Effects of infusion of different fluids during controlled hypotension on gastric intramucosal pH and postoperative gastroenterological function ☆
Guanglei Wang, Su Liu, Gongjian Liu
Department of Anesthesiology, the Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical College, Xuzhou, Jiangsu 221002, China.Received 11 November 2010, Revised 23 December 2010, Accepted 16 April 2011
INTRODUCTION
Hypervolemic hemodilution combined with controlled hypotension can lessen bleeding and save blood during surgery. It increases blood volume without increasing the cardiac load. It still remains unknown whether or not diluting blood under controlled hypotension will cause inadequate perfusion of vital organs and influence the microcirculation. Gastrotonometer can be used to evaluate localized blood flow of visceral vasculature. Compared with other conventional approaches, measurement of gastrointestinal mucosal pH using gastrotonometer is a considerably sensitive and specific method for estimation of microcirculatory blood flow and evaluation of the conditions of gastrointestinal blood perfusion and oxygenation[1]. The objective of this study is to investigate the effects of infusion of different liquids under controlled hypotension on gastric pH and gastrointestinal function after surgery using a gastrotonometer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
General materials
After the study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of local hospital and informed consent was obtained from the patients, we recruited forty five hepatic cancer patients [American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA)Ⅱ, male or female, age 25-62 years, and body weight 50-78 kg] undergoing elective surgery for this study. All the patients had normal hemoglobin levels, and normal hepatic and renal function. All the patients had no recent medication of nonsteroid anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)or steroid drugs and had no family history of hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, immunological or endocrinological diseases. Patients were randomly divided into three groups: 20 mL/kg Lactated Ringer’s solution group (R group), 6% HAES steril group (H group) and 6% Voluven group (W group).
Methods
All patients were fasted for 12 h for food and 6 h for drink prior to surgery. Midazolam (0.06 mg/kg) and scopolamine (0.3 mg) were intramuscularly injected at 30 min before anesthesia induction. Artery blood pressure, and mean artery blood pressure (MAP) were monitored through a catheter inserted in the radial artery in all patients. In addition, patients’ heart rate and lead II ECG were continuously monitored. Central venous pressure was monitored through a catheter inserted into the intrajugular vein. The three groups of patients were replenished for the loss of the physiological requirements owing to fasting. Etomidate emulsions (0.3 mg/kg), fentanyl (6-8 μg/kg), and cisatracurium (0.2 mg/kg) were intravenously administered for general anesthesia induction in all patients. Propofol [5 mg/(kg·h)] and cisatracurium [3 μg/(kg·min)]were continuously infused through micro pumps, and 1.5MAC isoflurane was inhaled for general anesthesia maintenance. During 1 h after induction, three groups received infusion of different fluids at 20 mL/kg according to the host group followed by balanced solution for maintenance. Nitroglycerin was continuously given through the jugular vein initially at a dose of 0.3 μg/(kg·min) to keep MAP lower than the baseline level and CVP at 5-12 cmH2O. At the beginning of surgery, the dose of nitroglycerin was increased to induce 25% to 30% decrease of basic MAP[2,3]. Controlled hypotension was terminated after tumor resection. All patients were given pure oxygen during the operation.
Determination of gastric intramucosal CO2 pressure (PgCO2) and gastric intramucosal pH(pHi)
Gastric intubation was performed on patients with the gastrotonometer (TRIP-NGS) tubes. An automated air tonometry technique was used to measure PgCO2using a catheter connected to a Tonocap monitor (Datex-Ohmeda Ltd., Hatfield, Herts, Finland). The catheter was inserted during anesthesia induction. Correct placement was confirmed by auscultating the epigastrium while 20 mL of air was insufflated through the nasogastric tube. The tonocap monitor automatically analyzed gastric gas samples for PgCO2and simultaneously drew artery blood for gas analysis. The intramucosal CO2pressure (PgCO2) and gastric intramucosal pH (pHi) were automatically calculated using the following formulas: pHi=pHa+lg(PaCO2/PgCO2)and Pg-aCO2=PgCO2-PaCO2[4]. All arterial blood gas measurements were obtained using the same blood gas analyser. The data before controlled hypotension was defined as the baseline value, and the value of artery blood gases and gastric mucosal pHi were recorded at 1 and 2 h after the onset of controlled hypotension,and 1 h after the termination of controlled hypotension. At some time point, blood was sampled for measuring hematocrit and hemoglobin (Hb).
Statistical analysis
Data were expressed as mean±SD. Paired t-test was used to compare changes of pre-treatment and post-treatment, and one-way ANOVAs followed by a Newman-Keuls post hoc test were used to compare difference among three groups. P < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Statistical analyses of data were generated using the SPSS 13.0 package.
