On the US Debt Crisis and Its Possible Solutions
Li Xuelian & Wei Min
On the US Debt Crisis and Its Possible Solutions
Li Xuelian & Wei Min
Following the eruption of European debt crisis in the wake of the financial crisis, a new debt crisis began to ferment on the US soils. On May 16th, with US debt exceeding its statutory ceiling of $14.29 trillion, US Treasury’s solvency became so stretched that it could hardly last to August 2nd. As a result, the country was plunged into great default risks. The two parties, through heated political struggles, finally managed to reach a consensus on raising the country’s debt ceiling. On August 2nd, President Obama signed the bill to raise the debt ceiling approved by both houses. The alarm of American debt default seemed to have temporarily silenced. Nevertheless, Standard & Poors soon lowered the long-term sovereign credit rating of the US from triple A to double A plus on grounds that existing measures were far from enough to stabilize the medium-term US bonds. This was the first time in history that the US was ripped off its triple A credit rating. The downgrade and related debates over US debt had since sent tremendous shock to the global financial markets, causing considerable public attention on the issue of US debt.
I. How the US Accumulates Its Huge Debt
The Unites States boasts close to 200 years of bond-issuing history, with the primary purposes of such activities being implementing expansionary fiscal policies and raising funds for wars. For example, when the War of Independence broke out in 1812, the states and their armies issued various kinds of medium-term bonds and temporary notes to fund the war, symbolizing the initial formation of the US bond market. During World War I, the US Treasury sold large amounts of short-term notes to fund the war. The great economic crisis from 1929 to 1933 brought catastrophic consequences to American economy and American people alike. To break out of the crisis as soon as possible, the US government guided by Keynesian theory intensified its efforts to issue debt. These soon culminated in the bonds peak during World War II.
After World War II, the US debts grew at low rates for almost two decades. During this period of time, the US Treasury used fiscal surpluses to service its debts owed to federal and commercial banks. However, during the past two decades, both US federal deficits and US debts experienced rapid growth. This we can see in Chart 1 listing the ratios between US debt and GDP from 1940 to 2010. As the chart shows, at the end of World War II, the US debt registered a historical high, being 121.96% of the country’s GDP. After the war, the ratio continued to fall to the historical low of 31.82% in 1981. Then it began to take off again.
The US debt has been rising rapidly since 1981. Almost all US administrations after the Reagan Administration used budget deficit to spur the economy more or less. As a result, US debts increased in every administration except the Clinton Administration. Beginning in 2002, the US budget deficit experienced another round of rapid growth. For example, during the Administration of George W. Bush, the American debt crossed its statutory ceiling five times, with the total debt rising from $5.8 trillion in 2001 to $10.7 trillion at the end of 2008. Soon after, the large scale economic stimulus plan in the wake of the financial crisis brought the number to its historical high of $14 trillion. US budget deficits in 2009-2011 registered 1.41, 1.29 and 1.5 trillion dollars, making these three years the most serious years in the US deficit history. Correspondingly, US treasury deficits in 2009 and 2010 accounted for 9.9% and 8.9% of the US GDP respectively, far exceeding the 3% safety line recognized by the international community.
In 2010, US debt accounted for 92.28% of the US GDP, whereas the international safety line is set at 60%. Although expansionary economic policies were conducive to the recovery and growth of US economy after the financial crisis, they raised the US deficit to historical highs. In consideration that the US debt/GDP ratio in 2010 was already 92.28%, it is expected that the ratio will rise to no less than 99% in 2011 and no less than 110% in 2015.
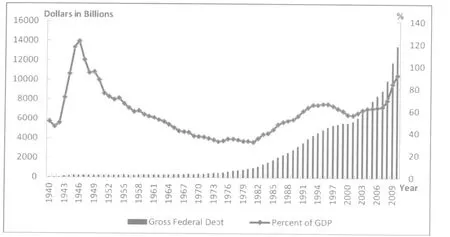
Chart 1 US Gross Federal Debt, 1940—2010
According to the statistics of US Government Accountability Office (GAO), the growth rate of US debt will accelerate in the 21st century (see Chart 2 below). Unless measures are taken to offset the acceleration, US debt will be no less than 200% of the GDP by 2050. And by 2080, the US debt will be 600% of the country’s GDP. The US government would have to prevent such things from happening if it did not want to announce itself bankrupt.
