Erythropoietin Receptor Positive Circulating Progenitor Cells and Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Patients with Different Stages of Diabetic Retinopathy△
Liu-mei Hu,Xia Lei,Bo Ma,Yu Zhang,Yan Yan,Ya-lan Wu,Ge-zhi Xu,Wen Ye,Ling Wang,Guo-xu Xu,Guo-tong Xu*,and Wei-ye Li,,*
1Department of Ophthalmology,Peking Union Medical College Hospital,Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences &Peking Union Medical College,Beijing 100730,China
2Tongji Eye Institute and Department of Regenerative Medicine,Tongji University School of Medicine,Shanghai 200092,China
3Laboratory of Clinical Visual Sciences,Institute of Health Sciences,Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences,Chinese Academy of Sciences &Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine,Shanghai 200025,China
4Department of Ophthalmology,Eye and ENT Hospital,Fudan University,Shanghai 200031,China
5Department of Ophthalmology,Huashan Hospital Affiliated to Fudan University,Shanghai 200040,China
6Department of Ophthalmology,Ruijin Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine,Shanghai 200025,China
7Department of Ophthalmology,Second Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University,Suzhou,Jiangsu 215004,China
8Department of Ophthalmology,Drexel University College of Medicine,Philadelphia,PA 19107,USA
DIABETIC retinopathy (DR) is a progressive disease that is comprised of the following stages:no apparent DR,non-proliferative DR(NPDR),and proliferative DR (PDR).Hallmarks of early DR are changes in microvascular structure and apoptosis of microvascular cells,i.e.,pericytes and endothelial cells.1Since the replacement of pericytes in DR is negligible,the normal regeneration of endothelial cells is responsible for maintaining the inner blood-retinal barrier.2There is a notion that the progressive loss of endothelial cells in early diabetes is repairable until the vascular endothelium reaches its Hayflick limit.3Accumulating evidence suggests that both circulating progenitor cells (CPCs)and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) contribute to vascular healing and remodeling under physiological and pathological conditions.Based on the different definitions and measures of CPCs,we defined CD34+cells as CPCs,whereas CD34+KDR+cells as EPCs.4In various animal models,transplantation of bone marrow-derived CPCs was found sufficiently improve organ function,and enhance vascular repair and tissue regeneration.5EPCs,isolated first in 1997,share some common properties and functions with CPCs,and have the specific ability to proliferate and differentiatein vitrointo endothelial cells.It was reported that the number of circulating EPCs was reduced in type 2 diabetic patients with peripheral vascular complications.4
Erythropoietin (EPO) treatment has been proposed as a novel therapeutic strategy for neuro-degenerative diseases and DR with macular edema.6EPO has been demonstrated to have anti-apoptotic,neurotrophic,anti-inflammatory,and stem cell-modulatory activities.7However,EPO is thought to be a potent ischemia-induced angiogenic factor that acts independently of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) during retinal neovascularization in larization in PDR.8Therefore,in order to understand the role of EPO/ EPOR system in retinal vascular regeneration in diabetes mellitus,we quantitatively study the circulating EPOR positive vascular progenitor cells (CPCs and EPCs) in type 2 diabetic patients with different stages of DR.
PATIENTS AND METHODS
Study population
Ethical approvals were obtained from the Internal Review Boards of Tongji University School of Medicine.The study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki Principles.The experiments were conducted with the understanding of the patients and written informed consents were obtained.Patients were excluded if they (1)underwent panretinal photocoagulation,vitrectomy,or anti-VEGF therapy in the past 3 months;(2) had systemic conditions such as overt cardiovascular disease,malignant disease,or hematologic disorders;or (3) received systemic EPO treatment.The age,gender,body weight,blood glucose,diabetes duration,blood pressure,and therapeutic regimen with oral antidiabetics or insulin were assessed in all the included patients at baseline.