RESULTS
All 45 patients in three groups completed the study protocol according to the anesthesia procedure, and all patients were induced by intravenous anesthesia,which was maintained by inhaled isoflurane successfully, and no patient was excluded.
General information of patients in three groups
The general information for the three groups are presented in Table 1. There were no significant differences among the three groups with regard to sex (male/female: the R group, 9/6; the H group, 8/7 and the W group, 7/8) (P > 0.05) and age [the R group, (46.2±3.5)years; the H group, (44.1±5.1) years; the W group,(46.3±4.8) years (P > 0.05)] and body weight [the R group, (61.1±7.8) kg; the H group, (59.4±8.2) kg;the W group, (62.3±8.6) kg (P > 0.05)]. The median duration of operation was similar among the three groups, (the R group, 180.4±48.6 min; the H group,(184.8±39.7) min; the W group, (178.5±42.7) min,(P > 0.05)].
Changes of hematocrit at each time point in three groups
The hematocrits at each time point are displayed in Table 2. There were no baseline differences between the groups. A progressive decline in the hematocrit was observed in the W group at 1 h after induction (31.5±1.5)% and during controlled hypotension(30.7±1.8)% comparing with the baseline value(43.9±5.7)% and that of the R group or H group at 1
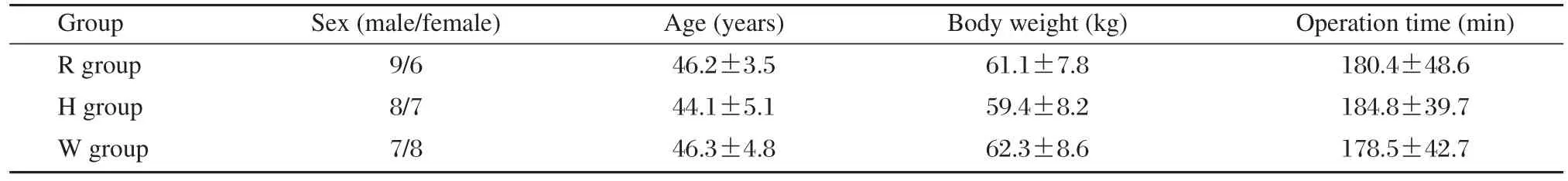
Table 1 Comparison of general conditions of patients in hepatic cancer patients under controlled hypotension and receiving infusion of different fluids (mean±SD, n = 15)
No significant difference in baseline characteristics was found among the three groups (P > 0.05). The H group: 6% HAES; the R group: 20 mL/kg Ringer’s solution; the W group: 6% Voluven.h after induction [(39.5±4.2)% and (33.6±1.9)%, respectively], during controlled hypotension [(38.3±5.4)%and (32.2±3.9)%, respectively]. However, there is no difference in the hematocrit values between the R group and H group not only at 1 h after induction (P > 0.05)but also during controlled hypotension (Table 2).

Table 2 Changes of hematocrit at each time point in hepatic cancer patients under controlled hypotension and receiving infusion of different fluids (%, mean±SD, n = 15)
Changes of heart rates in the three groups during controlled hypotension
The changes of heart rates are displayed in Table 3.No differences were observed in the baseline values of heart rate in the three groups. However, the heart rate was increased gradually in the R group due to the effect of controlled hypotension. There was a significant effect after 1 h (84.5±9.7 vs 77.1±8.3, P < 0.05) and especially after 2 h (86.4±9.5 vs 77.1±8.3, P < 0.01).Interestingly, the heart rate gradually decreased after 2 h. When recorded at the third h time point, the changes became similar to the baseline value (P > 0.05). Similarly, there was a trend of increase at the first and the second hour time point in both the H group (80.4±9.6,82.3±8.7 vs 76.7±8.5) and the W group (79.5±8.8,81.8±8.6 vs 78.8±8.5), but the effect was insignificant, and no significant difference was observed (P> 0.05). Additionally, there was a slight drop in heart rate at the 3 h time point in both two groups. When inter-group difference was analyzed, however, no difference was detected at all the time points during controlled hypotension (P > 0.05, Table 3).