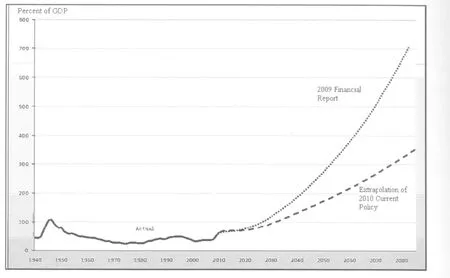
Chart 2 Historical and Current Policy Projections for Debt Held by the Public,1940-2085
II. Causes of American Debt
America’s huge debt has many causes, some of which are longterm and some short-term.
1. Economic structure and consumption patterns are fundamental causes of American debt.
For a long period of time, the US economy has been characterized by excessive consumption, over-indebtedness, low productivity, low saving rate, deficits and other hedonistic features. From 1990 to 2000, the average savings rate of Americans was 5%; from 2001 to 2008, the rate was 2%. Now, the rate is 6%, with consumer expenditure taking 68% of the GDP and consumption contribution to GDP being 85%. The US industrial structure is pretty much like an inverted pyramid, with governmental employees far outnumbering workers in manufacturing sectors. When economic situations are good, increases in revenues conceal the abnormal economic structure and consumption patterns; but when the economy slows down or steps into recessions, income shortage became an evident problem. The country then has to exploit US dollar’s strong position and resort to low-cost overseas financings to compensate for the lack of revenues. As a result, the percentage of foreign capital flowing into the US debt market has increased considerably. For example, in 1985, US bonds purchased by foreign countries and international institutions were valued only at $226.4 billion, taking 15.9% of total value of US bond market. 20 years later, the number increased by10 times, accounting for almost half of the total market value.
In a hedonistic social milieu, borrowing against the future enables the US government to cross debt ceilings again and again, brewing therefore a debt crisis to break out very soon.
2. Social security and medical expenditure bear heavily on US finance.
The US social security system took shape during the depression period of the 1930s. In 1935, President Roosevelt signed the Social Security Act passed by the congress covering five areas of social security, namely social security to the seniors, allowances to the blind and handicapped, grants to the seniors, grants to the adolescents and social insurance to the jobless. Administrations after Roosevelt’s continued to supplement and modify the system until it became a huge social security network. Of the US governmental expenditures, the most significant ones are expenditures for social insurance, medical insurance and national defense. According to US Governmental data, of the 3,456 billion dollar federal expenditures in 2010, social security took 38%, medical and health expenditures took 24%, education 4%, national defense 20%, Treasury bonds interests 6% and others 8%. Social security, medical & health insurance and education combined took about 70% of the total expenditure. If we include state and local governments’expenditures in the math, then these numbers will be much larger. As the US population grows older, the price of this policy becomes too high to bear. As social welfare expenditures drove high US treasury deficits, the US government was left with no choice but to bridge the deficits with debt.
3. Huge defense expenditure makes things worse.
For a long period of time, investing in national defense industry has been a priority for the US Government, as launching wars overseas is an important driver of American economic growth. But this also increases America’s debt. For example, during the Administration of George W. Bush, the US launched wars in Afghanistan and Iraq in the name of counterterrorism. These ushered in a global counter-terrorist warfare that created not only tremendous amounts of deficits but also tremendous amounts of debt. The two wars cost more than $1 trillion, making the US defense expenditure to double since 9.11. The wars were recently less heated, but the US defense expenditure in 2011 was still $708 billion and accounted for 20% of the total US governmental budget. Military expenditure and social security are therefore the two most important causes of America’s debt problem.
4. Deficit policy is culprit of debt dilemma.
US dollar’s reserve currency position plus well-developed US capital markets mean that the US can secure overseas financings at low cost. However, the country has little alert over its over-indebtedness. All administrations with the exception of the Clinton Administration failed to handle the financial deficit problem successfully. In order to prevent economic recession and take care of interest groups, the US government usually chose to neglect the danger of deficit and implement instead massive tax cut and other economic stimulation programs. The bubble of “New Economy” burst during the Bush Administration. Nevertheless, to deliver his campaign promises, President Bush introduced three tax cuts in 2001, 2003 and 2006 respectively, two of which were the largest and third largest tax cut in the US history. The $862 billion economic stimulus plan by Obamato prevent in-depth economic recession after the financial crisis further aggravated the debt problem. According to the analysis of the Washington Post, the policies adopted by the Bush Administration created a total of $7 trillion debt, whereas the policies of Obama so far already added $1.7 trillion to the old debt.