The type 2 diabetic patients were staged for DR according to the Early Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy Study (ETDRS) classification,9and categorized into the following 4 groups:control group,mainly age-and sexmatched cataract patients without diabetes (n=7);NPDR group (n=7),defined as hemorrhages and/or hard exudates,venous beadings,or intraretinal microvascular abnormalities;PDR group (n=8) (PDR is equal to active PDR throughout this study),defined as the existence of retinal neovascularization (on the optic disc or/and in other area of retina,according to the definition by American Academy of Ophthalmology) or vitreous hemorrhage with retinal neovascularization;PDR with diabetic nephropathy (PDR-DN,n=7),defined as urinary albumin excretion > 300 mg/24 hours,but no history of using EPO or history of hemodialysis.
Flow cytometry
After an overnight fast,peripheral blood samples (3 mL)were drawn by venipuncture and immediately transferred into EDTA collection tubes.Peripheral vascular progenitor cells were identified based on cell-surface antigens with direct three-color analysis by flow cytometry,as previously described.4Briefly,red blood cells were lysed with ACK lysing buffer (0.155 mol/L ammonium chloride,0.1 mol/L potassium bicarbonate,and 0.01 mol/L disodium EDTA) for 10 minutes at room temperature.The blood cells were then washed with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) twice,and resuspended in 1% fetal bovine serum/PBS,sites for nonspecific binding were thus saturated.The blood cells were then incubated with 10 μL of APC-conjugated anti-human CD34 monoclonal antibody (mAb) (Becton Dickinson,Sunnyvale,CA,USA),20 μL of PE-conjugated anti-human KDR mAb (R&D Systems,Minneapolis,MN,USA),and 20 μL of FITC-conjugated anti-human EPOR mAb (R&D Systems) for 30 minutes on ice protected from light.One million viable cells were analyzed using a FACSCalibur flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson).After appropriate gating,the frequency of peripheral blood cells that were positive for these antibodies was determined with a two-dimensional side-scatter fluorescence dot plot analysis of the samples,as previously reported.4Data were processed using the FCS Express software (De Novo Software,Thornhill,Ontario,Canada).
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
Plasma was collected from the same peripheral blood samples as those used for flow cytometry after centrifugation at 700 ×gfor 20 minutes at 4°C with no brake,and stored at-70°C.EPO was assessed with commercial ELISA kit (R&D Systems) following the manufacturer’s instructions.Undiluted plasma (100 μL) was used for the measurement.The normal reference values for EPO were within the range of 3.1-14.9 mU/mL.All the values were calculated using standard curves generated with specific standards,according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as means±SE.Inter-group differences were analyzed with analysis of variance (ANOVA).Results from flow cytometry were expressed as the number of cells per one million events.The statistical evaluations of CPCs and EPCs in the studied groups were performed using ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test for multiple comparisons or Student’st-test.P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Patient characteristics
General information of the patient is presented in Table 1.No significant differences were observed in age,gender,body weight,blood pressure,diabetes duration,and therapeutic regimen with oral anti-diabetics or insulin.According to ANOVA result,DR groups (NPDR,PDR,and PDR-DN) did not show significant difference in the above parameters including the glycemic control level (P=0.296),which is an important risk factor of DR.
Enumeration of CPCs and EPCs
Cells were gated on the basis of CD34 and analyzed for KDR and EPOR expression (Fig.1A).Differences in the quantity of CD34+,CD34+KDR+,CD34+EPOR+,and CD34+KDR+EPOR+cells in peripheral blood from the four groups of patients were shown by representative flow-cytometry dot plots (Fig.1B).
CPCs (CD34+cells) were significantly augmented in NPDR group compared with the control group (685.0±52.3vs.438.6±16.3,P<0.01,Fig.2A).The number declined remarkably in PDR group (271.0±24.6,P<0.01),but returned in PDR-DN group to a level that was not significantly different from that in the control group (502.6±38.0vs.438.6±16.3) (Fig.2A).When compared with NPDR group,the number of CPCs was decreased in both PDR and PDR-DN groups (P<0.01 andP<0.05,respectively,Fig.2A).
