Relationship between different surgical methods, hemorrhage position, hemorrhage volume, surgical timing, and treatment outcome of hypertensiveintracerebral hemorrhage
Feng-ling Chi, Tie-cheng Lang, Shu-jie Sun, Xue-jie Tang, Shu-yuan Xu, Hong-bo Zheng, Hui-song Zhao
1Department of Neurosurgery, Shanghai 7th Hospital, Shanghai 200137, China
2Yueyang Hospital Af fi liated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China
3Emergency Medicine Department, Dongfang Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai, China
4Second Hospltal of Dalian Medical University, Dlian, China
5Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Shanghai, China
6First People's Hospital of Qiqihaer City, Heilongjiang Province, China
7Third Af fi liated Hospital, Qiqihar Medical College, Heilongjiang Province, China
Corresponding Author:Shu-jie Sun, Email: sunshujie11@126.com
Relationship between different surgical methods, hemorrhage position, hemorrhage volume, surgical timing, and treatment outcome of hypertensive
intracerebral hemorrhage
Feng-ling Chi1, Tie-cheng Lang2, Shu-jie Sun3, Xue-jie Tang4, Shu-yuan Xu5, Hong-bo Zheng6, Hui-song Zhao7
1Department of Neurosurgery, Shanghai 7th Hospital, Shanghai 200137, China
2Yueyang Hospital Af fi liated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai 200437, China
3Emergency Medicine Department, Dongfang Hospital of Shanghai, Shanghai, China
4Second Hospltal of Dalian Medical University, Dlian, China
5Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Shanghai, China
6First People's Hospital of Qiqihaer City, Heilongjiang Province, China
7Third Af fi liated Hospital, Qiqihar Medical College, Heilongjiang Province, China
Corresponding Author:Shu-jie Sun, Email: sunshujie11@126.com
BACKGROUND:The present study aimed to explore the relationship between surgical methods, hemorrhage position, hemorrhage volume, surgical timing and treatment outcome of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage (HICH).
METHODS:A total of 1 310 patients, who had been admitted to six hospitals from January 2004 to January 2008, were divided into six groups according to different surgical methods: craniotomy through bone fl ap (group A), craniotomy through a small bone window (group B), stereotactic drilling drainage (group C1 and group C2), neuron-endoscopy operation (group D) and external ventricular drainage (group E) in consideration of hemorrhage position, hemorrhage volume and clinical practice. A retrospective analysis was made of surgical timing and curative effect of the surgical methods.
RESULTS:The effectiveness rate of the methods was 74.12% for 1 310 patients after onemonth follow-up. In this series, the disability rate was 44.82% 3–6 months after the operation. Among the 1 310 patients, 241 (18.40%) patients died after the operation. If hematoma volume was >80 mL and the operation was performed within 3 hours, the mortality rate of group A was signi fi cantly lower than that of groups B, C, D, and E (P<0.05). If hematoma volume was 50–80 mL and the operation was performed within 6–12 hours, the mortality rate of groups B and D was lower than that of groups A, C and E (P<0.05). If hematoma volume was 20–50 mL and the operation was performed within 6–24 hours, the mortality rate of group C was lower than that of groups A, B and D (P<0.05).
CONCLUSIONS:Craniotomy through a bone fl ap is suitable for patients with a large hematoma and hernia of the brain. Stereotactic drilling drainage is suggested for patients with hematoma volume less than 80 mL. The curative effect of HICH individualized treatment would be improved via the suitable selection of operation time and surgical method according to the position and volume of hemorrhage.
Hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage; Hemorrhage position; Hemorrhage volume; Surgical timing; Stereotactic drilling drainage; Treatment effect; Individualized; Polycentric
INTRODUCTION
The curative effect of standardized treatments for hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage (HICH) has shown that standardized surgical treatment is superior to standardized medication.[1,2]Many surgical methods are available for HICH, but physicians proposed surgical methods should be individualized. There is dispute over the timing of surgery. With the wide use of directional hose drainage,[3]the curative effect of minimally invasive surgery has been further approved.[4–7]Therefore we conducted a polycentric and retrospective study in 1 310 HICH patients to analyze the relationship between the surgical methods, surgical timing, and outcomes.
