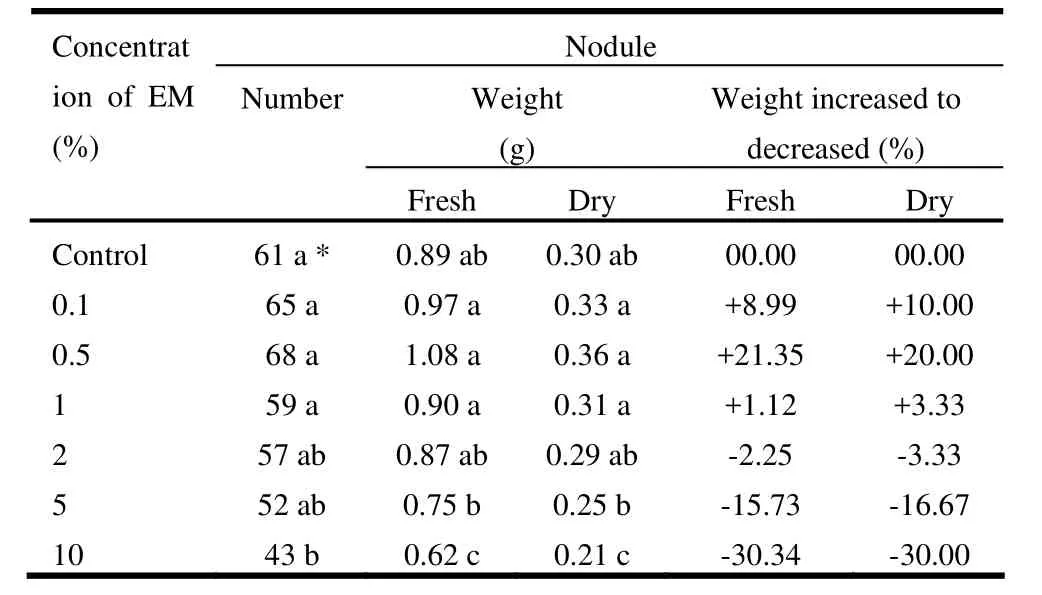
Table 3: Effect of microbial inoculant (EM) on nodule number and their fresh and dry weights of Acacia auriculiformis
Effects of EM on the contents of leaf pigments (Chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, and carotenoid), were also determined (Table 4). Chlorophyll a was highest (43.26 mg·L-1), in the 1% EM solution and lowest (26.38 mg·L-1), in the control treatment. Chlorophyll b was highest (13.56 mg·L-1) in 2% EM, followed by 12.77 mg·L-1in 10% and 11.58 mg·L-1in 5% EM solution, and was significantly different (p <0.05) from control. Carotenoid was maximum (17.99 mg·L-1) in 1% EM solution. Total pigment was recorded highest (72.7 mg·L-1), in 1% EM solution and was significantly (p <0.05) different from control. The results are in agreement with the findings of Xu (2000), Wang et al. (2000), Mridha et al. (1999, 2002), Khan et al. (2006, 2011) and Khan (2012). Low concentrations of EM with organic fertilizer promote root growth and activity to further enhance photosynthetic efficiency and yield of seedling.

Fig. 4: Effect of microbial inoculant (EM) on nodule number increased to decreased (%) with respect to control in Acacia auriculiformis
Hence, from our findings, it can be concluded that the low concentration of EM solution (up to 2%) can be recommended for gaining maximum seed germination and seedling development of A. auriculiformis in the nursery that may also be effective for seedling growth in the field.
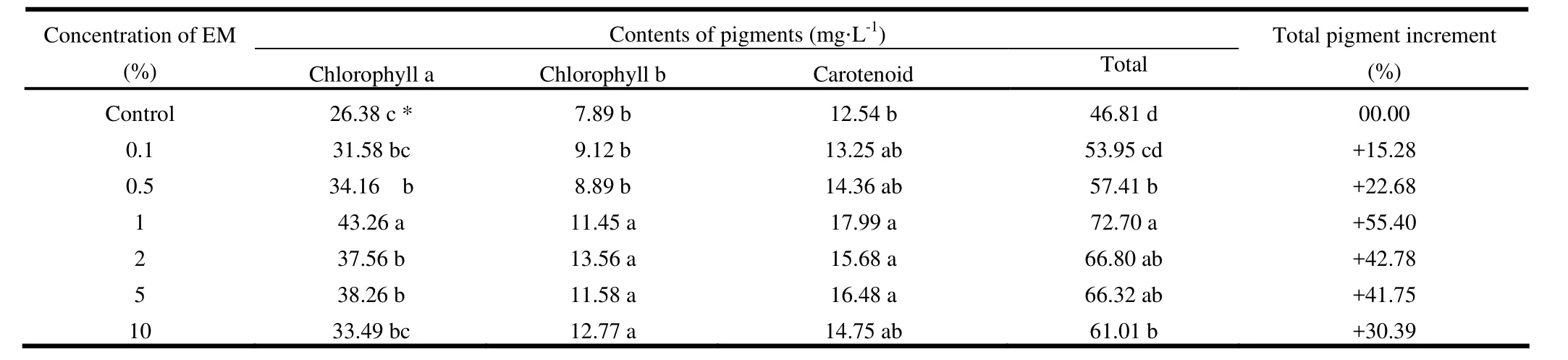
Table 4: Effect of microbial inoculant (EM) on pigment contents in fresh leaves (phyllode) of Acacia auriculiformis.