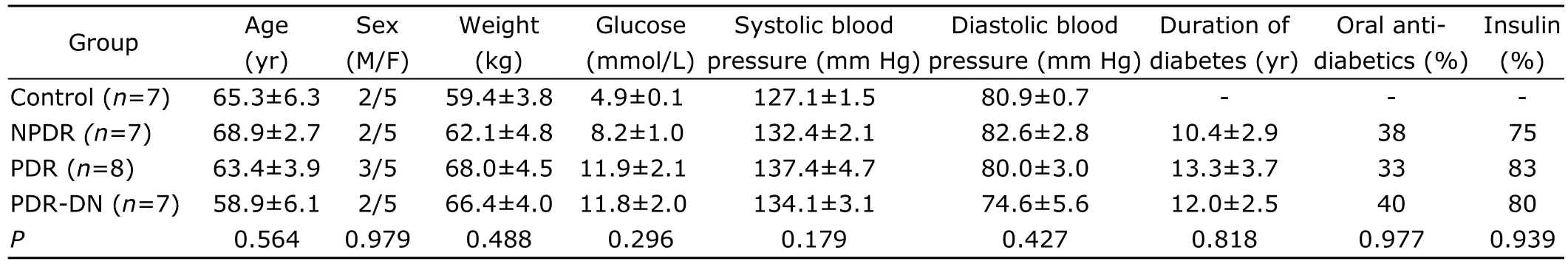
Table 1.Clinical information of enrolled patients§
EPCs (CD34+KDR+cells) were reduced by more than half of the control value in NPDR group (23.6±3.5vs.78.3±14.5,P<0.01) and PDR group (29.3±4.0vs.78.3±14.5,P<0.01),and to a lesser extent in PDR-DN group (52.1±4.4vs.78.3±14.5,P>0.05) (Fig.2B).When compared with NPDR group,EPCs were not changed in quantity in PDR (P>0.05) whereas increased in PDR-DN(P<0.01) (Fig.2B).
Enumeration of EPOR+ CPCs and EPOR+ EPCs
Strikingly similar patterns of decrease in EPOR expression were observed in both types of vascular progenitor cells.We found a significant reduction of EPOR+CPCs in NPDR group compared with the control group (37.7±6.6vs.93.7±8.9,P<0.01,Fig.3A).In both PDR and PDR-DN groups,decreases were also noticed but without statistical significance(PDR,49.6±6.7;PDR-DN,76.1±9.5).A significant difference was also observed between PDR-DN and NPDR groups(P<0.01,Fig.3A).Similarly,the number of EPOR+EPCs declined notably in NPDR group compared with the control group (7.9±2.2vs.45.0±6.8,P<0.01),and to a lesser extent in PDR (20.1±2.8,P<0.01) and PDR-DN groups (24.3 ±5.9,P<0.05)(Fig.3B).In addition,a significant increase was noted in both PDR and PDR-DN groups when compared with NPDR group (P<0.05 andP<0.01,respectively,Fig.3B).
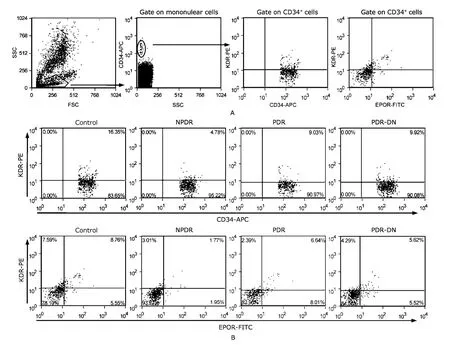
Figure 1.Enumeration of CPCs and EPCs by flow cytometry.
