Effect of early enteral nutrition on postoperative nutritional status and immune function in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer
Guiping Yu, Guoqiang Chen, Bin Huang, Wenlong Shao, Guangqiao Zeng
1Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The Affiliated Jiangyin Hospital, Southeast University Medical College, Jiangyin 214400, China;2Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510120, China;3Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease (GIRD), and China State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, The First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510120, China
Effect of early enteral nutrition on postoperative nutritional status and immune function in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer
Guiping Yu1, Guoqiang Chen1, Bin Huang1, Wenlong Shao2,3, Guangqiao Zeng3
1Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The Affiliated Jiangyin Hospital, Southeast University Medical College, Jiangyin 214400, China;2Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510120, China;3Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease (GIRD), and China State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, The First Affiliated Hospital, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510120, China
Corresponding to:Bin Huang, MD. Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The Affiliated Jiangyin Hospital, Southeast University, No. 163, Shoushan Rd, Jiangyin 214400, China. Email: drhuang2011@126.com; Guangqiao Zeng, MD. Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease (GIRD), and China State Key Laboratory of Respiratory Disease, The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou 510120, China. Email: zgqiao@vip.163.com.
Objective:To explore the effect of early enteral nutrition (EN) on postoperative nutritional status, intestinal permeability, and immune function in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer.
Methods:A total of 96 patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer who underwent surgical treatment in our hospital from June 2007 to December 2010 were enrolled in this study. They were divided into EN group (n=50) and parenteral nutrition (PN) group (n=46) based on the nutrition support modes. The body weight, time to first flatus/defecation, average hospital stay, complications and mortality after the surgery as well as the liver function indicators were recorded and analyzed. Peripheral blood samples were collected on the days 1, 4 and 7 after surgery. The plasma diamine oxidase (DAO) activity and D-lactate level were determined to assess the intestinal permeability. The plasma endotoxin levels were determined using dynamic turbidimetric assay to assess the protective effect of EN on intestinal mucosal barrier. The postoperative blood levels of inflammatory cytokines and immunoglobulins were determined using enzymelinked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Results:After the surgery, the time to first flatus/defecation, average hospital stay, and complications were significantly less in the EN group than those in the PN group (P<0.05), whereas the EN group had significantly higher albumin levels than the PN group (P<0.05). On the 7th postoperative day, the DAO activity, D-lactate level and endotoxin contents were significantly lower in the EN group than those in the PN group (all P<0.05). In addition, the EN group had significantly higher IgA, IgG, IgM, and CD4 levels than the PN group (P<0.05) but significantly lower IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α levels (P<0.05).
Conclusions:In elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer, early EN after surgery can effectively improve the nutritional status, protect intestinal mucosal barrier (by reducing plasma endoxins), and enhance the immune function
Enteral nutrition; nutritional status; intestinal permeability; endotoxin; immune function
Scan to your mobile device or view this article at:http://www.thecjcr.org/article/view/2195/3059
Introduction
Esophageal cancer is one of the common malignant tumors in the digestive system, and China has the highest incidence and mortality rate of esophageal cancer all over the world (1). The death toll from esophageal cancer in China reaches 150,000; unfortunately, the incidence is still increasing annually, particularly in the elderly, who account for 50% of the esophageal cancer cases (2). Currently surgery is still the best way for treatment of esophageal cancer. (3) Patients with cardiac cancer tend to have varying degrees of malnutrition because of the reduced food intake due to difficulty swallowing, preoperative diet restrictions, and nutrition consumption by tumors. Meanwhile, the surgeries for esophageal and cardiac cancers are highly invasive and often take a long time, inducing a strong stress response in human body. Therefore, postoperative catabolism hyperthyroidism may occur, which is characterized by obvious negative nitrogen balance, hypoproteinemia, and hyperglycemia, resulting in further malnutrition (4). The situation is even worse in the elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer. Zhuet al.found that the incidence of perioperative malnutrition among these patients reached 20-80%. Therefore, it is particularly important to investigate the postoperative nutritional status in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer.
The surgical trauma (caused by intestinal ischemia or intestinal paralysis) and lack of the intestinal stimulation and nutrition after the surgery (due to fasting) can increase the atrophy, damage and permeability of intestinal mucosa; as a result, the gut bacteria and endotoxins can easily migrate and enter the blood stream. For patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer, their nutritional status will be worsened after surgeries, along with the decrease of the cellular and humoral immunity (5).