Abdul-Baki A, Anderson JD. 1973. Vigor determination in Soybean seed by multiple criteria. Crop Science, 13: 630-633.
Ahmed R, Hussain T, Jilani G, Shahid SA, Akhtar SN, Abbas MA. 1995. Use of effective microorganisms for sustainable crop production in Pakistan. In: Sharifuddin HAH, Anuar AR, Shahbudin MF. (eds), Effective Microorganisms (EM), Proceedings of the 2ndInternational Conference on Effective Microorganisms (EM). Saraburi, Thailand: Kyusei Nature Farming Center, pp. 15-27.
Anuar AR, Sharifuddin HAH, Shahbudin MF, Zaharah AR. 1995. Effectiveness of effective microorganisms (EM) on maize grown on sandy tin tailings. In: Sharifuddin HAH, Anuar AR, Shahbudin MF. (eds), Effective Microorganisms (EM), Proceedings of the 2ndInternational Conference on Effective Microorganisms (EM). Saraburi, Thailand: Kyusei Nature Farming Center, pp. 42-54.
Azad MS, Manik MR, Hasan MS, Matin MA. 2011. Effect of different pre-sowing treatments on seed germination percentage and growth performance of Acacia auriculiformis. Journal of Forestry Research, 22(2): 183-188.
Chowdhury AR, Hussain MM, Mia MS, Karim AMMS, Haider J, Bhuyan NI, Shifuddin K. 1994. Effect of organic amendments and EM on crop production in Bangladesh. In: Parr JF, Hornick SB, Simpson ME. (eds), Kyusei Nature Farming, Proceedings of the 2ndInternational Conference on Kyusei Nature Farming, Piracicaba, Brazil, pp. 155-163.
Dickson A, Leaf AL, Hosner JF. 1960. Quality appraisal of white spruce and white pine seedling stock in nurseries. The Forestry Chronicle, 36: 10-13.
Girijashankar V. 2011. Micropropagation of multipurpose medicinal tree Acacia auriculiformis. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 5(3): 462-466.
Hossain MK, Islam SA, Zashimuddin M, Tarafdar MA, Islam QN. 1997. Growth and biomass production of some Acacia and Eucalyptus species in degraded sal forest areas in Bangladesh. Indian Forester, 123(3): 211-217.
Hossain MK, Zashimuddin M, Islam SA, Tarafdar MA, Islam QN. 1994. Growth and yield of coppice crops of three Eucalyptus species in the sal forests of Bangladesh. Bangladesh Journal of Forest Science, 23(2): 61-66.
Iwaishi S. 2000. Effect of organic fertilizer and effective microorganisms on growth, yield and quality of paddy-rice varieties. Journal of Crop Production, 3(1): 269-273.
Khan BM, Hossain MK, Mridha MAU, Rafiqul Haque ATM, Huda SMS. 2005. Impact of microbial inoculants on the growth of Melia azedarach L. seedlings. Bangladesh Journal of Life Science, 17(2): 151-155.
Khan BM, Hossain MK, Mridha MAU. 2006. Effect of microbial inoculants on Albizia saman germination and seedling growth. Journal of Forestry Research, 17(2): 99-102.
Khan BM, Hossain MK, Mridha MAU. 2011. Nursery practice on seed germination and seedling growth of Dalbergia sissoo using beneficial microbial inoculants. Journal of Forestry Research, 22(2): 189-192.
Khan BM. 2012. Environmental Biology: Growth improvement of forest seedlings using beneficial microbial inoculant (effective microorganisms). Germany: Lap Lambert Academic Publishing, p. 160.