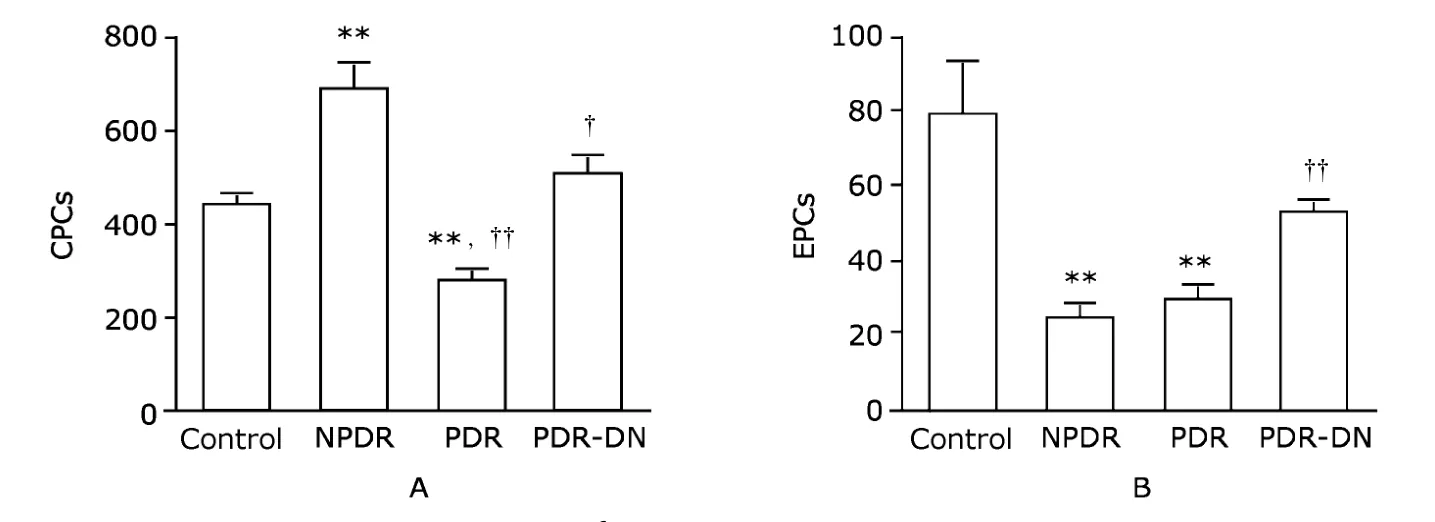
Figure 2.Enumeration of CPCs (A) and EPCs (B) per 1×106 white blood cells by flow cytometry shows changes of these cells in NPDR and PDR groups.Data are presented as means±SE.
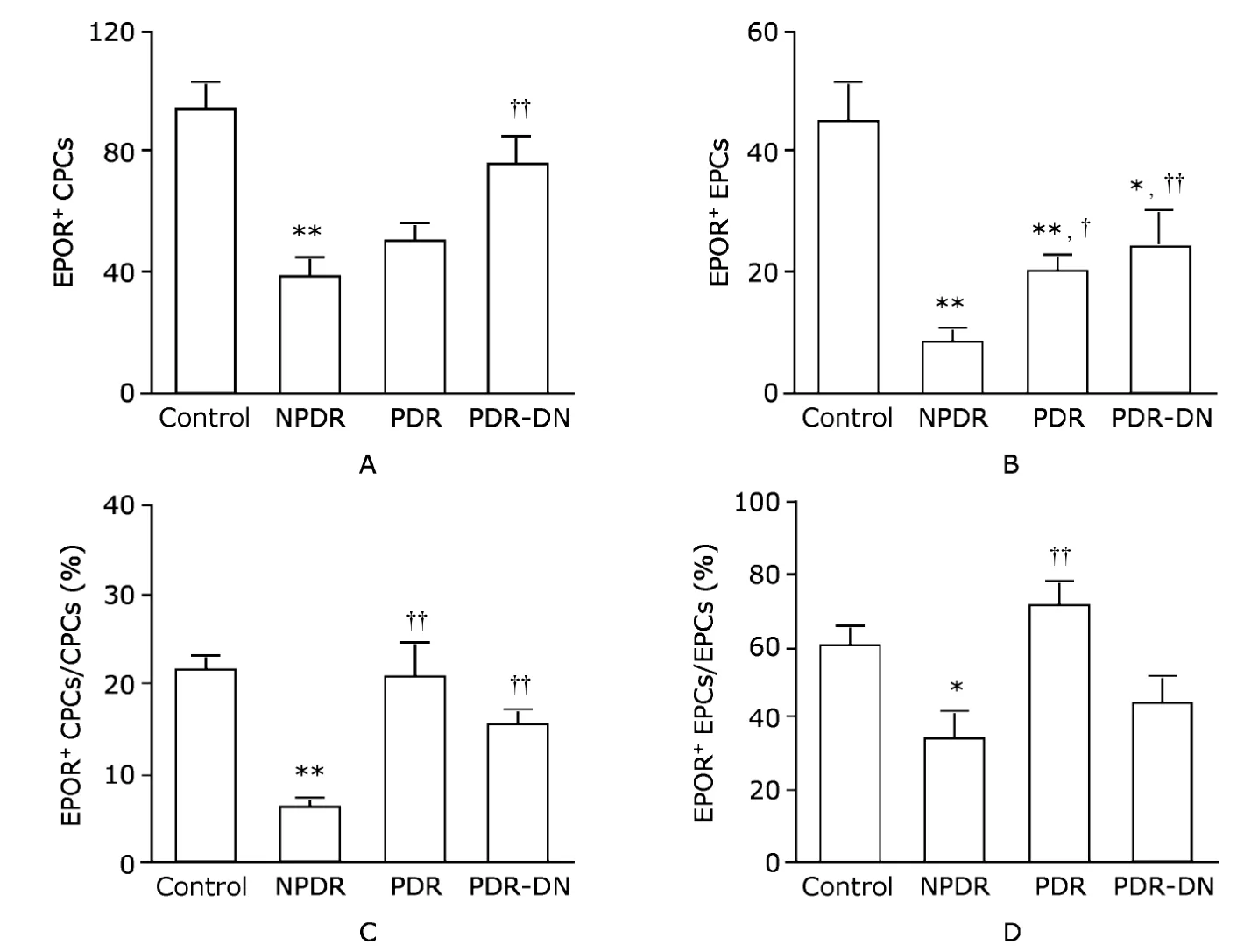
Figure 3.Enumeration of EPOR+ CPCs (A) and EPOR+ EPCs (B) per 1×106 white blood cells by flow cytometry,and percentage of EPOR+
When compared with the control group,the percentage of EPOR+CPCs in CPCs dropped significantly only in NPDR patients (5.9%±1.3%vs.21.3%±1.7%,P<0.01),while smaller and nonsignificant changes were observed in PDR (20.3%±4.0%) and PDR-DN groups (15.3%±1.7%).Dramatic changes were shown in these two groups compared with NPDR group (bothP<0.01,Fig.3C).A similar pattern in the percentage of EPOR+EPCs in EPCs was found.That