Clinically, nutritional support, particularly enteral nutrition (EN), is applied to facilitate the improvement of nutritional status, restoration of immune function, and protection of intestinal mucosal barrier after the surgeries. In our current randomized and controlled study, we explored the effect of early EN on postoperative nutritional status, intestinal permeability, and immune function in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer. Also, we investigated the effect of EN on the intestinal barrier function to identify the correlation of intestinal bacterial translocation with postoperative infections in cardiac surgery. By studying the influences of postoperative early EN on the intestinal barrier function and immune function in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer, we tried to verify the role of EN in improving the intestinal bacterial translocation and enterogenic infections.
Materials and methods
Subjects and grouping
A total of 96 patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer who underwent surgical treatment in our hospital from June 2007 to December 2010 were enrolled in this study. They were divided into EN group [n=50; 34 males and 16 females, aged 65-79 years (mean: 68.9 years)] and parenteral nutrition (PN) group [n=46; 26 males and 20 females, aged 65-78 years (mean: 67.5 years)] based on the nutrition support modes. Patients with diabetes, cirrhosis, and/or other chronic comorbidities were ruled out. The two groups showed no significant difference in terms of gender, age, site of lesion, surgical approach, and pathologic stage (all P>0.05).
Nutritional supports
EN group: The anesthetist and surgeon cooperated closely during the surgery. Under the guidance of the surgeon, duodenal feeding tube was nasally placed at 20-30 cm away from distal Treitz ligament. On the first postoperative day (day 1), the patients were provided with routine peripheral intravenous infusion of glucose solution (2,000-2,500 mL) plus potassium chloride; furthermore, the 30 °C normal saline (250 mL) was instilled via the nasal-intestinal tube. At day 2, the patients were perfused with Peptisorb (NUTRICIA, Netherland) 500 mL at a constant speed (30-50 mL/h). The dose was gradually increased according to the patients’ subjective feeling and tolerance. At day 2, the patients were tube-fed with Peptisorb 500 mL plus Nutrison Fibre (NUTRICIA, Netherland) 500 mL at a speed of 50-60 mL/h. At day 3, the patients were tubefed with 1,500-2,000 mL of the products at a speed of 80-100 mL/h, reaching the full dose. The full dosage was provided in the following four days. The total amount of nutrient solution was calculated based on the total daily energy intake (125.52 kJ). During the perfusion, the tube was flushed every four hours to maintain it unobstructed. Fluid warmer was applied to maintain the nutrient solution at a temperature of 38-42 °C. The initially insufficient fluid and heat were supplemented intravenously.
PN group: PN was provided using a standard three-liter package containing compound amino acid, long-chain fat emulsion, glucose, vitamins, electrolytes, and trace elements via the central vein after the surgery. Based on a total daily energy of 125.52 kJ (30 kcal)/kg, the carbohydrate:fat calorie percentage ratio was set at 2:1. PN was applied for 8-10 d. The patients in both groups were provided with liquid diet at day 8, semi-liquid diet at day 10, and ordinary diet at day 12.
Clinical observations and laboratory tests
The body weight, total serum protein, serum albumin, hemoglobin, liver function, lymphocytes 7 days before and after surgery as well as anal exhaust/defecation time, average hospital stay, complications, and mortality after the surgery were recorded for patients in both groups.
Effect of EN on intestinal permeability
Blood samples were collected on the days 1, 4 and 7 after surgery. Diamine oxidase (DAO) activity was determined by measuring the oxidation of o-dianisidine dihydrochloride, and D-lactic acid was detected using modified spectrophotometry. The plasma DAO kit and the agent kit for the semi-quantitative assay of lactic acid were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Company.
Determination of plasma endotoxin levels
The working standard endotoxin (WSE) was diluted 10 times using water for bacterial endotoxins test, yielding a series of endotoxin concentrations of 2.0, 0.2, and 0.02 EU/mL. After adding 0.1 mL of each solution into a reaction tube already containing 0.1 mL limulus amebocyte lysate, the solution was mixed evenly. Then, the samples were inserted into the EDS-99 Bacterial Endotoxin Dynamic Testing System, and the endotoxin level in each sample was detected for three times.
