Proteomics analysis of antimalarial targets of Garcinia mangostana Linn.
Wanna Chaijaroenkul, Artitiya Thiengsusuk, Kanchana Rungsihirunrat, Stephen Andrew Ward, Kesara Na-Bangchang*
1Chulabhorn International College of Medicine, Thammasat University (Rangsit Campus), Pathumtani 12121, Thailand
2College of Public Health Sciences, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 10330, Thailand
3Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, University of Liverpool, Liverpool L3 5QA, United Kingdom
Proteomics analysis of antimalarial targets of Garcinia mangostana Linn.
Wanna Chaijaroenkul1, Artitiya Thiengsusuk1, Kanchana Rungsihirunrat2, Stephen Andrew Ward3, Kesara Na-Bangchang1*
1Chulabhorn International College of Medicine, Thammasat University (Rangsit Campus), Pathumtani 12121, Thailand
2College of Public Health Sciences, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok 10330, Thailand
3Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology, Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, University of Liverpool, Liverpool L3 5QA, United Kingdom
PEER REVIEW
Peer reviewer
Parnpen Viriyavejakul, Mahidol University, Faculty of Tropical Pathology. E-mail: parnpen.vir@ mahidol.ac.th
Co-reviewer: Raewadee Wisedpanichkij, Bangkok, Thailand.
Comments
The paper is a basic research which looked at new antimalarial targetmangosteen extract and concluded its effect through glycolysis pathway.
Details on Page 519
Objective:To investigate possible protein targets for antimalarial activity of Garcinia mangostana Linn. (G. mangostana) (pericarp) in 3D7 Plasmodium falciparum clone using 2-dimensional electrophoresis and liquid chromatography mass-spectrometry (LC/MS/MS).
Malaria, Proteomics, Garcinia mangostana Linn.
1. Introduction
The success in elucidation of genome sequences of several micro-organisms includingPlasmodium falciparum (P. falciparum)in the pre-genomic era has challenged research for identification of potential proteomic markers correlated disease pathology, as well as protein targets of candidate drugs and vaccines in the post genomic era. Proteomics analysis is the large-scale study of proteins, particularly their structures and functions. It determines global protein expression including sub-cellular localization and posttranslational modification. The approach is much more complicated than the genomics approach due to the fact that, while the genome of an organism is relatively stable, its proteome differs from cell to cell and from time to time. This is because distinct genes are expressed in distinct celltypes. Detection of a marked change in the expression of proteins that are vital for the survival of a micro-organism represents one of the most important strategies in drug discovery research. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis (2-DE) is the common technique applied for investigation of the change in these expressed proteins. The proteins are firstly electrophoresed in one direction, followed by another direction which allows for the visualization of a small change in protein expression which is finally identified by mass spectrometry[1,2].
A large number of medicinal plants have been identified as potential antimalarial agents. The antimalarial activity ofGarcinia mangostana(G. mangostana) Linn. or mangosteen has previously been reported with IC50(concentration which inhibits parasite growth by 50%) ranging from 4.5 to 12.6 μg/mL[3,4]. Variety of biological activities of xanthones isolated from this fruit pericarp has also been reported[5-7]. The aim of the present study was to identify protein targets for antimalarial activity ofG. mangostanaLinn. (pericarp) in 3D7P. falciparumclone using 2-DE and liquid chromatography mass-spectrometry (LC/MS/MS).
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Crude extract of G. mangostana Linn. (pericarp), chemicals and reagents
TheG. mangostanafruit pericarps were washed, cut into small pieces, air-dried, weighed and ground into powder. The powder was then soaked in ethanol until exhaustion. The ethanol extract was filtrated and evaporated under reduced pressure by rotary evaporation. The extract yield was weighed and stored at -20 °C until used.
2.2. Assessment of antimalarial activity of crude ethanolic extract of G. mangostana Linn. in vitro
3D7P. falciparumclone was used in this study. The parasite was cultured according to the method of Trager and Jensen with some modifications[8]. Antimalarial activity of the crude ethanolic extract ofG. mangostanaLinn. (pericarp) was investigated using SYBR Green I assay[9,10]. Highly synchronous ring stage parasite was used in each assay. An aliquot of parasite inoculum (50 μL) with 2% parasitaemia and 1% haematocrit was added into each well of a 96-well microtiter plate. The 96-well drug plates were dosed with the extract at eight final concentrations as follows: 0.78125, 1.5625, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 and 100 μg/mL. The experiment was done in triplicate. The IC50and IC90values used as indicators of antimalarial activity were determined from a log-dose-response curve plotted using the CalcusynTMversion 1.1 (BioSoft, Cambridge, UK).