percentage decreased from 60.3%±5.3% in the control group to 33.3%±7.9% in NPDR group (P<0.05,Fig.3D).The percentage increased in PDR group (70.6%±7.5%) and reduced in PDR-DN group (44.4%± 7.4%),but without statistical significance.When compared with NPDR group,it was augmented in PDR group to a great extent(P<0.01,Fig.3D).
Plasma concentrations of EPO
ELISA results showed significant reduction of plasma EPO concentration in all the three DR groups (NPDR,6.4±0.9 mU/mL;PDR,5.8±0.7 mU/mL;PDR-DN,3.9±0.5 mU/mL)compared with the control group (10.3±0.6 mU/mL) (allP<0.01,Fig.4).
DISCUSSION
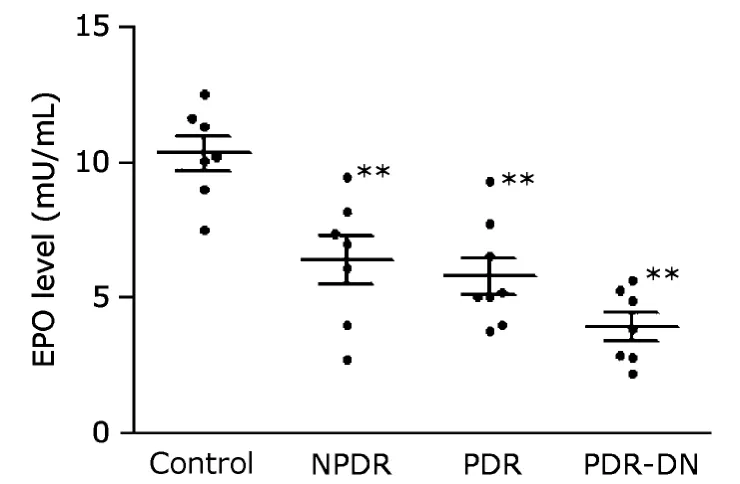
Figure 4.Plasma EPO concentrations were assessed by enzymelinked immunosorbent assay.The results demonstrate reduced expression levels of EPO in all the three DR groups.