Venous blood samples (1.0-2.0 mL; after anticoagulation) were collected before and after surgery. The blood sample was slowly placed into sterile centrifuge tubes, which was then closed to avoid contamination. After the sample was centrifuged at 3,000 r/min for 40 min, plasma was isolated and harvested, and stored in ice water bath for further determination. The plasma was pre-treated, and endotoxin standard curve was prepared, and the plasma bacterial endotoxin level was determined.
Effect of EN on the immune function
Blood immunoglobulins (IgA, IgG and IgM), cytokines (IL-2 and IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) before surgery and 1 day and 7 days after surgery were determined using enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). T lymphocyte subsets (CD4, CD8 and CD4/CD8) were determined using flow cytometry. The IgA, IgG, and IgM detection kits were purchased from Shanghai Sangon Biological Engineering Technology And Service Co., Ltd. The reagent kits for the determination of IL-2, IL-6 and TNF- were purchased from Jingmei Biological Engineering Co., Ltd.
Statistical analysis
All measurement data are presented asx±s. The intergroup difference was compared usingt-test. All the statistical analysis was performed using SPSS 13.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), and P<0.05 was regarded as statistically significant.
Results
Effect of early EN on postoperative nutritional status in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer
The postoperative body weight and liver function parameters were within the normal range. Serum albumin was significantly higher in the EN group than that in the PN group (P<0.05). The results are shown inTable 1. Also, as shown inTable 2, compared with the PN group, the EN group had significantly shorter time to first flatus/defecation and mean hospital stay, lower incidences of complications, and lower mortality (P<0.05).