METHODS
Data sources
From January 2004 to January 2012, 1 310 patients were operated on separately at the Seventh People's Hospital of Shanghai, the Second Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Yueyang Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Gongli Hospital of Shanghai Pudong New Area, the First People's Hospital of Qiqihaer City, and the Third Affiliated Hospital of Qiqihar Medical College. The patients were divided into six groups: craniotomy through bone fl ap (group A), craniotomy through a small bone window (group B), stereotactic drilling drainage (group C1 and group C2), neuron-endoscopy operation (group D), and external ventricular drainage (group E).
Inclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria for the patients in this study were as follows: (1) meeting the diagnosis criteria of hypertension cerebral hemorrhage;[8](2) CT: hemorrhage from the subcortex, basal ganglia, internal capsule or thalamus, with (without) the brain ventricle, and hematoma volume≥20 mL; (3) GCS scores≥5; (4) stable vital signs; (5) no serious visceral diseases or clotting disorders; and (6) age≤70 years old.
Exclusion criteria
Exclusion criteria for the patients in the study were as follows: age>70 years old; (2) GCS<5; (3) hemorrhage in the cerebellum and brain stem; (4) serious visceral disease or clotting disorders; (5) cerebral aneurysms, vascular malformation, hemorrhage; and (6) lost follow-up.
Selection of surgical timing
In patients with massive hemorrhage (>80 mL) and cerebral hernia, surgery was performed immediately. In those with a medium hemorrhage volume of 50–80 mL and consciousness or with light disturbance of consciousness, the optimal operation time was within 6–24 hours. In those patients with a little hemorrhage volume of 20–50 mL and a gradually increased hematoma, the timing of surgery should be made according to the real situation.
Selection of surgical method
In group A, there were a hemorrhage volume of >80 mL and cerebral hernia with a hematoma in the shallow or deep part of the brain. In group B, there were a hemorrhage volume of 50–80 mL, stable condition or cerebral hernia at early stage, the removal of hematoma that led to a hematoma shallow in the brain with sufficient decompression after the surgery and ventricle cast-form. In group C1, there were a hemorrhage volume of 50–80 mL and a stable condition or hematoma in the shallow or deep part of the brain with early stage indications of cerebral hernia. In group C2, there were a hemorrhage volume of 20–49 mL and a hematoma in the shallow or deep part of the brain. In group D, there were a hemorrhage volume of 50–80 mL, neural endoscopic operation conditions, light disturbance of consciousness or hematoma in the shallow or deep part of the brain at early stage of cerebral hernia, and ventricle cast. In group E, there was a ventricular hemorrhage or a medial hemorrhage breaking into the ventricles leading to obstructive hydrocephalus.
General information of patients
General information of patients is illustrated in Tables 1, 2, and 3.
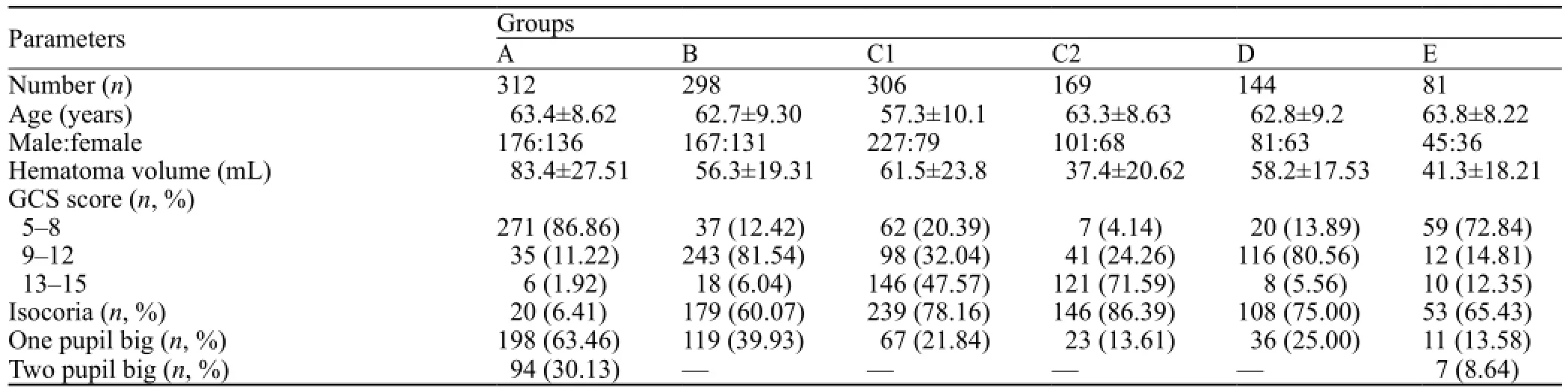
Table 1. General information of the 1 310 HICH patients
Evaluation of curative effect
Curative effect was evaluated based on the following:[4](1) decreased neural function defect score (NFDS); (2) the recovered activity of daily living (ADL): function defect assessment reduced by 91%–100%, ADL level I; (3) remarkable progress: function defect assessment reduced by 46%–90%, ADL level II; (4) progress: function defect assessment reduced by 11%–45%, ADL level III; (5) improvement: function defect assessment reduced by ≤10%, ADL level IV; and (6) worsening: function defect assessment increased by≥10%, ADL level V.