Microangiopathy of DR is associated with progressive cell death of both retinal capillary endothelial cells and pericytes.1However,cell proliferation is much higher in retinal endothelial cells than in pericytes.2In addition,endothelial cells newly derived from EPCs would be involved in forming blood vessels under physiologic or pathologic conditions.5In a rat model of type 2 diabetes,the decreased number of EPCs,presumably caused by a lack of sympathetic innervations and reduced norepinephrine release,preceded the retinopathy.10These findings indicate that the impaired vascular regeneration in NPDR is,at least partially,due to the decrease of EPCs.Circulating cells that express CD34 consist of EPCs and other undifferentiated progenitor cells lacking vascular potential such as hematopoietic progenitor cells.11In this study,the enumeration of bone marrow-derived progenitor cells in type 2 diabetic patients with DR revealed increased CPCs and decreased EPCs in NPDR patients,however,reduction in both CPCs and EPCs were detected in PDR patients.
Circulating CD34+cells (CPCs) have been reported to assimilate into vasculature in chronic and acute animal models of ocular vascular damage,5demonstrating the importance of this group of cells in vascular repair.Our results showed that CPCs were increased significantly in NPDR,which was in agreement with the data of Lee et al.12They were the first to observe that CD34+cells may be increased in NPDR and PDR patients compared with the age-and sex-matched healthy controls.12Nevertheless,the increase of CPCs in NPDR patients suggests that there is an increased demand of generalized organ vascular regeneration including retina,and a sufficient capacity of CPCs in these patients.In contrast,EPCs were markedly decreased in type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients relative to matched healthy subjects.4,13EPCs constitute a circulating pool of cells able to form a“patch”that actively repairs the denuded or dysfunctional endothelium,hence a reduced EPC pool may lead to the inability to maintain adequate endothelial homeostasis.14There is a possibility that the increased CPCs but decreased EPCs (a small endothelial fraction of all CPCs) in DR may reflect a shortened peripheral survival or a weak bone marrow mobilization of EPCs.4
In a recent study on type 1 diabetic patients with DR,EPCs were found decreased in NPDR,unchanged in mild-moderate PDR,and increased in high-risk PDR compared with control patients without DR.15In the present study on type 2 diabetic patients with DR,a significant reduction of EPCs in NPDR patients and a rebound in PDR-DN patients were observed.Some quantitative differences among the reported studies may be related to the various surface markers used to define EPCs or the different systemic medications taken by the diabetic patients.For instance,many drugs with beneficial cardiovascular effects,such as statins,angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors,and glitazones,have been shown to stimulate EPCs.16Nevertheless,the general trend of decreased EPCs in diabetic patients may be an indicator of impaired vascular regeneration when DR progresses.The rebound of EPCs in PDR suggests that an associated ischemic condition may further stimulate their mobilization from the bone marrow.17
It has been reported that by stimulating normal EPC-mediated endothelial turnover,EPO improves cardiac microvascularization and function in the presence of ischemia.18Exogenous EPO is an FDA approved drug for anaemia.Recent data have demonstrated that a single intravitreal injection of EPO at the onset of diabetes in rats prevented retinal neuron death and protected the integrity of the blood-retinal barrier.19Furthermore,intravitreal treatment with EPO in diabetic patients with NPDR has a beneficial effect on macular edema.6Meanwhile,a number of reports have shown increased vitreous levels of EPO in eyes with PDR compared with eyes with minimal or no retinopathy,8suggesting that EPO may act as an angiogenic factor potentially aggravating PDR.However,the same high vitreous EPO levels have been observed also in eyes with diabetic macular edema but without prominent ischemia,indicating that the elevated vitreous EPO level may be due to factors other than ischemia.20Moreover,the examinations of epiretinal membranes of eyes with PDR revealed significant correlation of the number of blood vessels expressing the panendothelial marker CD34 with those expressing hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and VEGF,but not with immunoreactivity for EPO,suggesting that HIF-1α and VEGF,not EPO,play the major angiogenic roles in PDR.21It is noteworthy that a recent study on toxicity of intravitreal EPO in rabbits and another one on administration of a single high dose of EPO to three human eyes with retinal vein occlusion showed no toxicity and no neovascularization.22,23