Effect of early EN on postoperative intestinal permeability in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer
The effect of early EN on postoperative intestinal permeability in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer was assessed based on the blood DAO and D-lactic acid levels. As shown inTable 3, the DAO and D-lactic acid levels showed no significant differences between these two groups at day 4; at day 7, however, the EN group had significantly lower DAO and D-lactic acid levels than the PN group (P<0.05).GroupnTime to first flatus (h)Time to first defecation (h)Mean hospital stay (d)ComplicationsMortality ARDSARFAHFStress ulcer
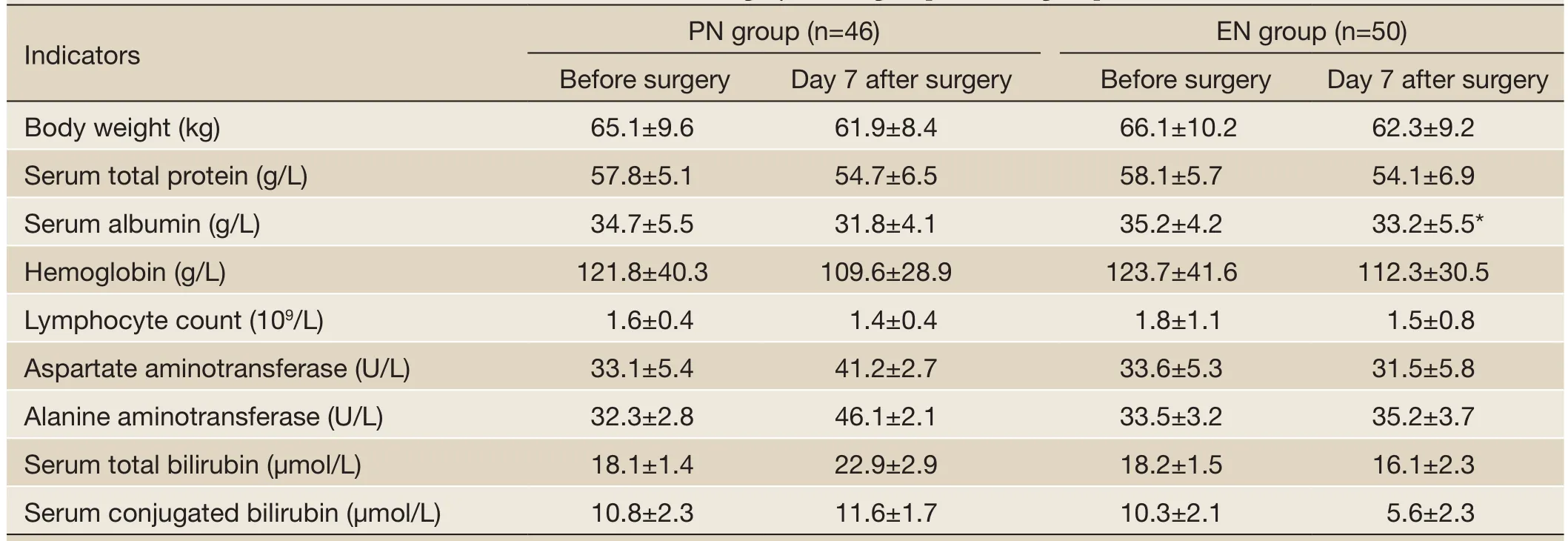
Table 1 Nutritional status and liver function before and after surgery in PN group and EN group

Table 2 Comparison of time to first flatus/defecation, mean hospital stay, complications, and mortality between PN group and EN group
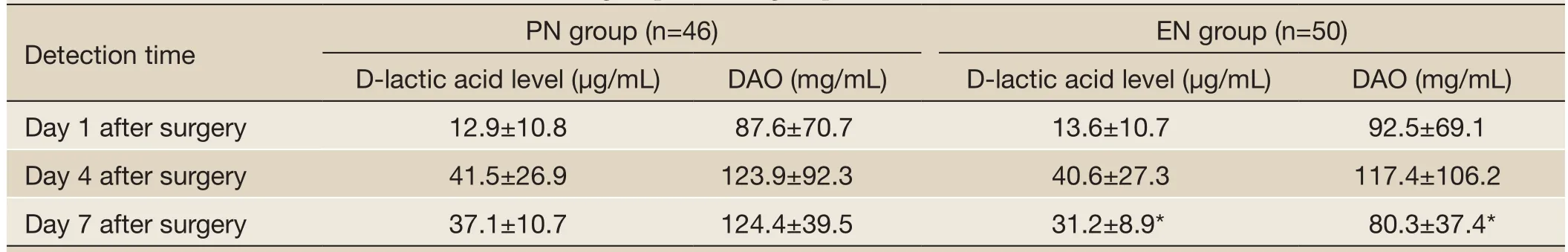
Table 3 Blood DAO and D-lactic acid levels in PN group and EN group
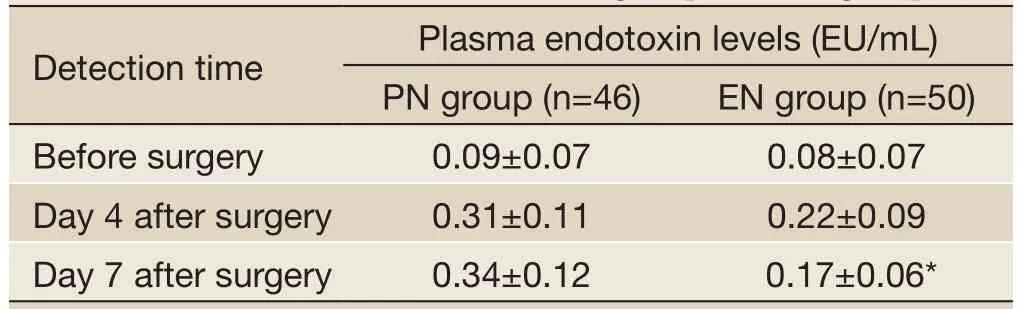
Table 4 Blood endotoxin levels in PN group and EN group
Effect of early EN on intestinal mucosal barrier in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer
The effect of early EN on intestinal mucosal barrier in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer was assessed based on the endotoxins in both groups. The endotoxin levels showed no significant differences between these two groups at day 4; at day 7, however, the EN group had significantly lower endotoxin levels than the PN group (P<0.05) (Table 4).