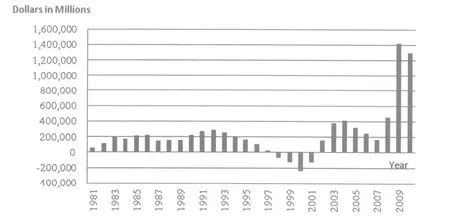
Chart 3 Deficit/Surplus of US Government, 1981-2010
5. Low financing cost
The US bond bull market has been running for almost 30 years. During this period, the yields of US bonds were basically dropping. By the end of May 2011, the benchmark yield of tenyear US bond was just 3%, and the yield of two-year note was even below 0.5%. Low yields significantly lowered the bonds issuance costs, allowing the US government to raise funds unscrupulously to stimulate the economy.
III. Unoptimistic Prospect for Solving the US Debt Problem
It is estimated that if the US allows its debt and deficit to grow at the current speed, by 2023 the US government shall have to devote its total treasury revenue to service debt and have no residual resources for other public needs such as defense, education and public health. In other words, by that time, the US government should have been crushed by its huge debt. What on earth is the solution to the US debt problem? Will the US debt problem evolve to a sovereign debt crisis similar to the European ones? Will the US government default or deliberately postpone debt repayment by exploiting dollar’s international reserve currency status? Based on the current situations, it seems a US default is unlikely because that will shake dollar’s international reserve currency position, destroy the US credit and render heavy blows to the global economy. As a result, leaders of both houses of US congress explicitly rejected the option of a possible US default. The US debt problem may evolve in one of the following possible directions in the future:
1. Servicing old debt with new debt by repeated debt ceiling raises
The US Congress passed the second Liberty Bond Act in 1917, allowing the US Treasury to raise funds for World War II by issuing Patriot Savings Bond. But the Act also provided that once the Federal debt reached its ceiling, the Treasury Department was not allowed to issue new bonds to service old debts; instead, it should generate treasury revenues to balance the Federal expenditures. With the deterioration of US government’s financial conditions, however, the US debt ceiling was repeatedly raised. According to statistics, from 1960 to the present, the US congress has raised Federal government’s debt ceiling 78 times. During the past decade, the US congress raised the ceiling 10 times, 4 of which occurred in 2008 and 2009. The US debt ceilings in 2008, 2009 and 2010 were $10.61 trillion, $12.10 trillion and $14.29 trillion respectively, taking 70%, 84.1% and 92.1% of each year’s GDP. Due to party politics, the US congress did not raise the debt ceiling in 1985, 1995, 1996, 2002 and 2003.
In the past few months, as more and more old debts became due, President Obama warned the congress that unless the US debt ceiling was raised again, the American economy would experience recessions. And once global investors became suspicious over the America’s credit standing and worried about an American default, “the global financial system will crush and America will sink into an economic recession much more serious than earlier ones”. After a series of political gaming, the two houses of the congress finally approved the debt ceiling raise on August 2nd to relieve the US debt crisis. However, this move was rather a forced maneuver than a fundamental approach to addressing the debt crisis. Raising debt ceiling frequently only leads to the loss of people’s confidence in the effectiveness of US governmental policies. The US debt crisis has indeed become a Sword of Damocles hanging over the US economy.
2. Devaluating dollar to cut debt at the cost of others
Inflation and dollar devaluation can reduce the US debt. Servicing old debt with devaluated money is equivalent to US citizens and foreign countries shouldering the cost of inflation in support of US government’s extravagant spending. Of course, many other governments have resorted to this sort of immoral dealing before. In the middle and long term, diluting debt by devaluating money will shrink the wealth of America’s creditors generated from trade surpluses. It is estimated that the US reduced its external debt by $3.58 trillion through dollar devaluation from 2002 to 2006.