In the first month after the operation, according to the criteria of neurological defect scores for clinicalstroke, the short-term curative effect was evaluated by the reduced percentage. The patients who were classified into categories of recovery, remarkable progress, progress and improvement were considered to be effectively treated. At 3–6 months after the operation, the long-term curative effect was determined by the defect level of ADL.[8]
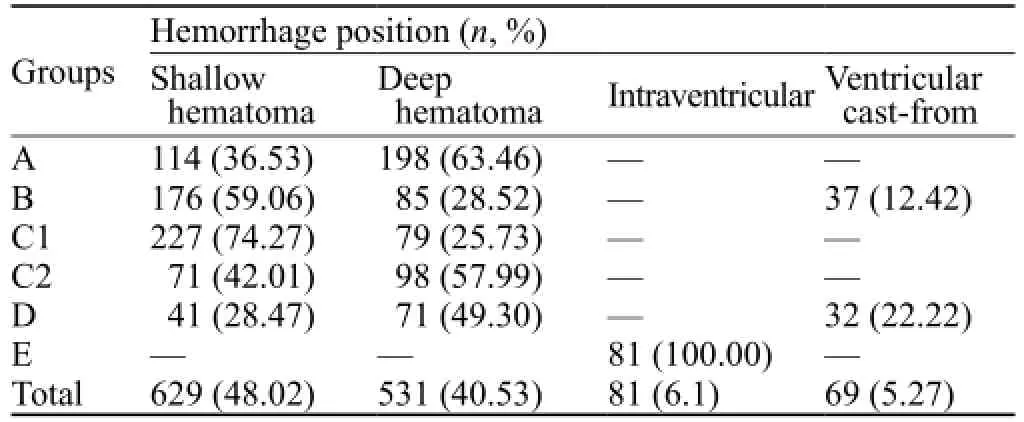
Table 2. Distribution of hemorrhage position and selection of surgical methods
Statistical analysis
SPSS 13.0 was used in this study, and measurement data were expressed as mean±SD. Student's t test, the chi-square test and the rank-sum test were used to analyze the data. P<0.05 was considered as statistically signi fi cant.
RESULTS
Short-term curative effect post operation
The effectiveness rate was 74.12% in the 1 310 patients after one-month follow-up (Table 4).
Long-term curative effect post operation
The disability rate of the patients was 44.82% 3–6 months after operation. The ADL defect levels of all groups were listed in the Table 5.
