Magnetic resonance imaging characteristics of postoperative intracranial dissemination of recurrent gliomas*****☆
Department of Radiology, Shanghai First People’s Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200080, China
INTRODUCTION
Currently, the postoperative diagnosis of cerebral glioma metastasis is based on the assessment of clinical symptoms and the examination of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)[1-3].However, lumbar puncture is an invasive procedure with a high rate of post-procedure headache, and almost 50% of procedures can yield false negatives[4-5].Therefore,there is no strong basis for the early diagnosis of metastasis, and as a result of delayed treatment there is reduced opportunity for cure[6].Due to the rapid development of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology, as well as increasing recognition of the different routes of postoperative metastasis from glioma, the ability to make an early diagnosis may improve[7-10].In the present study, the follow-up data from 10 patients who had undergone surgery for cerebral glioma was analyzed retrospectively.This included evaluation of the results from MRI studies,operative notes and histopathological data with the objective of enhancing the diagnostic ability of MRI for different routes of glioma metastasis, and reinforcing safety consciousness related to the surgical procedure.
RESULTS
Quantitative analysis of subjects
A total of 10 cases were included in the final analysis (Table 1).
Primary sites and pathological types of primary gliomas
Primary tumors were located in the lobus frontalis (n=5), temporal lobe (n=2), lobus parietalis (n=1), cerebellum (n=1) and triangular zone (n=1).The minimum diameter of the primary tumor was 21 mm and the maximum diameter was 67 mm(median 40 mm).There were seven glioblastomas (Figure 1), two grade II astrocytic gliomas and one grade III astrocytic glioma.
Preoperative tumor signal intensity
Prior to surgery, the plain MRI scans of the primary gliomas showed a high but inhomogeneous intensity on T2 weighted imaging (T2WI) in seven cases (Figure 2A),and inhomogeneous isointensities in three cases.MRI scans showed inhomogeneous intensity on T1 weighted imaging (T1WI) in eight cases (Figure 2B), and inhomogeneous isointensities were mixed with high-intensity signals in two cases.Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) scans showed that tumors displayed high and low heterogeneous intensities in nine cases, and a combination of equi-signal and heterogeneous intensities in one case.
Contrast-enhanced scans of the 10 gliomas all showed enhancement and necrosis to varying degrees, with irregular tumor boundaries (Figures 2C, D).Infiltrating astrocytomas had broadly smooth boundaries and comparatively homogenous signals with few areas of necrosis.Anaplastic astrocytomas had irregular shapes,with inhomogeneous signals and obviously enhanced tumor boundaries.Cases of glioblastoma multiforme had irregular shapes, with inner necrotic and liquefacient areas, inhomogeneous enhancement, unclear boundaries and obvious signs of infiltration.Tumors in four cases underwent diffusion weighted imaging scans,of which two had a low intensity and two exhibited an inhomogeneous high intensity, with an average apparent diffusion coefficient value < 0.006 1 mm2/s.In three cases metastasis developed along white matter fibers: in one case it diffused to the contralateral side along white matter fibers of the corpus callosum splenium (Figure 3); in one case it invaded the contralateral brain tissues along the genu of the corpus callosum; and in one case it invaded the occipital lobe along the white matter fibers after tumor surgery in the trigone.Diffusion tensor imaging scans all demonstrated fibrous continuity between the primary glioma white matter fibers and the new sub-foci of tumor; fibers in the focal zone were interrupted, reduced in number or displaced by the deposits.In one case a susceptibility-weighted imaging examination showed inhomogeneous patchy low intensity within the tumor and the phase diagram showed diamagnetic signs.
Time to metastasis after surgery
After the inspection of follow-up clinic visit documentation,the shortest recurrence time was found to be 4 months and the longest recurrence time was 56 months.
Postoperative signal intensity
MRI follow-up scans were performed between one and five times in the 10 patients in our cohort.Figure 4 shows the preoperative and postoperative follow-up images of one patient.Positive MRI signs, evaluated by means of comparison of pre- and post-operation MR images which included non-contrast enhanced and contrast enhanced images, were regarded as the criteria for all cases.
