Epidemiology of community pre-hypertensive patients and related risk factors in Chengdu city
Xinyun Chen, Yafei Yan, Fang Qin, Xiaojing Jiang, Bo Yu, Fang Shang, Jian Liu, Yuelei Wu, Dan Tang, Yuanyuan Yao, Tingjie Zhang
Epidemiology of community pre-hypertensive patients and related risk factors in Chengdu city
Xinyun Chen1, Yafei Yan1, Fang Qin, Xiaojing Jiang1, Bo Yu2, Fang Shang3, Jian Liu4, Yuelei Wu1, Dan Tang1, Yuanyuan Yao1, Tingjie Zhang1
Objective:This study aims to explore the epidemiologic characteristics of pre-hypertension, its related risk factors of cardiovascular diseases and its relativity with metabolic disorders among community residents of Chengdu city.
Methods:Cluster random sampling was performed in three districts and counties of Chengdu. A total of 3524 residents (resident for ≥1 year, ≥18 years of age) were enrolled in the investigation. All the participants were interviewed in the questionnaire survey. Physical examination, blood pressure measurements, and blood sampling were also performed.
Results:The overall prevalence of pre-hypertension was 34.07%. The prevalence of prehypertension was higher in males than in females (41.16% vs. 23.89%,P<0.05). The prevalence of prehypertension among patients with systolic/diastolic blood pressures of 120–129 mmHg/80–84 mmHg and 130–139 mmHg/85–89 mmHg were 34.90% and 17.16%, respectively. The prevalence of prehypertension increased with age, reaching a peak at 30–39 years (39.93%), and then declined. Multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease were more common in patients with hypertension and prehypertension than in the population with normal blood pressure. Pre-hypertension was associated with increased fasting blood glucose and increased relative risks of hypertriglyceridemia, hyperuricemia, overweight, obesity, and abdominal obesity, compared with patients who had normal blood pressure.
Conclusion:The prevalence of pre-hypertension in residents of Chengdu was high. Multiple metabolic disorders were already present in the population, and multiple cardiovascular disease risk factors were more common than in the population with normal blood pressure. Early screening for cardiovascular risk factors should be performed in patients with pre-hypertension. In addition, comprehensive measures, such as lifestyle improvement and medications, should be implemented.
Pre-hypertension, Epidemiological characteristics, Multiple metabolic disorders, Cardiovascular risk factor, Early screening, Lifestyle improvement
Introduction
Hypertension is one of the major diseases harmful to human health. The incidence of hypertension is increasing year-by-year. The prevalence of hypertension in China increased from 5.8% in 1959 to 18.8% in 2002, and >170 million patients suffer from hypertension. The increase in prevalence of hypertension is related, in part, to uncontrolled blood pressure in some patients with pre-hypertension. On thebasis of previous studies, the USA JNC7 proposed the concept of pre-hypertension, which is also referred to as high-normal blood pressure in China, according to the “2010 Chinese Guidelines for Management of Hypertension”. Specifically, pre-hypertension refers to a systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 120–139 mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of 80–89 mmHg [1]. In the present study, we investigated the prevalence of pre-hypertension in Chengdu, and compared the risk factors and metabolic indicators in patients with hypertension and the population with normal blood pressure. The results will help to explore interventions targeting pre-hypertension, and ultimately reduce the incidence of hypertension, thereby providing a basis for the prevention and treatment of hypertension and related cardiovascular diseases.
Methods
Subjects
Subjects were selected from one rural, one suburban and one urban community in Chengdu, from December 2007 to December 2008. Cluster stratified sampling was performed based on a residents’ committee. People ≥18 years of age with a permanent residence >1 year were enrolled. Residents who had left the community for >6 months or residents with mental illnesses were excluded.
Methods
Data collection and blood pressure measurements:The
questionnaires were distributed and collected onsite. The investigation team consisted of 6–8 medical personnel who had received uniform training and who were qualified in performing examinations. The methods of investigation and requirements were understood by the team members. A unified questionnaire was developed. The investigation was started in December 2007. To exclude the impact of lifestyle changes during the holiday period on the investigation results, measurements were not performed for 1 week before and 1 week after the festivals. The following data were collected: (1) demographic indicators (age, sex, occupation, education level, height, weight, and per capita income); (2) personal case history (mainly referring to diagnosis and treatment information on important or chronic diseases, including high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, stroke, coronary heart disease, gout, and kidney disease); (3) personal living habits (including duration of cigarette use and alcohol consumption, average consumptions, and withdrawal time); (4) systemic examinations, including blood pressure (mean value of sitting position blood pressures measured twice) and heart rate; and (5) fasting blood biochemical tests (including blood glucose, total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL), uric acid, creatinine, and urea nitrogen). Related parameters were standardized with reference to the 2004 census data for Chengdu.