Kyan T, Shintani M, Kanda S, Sakuria M, Ohashi H, Fujisawa A, Pongdit S. 1999. Kyusei Farming and the Technology of Effective Microorganisms. Bangkok, Thailand: International Nature Farming and Research Center, Atami, Japan and Asia Pacific Natural Agriculture Network, p. 44.
Lim TD, Pak TW, Jong CB. 1999. Yields of rice and maize as affected by effective microorganisms. In: Senanayake YDA, Sangakkara UR. (eds), Kyusei Nature Farming and Effective Microorganisms, Proceedings of the 5thInternational Conference on Kyusei Nature Farming and Effective Microorganisms for Agricultural and Environmental Sustainability. Bangkok, Thailand: Embassy Suites Windsor Palace, pp. 92-98.
Luna RK. 1996. Plantation Trees. Dehra Dun, India: International Book Distributors, p. 975.
Mridha MAU, Chowdhuary HU, Xu HL, Umemura H. 1999. Influences of effective microorganisms on seed germination and seedling growth of some crop plants. In: Nature Farming and Sustainable Environment, Vol. II. Atami, Japan: International Nature Farming Research Center, pp. 125-136.
Mridha MAU, Khan BM, Hossain MK, Tasnim H, Rahman MF. 2002. Effective microorganisms (EM) for neem tree. APANews, 20: 5-6.
Osman KT, Rahman MM, Barua P. 2001. Effects of some forest tree species on soil properties in Chittagong University Campus, Bangladesh. Indian Forester, 127(4): 431-442.
Rashid H. 1991. Geography of Bangladesh. Dhaka, Bangladesh: University Press Ltd., p. 256.
Shin HS, Ryu GH, Lee JO, Lee KH. 1995. Studies of effective microorganisms (EM) and problem weeds in paddy rice field of Korea. In: Sharifuddin HAH, Anuar AR, Shahbudin MF. (eds), Effective Microorganisms (EM), Proceedings of the 2ndInternational Conference on Effective Microorganisms (EM). Saraburi, Thailand: Kyusei Nature Farming Center, pp. 82-84.
Thach NQ, Long CA, Liet VV, Trung NV, Thanh NX, Dich TV, Duong N, Tuna NK, Xuan LTH, Dan PV. 1999. Preliminary results of effective microorganisms (EM) application in Vietnam. In: Senanayake YDA, Sangakkara UR. (eds), Kyusei Nature Farming and Effective Microorganisms, Proceedings of the 5thInternational Conference on Kyusei Nature Farming and Effective Microorganisms for Agricultural and Environmental Sustainability. Bangkok, Thailand: Embassy Suites Windsor Palace, pp. 254-260.
Vongprachanch B. 1995. The use of EM fermented materials in farm trials. In: Sharifuddin HAH, Anuar AR, Shahbudin MF. Effective Microorganisms (EM), Proceedings of the 2ndInternational Conference on Effective Microorganisms (EM). Saraburi, Thailand: Kyusei Nature Farming Center, pp. 90-94.
Wang R, Xu HL, Mridha MAU. 2000. Effect of organic fertilizer and EM inoculation on leaf photosynthesis and fruit yield and quality of tomato plants. Journal of Crop Production, 3(1): 173-182.
Wettstein D. 1957. Formula of chlorophyll determination. Exp. Cell Research, 12(3): 427-489.
Xu HL. 2000. Effect of a microbial inoculants and organic fertilizer on the growth, photosynthesis and yield of sweet corn. Journal of Crop Production, 3(1): 183-214.
Zacharia PP. 1995. Studies on the application of effective microorganisms (EM) in paddy, sugarcane and vegetables in India. In: Sharifuddin HAH, Anuar AR, Shahbudin MF. (eds), Effective Microorganisms (EM), Proceedings of the 2ndInternational Conference on Effective Microorganisms (EM). Saraburi, Thailand: Kyusei Nature Farming Center, pp. 31-41.
 Journal of Forestry Research2014年2期
Journal of Forestry Research2014年2期
- Journal of Forestry Research的其它文章
- Compatibility and complementarity of indigenous and scientific knowledge of wild plants in the highlands of southwest Saudi Arabia
- Fragmentation patterns and systematic transitions of the forested landscape in the upper Amazon region, Ecuador 1990?2008
- Carbon sequestration in Chir-Pine (Pinus roxburghii Sarg.) forests under various disturbance levels in Kumaun Central Himalaya
- Genetic variability and divergence studies in pod and seed traits of Pongamia pinnata (L.) Pierre., accessions in Bay Islands
- Spatial distributions of tropical tree species in northern Vietnam under environmentally variable site conditions
- Goal programming approach for sustainable forest management (case study in Iranian Caspian forests)