Changes of pHa, PaO2, PaCO2, BE, pHi, and PgCO2 before, during and after controlled hypotension
The changes of artery blood gases and gastric mucosal metabolisms are illustrated in Table 4. No significant difference was detected in artery blood gas including pH, PaO2and PaCO2in the three groups at the different time points (P > 0.05). Compared withthe W group, base excess (BE) was decreased at the 1 h (-2.243±0.522 vs 0.921±0.632, P < 0.05) and 2 h(-3.306±2.243 vs 0.322±0.832, P < 0.05) time-point after nitroglycerin-induced controlled hypotension and 1 h (-2.918±0.908 vs 0.414±0.721, P < 0.05) after the termination of controlled hypotension in the R group,and the BE value in the H group showed no changes at each time point (0.611±0.532, 0.142±1.107 and 0.218±0.921, respectively). However, pHi in the R group was significantly lowered at 1 h (7.391±0.035)and 2 h (7.371±0.015) after the establishment of controlled hypotension compared with that of the W group (7.422±0.025 and 7.418±0.033) (P < 0.05).But fortunately, pHi values were still above 7.35.PgCO2[(41.144±4.091) mmHg and (41.972±2.964)mmHg] of the R group was significantly elevated at the same time points compared with that of the W group [(37.872±1.981) mmHg and (39.273±2.151)mmHg] (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01, Table 4).
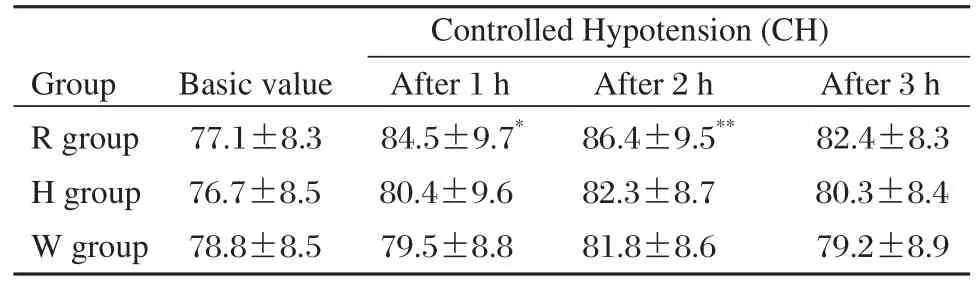
Table 3 Changes of heart rates of patients in hepatic cancer patients under controlled hypotension and receiving infusion of different fluids(bpm, mean±SD, n = 15)
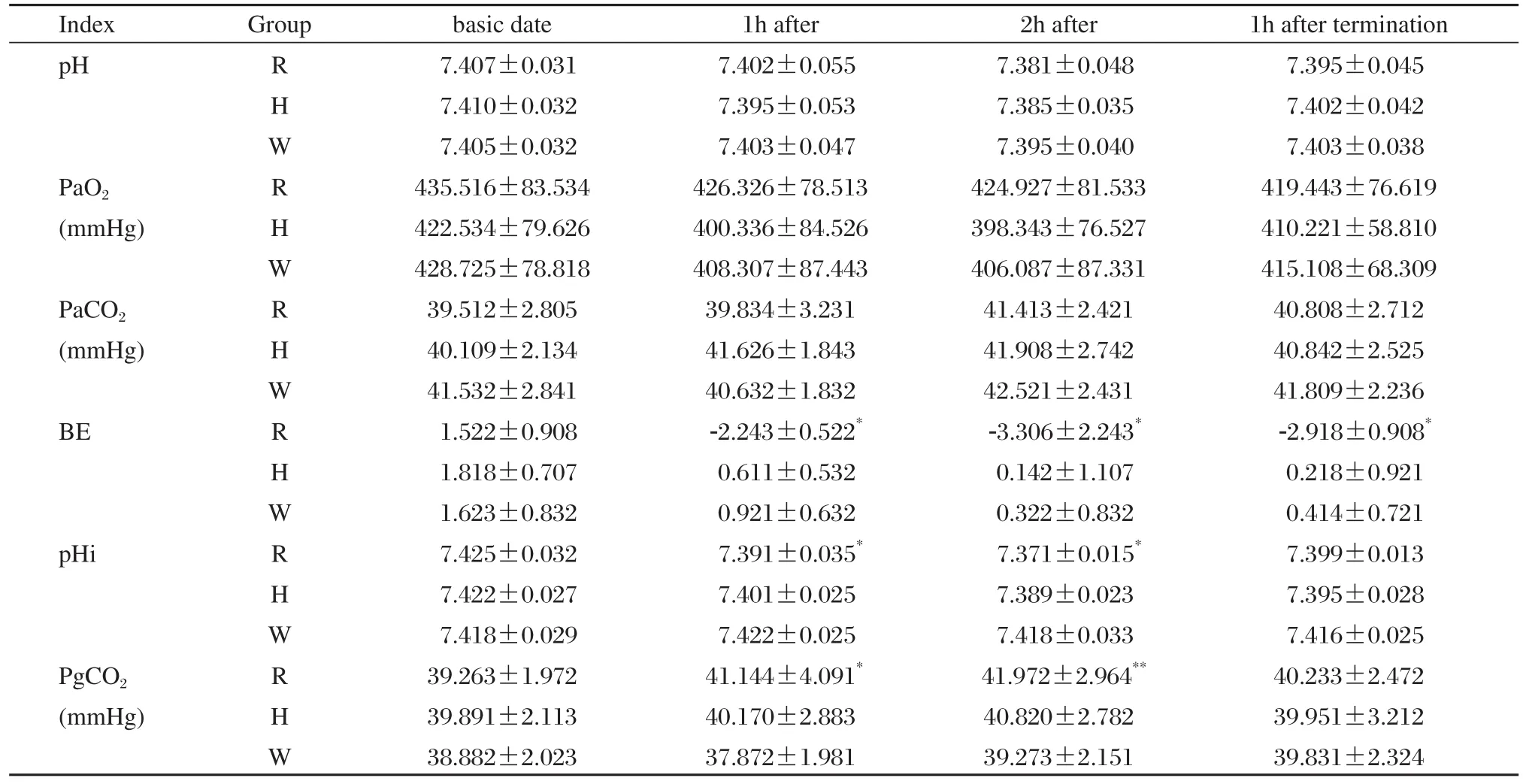
Table 4 Comparison of artery gases and gastric mucosal metabolisms in hepatic cancer patients under controlled hypotension and receiving infusion of different fluids (mean±SD, n = 15)
Changes of post-operational gastrointestinal recovery in three groups
Recovery of gastrointestinal function was determined by the first passage of flatus and defecation postoperatively. Time of first passing flatus and defection were recorded by patients, and collected by investigators. Median time to first flatus was (39.5±7.6) h and defecation was (72.6±8.4) h in W group, respectively, which was significantly more rapid comparing with either of the two groups (P < 0.05). These two parameters were not significantly different between the R group and H group (P > 0.05).
DISCUSSION