Participants were kept quiet and rested for 10 minutes in a separate room before blood pressure measurements were taken using mercury sphygmomanometer. With the participants in a sitting position, the blood pressure cuff was applied to the right arm; the mid-points were positioned at the level of the heart. The sphygmomanometer was placed at the height of the heart, and the probe of the stethoscope was placed on the brachial artery of the elbow so that the upper end of the mercury column of the sphygmomanometer was at the eye level of the examiner. The deflation speed was 2–3 mm/s. The blood pressure was measured three times in each subject. Additional measurements were performed if the results of two consecutive measurements indicated a SBP difference of ≥8 mmHg or a DBP difference of ≥4 mmHg. The results of three measurements with differences <8/4 mmHg were recorded. The diagnostic and grading criteria recommended in the “Chinese Guidelines for Hypertension Prevention and Treatment (revised edition 2005)” were adopted.
Quality control:The investigators were uniformly trained. All data were entered twice and checked, and logical errors were corrected.
Statistical analysis
A database was established using EPidata3.0 software. The obtained data were processed using SPSS13.0 statistical software. All the measurement data were expressed as the mean±standard deviation. Data were compared between groups usingt-tests or analysis of variance (LSD methodwas used for pairwise comparisons). Numerical data were compared between groups using χ2-tests, while risk factors were analyzed using multivariate logistic regression analysis. A statistical significance level of 0.05 was used.
Results
General information
The total number of participants ≥18 years of age was 3679, of whom 3524 completed valid questionnaires, giving a response rate of 95.8%. Of the participants, 1805 were women and 1719 were men, with an age range of 20–95 years (mean age, 58.8±10.2 years). The general information is shown in Table 1.
Prevalence of pre-hypertension
The prevalence of pre-hypertension in the community population of Chengdu city was 34.07% (after standardization). The prevalences of pre-hypertension in women and men after standardization were 41.16% and 23.89%, respectively. The changes in incidences of normal blood pressure, prehypertension, and hypertension according to with ages are shown in Figure 1. The prevalence of pre-hypertension initially increased, then decreased with age, reaching a peak at 30–39 years of age (39.93%), and then declined. However, the prevalence of hypertension increased with age, and accelerated in patients 30–39 years of age. The prevalence of individuals with blood pressures of 120–129/80–84 mmHg and 130–139/85–89 mmHg were 34.90% and 17.16%, respectively.
Classification and comparison of patients with pre-hypertension showed that the majority of patients with pre-hypertension had a simple elevation of SBP (582 cases); the mean age was 57.55±14.80 years, and accounted for 48.52% of the population studied. Participants with elevated of the SBP and DBP (511 cases) accounted for 42.61% of the total population, with an average age of 54.58±12.86 years. Participants with a simple elevation of DBP (106 cases) accounted for only 8.86% of the total population, and had an average age of 51.85±11.86 years.