2.3. Extraction of P. falciparum proteins following exposure to the ethanolic extract of G. mangostana Linn.
Synchronized 3D7P. falciparumwas exposed to the ethanolic extract ofG. mangostanaLinn. at the IC50and IC90for 12 h. Parasite culture was harvested and cell pellet was re-suspended in 0.15% saponin and incubated on ice for 1 h in order to lyse red blood cells. The lysate was collected through centrifugation at 8 500 r/min for 5 min (4 °C) and washed three times with 1 mL of 50 mmol/L Tris (pH 7.5) until the supernatant was clear. The parasite pellet was resuspended in 500 μL of rehydration buffer (8 mol/L urea, 2 mol/L thiourea, 2% CHAPS, 65 mmol/L DL-Dithiothreitol, 1% ampholyte (pH 3-10), and 1× of protease inhibitor). Sample was vortexed and sonicated on ice for four times, six seconds each (21% amplitude, 6 seconds, interspersed with 9 seconds), followed by centrifugation at 8 500 r/min for 1 h (4 °C). Protein concentration was measured using Bradford reagent (BioRad Co. Ltd., California, USA) and the supernatant was subjected to 2-DE analysis[11,12].
2.4. 2-DE
The extract of parasite protein (100 μg) was mixed with rehydration buffer (8 mol/L urea, 1% CHAP, 15 mmol/L dithiothretol, and 0.001% bromophenol blue) to prepare 125 μL of protein mixture and then applied onto 7 cm immobilized pH gradient strips (non-linear) with a pH range of 3-10 in an isoelectric focusing (IEF) system (PROTEAN? i12? IEF Cell, BioRad Co. Ltd., California, USA). The IEF was initially performed at 250 V for 15 min, followed by 4 000 V for 1 h and 4 000-20 000 volt-hour. The focused strips were equilibrated in equilibration solution I [10 mL of 50 mmol/L Tris-HCl pH 8.8, 6 mol/L urea, 30% glycerol, and 2% sodium dodecyl sulfonate (SDS)] containing the reducing agent DL-Dithiothreitol (100 mg) for 10 min, followed by equilibration solution II (5 mL) containing iodoacetamide (450 mg) for additional 10 min. Finally, the strips were equilibrated with 1× electrode buffer (pH 8.3) for 10 min. The strips were then loaded onto 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for second dimension separation. The gels were run on 1× electrode buffer (pH 8.3). After electrophoresis, gels were fixed and stained with silver stain (BioRad Co. Ltd., California, USA) according the manufacturer’s recommendation. The 2-DE gel images were scanned and analyzed using PDQuestTMsoftware (BioRad Co.Ltd., California, USA). At least four independent gels were analyzed for each sample group.
2.5. Identification of proteins
Selection of protein spots separated by 2-dimensional gels was guided through images on quadruple gels. Briefly, the excised gel spot was put into a 1.5 mL centrifuge tube and acetonitrile (400 μL) was added. The mixture was incubated at room temperature for 10 min. The gel slices were then incubated overnight at 37 °C in 10-20 μL of sequence grade trypsin (Sigma, Dorset, UK) (10 μg/mL of 25 mmol/L ammonium bicarbonate with 10% acetonitrile). The supernatant was collected through centrifuge at 6 560 r/min (4 °C), and the gel was incubated with 20 μL of the mixture of acetonitrile and 100 mmol/L ammonium bicarbonate (2:1, v/v) at room temperature for 15 min. The supernatant was removed and pooled together with the first aliquot. The combined supernatant was dried in a rotational vacuum concentrator (at 37 °C for 3 h), and the dried samples were kept at -80 °C until used.