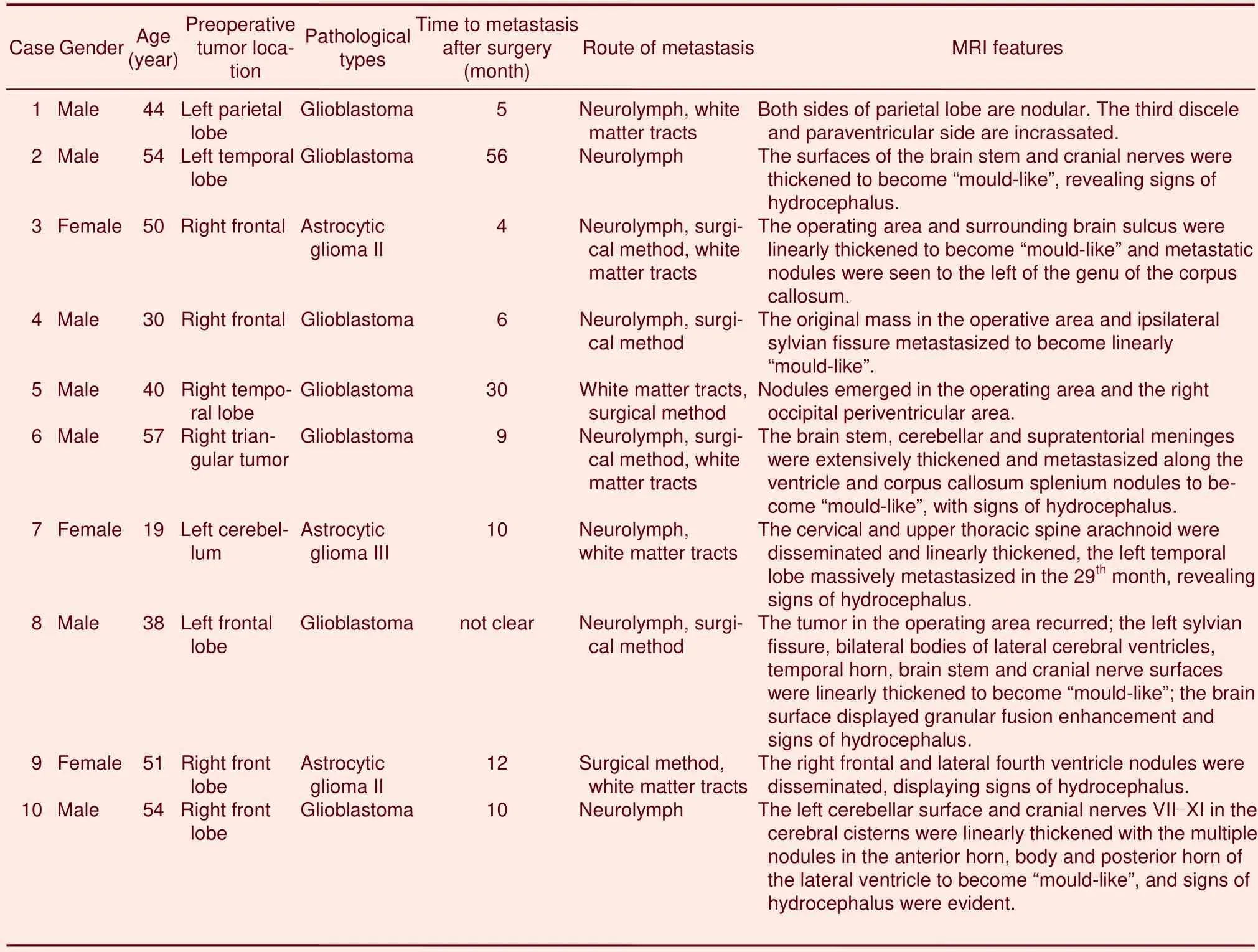
Table 1 Demographic and clinical data, routes of metastasis and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings from 10 patients

Figure 1 Pathological section of glioblastoma(hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 200).The tumor cells demonstrate clear atypia.They are irregularly shaped,polymorphous and have dense chromosomes, with pathological mitotic figures.