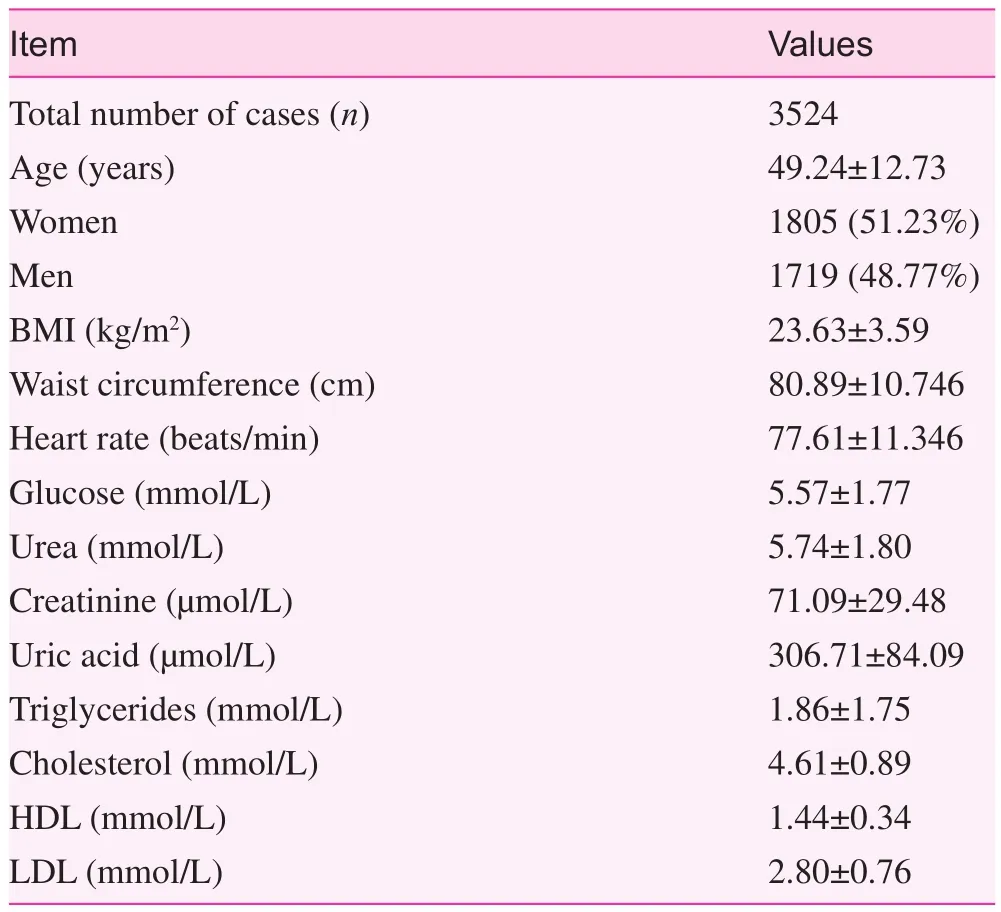
Table 1. Basic information of participants (means±standard error)
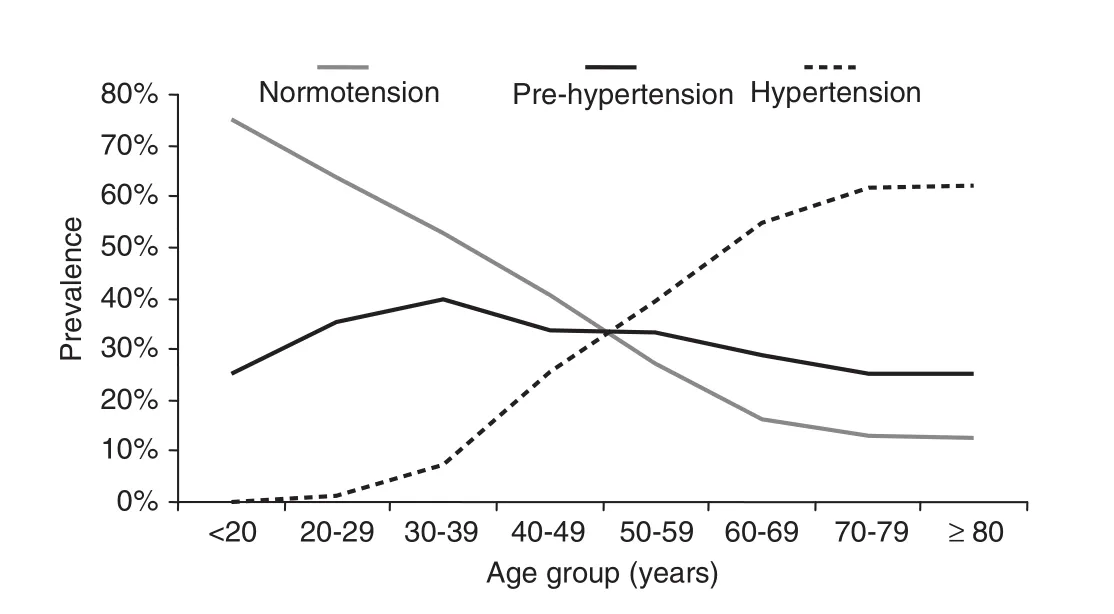
Fig. 1. Age-specific prevalence rates of hypertension, prehypertension, and normotension
Comparison of clinical and biochemical indicators
Age, alcohol consumption rate, BMI, and waist circumference were higher in patients with hypertension and pre-hypertension than in participants with normal blood pressure. The biochemical examinations in the three groups of participants showed that the BMI and total cholesterol, triglycerides, uric acid, fasting blood glucose, serum creatinine, and urea nitrogen levels in patients with hypertension and pre-hypertension were significantly higher than participants with normal blood pressure (P<0.05); however, the HDL cholesterol levels in the former two groups were lower than the participants with normal blood pressure, but without statistical significance (Table 2).