The sample was re-suspended in 20 μL of 0.1% formic acid and centrifuge at 8 500 r/min (4 °C) for 20 min. Proteins were separated using nano-flow high-performance liquid chromatography on a C18 reverse phase Dionex Ultimate 3000 column (Thermo Scientific, California, USA) and the mobile phase consisting of 50% acetonitrile for 30 min. The elute proteins were detected using LTQ ion-trap mass spectrometer (Thermo Scientific, California, USA). The resulting MS/MS spectra were submitted to TurboSequest Bioworks version 3.1 (Thermo Electron, California, USA) and the individual spectrum was merged into an MGF file before submitting to Mascot (v2.2).
3. Results
The median (range) IC50and IC90values of the ethanolic extract ofG. mangostanaLinn. (pericarp) for the 3D7P. falciparumclone were 12.6 (10.5-13.2) and 27.3 (24.7-48.4) μg/ mL, respectively. The patterns of protein spots separated from the parasite extract following exposure to 12 (IC50) and 30 (IC90) μg/mL of the plant extract including the nonexposed parasite are shown in Figure 1. The number of protein spots from the parasite extract following exposure to 12 and 30 μg/mL and the control were 102, 73 and 95, respectively. The number of matched protein spots with the control for the parasite exposed to the plant extract at the concentrations of 12 and 30 μg/mL were 84 (82%) and 11 (15%), respectively. Among these matched spots, the number of clear up-regulated protein spots (at least 3 out of 4 