The nature of America’s Quantitative Easing Policy is monetization of debt. The Fed’s massive purchases of US bonds with printed paper money plus significant dollar devaluation will doubtlessly accelerate the shift and re-distribution of global wealth. In March 2009, the Fed made a decision to purchase 300 billion dollar of US bonds in the following six months. To boost the US economy, the government announced in November 2010 the second round of qualitative easing measures, including purchasing 600 billion dollar of debt by the end of June 2011. These measures significantly worsened the Fed’s debt positions. From the eruption of financial crisis to the present, the total amount of Fed’s debt balance has increased from $899.3 billion as of June 2007 to $2.6529 trillion as of early April 2011, almost 2.95 times of the pre-crisis level.
The Fed’s direct purchase of debt, namely printing paper money to relieve debt crisis, boosted the demand for US bonds in the short run, prevented the yields of new issued bonds from rising and lowered financing costs. This was conducive to the earlier recovery of US economy but it also caused problems, including sacrificed independence of Fed’s monetary policy, serious inflation, huge pressures on the Treasury to pay debt, financial instability, and economic bubbles.
3. Recovering economy by tax increase and spending cut
Cutting America’s huge deficit by means of tax increase, spending cut, revenue generation and repaying debt with assets should be the fundamental approach to solving the country’s debt crisis and downsizing its debt. This is the only correct way to bring the US economy back to its normal track. However, for the American public who has grown accustomed to extravagant life styles, this might not be so easy.
The US government generates its revenue mostly from personal income tax and payroll tax (including social security tax and medical insurance tax) which together make up 80% of the annual tax income of the Federal government. In comparison, corporate income tax takes 12% of the Federal tax income. On the expenditure side, social security, health care, education and national defense are major fields to spend money. To win the support of voters on the issue of deficit cut, the two parties fought with each other relentlessly. The Republican Party insisted on cutting governmental spending, including spending on medical insurance, social security, pension and poverty relief programs. In contrast, the Obama Administration’s proposal was to levy more taxes on the middle class. However, in consideration of the weak American economy, spending cut may curb consumption and private investment and therefore is not conducive to the recovery of American economy; instead, it might expose the Administration to the risk of losing voters’support. Therefore, this option was not so much wanted by the US government. Currently, the two parties have reached an agreement on cutting the spending in the next decade by 2.1-2.4 trillion dollars. This number is thought too little to meet the debt cut purpose. And whether it can be smoothly implemented is yet to be observed.
4. Expanding US bond market overseas
The US can maintain a high level of debt because dollar’s reserve currency status and US Treasury bonds’ credibility attract foreign investors. From the eruption of subprime mortgage crisis in 2007 to the present, increasing bond issuances has become the major tool for the US government to raise money. Huge debts need good investors. As we have seen above, if the bonds were sold to the Fed, then serious inflation would occur. Selling US Treasury bonds to foreign investors became therefore a better option to stimulate the economy, especially because US Treasury bonds enjoy good credit rating worldwide. However, it is impossible for foreign countries to keep buying US bonds unconditionally, especially at a time when America faces serious market crisis. Buying more US bonds in this case could expose investors’ foreign reserve assets to greater liquidity risk and devaluation loss. Therefore, whether this option can be actually taken depends to a large extent on the interest calculations of both the US and foreign countries.
5. Alternative solutions
Insightful people in the US who have realized the harm of huge debt usually choose to criticize the debt-dependent growth path of the country. Although the US debt crisis is not yet serious enough to cause a full crush, they argue, the situation is already dangerous enough. For example, the Brookings Institution which proposed a GPI (Global Public Investment) concept to relieve the US debt crisis openly advocated introduction of foreign sovereign capital, especially Chinese capital, into American infrastructure projects. The institution believed GPI could compensate for the shortage of American treasury funds, alleviate American debt crisis and increase job opportunities. In contrast, scholars of America’s Institute for International Economics proposed levying taxes on Chinese assets in America to increase US treasury revenue and dissuade China from buying US assets. They also argued for the devaluation of dollar against RMB to cut US debt. These alternative solutions proposed by the American scholars are normally based on America’s interests only; therefore, they can hardly be accepted by the Chinese side. Being pure academic conceptions, these ideas did not become concrete policies due to their restricted practicality and feasibility. However, they do show that US decision-makers and think tanks are exploring ways to address their debt problems.