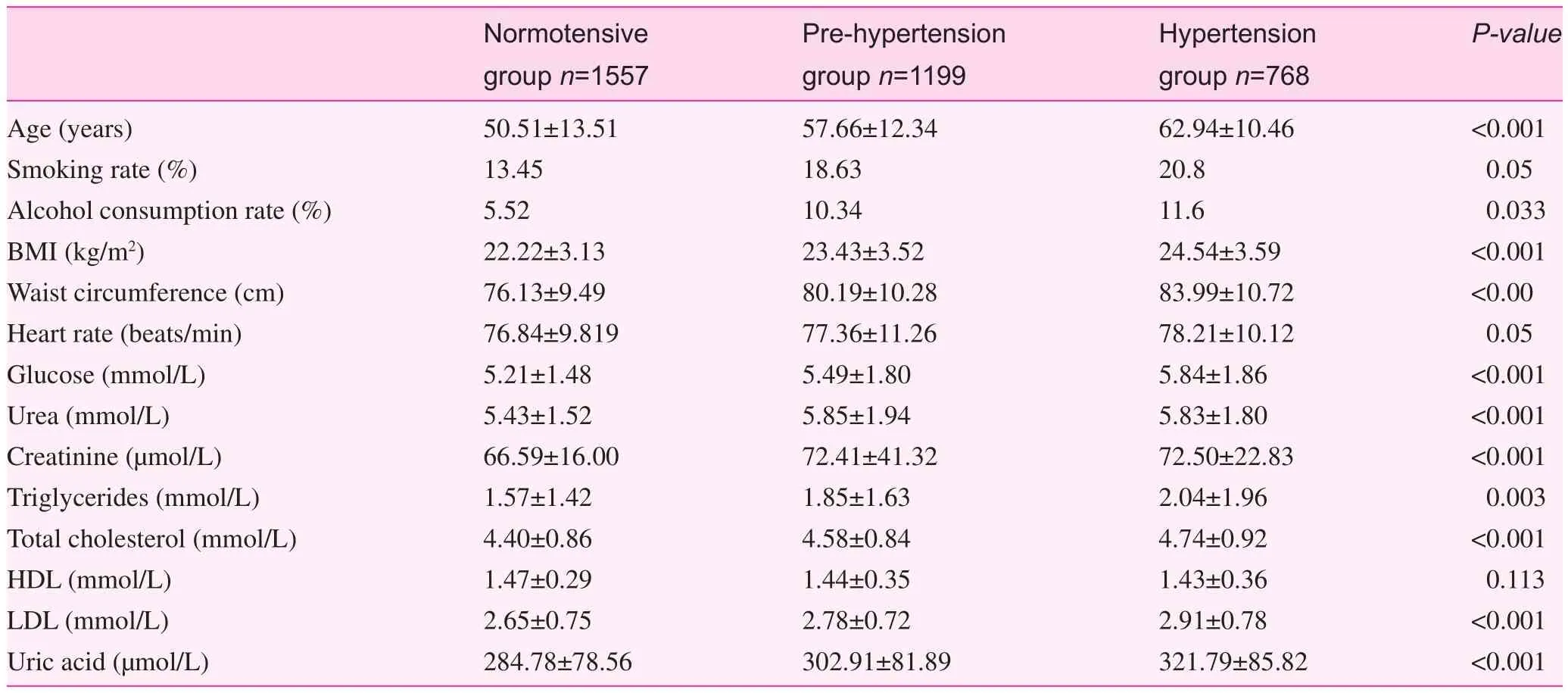
Table 2. Clinical and biochemical indexes of participants according to BP levels
Risk factors of cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders
A variety of risk factors for cardiovascular disease and metabolic disorders were increased in patients with pre-hypertension and increased more significantly in patients with hypertension, compared with the participants with normal blood pressure (Table 3).
Discussion
Worldwide studies on pre-hypertension have recently made progress. It has been gradually revealed that the patients with pre-hypertension are affected by reduced elasticity and increased hardness of large arteries, cardiac structural changes and dysfunction, insulin resistance, and other hazards. A large proportion of patients can develop hypertensionwithin a short time. Previous studies have shown that a significantly higher proportion of patients with pre-hypertension develop hypertension, compared with the population with ideal blood pressures. The proportion of adults who develop hypertension with baseline blood pressures of 120–129/80–84 mmHg and 130–139/85–89 mmHg within 2 years were 27.2% and 43.8% respectively, while the proportion who developed hypertension within 10 years increased to 52.6%. The risks of coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, heart failure, other cardiovascular events, and stroke in population with pre-hypertension were significantly higher than the population with ideal blood pressure [2–6].