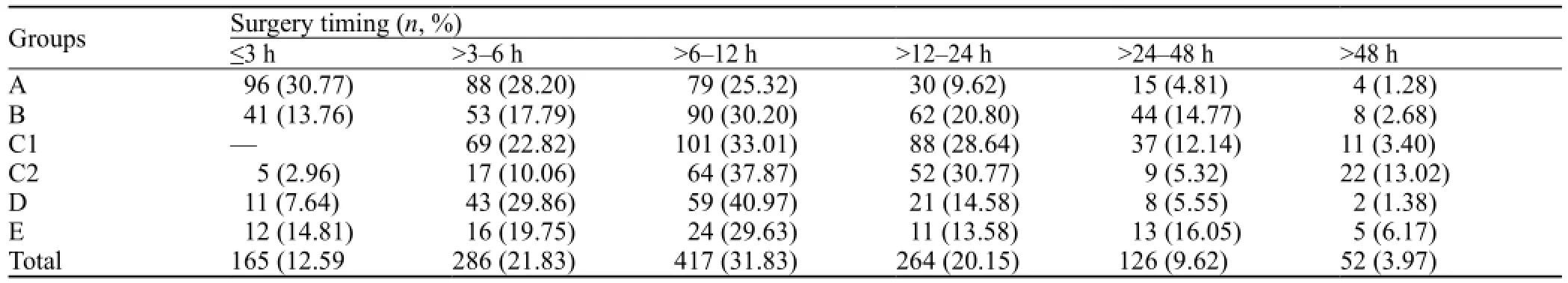
Table 3. Selection of surgical methods and surgery timing
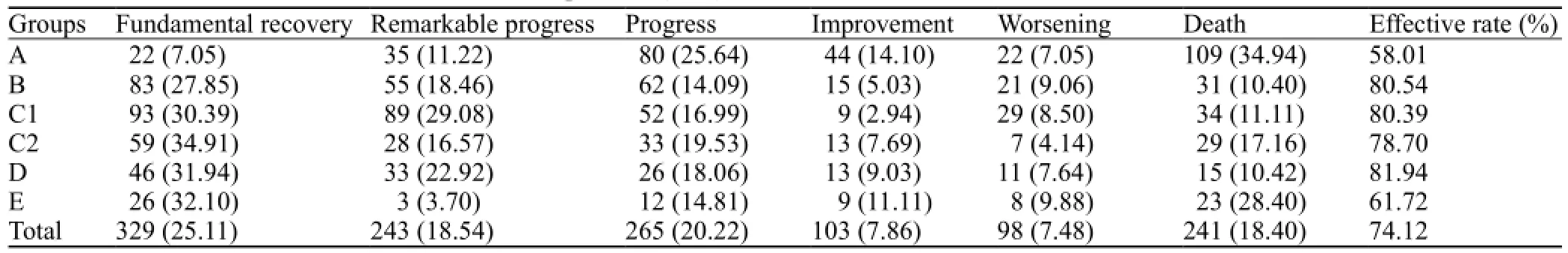
Table 4. The curative effect in the fi rst month after operation (n, %)
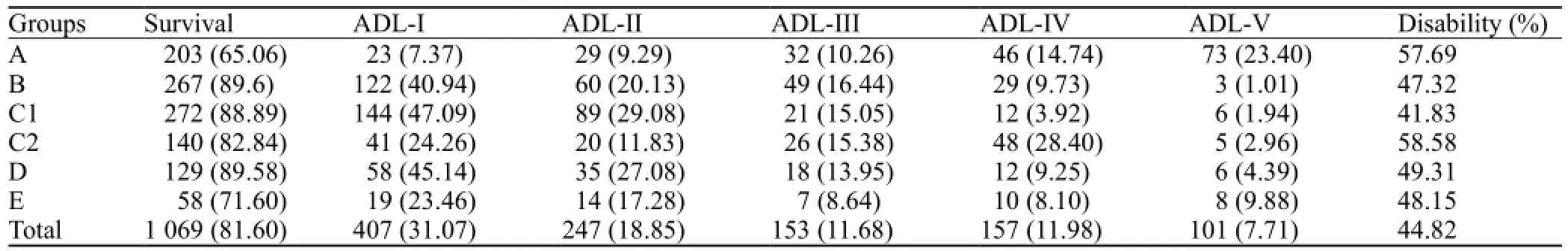
Table 5. ADL defect level in 3–6 months after operation (n, %)
Hemorrhage position, hemorrhage volume, surgical timing and curative effect
In the 1 310 patients, 241 died after the operation with a mortality rate of 18.40%. If hematoma volume was more than 80 mL and operations were performed within 3 hours, the mortality rate in group A was signi fi cantly lower than that in groups B, C, D, and E (P<0.05). If hematoma volume was 50–80 mL and operations were performed within 6–12 hours, the mortality rates of groups B and D were lower than those of groups A, C and E (P<0.05). If hematoma volume was 20–50 mL and operations were performed within 6–24 hours, the mortality rate of group C was lower than that of groups A, B and D (P<0.05).