Hypervolemic hemodilution, which can inevitably lead to increased cardiac preload, increases myocardial oxygen consumption and pulmonary capillary leakage, is usually practiced for some patients to save blood[5,6]. We used hypervolemic hemodilution in the same time to induce hypotension to reduce cardiac stress. Sixty g/L hydroxyethyl starch (HAES200/0.5,HAES; HAES130/0.4, Voluven) is an effective plasma substitute for capacity of the treatment, especially because Voluven has the characteristics of moderate molecular weight, can efficiently expand the plasma volume, and possesses the characteristics of hemorheology that can improve the microcirculation[7-10],and prevent capillary leakage[11,12]. In this study, we expand blood volume using hydroxyethyl starch, and as indicated by the changes in hematocrit before and after volume expansion, we found that hydroxyethyl starch significantly decreased the hematocrit after the infusion, which, though, remained above 0.3. Studies have pointed out that hematocrit between 25%and 30% can offer the maximum amount of oxygen transport, decrease blood viscosity, and improve tissue oxygenation. After compound sodium lactate was infused, more than two thirds of it will move out of blood vessels while only 20% can contribute to capacity expansion and volume expansion is maintained for only 20-30 min.
Controlled hypotension during surgical operation has been widely adopted. More frequently, the protection of gastrointestinal function during controlled hypotension is overlooked, compared with the awareness of surgeons for blood supplies to vital organs such as the heart, brain and kidney[13-16]. It is well accepted that the gastrointestinal system is richly perfused and very sensitive to hypoxia and ischemia. Researchers have found that the gastrointestinal mucosa is among the first inflicted organs during tissue ischemia and the last organs that ameliorate after cessation of ischemia[17-20]. Reports have shown that exceedingly low pHi value during operation as a result of hypoxia/ischemia of the gastrointestinal mucosa results in slow recovery of gastrointestinal function, breakage of the gastrointestinal barrier and disruption of the epithelial metabolisms. The gastrointestinal mucosa is therefore more permeable to endotoxins and bacterium, which translocate into the blood stream to cause "endogenous" infections[21-23], and in severe cases, it can cause even more serious complications such as peptic ulcer.Therefore, monitoring of gastrointestinal pH can reflect not only overall hypoxic conditions of the body,but also the oxygenation states of individual organs.