Pre-hypertension has a relatively high global prevalence rate. The prevalence rate of pre-hypertension is 31% in the US, 31.6% in South Korea, 52.8% in Koreans 45–64 years of age, 30.2% in Taiwan, and 40.5% in Northeast China [7–11]. The current study revealed that the prevalence of pre-hypertension was 34.07% in Chengdu city, which was lower than northeast China and approximating that in Taiwan. This result was presumably related to the geographic distributions of the disease and lifestyles (especially salt intake). The prevalence of prehypertension in males is higher than females. It increases and then slightly declines with age <40 years; however, the prevalence of hypertension increases rapidly after 40 years of age, suggesting that the management and treatment of the population with pre-hypertension should be strengthened to reduce the risks of further development into hypertension.
Pre-hypertension is closely associated with various risk factors for cardiovascular diseases. Population surveys in the US, Japan, and South Korea have shown that patients with pre-hypertension are more susceptive to complications of metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, overweight/obesity, and insulin resistance. In addition, the risk for cardiovascular disease within 10 years is >15% [12–14]. The current investigation also showed that the BMI and serum total cholesterol, triglycerides, uric acid, fasting blood glucose, serum creatinine, and urea nitrogen levels in populations with pre-hypertension were significantly higher than populations with normal blood pressure (P<0.05), while the HDL-cholesterol levels in the population with pre-hypertension were lower than the population with normal blood pressure (P=0.02). A variety of risk factors for metabolic disorders in the population with pre-hypertension were increased. It was shown that the relative risk of co-existing fasting hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, low HDL levels, hyperuricemia, overweight, obesity, and abdominal obesity in patients with pre-hypertension were higher than the population with normal blood pressure, suggesting that multiple metabolic disorders were present in patients with pre-hypertension and ultimately increased the incidence of metabolic-related cardiovascular diseases.
The results showed that those participants with pre-hypertension had multiple metabolic disorders and multiple cardiovascular risk factors. The risks for various cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases were higher than those in the population with normal blood pressure. In a study performed by Trophy et al. [15], patients with pre-hypertension were treated with candesartan for 2 years. According to the subsequent 2 years of observations, it was found that drug treatments could reduce the risk of developing hypertension by 66% and delayed the occurrence of hypertension. Numerous investigations with small sample sizes targeting lifestyle and drug intervention therapy of patients with pre-hypertension have been performed extensively worldwide. Multi-center prospective randomized double-blind studies are being performed, indicating that researchers have started to pay close attention to the treatment and prognosis of prehypertension [16]. However, the grassroots medical workers are paying insufficient attention to the population with pre-hypertension compared to patients with hypertension. Currently, the close relationship between unhealthy lifestyles, such as drinking, smoking, salt addiction, obesity, high life stress, and failing to self-monitor blood pressures, with the development of hypertension has been widely recognized [17]. Relevant departments in China have strengthened the management of community health in hypertensive patients. This survey showed that multiple risk factors in patients with pre-hypertension were higher than the population with normal blood pressure. Therefore, the health education and lifestyle intervention of these patients should also be strengthened and considered in the hypertension management system of community health services, which will contribute to a reduction in the risks of hypertension and related diseases long-term.
The Chinese government has devoted significant efforts into the community management of hypertension. Althoughawareness, treatment, and control of hypertension has been improved, the prevalence has increased year-by-year. Such an unsatisfactory result is probably related to the mismanagement of patients with pre-hypertension. A large number of studies have shown the importance of early attention and early intervention on the population with pre-hypertension. This study also suggests the high prevalence of pre-hypertension and the close correlation with multiple cardiovascular risk factors. Therefore, it is timely and feasible to strengthen the screening of patients with pre-hypertension and assess the risk factors. Appropriate interventions on high-risk patients should also be performed, so as to effectively prevent and control the disease at a lower cost.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
1. Liu LS. 2010 Chinese guidelines for management of hypertension. Chin J Hypertens 2011;19:701–43.
2. Kshirsagar AV, Carpenter M, Bang H, Wyatt SB, Colindres RE. Blood pressure usually considered normal is associated with an elevated risk of cardiovascular disease. Am J Med 2006;119:133–41.