spots) were 22 and 11 for the parasite extract following exposure to 12 and 30 μg/mL extract, respectively (Table 1 and 2). The six protein spots at least two-fold upregulated were identified by LC/MS/MS as phosphoglycerate mutase putative (PGM1), L-lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)/ glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), and fructose-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) (Table 3). All these proteins were enzymes that play role in glycolysis pathway. The proteosome subunit putative protein was found only in parasite extract following exposure to 30 μg/mL of the plant extract.
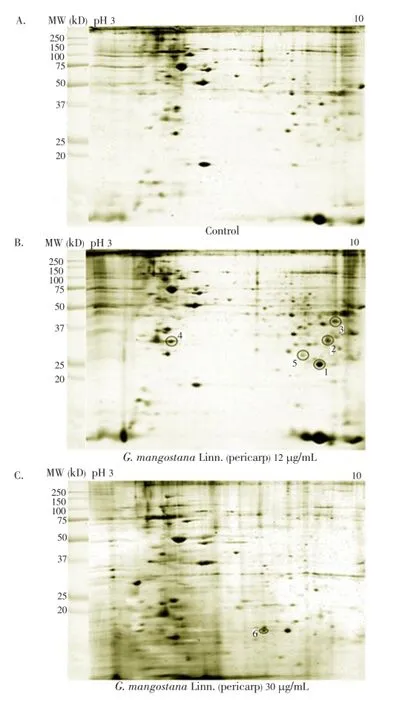
Figure 1. Differential expression of protein spots from the extract of 3D7 P. falciparum separated by 2-DE: (A) control (non-exposed), (B) following exposure to the extract of G. mangostana Linn. (pericarp) at the IC50level (12 μg/mL), and (C) following exposure to the extract of G. mangostana Linn. (pericarp) at the IC90level (30 μg/mL).
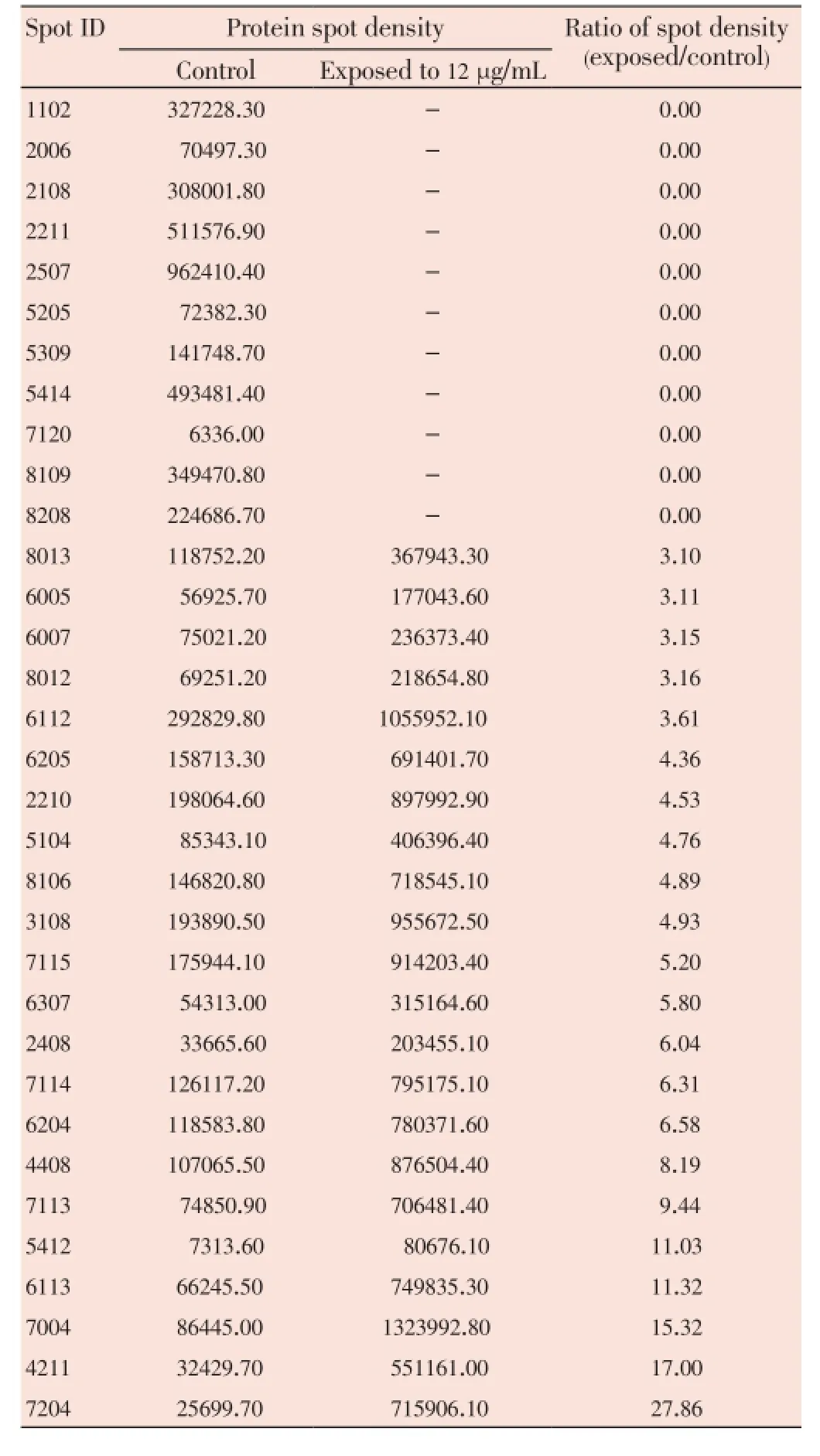
Table 1 Comparison of 2-DE protein spots from 3D7 P. falciparum exposure to G. mangostana Linn. (pericarp) at 12 μg/mL with at least 2-fold increase in density compared with control.
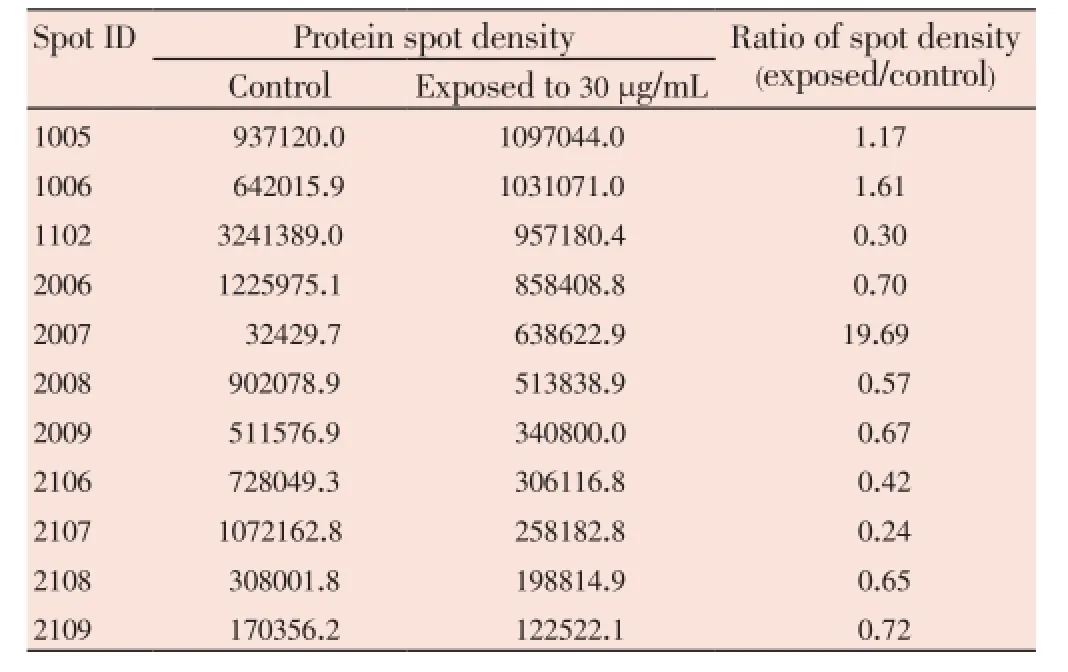
Table 2 Comparison of 2-DE protein spots from 3D7 P. falciparum exposure to G. mangostana Linn. (pericarp) at 30 μg/mL with at least 2-fold increase in density compared with control.