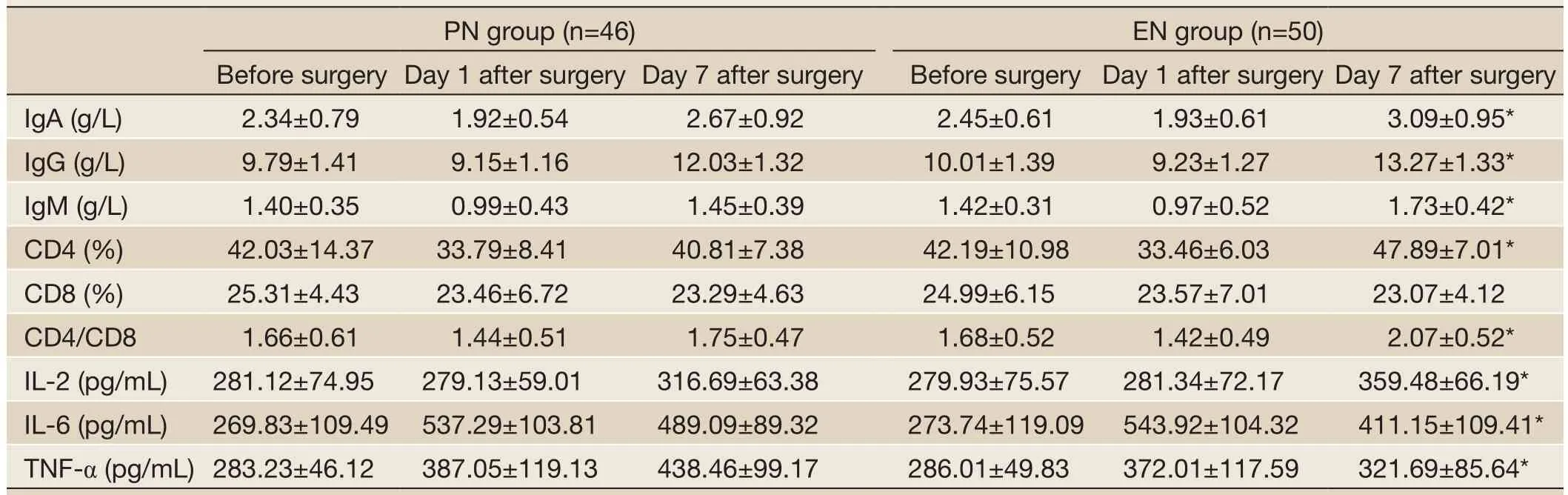
Table 5 Changes of immune indicators in PN group and EN group
Effect of early EN on postoperative immune function in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer
The immune function was low in both groups before surgery and 1 day after surgery, showing no significant difference. At day 7 after surgery, the immune function indicators increased in both groups. In the EN group, the immune globulins (IgA, IgG and IgM), T lymphocyte subsets (CD4 and CD4/CD8), and IL-2 were significantly higher than those in the PN group (P<0.05), whereas IL-6 and TNF-α were significantly lower (P<0.05). The results are shown inTable 5.
Discussion
Esophageal cancer is a common malignant tumor of the gastrointestinal tract. Before surgery, patients often already have poor nutritional status and low immune function; the surgical trauma and the further decreased immune function after surgery will make the residual tumor cells easily escape from immune surveillance and result in the early relapse of tumors (6). It has been found that the incidence of postoperative infections is about 10% in patients with cardiac cancer, which is remarkably higher than those of other tumors (e.g., lung cancer). In fact, infection is the leading cause of postoperative death among cardiac cancer patients (7). Therefore, it is critically important to improve the postoperative nutritional status and restore the immune function in patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer (8). EN has been well recognized as an economical, safe, and effective nutritional support method that complies with the physiological state, helps to maintain the digestive tract morphology and function, operates in a simple way, and has few complications. Therefore, it can effectively regulate the restoration of intestinal mucosa (9). In our current study, the postoperative body weight and liver function parameters were within the normal range in both EN group and PN group. Serum albumin was significantly higher in the EN group than that in the PN group (P<0.05). Also, compared with the PN group, the EN group had significantly shorter time to first flatus/defecation and mean hospital stay, lower incidences of complications, and lower mortality (P<0.05). Obviously, early EN is helpful to improve the nutritional status in the elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer, shorten the postoperative recovery phase, and reduce the complications.
The surgical trauma (caused by intestinal ischemia or intestinal paralysis) and lack of the intestinal stimulation and nutrition after the surgery (due to fasting) can increase the atrophy, damage, and permeability of intestinal mucosa; as a result, the gut bacteria and endotoxins can easily migrate and enter the blood stream (8,10). This may result in many hazards: the bacteria and endotoxins can cause enterogenic systemic infection; meanwhile, the bacterial toxins also stimulate the monocytes, macrophages and other tissue cells to release a variety of proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α) (11,12) and reduce the release of the protective anti-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-2, IL-4, and IL-10) (13). The excessive release of proinflammatory cytokines and inhibition of anti-inflammatory cytokines will unavoidably trigger excessive inflammatory response, resulting in systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) and multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)(14,15). In recent years, the intestinal function has been applied as a major indicator for the prognosis of critically ill patients. Gut is regarded as a central organ after surgical stress; also, among the intestinal mucosal barrier functions, immune barrier plays an important role (16). A recent study has found that the postoperative gastrointestinal paralysis mainly occurs in the stomach and colon; the functions of small intestine often return normal 6-12 h after the surgery, which supports the early application of EN after surgery for cardiac cancer (17).