IV. Impact of US Debt on World Economy
The US has huge treasury deficit and huge external debt at the same time. Therefore, in the middle and long term, the possibility of an international payment and financial crisis can not be ruled out. This has become the number one threat to the world’s financial stability. The anti-crisis measures/ policies taken by the US government have put the country up to the throat in the water. How much longer can the strategy of “borrowing tomorrow’s money to service today’s debt” still hold? In 2010, interest payment took 6% of the US treasury expenditure. It is expected that in the future the ratio will grew considerably (see Chart 4). If the US does not change its behaviors, its credit standing will doubtlessly be discounted and dollar’s international reserve currency status will be challenged too.
1. High inflation risk to creditors
The nature of the Qualitative Easing Policy is monetization of debt. Monetization of treasury deficit will cause excessive market liquidity and inflation. And unlimited supplies of paper money will force other countries to adopt qualitative easing policies too to prevent appreciation of their own currencies and rampant inflows of “hot money”. Competitive and expansive monetary policies will unleash more and more cash into the market, accelerating the tempo of inflation. If prices are high, inventories are increased and capital investment efficiencies are lowered at a time when the real economy has not completely recovered, the economy will definitely head for another round of downward spiral. Eventually, the confidence of investors who hold US dollars will be shaken as Fed prints more paper money to buy Treasury bonds. The world economy will be at great risk of low growth and hypertension then.
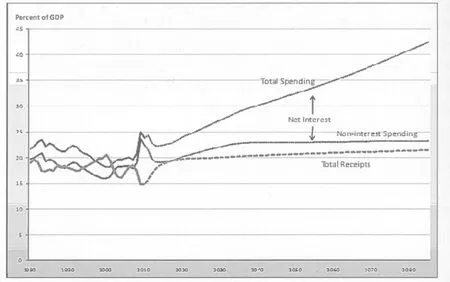
Chart 4 Historical and Current Policy Projections for Total Spending, Net Interest, Non-interest Spending, and Total Receipts, 1980-2085
2. High asset risk to asset investors
US debt market underwent rapid expansion in the 1990s. During this period, the percentage of foreign-held US Treasury bonds grew from 20% to 50%. However, some changes occurred to the distribution of US Treasury bonds worldwide. Although the percentage of dollar denominated assets held by foreign countries(regions) were decreasing, Japan and China increased their holding of US bonds, with China’s holding increasing much faster than that of Japan (Table 1). This means once the US economy was caught in fluctuations, China will be the most affected among the creditors.
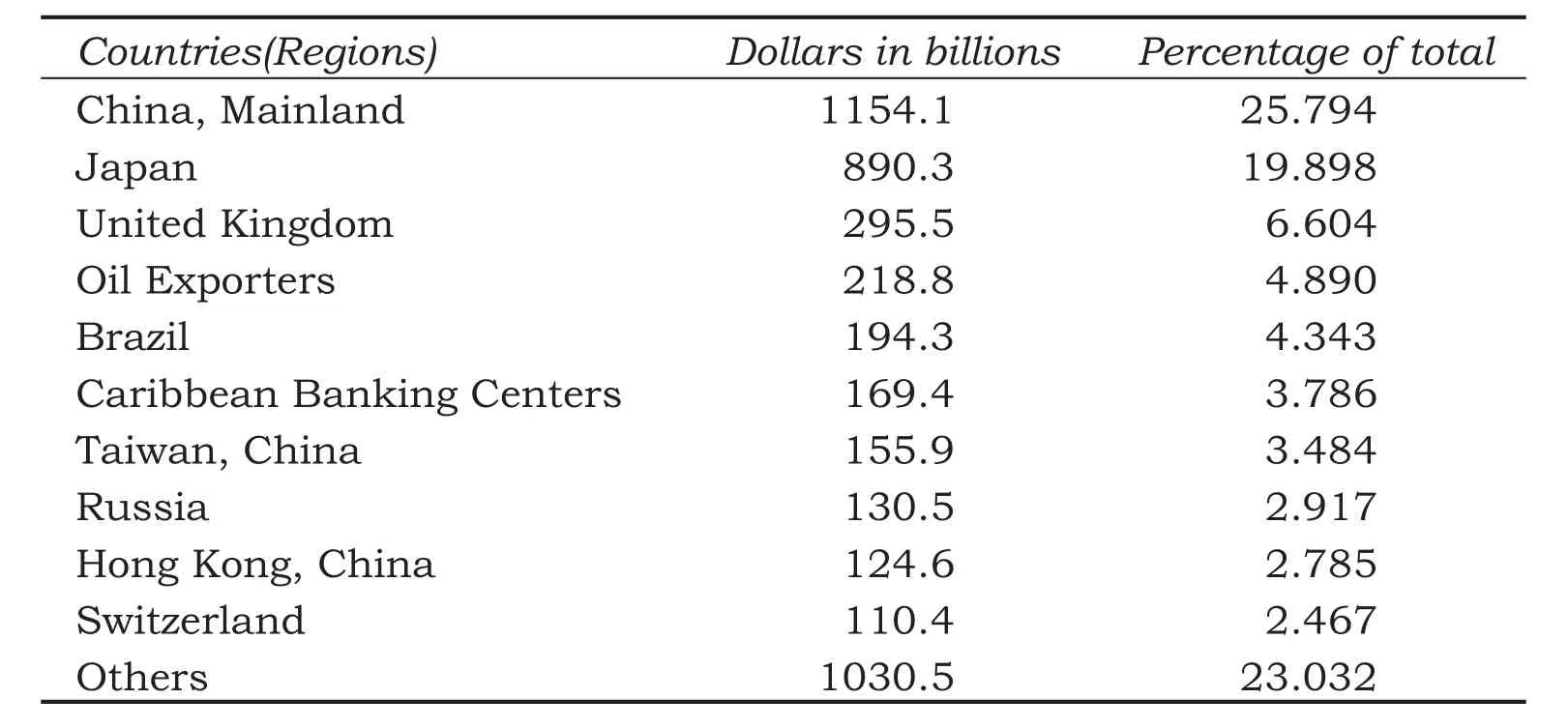
Table 1 Major Foreign Holders Of US Treasury Securities (by the end of Feb 2011)