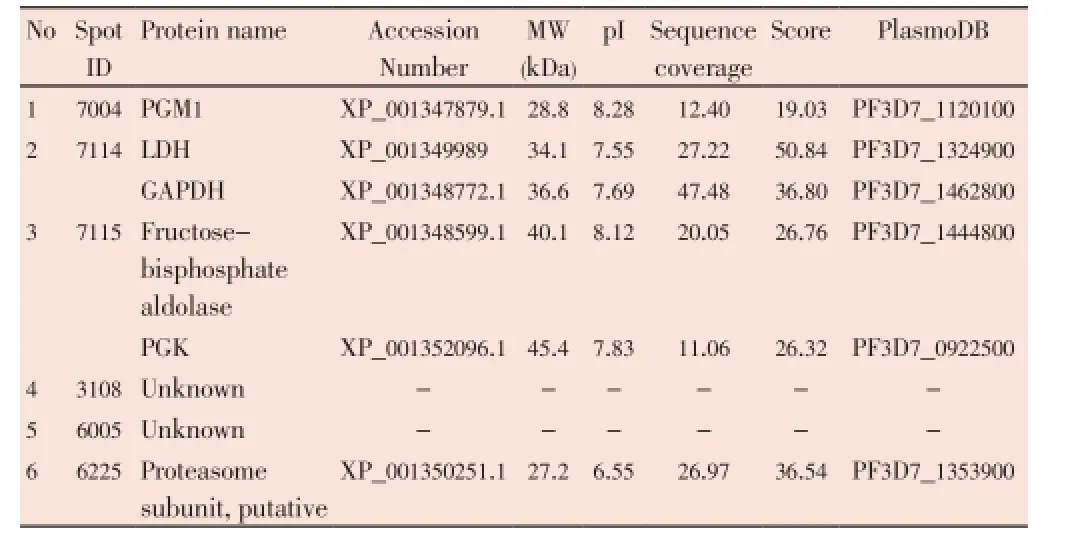
Table 3 Identification of protein spots (by LC/MS/MS) separated from the extract of 3D7 P. falciparum following exposure to the extract of G. mangostana Linn. (pericarp) at either concentration of IC50(12 μg/mL) or IC90(30 μg/mL).