In our current study, the DAO and D-lactic acid levels showed no significant differences between these two groups at day 4; at day 7, however, the EN group had significantly lower DAO and D-lactic acid levels than the PN group (P<0.05). Therefore, the early EN can help to reduce the postoperative intestinal permeability and protect the intestinal mucosal barrier in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer. Quite a few elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer have suffered from eating disorder for a long period of time, and therefore intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction is highly possible among these patients. In addition, the surgical trauma and postoperative fasting (for about one week) further increase the intestinal mucosal barrier dysfunction. EN is helpful to maintain the integrity of the structure and function of intestinal mucosal cells, protect the intestinal mucosal barrier (18), remarkably decrease enterogenic infection, and prevent the intestinal mucosal atrophy. Meanwhile, EN has more comprehensive and reasonable nutrients; compared with PE, it is physiologically more compatible, and more flexible, safe and affordable (19).
The normal human intestinal mucosal barrier is composed of intestinal mucosal epithelium, normal intestinal flora, intestinal secretions, and intestinal immune cells (20). The intact intestinal barrier can effectively block the translocation of intestinal parasitic fungi and their toxins from the gut to other tissues and organs and thus prevent the invasion of endogenous microorganisms and their toxins. The permeability of the intestinal mucosa increases when the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier is damaged; as a result, the bacteria and toxins originally in the gut will pass through the damaged intestinal mucosa, resulting in bacterial translocation and endotoxemia; after having entered the blood stream, the bacteria and their toxins will in turn exert their effects on the intestinal mucosa, further aggravating the damage of intestinal mucosal barrier and increasing the permeability of the intestinal mucosa. Such a vicious circle may cause SIRS, MODS, and, ultimately, death (21). In our current study, the endotoxin levels showed no significant difference between these two groups at day 4; at day 7, however, the EN group had significantly lower endotoxin levels than the PN group (P<0.05). Therefore, the early EN can help to lower the postoperative endotoxin levels and protect the intestinal mucosal barrier in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer.
TNF-α is one of the key factors leading to inflammatory reaction. It is an endogenous cytokine produced by activated monocyte-macrophage system (22). IL-2 is one of the most important lymphokines in the immune network, reflecting the change of IL-2 level and thus the immune response in human body (23). IL-6 is known to be a major mediator of the acute-phase response. It can stimulate the liver to synthesize C-reactive protein (CRP), enhance inflammatory reaction by promoting B cell differentiation and antibody formation, and assist the T cells to produce the expressions of IL-2 and its receptor (24). In our current study, the immune function was low in both groups before surgery and 1 day after surgery, showing no significant difference. At day 7 after surgery, the immune function indicators increased in both groups. In the EN group, the immune globulins (IgA, IgG and IgM), T lymphocyte subsets (CD4 and CD4/CD8), and IL-2 were significantly higher than those in the PN group (P<0.05), whereas IL-6 and TNF-α were significantly lower (P<0.05). Therefore, the early EN is helpful to improve the immune function in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer.
In summary, in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer, early EN after surgery can effectively improve the nutritional status, protect intestinal mucosal barrier (by reducing plasma endotoxins), and enhance the immune function.
Acknowledgements
Disclosure:The authors declare no conflict of interest.
1. Chen W, He Y, Zheng R, et al. Esophageal cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2009. J Thorac Dis 2013;5:19-26.
2. Niu J, Weber J, Gelbspan D. Change of HER2 status in metastatic esophageal adenocarcinoma: heterogeneity of the disease? Case report and review of literature. J Gastrointest Oncol 2012;3:358-61.
3. Khan O, Nizar S, Vasilikostas G, et al. Minimally invasive versus open oesophagectomy for patients with oesophageal cancer: a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. J Thorac Dis 2012;4:465-6.
4. Fernández-Sordo JO, Konda VJ, Chennat J, et al. Is Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS) necessary in the pretherapeutic assessment of Barrett's esophagus with early neoplasia? J Gastrointest Oncol 2012;3:314-21.
5. Cuesta MA, Biere SS, Henegouwen MI, et al. Randomised trial, Minimally Invasive Oesophagectomy versus open oesophagectomy for patients with resectable oesophageal cancer. J Thorac Dis 2012;4:462-4.