Although the source of the high EPO level in eyes with PDR and diabetic macular edema remains unclear,there is a genuine concern that EPO/EPOR signaling system in EPCs is involved in retinal neovascularization.24As for the absolute number shown by the results of enumeration in the present study,EPOR+CPCs and EPOR+EPCs were downregulated in all the three DR groups,particularly in NPDR.When the percentage of EPOR+CPCs in CPCs and that of EPOR+EPCs in EPCs were compared with those in the control group,there was a significant reduction in NPDR group,whereas both EPOR+CPCs/CPCs and EPOR+EPCs/EPCs in PDR patients were higher than those in NPDR patients.Because PDR is a process related to pathological angiogenesis,the damage to retinal microvasculature at this stage is beyond repair.The detection of excessive EPOR+EPCs may be a warning sign for further stimulation by intraocularly administered exogenous EPO.In the meantime,the neuroprotective function of EPO should be weighed to the second place.In NPDR patients,the remarkable depression in both EPOR+CPCs/CPCs and EPOR+EPCs/EPCs indicates that exogenous EPO,an angiogenic factor,may have much less impact on vascular regeneration,if the retinal microvasculature is reparable.On the other hand,the exogenous EPO could play a remarkable role in the protection of retinal neurons from diabetic insults.19We agree with the notion that the particular stage of DR,reflecting a global ischemic condition,determines whether EPO administration is beneficial or harmful.25It has been proposed that as a precaution,intraocular EPO administration should be avoided in PDR patients.6
Our results show that there is no significant difference between PDR-DN and PDR groups in either the number of EPOR+CPCs and EPOR+EPCs or the proportions of these cells in CPCs and EPCs,suggesting that the same precaution may be necessary in PDR patients complicated with DN as well.The even lower plasma EPO level in PDR-DN patients compared with PDR patients may be due to the increase in latency of the kidney-derived EPO system caused by the progressive tubulointerstitial fibrosis in DN.26
In summary,our findings demonstrate the DR-stagedependent concentrations of EPOR+CPCs and EPOR+EPCs in type 2 diabetic patients.Most importantly,the dramatic reductions of EPOR+CPCs and EPOR+EPCs in NPDR patients might provide a safety zone for therapeutic intervention using EPO as a neuroprotectant in NPDR patients.In the meantime,it is critical to know that the rebound in the proportion of EPOR+EPCs in PDR patients may warn against exogenous EPO application at this stage.
1.Li W,Yanoff M,Jian B,et al.Altered mRNA levels of antioxidant enzymes in pre-apoptotic pericytes from human diabetic retinas.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 1999;45:59-66.
2.Kaur C,Foulds WS,Ling EA.Blood-retinal barrier in hypoxic ischaemic conditions:basic concepts,clinical features and management.Prog Retin Eye Res 2008;27:622-47.
3.Joussen AM,Poulaki V,Mitsiades N,et al.Suppression of Fas-FasL-induced endothelial cell apoptosis prevents diabetic blood-retinal barrier breakdown in a model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes.Faseb J 2003;17:76-8.
4.Fadini GP,Miorin M,Facco M,et al.Circulating endothelial progenitor cells are reduced in peripheral vascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Am Coll Cardiol 2005;45:1449-57.
5.Caballero S,Sengupta N,Afzal A,et al.Ischemic vascular damage can be repaired by healthy,but not diabetic,endothelial progenitor cells.Diabetes 2007;56:960-7.
6.Li W,Sinclair SH,Xu GT.Effects of intravitreal erythropoietin therapy for patients with chronic and progressive diabetic macular edema.Ophthalmic Surg,Lasers Imaging 2010;41:18-25.
7.Lipton SA.Erythropoietin for neurologic protection and diabetic neuropathy.N Engl J Med 2004;350:2516-7.
8.Watanabe D,Suzuma K,Matsui S,et al.Erythropoietin as a retinal angiogenic factor in proliferative diabetic retinopathy.N Engl J Med 2005;353:782-92.