On the plain MRI scans, 1/7 cases were linearly thickened with isointensity and 5/7 cases exhibited nodular foci on T1WI; the cerebral sulci and cisterns in 2/7 cases had become shallow and in five cases had nodular foci on T2WI.FLAIR imaging demonstrated that the cerebral sulci and cisterns in 2/7 cases had become shallow, and that in six cases nodular foci had developed.Signals from nodulated disseminated foci and the main areas of the primary tumor were broadly consistent in seven cases,and inconsistent in three cases.The contrast-enhanced MRI scans revealed linear thickening in seven cases,nodules in seven cases (Figure 4D), similarities to“mould-like” signs in six cases and hydrocephalus in six cases.There was low intensity susceptibility-weighted imaging in one case and the phase diagram paramagnetic confirmed a history of local hemorrhage.
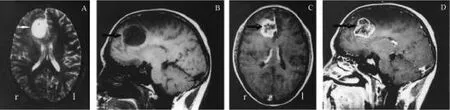
Figure 2 Preoperative glioblastoma multiforme in the right frontal lobe.(A) Axial T2 weighted image showing a high intensity area and the surrounding mild cerebral edema.(B) Sagittal T1 weighted image (T1WI) showing a low intensity mass in the right frontal lobe.(C) Axial T1WI gadolinium-diethylene-triamine pentaacetic acid (Gd-DTPA) image showing tumor enhancement and necrosis.(D) Sagittal T1WI Gd-DTPA image showing tumor enhancement and necrosis in the right frontal lobe.Arrows indicate the tumor.r: right and l: left.
Figure 3 Tumor metastasis along brain white matter fiber bundles.(A) T1 weighted image (T1WI) of preoperative glioma.(B)T1WI contrast-enhanced image of preoperative glioma.(C) T2 Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery image of contrast-enhanced image of preoperative glioma.(D) and (E) are T1WI and diffusion-weighted images, respectively, showing tumor metastasis along brain white matter fiber bundles.In (E), the red color represents high diffusion-weighted imaging signal, and the blue color represents low diffusion-weighted imaging signal.(F) Tumor pathological section showing glioma cells (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 100).The white arrows in panel A to E indicate the tumor.r: right and l: left.