DISCUSSION
This study retrospectively analyzed the 1 310 patients with HICH. We found that suitable operation timing and appropriate surgical method can improve curative effect. Treatment decision should be made according to hemorrhage volume and position, patient's general condition, complications and hospital's equipments.
Operative timing
It was reported that most patients stopped bleeding at 2 hours after HICH, but the hematoma was not dense, and rehaemorrhagia would often happen.[9]At 3–6 hours, the secondary neuron was observed around hematoma apoptos, but neuron damage and metabolic disorders were not obvious.[10]At 6–7 hours, edema began to appear around the hematoma, and the apopotosis of neurocytes accelerated.[11,12]After the consecutive observation of CT results in patients with cerebral hemorrhage, researchers found that few patients continued to bleed after 6 hours, therefore they proposed that 6-hour is the time threshold of hemorrhage cessation[13]and that patient condition was easy to aggravate after 48 hours.[14]As the cause of HICH caused death is cerebral hernia or vital center failure caused by swelling and extrusion of the hematoma, the removal of hematoma is crucial. Thus, the early operation is considered as the best way to minimize brain tissue damage and prevent the deterioration of cerebral edema. Nowadays, many researchers recommend early or ultraearly operation. Although the ultra-early operation within 3 hours can remove the mass effect and help to recover the brain function, postoperative hemorrhage and mortality rates are signi fi cantly higher than those at other periods. Therefore, it was suggested that the removal of hematoma should be less than 20% within 6 hours, and 20%–50% after 6 hours.[15]Animal experiments showed that the best time window of minimally invasive treatment is 6–12 hours after cerebral hemorrhage.[16]
In the present study patients with a small or medium amount of hemorrhage had a high risk of postoperative rehemorrhagia if the operation was done within 3–6 hours. The probability of rehemorrhagia was low if the operation was performed within 6–24 hours, but the brain function recovered within 12–24 hours was worse than that within 6–12 hours (P<0.05). A postoperative follow-up for 3–6 months showed that in patients with a small or medium amount of hemorrhage, there was a small difference (not statistically significant) in life quality between patients receiving operation within 3–6 hours and those receiving operation within 6–12 hours. Their mortality rate was similar between the group of >24 hours and the group of 6–24 hours, but the former had a poor recovery of neural function (P<0.05), which may be due to the irreversible degeneration and necrosis of surrounding brain tissues with the appearance of hematoma.
We concluded that ultra-early operation within 3 hours should be carefully considered. If hemorrhage volume is large, the operation must be done as soon as possible to save lives. Otherwise, the early operation would take a high risk of rehemorrhagia. Thus the operation time of 6–12 hours after hemorrhage is suggested.
Operative methods
Researchers proposed that the minimal invasive removal of brain hematoma caused by HICH can get a high effective rate. Zhao et al[17]reported the similar conclusion in a multi-center single-blind study, and considered that the volume of hematoma was not the determinant factor for the selection of surgical method. But some scholars emphasized that the selection of surgical method should be based on hemorrhage position, hemorrhage volume and patient condition. Currently, directional catheter drainage is thought to have positive clinical effects.[3,18]Especially, directional tube insertion under CT[19–21]greatly reduces hematoma and iatrogenic damage, which can be proved by DTI imaging.[22–27]Small bone window craniotomy surgery under an operation microscope can timely and effectively remove the brain compression and relieve high intracranial pressure. But intraoperative rehemorrhagia from deep hematoma is difficult to stop because of the limited vision; therefore, this surgical method is inappropriate for patients with medium volume of deep hematoma. In our patients with shallow and deep hematoma of >80 mL caused by cerebral hernia, the mortality rate of bone fl ap craniotomywas signi fi cantly lower than that in other operative groups (P<0.05); but the operation effect was unsatis fi ed[28]with a large trauma and many postoperative complications. In patients with shallow hematoma of 50–80 mL, the disability rate decreased in the order of small bone window, neural endoscopic surgery and directional catheter drainage (P<0.05). The reason may be due to the decreased size of surgical trauma in the same order. Neural endoscopic keyhole surgery, the minimal invasive surgery under an operation microscope, provides adequate hemostasis and has advantages of catheter drainage and small bone window craniotomy. Its curative effect is especially marked for patients with a deep hematoma of 50–80 mL. But it is difficult to adjust surgical approach during the operation, so it is not suitable for patients with massive hemorrhage or acute cerebral hernia. However, directional catheter drainage not only has the advantages of the minimal invasive method, but also makes up the aforementioned shortcomings. In patients with a shallow and deep hematoma of 20–50 mL, the disability rate of directional catheter drainage was lower than that of other surgical methods (P<0.01). The reason was due to the small size of the trauma. In patients with ventricle cast, catheter drainage cannot remove the obstruction timely, but neural endoscopic surgery could remove hematoma and relieve obstruction, and further remove the contralateral hematoma. The small bone window approach can be selected if hospital's condition is poor.