9.Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group.Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs--an extension of the modified Airlie House classification:ETDRS report number 10.Ophthalmology 1991;98:786-806.
10.Busik JV,Tikhonenko M,Bhatwadekar A,et al.Diabetic retinopathy is associated with bone marrow neuropathy and a depressed peripheral clock.J Exp Med 2009;206:2897-906.
11.Boilson BA,Kiernan TJ,Harbuzariu A,et al.Circulating CD34+cell subsets in patients with coronary endothelial dysfunction.Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 2008;5:489-96.
12.Lee IG,Chae SL,Kim JC.Involvement of circulating endothelial progenitor cells and vasculogenic factors in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy.Eye (Lond) 2006;20:546-52.
13.Loomans CJ,de Koning EJ,Staal FJ,et al.Endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction:a novel concept in the pathogenesis of vascular complications of type 1 diabetes.Diabetes 2004;53:195-9.
14.Fadini GP,Coracina A,Baesso I,et al.Peripheral blood CD34+KDR+endothelial progenitor cells are determinants of subclinical atherosclerosis in a middle-aged general population.Stroke 2006;37:2277-82.
15.Brunner S,Schernthaner GH,Satler M,et al.Correlation of different circulating endothelial progenitor cells to stages of diabetic retinopathy:firstin vivodata.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2009;50:392-8.
16.Imanishi T,Hano T,Nishio I.Angiotensin II potentiates vascular endothelial growth factor-induced proliferation and network formation of endothelial progenitor cells.Hypertens Res 2004;27:101-8.
17.Wang CH,Verma S,Hsieh IC,et al.Enalapril increases ischemia-induced endothelial progenitor cell mobilization through manipulation of the CD26 system.J Mol Cell Cardiol 2006;41:34-43.
18.Westenbrink BD,Oeseburg H,Kleijn L,et al.Erythropoietin stimulates normal endothelial progenitor cell-mediated endothelial turnover,but attributes to neovascularization only in the presence of local ischemia.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2008;22:265-74.
19.Zhang J,Wu Y,Jin Y,et al.Intravitreal injection of erythropoietin protects both retinal vascular and neuronal cells in early diabetes.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008;49:732-42.
20.Hernández C,Fonollosa A,García-Ramírez M,et al.Erythropoietin is expressed in the human retina and it is highly elevated in the vitreous fluid of patients with diabetic macular edema.Diabetes Care 2006;29:2028-33.
21.Abu El-Asrar AM,Missotten L,Geboes K.Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and the protein products of its target genes in diabetic fibrovascular epiretinal membranes.Br J Ophthalmol 2007;91:822-6.
22.Zhang JF,Wu YL,Xu JY,et al.Pharmacokinetic and toxicity study of intravitreal erythropoietin in rabbits.Acta Pharmacol Sin 2008;29:1383-90.
23.Lagrèze WA,Feltgen N,Bach M,et al.Feasibility of intravitreal erythropoietin injections in humans.Br J Ophthalmol 2009;93:1667-71.
24.Yip HK,Tsai TH,Lin HS,et al.Effect of erythropoietin on level of circulating endothelial progenitor cells and outcome in patients after acute ischemic stroke.Crit Care 2011;15:R40.
25.Brines M,Cerami A.Erythropoietin-mediated tissue protection:reducing collateral damage from the primary injury response.J Intern Med 2008;264:405-32.
26.Fadini GP,Sartore S,Agostini C,et al.Significance of endothelial progenitor cells in subjects with diabetes.Diabetes Care 2007;30:1305-13.
 Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2011年2期
Chinese Medical Sciences Journal2011年2期
- Chinese Medical Sciences Journal的其它文章
- Risk Factors Analysis on Traumatic Brain Injury Prognosis
- Inhibition of SIRT1 Increases EZH2 Protein Level and Enhances the Repression of EZH2 on Target Gene Expression△
- Immediate Surgical Intervention for Penile Fracture:a Case Report and Literature Review
- Clinical Treatment and Anatomy Study of Maxillary First Molars with Five Root Canals
- Magnetic Resonance Urography and X-ray Urography Findings of Congenital Megaureter
- Changes of Nerve Growth Factor in Amniotic Fluid and Correlation with Ventriculomegaly△