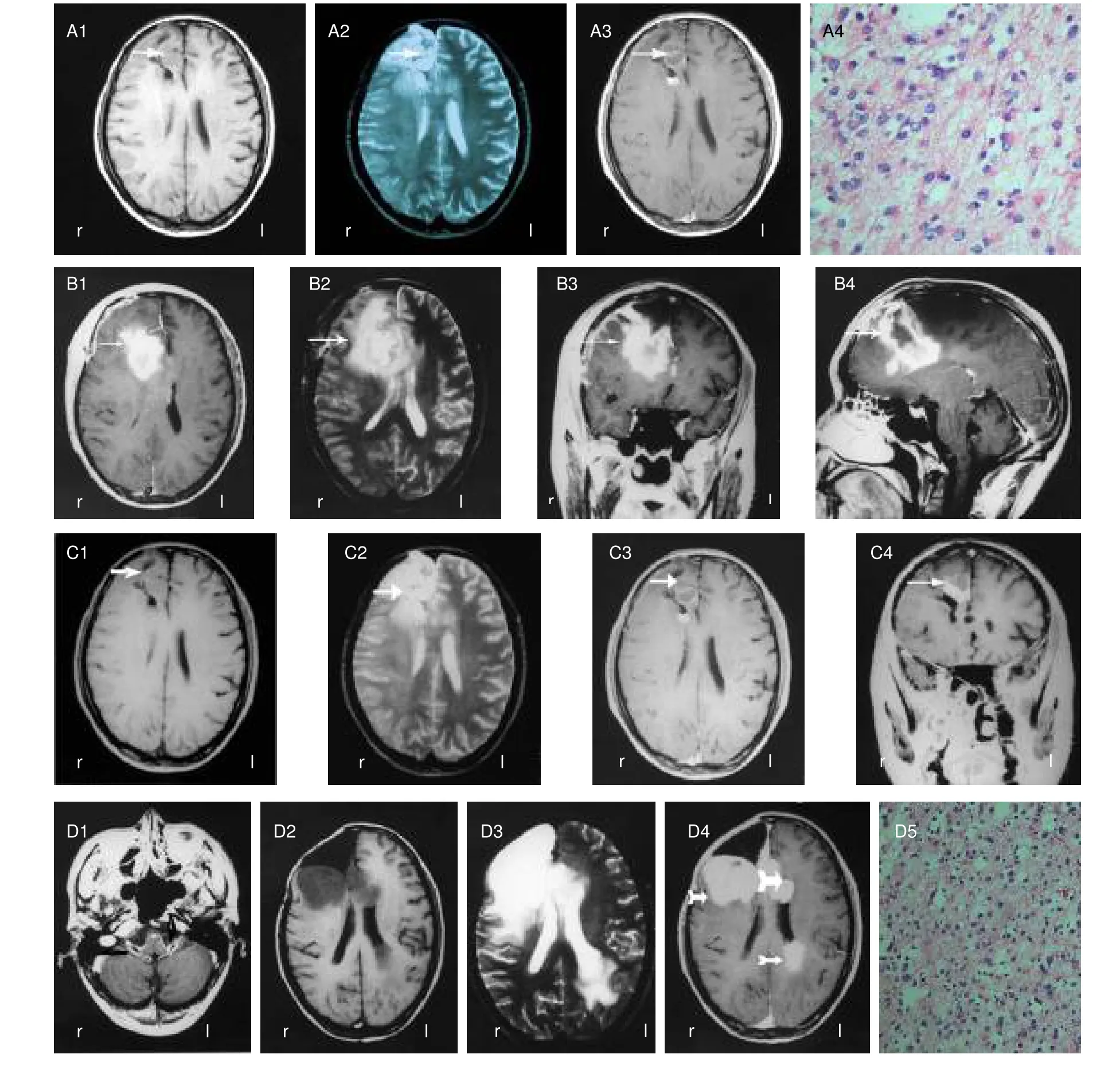
Figure 4 Preoperative and postoperative follow-up images of one patient.Arrows indicate the tumor.r: ight and l: left.(A)Preoperative magnetic resonance images and a pathological section.(A1) Plain axial T1 weighted image (T1WI); (A2) axial T2 weighted image (T2WI); (A3) axial T1WI gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetate (Gd-DTPA) image; (A4) tumor pathological section showing glioma cells (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 400).(B)Two-week postoperative follow-up.(B1) Plain axial T1WI scan showing high intensity bleeding in the original tumor zone and the surface of the right frontal lobe; (B2) axial T2WI image showing bleeding as high intensity in the original tumor zone and the surface of the right frontal lobe; (B3) coronal T1WI Gd-DTPA image showing high intensity bleeding in the original tumor zone and surface of the right frontal lobe; (B4) sagittal T1WI Gd-DTPA image showing high intensity in the original tumor zone.(C) Postoperative eight-month follow-up.(C1) Axial T1WI scan showing space-occupying signs of isointensity in the original tumor zone; (C2) axial T2WI image showing high intensity in the original tumor zone; (C3) axial T1WI Gd-DTPA image showing local enhancement; (C4) coronal T1WI Gd-DTPA scan showing mild local enhancement.(D) Postoperative 10-month follow-up.(D1) Axial T1WI Gd-DTPA image showing nodulated and linear enhancement in the brain stem and around sections of the cranial nerves; (D2) axial T1WI image showing multiple low intensity nodular foci in the right frontal lobe and left ventricular wall; (D3) axial T2WI scan showing multiple high intensity nodular foci in the right frontal lobe and wall of the left lateral ventricle; (D4) axial T1WI Gd-DTPA image showing multiple high intensity nodular foci in the right frontal lobe and left ventricular wall; (D5) tumor pathological section showing glioma cells (hematoxylin and eosin staining, × 200).