In summary, there are two purposes for the HICH operation: saving lives and recovering nerve function.[29,30]In patients with middle or advanced stage of cerebral hernia caused by massive hemorrhage, saving lives is the highest priority, and bone flap craniotomy is suggested. For the patients with hemorrhage of < 80 mL, directional catheter drainage is suggested. The advisable operation time is within 6–12 hours, but patients' condition should be highly considered.
Funding:This study was supported by a grant from Shanghai Pudong New Area (PWZxkq2011-01).
Ethical approval:The ethical committee of hospital approved this study.
Con fl icts of interest:We have no con fl icts of interest to report.
Contributors:Chi FL proposed the study, analyzed the data and wrote the first draft. All authors contributed to the design and interpretation of the study and to further drafts.
REFERENCES
1 Zhou LF, Pang L. minimally invasive surgery for hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage --A prospective randomized multicenter study. Chin J Clin Neurosur 2001; 6: 151–154.
2 Zhao YD. Role of surgical treatment in hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Chin J Neurosurgery 2011; 27: 757–758.
3 Li F, Chen QX. Risk factors for mental disorders in patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage following neurosurgical treatment. J Neurol Sci 2014; 341: 128–132.
4 Liu BS, Wang RM. Status of minimally invasive surgery for hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage. Chin J Minimally Invasive Neurosur 2010; 15: 237–240.
5 Zhang YR, Chang J, Qi X. Puncture and drainage of soft and hard channels in hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage. Chin J Practical Nervous 2014; 14: 68–69.
6 Delcourt C. Acutc intracerebral haemorrhage: grounds for optism in management. J Clin Neurosci 2012; 19: 1622–1626.
7 Zhou H, Zhang Y, Liu L, Huang Y, Tang Y, Su J, et al. Minimally invasive sterotactic puncture and thrombolysis therapy improves long term outcome after acute intracebral hemorrhage. J Nerol 2011; 358: 661–669.
8 Fletcher JJ, Meurer W, Dunne M, Rajajee V, Jacobs TL, Sheehan KM, et al. Inter-observer agreement on the diagnosis of neurocardiogenic injury following aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care 2014; 20: 263–269.
9 Takeda R, Ogura T, Ooigawa H, Fushihara G, Yoshikawa S, Okada D, et al. A practical prediction model for early hematoma expansion in spontaneous deep ganglionic intracerebral hemorrhage. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 2013; 115: 1028–1031.
10 Yin XP, Zhang XJ, Wang P. Experimental study on the perifocal injury at different time points after cerebral hemorrhage. Chin J Neurol 2004; 37: 101.
11 Zhang XM, Tang ZP. Clinical evaluation of cerebral hemorrhage. Chin J Neurol 2003; 36: 241–243.
12 Zhang XQ, Zhang ZM, Yin XL, Zhang K, Cai H, Ling F. Exploring the optimal operation time for patients with hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage: tracking the expression and progress of cell apoptosis of prehematomal brain tissues. Chin Med J (Engl) 2010; 123: 1246–1250.
13 Wang X, Wang Y, Rong S, Ma H, Ma Q, Zhao J. Hepatocyte growth factor improves right ventricular remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertensive rats via decreasing neurohormonal activation and inhibiting apoptosis. Chin Med J (Engl) 2014; 127: 1924–1930.