3. Qureshi AI, Suri MF, Kirmani JF, Divani AA, Mohammad Y. Is prehypertension a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases? Stroke 2005;36:1859–63.
4. Wu SL, Zhang ZQ, Song SB, Yao TC, Li Y, Wang JL, et al. Outcome of blood pressure and its influencing factors in population with prehypertension. Chin J Cardiol 2010;38:415–9.
5. Sun JY, Zhao D, Wang W, Liu J, Wu GX, Wang WH, et al. Changes of blood pressures of 2740 people in Beijing within 10 years (1992-2002). Chin J Hypertens 2005;13:115–9.
6. Zhao D, Li CF, Wang W, Liu J, Zeng ZC, Wang WH, et al. Analysis of risk of cardiovascular diseases in population with highnormal blood pressure within 10 years. Chin J Geriatr Cadiovasc Cerebrovasc Dis 2006;8:730–3.
7. Choi KM, Park HS, Han JH, Lee JS, Lee J, Ryu OH, et al. Prevalence of prehypertension and hypertension in a Korean population: Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey 2001. J Hypertens 2006;24:1515–21.
8. Jang SY, Ju EY, Choi S, Seo S, Kim DE, Kim DK, et al. Prehypertension and obesity in middle-aged Korean men and women: the third Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (KNHANES III) study. J Public Health (Oxf) 2012;34:562–9.
9. Lin SJ, Lee KT, Lin KC, Cheng KH, Tsai WC, Sheu SH, et al. Prevalence of prehypertension and associated risk factors in a rural Taiwanese adult population. Int J Cardiol 2010;144:269–73.
10. Wang Y, Wang QJ. The prevalence of prehypertension and hypertension among US adults according to the new joint national committee guidelines: new challenges of the old problem. Arch Intern Med 2004;164:2126–34.
11. Meng XJ, Dong GH, Wang D, Liu MM, Liu YQ, Zhao Y, et al. Epidemiology of prehypertension and associated risk factors in urban adults from 33 communities in China – the CHPSNE study. Circ J 2012;76:900–6.
12. Charles JE, Ivar LF. Evidence that prehypertension is a risk factor for Type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Ther 2010;8:335–7.
13. Kawamoto R, Kohara K, Tasuharu Y, Abe M, Kusunoki T, Miki T. Insulin resistance and prevalence of prehypertension and hypertension among community-dwelling persons. J Atheroscler Thromb 2010;17:148–55.
14. Duprez D, Toleuova A. Prehypertension and the cardiometabolic syndrome: pathological and clinical consequences. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 2013;11:1725–33.
15. Julius S, Nedaift SD, Egan BM, Weber MA, Michelson EL, Kaciroti N, et al. Feasiblity of treating prehypertension with angiotensive-receptor blocker. N Engl J Med 2006;354:1685–97.
16. Beck DT, Casey DP, Martin JS, Emerson BD, Braith RW. Exercise training improves endothelial function in young prehypertensives. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2013; 238:433–41.
17. Yu HP, Guo HY, He JX, Peng YQ. The investigation and analysis of status of unhealthy lifestyles in hypertensive patients. Chin Gen Pract 2010;13:20–2.
1. Key Laboratory of Hypertension and Related Diseases, First People’s Hospital of Chengdu, Chengdu, China, 610041
2. Shiyang Community Health Center, Chengdu, China, 610000
3. Dong Sheng Community Health Center, Chengdu, China, 610041
4. Qinglong Community Health Center, Chengdu, China, 610000
Xinyun Chen
Key Laboratory of Hypertension and Related Diseases, First People’s Hospital of Chengdu, Chengdu, China, 610041, E-mail: cissy1002@126.com
This work was funded by the major project of the Eleventh Five-Year Plan of Chengdu“Prevention and treatment of commonly and frequently encountered chronic diseases in urban and rural communities (Project number: 08YTB-931SF-020).”
4 October 2013;
Accepted 23 December 2013
 Family Medicine and Community Health2013年3期
Family Medicine and Community Health2013年3期
- Family Medicine and Community Health的其它文章
- INSTRUCTIONS FOR AUTHORS
- The ‘physical-mental’ treatment of cardiovascular disease co-morbid with mental disorders
- Head injury in a 62-year-old man affected by alcohol
- Optimal incentive mechanism for dual referral based on the analytic hierarchy process
- Performance evaluation indicator system for the implementation of essential drug system in community health service institutions
- General medical practice in China: evaluation of urban community health care service functions based on a rough set reduction theory