Sites of dissemination
(1) Tumor metastasis along the CSF: Four cases developed nodular foci or thickening of the pia mater with boundary enhancement in the cerebral cisterns that surrounded the cranial nerves, primarily nerves VII-XI(Figure 4).Three cases developed multiple paraventricular nodular foci accompanied by ependymal enhancement, and enhancement of the cerebral cisterns or pia mater in the sulci.In two cases shallow cortical sulci became evident or vanished along the suprasellar cistern, sylvian fissure cistern, interpeduncular cistern and quadrigeminal cistern sulci.Mold-like signs were displayed that were identical to the signs of subarachnoid hemorrhage after enhancement.(2) Tumor metastasis along the access of the surgical zone: One case exhibited recurrence along the route into the surgical area, which disseminated to involve the adjacent brain tissues and meninges (Figure 5).MRI manifestations included thickening of the pia mater and enhancement along the cisterns, with the brain sulci becoming shallow and ultimately disappearing.Multiple ventricular wall nodular foci were accompanied by ependymal enhancement, in addition to the aforementioned types of metastasis.In one case, signs of thickening of the spinal pia mater and arachnoid developed in the superior cervical segment.(3) Tumor metastasis along brain white matter fibers: In two cases the tumor had spread directly to the contralateral side along the fibers of the corpus callosum.One invaded the contralateral sideviathe fibers in the genu and formed a mass, and the other spread along the fibers of the splenium of the corpus callosum.In a third case the tumor invaded the occipital lobe along white matter fibers following prior tumor surgery in the trigone (Table 1).
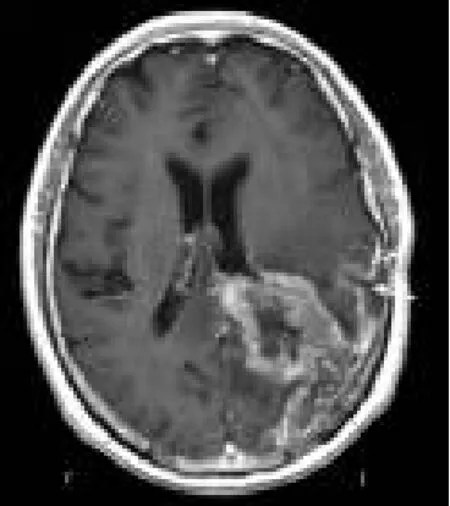
Figure 5 Tumor metastasis along the routes of surgical access (T1 weighted imaging).The white arrow indicates the tumor.r: Right;l: left.
Other signs
Six cases experienced various degrees of ventriculomegaly and hydrocephalus.The T2WI and FLAIR sequence indicated high signal around the ventricles; the T1W1 sequence appeared as an exudate with a low signal.
DISCUSSION
MRI features of intracranial glioma metastasis
The protective effect of the immune system limits tumor diffusion under physiological conditions.In particular,benign astrocytomas do not have metastatic characteristics.We believe that the factors listed above may lead to the entry of glioma cells into the CSF, which then circulate through the CSF to reach a specific location where they seed and create their own microenvironment to support growth.Therefore,metastatic tumors can be found in any region that the CSF flows through.The major manifestations of tumor metastasis along the CSF are multiple diffuse nodules that predominate in the lateral ventricle walls, ependyma,cerebral pia mater, cerebral cistern, and the cranial nerves in the cerebral cisterns, amongst other locations.
In addition there is linear enhancement of ependymal or pia mater thickening, as well as concomitant brain stem and cranial nerve linear thickening and enhancement.Since comparison of the location of the brain stem nerve root with the surrounding CSF more easily revealed abnormal signs, it is believed that metastasis is more specific along cranial nerves.Once the aforementioned signs occur and are viewed in combination with the history of the relevant intracranial conditions, CSF dissemination can be definitively diagnosed.
In the present study, postoperative tumor metastasis along the route of surgical access was observed at follow-up, which disseminated along the subarachnoid cavity accompanying the local tumor.Histological findings showed that glioma cells can disseminate along white matter fibers.These findings were consistent with the surgical findings, and the reconstructive diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) in combination with other MRI signs, before and after surgery (Figure 5, data not shown).Due to the low volume of samples involved, further large-sample studies are required to confirm this finding.
Glioma CSF metastasis often leads to hydrocephalus
The regulation of intracranial pressure maintains the balance between cerebral blood flow and the CSF.If the physiological regulatory function related to intracranial pressure is impaired by intracranial foci and damage to the blood-brain barrier, the cerebral blood flow is reduced and aberrations in the circulation of CSF will occur.This leads to hydrocephalus and increased intracranial pressure.Inamasuet al[11]reported that approximately 10% of hydrocephalus cases were caused by supratentorial gliomas.Our analysis found that the postoperative incidence of hydrocephalus was 60% (6/10 cases), and inferred that this was due to the deposition of diffuse and exfoliated tumor cells in brain arachnoidal granulations.The high level of protein that is secreted by tumor cells leads to an increased protein quotient within the CSF and affects the absorption of CSF.Therefore, hydrocephalus is one of the characteristic effects of tumor dissemination by the CSF.A full awareness of the signs of metastasisviathe CSF or dissemination along white matter fibers through the perivascular spaces in the brain, and at the site of surgical pathways after cerebral glioma surgery is necessary.Any reduction in the timing of definitive diagnosis during postoperative follow-up, would be of great value in enabling early intervention measures that elevate the survival rate of patients following surgery for cerebral glioma[7-9,12].