The inflation caused by qualitative easing policies, if projected into the exchange rate side of the equation, should result in the devaluation of dollar. According to Fed statistics, dollar dropped considerably in value against most major currencies in 2010, as compared with 2007. Specifically, dollar devaluated 10.99% against RMB, 3.39% against Euro, 22.81% against Pound and 25.46% against Yen. Additionally, according to Fed’s statistics on weighted trading index, dollar’s exchange rate against a basket of currencies dropped 1.55% in 2010. The significant devaluation of dollar will inevitably result in shrinkage in value for dollar-denominated assets of foreign countries. That is to say, foreign countries holding dollar-denominated assets were forced to bear a significant portion of America’s market rescue costs. In other words, the US was levying an inflation tax on these foreign countries. Worse still, the dollar devaluation would reduce the exports and exacerbate the foreign trade positions of these countries, forcing them to accept additional economic losses. 3. High opportunity cost to bond investors
The opportunity cost for a country’s foreign reserve should be the differential between the reserve’s domestic investment proceeds if it is invested in the home country and its overseas investment proceeds if it is invested overseas. Take China for example. Currently, the annual yield of US Treasury bond is about 3%. However, the average investment return of Chinese enterprises in China is about 10%. Therefore, the opportunity cost of China’s foreign reserve should be around 7% of its foreign reserve. In view of the US inflation and dollar devaluation, the actual investment return of US Treasury bonds should be even lower.
V. China’s Investment in US Treasury Bonds and Related Anti-risk Measures
1. China’s foreign reserve investment in US treasury bonds
China and the US currently find themselves in a highly interdependent situation. On the one hand, the huge treasury deficit of the US needs China’s foreign reserve to cover; on the other hand, the huge foreign reserve of China calls for safe and reliable US investment opportunities. Therefore, neither party benefits from dramatic changes on the part of the other. For a long period of time, China’s foreign reserve was primarily made up of dollar denominated assets, and the most preferred investment product was US Treasury bonds. For example, China’s holding of US Treasury bonds in 2000 was only $60 billion; however, from 2001 onwards, the figure grew rapidly and by September 2008 it grew to $727.4 billion. It was then that China overtook Japan to become the largest creditor of the United States. By the end of May 2011, US Treasury bonds held by China accumulated to $1.16 trillion.