14 Zhao JZ, Zhou DB, Zhou LF, Wang RZ, Wang DJ, Wang S, et al. The efficacy of three different approaches in treatment of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage: a multi-center singleblind study of 2464 patients. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2005; 85: 2238–2242.
15 Tang ZP, Shi YH, Yin XP, Xu JZ, Zhang SM, Wang W. Modifying the details of aspiration operation may contribute to the improvement of prognosis of patients with HICH. Turk Neurosurg 2012; 22: 13–20.
16 Wu G, Sun S, Long X, Wang L, Ren S. Early stage minimally invasive procedures reduce perihematomal MMP-9 and bloodbrain barrier disruption in a rabbit model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurol Res 2013; 35: 649–658.
17 Makarenko AN, Kositsyn NS, Pasikova NV, Svinov MM. Simulation of local cerebral hemorrhage in different brain structures of experimental animals. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlova 2002; 52: 765–768.
18 Luo JB, Peng B, Quan W, Cao ZK, Xiao GC, Lu JP, et al. Therapeutic effects of aspiration with a directional soft tube and conservative treatment on mild hemorrhage in the basal ganglion. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2008; 28: 1352–1353.
19 Baumann BM, Cline DM, Pimenta E. Treatment of hypertension in the emergency department. J Am Soc Hypertens 2011; 5: 366–377.
20 Liu M, Wang HR, Liu JF, Li HJ, Chen SX, Shen S, et al. Therapeutic effect of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator on acute cerebral infarction at different times. World J Emerg Med 2013; 4: 205–209.
21 Meng SQ, Zhang H, Li L. Comparison of soft-channel stereotactic intracranial hematoma with conservative treatment for hypertensive cerebral hemorrhage: Meta analysis. Chin J Stroke 2014; 19: 106–116.
22 Li G, Qin X, Pen G, Wu W, Yang J, Yang Q. Effect of minimally invasive aspiration in treatment of massive intracerebral hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir Suppl 2011; 111: 381–382.
23 Hou XL, Gu YJ. Advances in hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage in magnetic resonance diffusion. Chin J Cerebrovascular 2014; 11: 161–164.
24 Koyama T, Tsuji M, Nishimura H, Miyake H, Ohmura T, Domen K. Diffusion tensor imaging for intracerebral hemorrhage outcome prediction;comparison using data from the corona radiate/internal capsule and the cerebral peduncle. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2013; 22: 72–79.
25 Seo JP, Choi BY, Chang CH, Jung YJ, Byun WM, Kim SH, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging findings of optic radiation in patients with putaminal hemorrhag. Eur Neurol 2013; 69: 236–241.
26 Takeuchi N, Izumi S. Rehabilitation with poststroke motor recovery: a review with a focus on neural plsticity. Stroke Res Treat 2013; 2013: 128641.
27 Lee MH, Smyser CD, Shimony JS. Resting-state fMRI: a review of methods and clinical applications. Am J Neuroradiol 2013; 34: 1866–1872.
28 Zhu H, Wang Z, Shi W. Keyhole endoscopic hematoma evacuation in patients. Turk Neurosurg 2012; 22: 294–299.
29 Wang JN, Wei JJ. Advances in the pathogenesis and treatment of neurosurgical emergency with coagulation disorders. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2013; 35: 576–580.
30 Escobedo LV, Habboushe J, Kaafarani H, Velmahos G, Shah K, Lee J. Traumatic brain injury: A case-based review. World J Emerg Med 2013; 4: 252–259.
Received March 3, 2014
Accepted after revision July 19, 2014
World J Emerg Med 2014;5(3):203–208
10.5847/ wjem.j.issn.1920–8642.2014.03.008
 World journal of emergency medicine2014年3期
World journal of emergency medicine2014年3期
- World journal of emergency medicine的其它文章
- Cardiac arrest: a case-based review
- Life-threatening complications of ascariasis in trauma patients: a review of the literature
- Instructions for Authors
- Abdominal cocoon in a young man
- Effects of aspirin on the expression of nuclear factor-κB in a rat model of acute pulmonary embolism
- Attitudes towards child restrains and seat belts usage in the learned population of Karachi, Pakistan