In conclusion, intracranial gliomas can disseminateviathe cerebrospinal fluid, white matter fibers and the surgical access site.Magnetic resonance imaging examinations, including T1WI, fat-suppressed T1WI,T2WI and Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery, were reliable in the detection of invasive recurrent glioma.However, a major limitation of the study was the low number of patients involved, and a future larger study should be carried out.
SUBJECTS AND METHODS
Design
The study was designed to retrospectively evaluate different routes of glioma metastasis using data from MRI,histopathology and surgical notes.
Time and setting
The study was performed at the Department of Radiology,Shanghai First People’s Hospital, School of Medicine,Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China from April 2000 to December 2008.
Subjects
Ten patients diagnosed with cerebral glioma were recruited between April 2000 and December 2008.All of these patients had developed intracranial metastasis according to MRI scans during postoperative follow-up.The initial diagnosis was confirmed by MRI, surgical findings and histopathology[13-15].Seven patients in this cohort were male and three were female.The median age was 45 years (range: 19–57 years).The clinical symptoms of disease recurrence were headache,nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, epilepsy, unstable gait,limb numbness and mental disorders.The principal signs on examination included impaired vision, oculomotor paralysis, signs of meningeal irritation and positive pathological reflexes.With the approval of the Medical Ethics Committee of Shanghai First People’s Hospital,informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Methods
MRI protocol
This study used a GE excite HD 1.5T or 3.0T excite HD superconducting MRI system (GE Medical Systems,Milwaukee, WI, USA).Using an eight channel neurovascular array, all 10 patients underwent plain scans before and after surgery.The scans consisted of axial and sagittal T1 FLAIR (repetition time 2350 ms;echo time 25 ms; time of inversion 800 ms)[16], axial T2WI(repetition time 4 000 ms; echo time 130 ms) and axial T2 FLAIR (repetition time 9 000 ms; echo time 110 ms;time of inversion 2 100 ms).A contrast-enhanced scan was performed after the intravenous injection of 2 mL/s of the contrast agent, gadolinium-diethylene-triamine pentaacetic acid (0.1 mmol/kg; Bayer Schering Pharma AG, Berlin, Germany)[17-18], followed by immediate axial T1 FLAIR (repetition time 2600 ms; echo time 25 ms;time of inversion 1 800 ms), coronal T1 FLAIR fat-suppressed sequence (repetition time 2160; echo time 25; time of inversion 720 ms), field of view 220 ×165 mm, slice thickness 5 mm, slice distance 1 mm and number of excitations 1.Diffusion-weighted imaging examination used spin echo-echo planar imaging sequence, repetition time/echo time=4 800/85 ms, field of view 240 × 240 mm, slice thickness 5 mm, slice distance 1.5 mm, matrix 192 × 192, number of excitations 2, b=1 000 s/mm2and b=0 s/mm2.The scan data obtained were transferred to the GE Advantage Windows 4.3 workstation to generate apparent diffusion coefficient maps after the automatic post-processing using GE FUNCTOOL 4.4.05 software(GE Medical Systems).Apparent diffusion coefficient values were recorded.Diffusion tensor imaging examination used the following parameters[19]:
25-direction acquisition; repetition time/echo time=6 200/70 ms; field of view 240 × 240 mm, slice thickness 5 mm; slice distance 1.0 mm; matrix 192 × 192; number of excitations 2; and b=1 000 s/mm2.Susceptibilityweighted imaging examination involved: RM/3D acquisition; axial, repetition time 34.0/echo time 25.0 ms;slice thickness 2.0 mm; slice distance 0 mm; flip angle 20;number of excitations 0.75; bandwidth 31.2 kHz; position Head First-Supine; matrix 384 × 320; field of view 240 ×240 mm; and scan time 265 s.The intensity and phase information were obtained respectively during susceptibilityweighted imaging acquisition; off-line post-processing was performed on phase information using the GE Advantage Windows 4.3 workstation, filter width 32 and mask number 4 to obtain the corrected phase images which were weighted on intensity information.Images underwent minimum intensity projection reconstruction using REFORMAT software (GE Medical Systems) to obtain the final susceptibility-weighted images and reconstruct the slice thickness, so that it was identical to that used in conventional MR imaging[20].