The rapid increase in China’s foreign reserve led to rapid increase in China’s investment in US Treasury bonds. According to statistics, from 2002 to 2010, around 40% of China’s foreign reserve was invested in US Treasury bonds.
2. China’s anti-risk measures
China holds large quantities of US Treasury bonds largely out of economic considerations. But this is a Hobson’s choice too. As export situations grow better, China’s unique trade structure may make favorable balance of trade a long-term phenomenon. In addition, as China received limited impact from the economic crisis and its growth has been kept stable, many people believe China’s economic growth rate will be high and its currency will appreciate in value. This attracts inflow of foreign capital. Under the current foreign exchange rate mechanism, there may even be dual trade surpluses to drive foreign reserve higher. As long as this trend does not stop, under the current international financial system, investment in US Treasury bonds will remain an option. Because in terms of security and liquidity, US Treasury bonds compared with European bonds and Japanese bonds are still higher in liquidity and lower in risk. However, if problems continue to surface around the US debt issue, China will have to take precautious measures to minimize risks and losses.
—Safeguarding China’s dollar-denominated assets through diplomatic channels. As the largest creditor of the US and the second largest economy in the world, China should play an important role in maintaining the stability of world financial system by keeping the safety of China’s foreign reserve. China should monitor closely the US economy and its Treasury bonds and request the US to protect China’s interests on occasions such as Sino-US strategic dialogue on economy and G20 summit meetings. Besides, China should demand the US to improve its financial conditions, execute stricter deficit control and make trustworthy commitments to maintain the market value of US bonds. China also needs to urge the US and IMF to make fundamental institutional reforms.
—Expanding foreign investment and optimizing the structure of foreign reserve. High portion of dollar-denominated assets in the overall foreign reserve structure constitutes a major risk for China’s foreign reserve. To control risks relating to the foreign reserve, the currency basket should be diversified in a planned manner by increasing the percentages of currencies other than US dollar. Meanwhile, the portion of monetized assets should be lowered by increasing overseas investment and acquiring more businesses and strategic resources. In this way, both the assets in the basket and their risks will be effectively diversified. Overseas economic experiences show that when a country experiences appreciation in its currency, it is very normal for it to expand its overseas investment. During this process, the government should provide strategic directions. In short, diversification of foreign reserve is a long-term task; therefore, reducing the stock of US bonds must be a gradual process.
—Hedging Risk with financial instruments. To prevent losses from price drops of US Treasury bonds, financial instruments such as put options and futures contracts should be used. Exchange rate risk of dollar denominated assets, i.e. risk caused by devaluation of US dollars, can also be hedged with instruments such as US dollar futures, options and currency swap. However, these instruments are effective only against short-term risks caused by US Treasury bonds and dollar devaluations.
—Expanding domestic demands. Increases in foreign reserve causing China to purchase US bonds continuously resulted from China’s export-oriented economy. If a fundamental strategic change could be made, then China’s future economic growth may be fuelled more by domestic demand than overseas demand. This shift can on the one hand address the balance of trade issue and on the other hand enhance the living standards and welfare of the Chinese people.
—Internationalization of RMB. The internationalization of RMB to become a world reserve currency is not only a fundamental solution to China’s foreign reserve dilemma, but also a long-term goal of China. In international trade, settlements and credits could be arranged in RMB by currency swap or other means. In this way, the ratio of RMB payments in import and export transactions would be increased. Meanwhile, China should actively participate in the restructuring of international monetary system. This would also facilitate the internationalization of RMB in the world.
Li Xuelian is Associate Professor at the Department of Finance, Nankai University; Wei Min is Associate Research Fellow at China Institute of International Studies.
 China International Studies2011年6期
China International Studies2011年6期
- China International Studies的其它文章
- The Trend of Ukraine’s Foreign Policy under the Yanukovych Administration
- EU Pushing Forward an Economic and Trade Oriented China-EU Strategic Partnership
- The Impact of the Rise of Emerging Economics on the Larger World Economy
- The Implications of New Thinking in Turkish Diplomacy
- Current Economic and Security Situation in Central Asia and Its Impacts on the Shanghai Cooperation Organization
- The Implications of Changes in the Middle East and North Africa