6. Ling Y, Chen J, Tao M, et al. A pilot study of nimotuzumab combined with cisplatin and 5-FU in patients with advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Thorac Dis 2012;4:58-62.
7. Jensen K, Afroze S, Munshi MK, et al. Mechanisms for nicotine in the development and progression of gastrointestinal cancers. Transl Gastrointest Cancer 2012;1:81-7.
8. Chen WQ, Zheng RS, Zhang SW, et al. Report of incidence and mortality in china cancer registries, 2008. Chin J Cancer Res 2012;24:171-80.
9. Kennedy L, Hodges K, Meng F, et al. Histamine and histamine receptor regulation of gastrointestinal cancers. Transl Gastrointest Cancer 2012;1:215-27.
10. Uzunoglu FG, Reeh M, Kutup A, et al. Surgery of esophageal cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2013;398:189-93.
11. Groblewska M, Mroczko B, Sosnowska D, et al. Interleukin 6 and C-reactive protein in esophageal cancer. Clin Chim Acta 2012;413:1583-90.
12. Anderson MR, Jankowski JA. The treatment, management and prevention of oesophageal cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther 2001;1:1017-28.
13. Farthing MJ, Fitzgerald R, Zhang ZW. Acid, helicobacter and immunity: a new paradigm for oesophagogastric cancer. J Physiol Paris 2001;95:423-7.
14. Makino H, Kunisaki C, Kosaka T, et al. Perioperative use of a neutrophil elastase inhibitor in video-assisted thoracoscopic oesophagectomy for cancer. Br J Surg 2011;98:975-82.
15. Shah MB, Schnoll-Sussman F. Novel use of cryotherapy to control bleeding in advanced esophageal cancer. Endoscopy 2010;42 Suppl 2:E46.
16. Experts Committee on Cancer -Related Anemia, Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO). Clinical practice guidelines on cancer-related anemia (2012-2013 Edition). Chin Clin Oncol 2012;1:18.
17. Wagner IJ, Rombeau JL. Nutritional support of surgical patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Surg Clin North Am 2011;91:787-803, viii.
18. Zhan P, Wang Q, Qian Q, et al. Megestrol acetate in cancer patients with anorexia-cachexia syndrome: a metaanalysis. Transl Cancer Res 2013;2:74-9.
19. Zou XP, Chen M, Wei W, et al. Effects of enteral immunonutrition on the maintenance of gut barrier function and immune function in pigs with severe acute pancreatitis. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 2010;34:554-66.
20. Havenaar R. Intestinal health functions of colonic microbial metabolites: a review. Benef Microbes 2011;2:103-14.
21. Bastian L, Weimann A. Immunonutrition in patients after multiple trauma. Br J Nutr 2002;87 Suppl 1:S133-4.
22. Van Hauwermeiren F, Vandenbroucke RE, Libert C. Treatment of TNF mediated diseases by selective inhibition of soluble TNF or TNFR1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 2011;22:311-9.
23. Barlow JL, McKenzie AN. Nuocytes: expanding the innate cell repertoire in type-2 immunity. J Leukoc Biol 2011;90:867-74.
24. Yoshimura A, Wakabayashi Y, Mori T. Cellular and molecular basis for the regulation of inflammation by TGF-beta. J Biochem 2010;147:781-92.
Cite this article as:Yu G, Chen G, Huang B, Shao W, Zeng G. Effect of early enteral nutrition on postoperative nutritional status and immune function in elderly patients with esophageal cancer or cardiac cancer. Chin J Cancer Res 2013;25(3):299-305. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2013.06.01

10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2013.06.01
Submitted Apr 08, 2013. Accepted for publication May 25, 2013
 Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2013年3期
Chinese Journal of Cancer Research2013年3期
- Chinese Journal of Cancer Research的其它文章
- Intrinsic apoptotic pathway and G2/M cell cycle arrest involved in tubeimoside I-induced EC109 cell death
- New frontiers in peritoneal malignancies
- Pharmacological blockage of CYP2E1 and alcohol-mediated liver cancer: is the time ready?
- Risk factors associated with early recurrence of adenocarcinoma of gastroesophageal junction after curative resection
- Hedgehog signaling pathway and ovarian cancer
- Matrix metalloproteinase gene expressions might be oxidative stress targets in gastric cancer cell lines