MRI evaluation criteria
All cases were standardized by positive signs that were compared pre- and postoperatively: (1) Diagnostic criteria for tumor metastasis along the CSF were based on the Meltzer meninges tumor index[21-22], which was revised into: (I) thickened and reinforced in-line pattern along the pia mater, nerves or brain surface, thickness >2 mm and thickened length > 25 mm over the convexity of brain; (II) nodules along the paraventricular walls, sulci,nerve or brain surface with a diameter > 2 mm should be treated as abnormal; and (III) the “cast” sign which was similar to subarachnoid hemorrhage along some ventricles or parts of the sulcus.(2) Diagnostic criteria for tumor metastasis along the route of surgical access: This was manifested by postoperative tumor formation in the surgical zone where there was no tumor previously,accompanied by the disappearance of the local subarachnoid cavity, meningeal thickening or, more frequently, accompanied by tumor disseminationviaCSF[12].(3) Diagnostic criteria for tumor metastasis along brain white matter fibers: Sub-foci with similar signals emerged at the conduction and connection sites between brain glioma and related white matter fibers, and local white matter fibers were disrupted, reduced in number or displaced[15,23-24].
Author contributions:Guixiang Zhang and Linfeng Zheng were responsible for ensuring the integrity of entire study, final version approval of the manuscript, manuscript editing and literature research.Linfeng Zheng, Guixiang Zhang, Jinglong Zhao, Han Wang, Kang’an Li, Lin Zhang, Xifu Wang, Pengpeng Sun and Yunsheng Hu participated in study concept, study design or data acquisition or data analysis, interpretation,manuscript drafting or manuscript revision for important intellectual content.Linfeng Zheng, Guixiang Zhang, Jinglong Zhao and Xifu Wang were in charge of clinical studies.Linfeng Zheng participated in statistical analysis.Guixiang Zhang obtained funding for the study.
Conflicts of interest:None declared.
Funding:This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.300570539; the Major Subject of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, No.07jc14032 and 074119504; the Doctoral Innovation Fund of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, No.BXJ201043; and the Nano Specialized Research Fund of Shanghai Science and Technology Commission, No.1052nm05800.
Ethical approval:All of the patients that participated in our study gave their informed consent.The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Shanghai First People’s Hospital.
[1] Sanai N, Chang S, Berger MS.Low-grade gliomas in adults.J Neurosurg.in press.
[2] Chang EF, Smith JS, Chang SM, et al.Preoperative prognostic classification system for hemispheric low-grade gliomas in adults.J Neurosurg.2008;109(5):817-824.
[3] Mittal S, Szlaczky MC, Barger GR.Low-grade gliomas in adults.Curr Treat Options Neurol.2008;10(4):271-284.
[4] Chamberlain MC.Neoplastic meningitis.Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.2008;8(3):249-258.
[5] Walbert T, Mikkelsen T.Recurrent high-grade glioma: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge.Expert Rev Neurother.2011;11(4):509-518.
[6] Maroldi R, Ambrosi C, Farina D.Metastatic disease of the brain:extra-axial metastases (skull, dura, leptomeningeal) and tumour spread.Eur Radiol.2005;15(3):617-626.
[7] Bisdas S, Naegele T, Ritz R, et al.Distinguishing recurrent high-grade gliomas from radiation injury: a pilot study using dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging.Acad Radiol.2011;18(5):575-583.
[8] Narang J, Jain R, Arbab AS, et al.Differentiating treatment-induced necrosis from recurrent/progressive brain tumor using nonmodel-based semiquantitative indices derived from dynamic contrast-enhanced T1-weighted MR perfusion.Neuro Oncol.2011;13(9):1037-1046.