4. Discussion
The proteomics approach is a potential tool for target identification in the discovery of medicines and vaccines. For malaria research in the post-genomics era, this tool has facilitated the search for new promising targets that are selective and biologically significant for parasite’s growth and survival. Nevertheless, the application of 2-DE in the investigation of malaria parasite proteomes has been limited due to the problem relating to the extraction and solubilization of parasite proteins. In our previous study, the ethanolic extract ofG. mangostanaLinn. (pericarp) was shown to exhibit good to moderate antimalarial activity with IC50of 4.5-12.6 μg/mL[4]. In the present study, the proteomics approach was applied to analyze possible malarial parasite’s protein targets ofG. mangostanaLinn. (pericarp). Difference in protein patterns of 3D7P. falciparumextract following exposure to the plant extract at the concentrations of 12 (IC50) and 30 (IC90) μg/mL was observed. At the IC50concentration, about 82% of the expressed parasite proteins were found to be matched with the control, while at the IC90concentration, only 15% matched proteins were found. The possible explanation for this phenomenon is that the concentration at IC90level was too high to detect an initial change in protein expression. This supposition was supported by the detection of proteasome subunit protein expressed following parasite’s exposure to the extract at the IC90level. Although malaria parasites critically rely on lysosomes and the ubiquitin proteasome system for their growth and survival[13,14], this proteasome subunit protein plays a major role in the degradation of cellular contents of the damaged parasites[13,14]. Following parasite’s exposure to the extract at the IC50level on the other hand, an initial change in protein expression was observed, but with absence of this protein. The expression of proteins that were markedly changed (at least three-fold up-regulated) are proteins which are involved in the glycolysis pathway,i.e., PGM1, LDH/GAPDH, and fructose-bisphosphate aldolase/PGK[15,16]. The malaria parasite utilizes glucose for energy production, which is converted to lactate[15]. Several glycolytic intermediates may be diverted into other products that serve as precursors for the synthesis of other final products, particularly those involved in the redox system[16]. In the footprinting metabolites, pyruvates were expressed at the level of aboutsix times of the control (Chaijaroenkulet al, unpublished data). The metabolism of pyruvate may provide intermediates in several biosynthetic pathways. Furthermore, direct evidence showed thatG. mangostanaLinn. (pericarp) might affect glucose or glycolysis pathway of malaria parasite.
The proteomics approach is a potential tool for target identification in the drug discovery. Investigation of possible protein targets for antimalarial activity of ethanolic extract ofG. mangostanaLinn. suggested that the glycolysis pathway may be the major protein target from this extract.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by The National Research Council of Thailand, (Grant No.034/2556) and the Commission on Higher Education, Ministry of Education of Thailand (NRU Project). Wanna Chaijaroenkul receives financial support from Thailand Research Fund, (Grant No. MRG5380192). We would like to thank Dr. Gavin Laing for protein analysis (LC/
MS/MS).
Comments
Background
Though, its clinical application is far from present, the present paper has generated a significant contribution of the proof of concept, and deeper understanding of using mangosteen extract as antimalarial drug target.
Research frontiers
The paper addresses the effect of mangosteen extract on malaria glycolysis pathway. Methodology applied is straight forward and has yielded appreciable results. The work generated scientific idea to bridge between “concept” and future “clinical application”.
Innovations and breakthroughs
The paper concluded that mangosteen affects parasite glycolysis pathway. The paper initiates further research interest in looking for new antimarial drug target using medicinal plants/fruits parts.
Applications
The proteomics approach is a potential tool for target identification in the drug discovery. Investigation of possible protein targets for antimalarial activity of ethanolic extract ofG. mangostanaLinn. suggested that the glycolysis pathway may be the major protein target from this extracts.
Peer review
The paper is a basic research which looked at new antimalarial target-mangosteen extract and concluded its effect through glycolysis pathway.
[1] Brewis IA, Brennan P. Proteomics technologies for the global identification and quantification of proteins. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 2010; 80: 1-44.
[2] Stoyanov A. IEF-based multidimensional applications in proteomics: toward higher resolution. Electrophoresis 2012; 33(22): 3281-3290.
[3] Mahabusarakam W, Kuaha K, Wilairat P, Taylor WC. Prenylated xanthones as potential antiplasmodial substances. Planta Med 2006; 72(10): 912-916.
[4] Thiengsusuk A, Chaijaroenkul W, Na-Bangchang K. Antimalarial activities of medicinal plants and herbal formulations used in Thai traditional medicine. Parasitol Res 2013; 112(4): 1475-1481.
[5] Shan T, Ma Q, Guo K, Liu J, Li W, Wang F, et al. Xanthones from mangosteen extracts as natural chemopreventive agents: potential anticancer drugs. Curr Mol Med 2011; 11(8): 666-677.
[6] Obolskiy D, Pischel I, Siriwatanametanon N, Heinrich M. Garcinia mangostana L.: a phytochemical and pharmacological review. Phytother Res 2009; 23(8): 1047-1065.
[7] Pedraza-Chaverri J, Cardenas-Rodriguez N, Orozco-Ibarra M, Perez-Rojas JM. Medicinal properties of mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana). Food Chem Toxicol 2008; 46(10): 3227-3239.
[8] Trager W, Jensen JB. Human malaria parasites in continuous culture. Science 1976; 193(4254): 673-675.
[9] Bennett TN, Paguio M, Gligorijevic B, Seudieu C, Kosar AD, Davidson E, et al. Novel, rapid, and inexpensive cell-based quantification of antimalarial drug efficacy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004; 48(5): 1807-1810.
[10] Smilkstein M, Sriwilaijaroen N, Kelly JX, Wilairat P, Riscoe M. Simple and inexpensive fluorescence-based technique for high-throughput antimalarial drug screening. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2004; 48(5): 1803-1806.
[11] Makanga M, Bray PG, Horrocks P, Ward SA. Towards a proteomic definition of CoArtem action in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Proteomics 2005; 5(7): 1849-1858.
[12] Rungsihirunrat K, Chaijaroenkul W, Siripoon N, Seugorn A, Thaithong S, Na-Bangchang K. Comparison of protein patterns between Plasmodium falciparum mutant clone T9/94-M1-1(b3) induced by pyrimethamine and the original parent clone T9/94. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2012; 2(1): 66-69.
[13] Chung DW, Ponts N, Prudhomme J, Rodrigues EM, Le Roch KG. Characterization of the ubiquitylating components of the human malaria parasite’s protein degradation pathway. PLoS One 2012; doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043477.
[14] Rosenthal PJ. Falcipains and other cysteine proteases of malaria parasites. Adv Exp Med Biol 2011; 712: 30-48.
[15] Sander BJ, Lowery MS, Kruckeberg WC. Glycolytic metabolism in malaria infected red cells. Prog Clin Biol Res 1981; 55: 469-490.
[16] MacRae JI, Dixon MW, Dearnley MK, Chua HH, Chambers JM, Kenny S, et al. Mitochondrial metabolism of sexual and asexual blood stages of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. BMC Biol 2013; 11: 67.
10.12980/APJTB.4.2014APJTB-2014-0043
*Corresponding author: Prof. Dr. Kesara Na- Bangchang, Chulabhorn International College of Medicine, Thammasat University (Rangsit Campus), Pathumtani 12121, Thailand.
Tel: +662-564-4440-79 Ext.1803
Fax: +662-564-4398
E-mail: kesaratmu@yahoo.com
Foundation Project: supported by The National Research Council of Thailand, (Grant No.034/2556) and Thailand Research Fund, (Grant No. MRG5380192).
Article history:
Received 28 Apr 2014
Received in revised form 5 May, 2nd revised form 13 May, 3rd revised form 20 May 2014
Accepted 15 Jun 2014
Available online 28 Jul 2014
Methods:3D7 Plasmodium falciparum was exposed to the crude ethanolic extract of G. mangostana Linn. (pericarp) at the concentrations of 12μg/mL (IC50level: concentration that inhibits parasite growth by 50%) and 30 μg/mL (IC90level: concentration that inhibits parasite growth by 90%) for 12 h. Parasite proteins were separated by 2-dimensional electrophoresis and identified by LC/MS/MS.
Results:At the IC50concentration, about 82% of the expressed parasite proteins were matched with the control (non-exposed), while at the IC90concentration, only 15% matched proteins were found. The selected protein spots from parasite exposed to the plant extract at the concentration of 12 μg/mL were identified as enzymes that play role in glycolysis pathway, i.e., phosphoglycerate mutase putative, L-lactate dehydrogenase/glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and fructose-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphoglycerate kinase. The proteosome was found in parasite exposed to 30 μg/mL of the extract.
Conclusions:Results suggest that proteins involved in the glycolysis pathway may be the targets for antimalarial activity of G. mangostana Linn. (pericarp).
 Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2014年7期
Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine2014年7期
- Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine的其它文章
- Reticulo-cutaneous fistula due to the ingestion of a long metallic rod in a cow
- Clinical, radiological and molecular diagnosis correlation in serum samples from patients with osteoarticular tuberculosis
- Anti-diabetic effects of Caulerpa lentillifera: stimulation of insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells and enhancement of glucose uptake in adipocytes
- Down-regulated expression of NPM1 in IMS-M2 cell line by (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate
- Knowledge, attitude, and practices related to cutaneous leishmaniasis in an endemic focus of cutaneous leishmaniasis, Southern Iran
- An initial study of insect succession on decomposing rabbit carrions in Harare, Zimbabwe