[9] Santra A, Kumar R, Sharma P, et al.F-18 FDG PET-CT in patients with recurrent glioma: Comparison with contrast enhanced MRI.Eur J Radiol.in press.
[10]Sankar T, Caramanos Z, Assina R, et al.Prospective serial proton MR spectroscopic assessment of response to tamoxifen for recurrent malignant glioma.J Neurooncol.2008;90(1):63-76.
[11]Inamasu J, Nakamura Y, Saito R, et al.Postoperative communicating hydrocephalus in patients with supratentorial malignant glioma.Clin Neurol Neurosurg.2003;106(1):9-15.
[12]Zhang GX, Xu ZX, Han YD, et al.MRI analysis for different routing meningeal metastasis.Zhonghua Fangshe Xue Zazhi.2001;35(1):17-20.
[13]Watanabe M, Tanaka R, Takeda N.Magnetic resonance imaging and histopathology of cerebral gliomas.Neuroradiology.1992;34(6):463-469.
[14]Kumar RA, Khandelwal N, Sodhi KS, et al.Comparison between contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and technetium 99m glucohepatonic acid single photon emission computed tomography with histopathologic correlation in gliomas.J Comput Assist Tomogr.2006;30(5):723-733.
[15]Sanghvi DA.Recent advances in imaging of brain tumors.Indian J Cancer.2009;46(2):82-87.
[16]Gurwara S, Azzawe A, Jacobs S, et al.Comparing the volume of gliomas in the brain in FLAIR and post-contrast T1-weighted MRI sequences.J La State Med Soc.2010;162(5):265-266.
[17]Voth M, Michaely HJ, Schwenke C, et al.Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (MRA): evaluation of three different contrast agents at two different doses (0.05 and 0.1 mmol/kg) in pigs at 1.5 Tesla.Eur Radiol.2011;21(2):337-344.
[18]Bauner KU, Reiser MF, Huber AM.Low dose gadobenate dimeglumine for imaging of chronic myocardial infarction in comparison with standard dose gadopentetate dimeglumine.Invest Radiol.2009;44(2):95-104.
[19]Liu X, Tian W, Kolar B, et al.MR diffusion tensor and perfusionweighted imaging in preoperative grading of supratentorial nonenhancing gliomas.Neuro Oncol.2011;13(4):447-455.
[20]Pinker K, Noebauer-Huhmann IM, Stavrou I, et al.High-field,high-resolution, susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: improved image quality by addition of contrast agent and higher field strength in patients with brain tumors.Neuroradiology.2008;50(1):9-16.
[21]Meltzer CC, Fukui MB, Kanal E, et al.MR imaging of the meninges.Part I.Normal anatomic features and nonneoplastic disease.Radiology.1996;201(2):297-308.
[22]Dietemann JL, Correia Bernardo R, Bogorin A, et al.Normal and abnormal meningeal enhancement: MRI features.J Radiol.2005;86(11):1659-1683.
[23]Li YZ, Huang ZL, Wei DN, et al.Diffusion tensor imaging of the white matter tracts in preoperative patients with cerebral neoplasm.Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao.2006;26(11):1648-1651.
[24]Witwer BP, Moftakhar R, Hasan KM, et al.Diffusion-tensor imaging of white matter tracts in patients with cerebral neoplasm.J Neurosurg.2002;97(3):568-575.
- 中國神經(jīng)再生研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Effects of electroacupuncture at Zusanli (ST 36) on neurons in the colonic myenteric plexus in rats with irritable bowel syndrome with constipation*★
- Effects of Shuyusan on monoamine neurotransmitters expression in a rat model of chronic stress-induced depression*★
- Quiet rest ameliorates biochemical metabolism in the brain in a simple concussion rabbit model Evaluation of hydrogen proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy*☆
- Dynamic analysis of 10 components of the Chinese herbal compound Wuzhuyu-tang absorbed into rat plasma**☆
- Sidiming attenuates morphine withdrawal syndrome and nitric oxide (synthase) levels in morphine-dependent rats and rhesus monkeys*★
- Effects of Fujian tablet on Nogo-A mRNA expression and plasticity of the corticospinal tract in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia*☆