Due to affluent blood supply of the liver, hepatic surgery is usually more traumatic and blood loss is heavier. In addition, circulation is more prone to fluctuation, resulting in hypotension and arrhythmia[24].Therefore, controlling blood loss is critical to improve the safety of the operation and anesthesia conditions[25].In order to control bleeding effectively, we used highvolume hemodilution combined with controlled hypotension[26,27], resulting in systemic blood volume increase and hematocrit decrease, improving the blood rheology and microcirculation of organ[28,29]. Studies have confirmed that acute hypervolemic hemodilution with rapid infusion of a large amount of hydroxyethyl starch can produce significant increase in effective circulating blood volume, diluting the circulation of vasoactive substances and the concentration of harmful metabolites, and will be helpful to reduce the stress of the negative impact on organs and tissues. Acute hypervolemic hemodilution can significantly reduce perioperative blood viscosity, hematocrit and erythrocyte aggregation index, and make the tissue blood perfusion improve significantly. In addition, hypervolemic hemodilution also enable red blood cell deformability significantly higher. With incrased deformability, red blood cells can easily transit through the capillaries,thus contributing to tissue oxygen supply. The results of our study also confirmed that pHi of the W group after controlled hypotension was significantly higher than that of the R group. In the H group, pHi seems to be higher than that of the R group, but no significant difference was noted. Perhaps our sample size was too small to render appropriate power, and perhaps Voluven surpasses HAES in fluid expansion and improving microcirculation, pending further study in the future.
pHi could indirectly reflect the supply of oxygenation of tissues and monitor visceral blood flow.The tonometry is the only non-invasive method used in clinic now in evaluating visceral blood flow. By measuring PgCO2, the pHi values can be deduced.Therefore, intramucosal acidosis and the decrease of visceral blood flow can be detected at an early stage.It has been shown that an elevated local PgCO2is correlated with poor prognosis in patients undergoing major surgery, suffering severe traumas or being critically ill[30,31]. The tonometry uses conventional tubes(a type of gastric tube with silicon air bag attached to the end). The air bag is automatically inflated with 5 ml air, which is equilibrated in the gut environment for 10 min before an air sample is measured for CO2pressure using infrared lights. The sampling air is then returned to the air bag, equilibrated, and is then ready for the next measurement. Compared with salt-water tonometry, this approach takes less time to equilibrate,provides excellent accuracy and is more reproducible[32]. This technique can detect reduced gastric mucoal perfusion within a short time period (5 min), and can provide a continuous, automatic monitoring for gut blood perfusion.
In summary, our study has shown that systemic oxygen delivery index (such as PaO2) has no significant change in deliberate hypotension with infusion of different liquids, but the BE decreased significantly,gastrointestinal PgCO2increased significantly and pHi was significantly reduced in the R group during controlled hypotension, suggesting a tendency of metabolic acidosis had developed. The results suggested that pHi was a more sensitive index than systemic oxygen delivery in monitoring local tissue oxygen supply. To some extent, it could be used to predict the degree of ischemia and provide us with a reliable and objective basis for early clinical intervention. In addition, pHi, as a non-invasive, simple, reliable, dynamic monitoring method, also could be used in critically-ill patients in the perioperative period.
We believed that infusion of 6% hydroxyethyl starch, especially of Voluven, was beneficial for the microcirculation perfusion. This infusion can also help to save blood and prevent transfusion complications in the perioperative period.
[1] Kolkman JJ, Otte JA, Groeneveld AB. Gastrointestinal luminal PCO2tonometry: an update on physiology,methodology and clinical applications. Br J Anaesth 2000;84:74-86.
[2] Wang G, Cao J, Liu G. Differential effects of controlled hypotension on gastric intramucosal pH and post-operational gastrointestinal functional under two different anesthesia methods. Journal of Nanjing Medical University 2008;22:47-51.
[3] Pakulski C, Nowicki R, Kowalczyk, P, Bak P, Mikulski K,Badowicz B. The influence of controlled hypotension on splanchnic mucosal perfusion using gastric tonometry in patients undergoing resection of meningioma. Med Sci Monit 2002;8:CR28-30.
[4] Huang CC, Shih MJ, Tsai YH, Chang YC, Tsao TC, Hsu KH. Effects of inverse ratio ventilation versus positive end-expiratory pressure on gas exchange and gastric intramucosal PCO2and pH under constant mean airway pressure in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Anesthesiology 2001;95:1182-8.
[5] Mori K, Arai H, Nakajima K, Tajima A, Maeda M. Hemorheological and hemodynamic analysis of hypervolemic hemodilution therapy for cerebral vasospasm after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 1995;26:1620-6.
[6] Kivik P. Relationship between hemodynamics and blood volume changes after cardiopulmonary bypass during coronary artery bypass grafting. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 1993;7:231-4.
[7] Kimberger O, Arnberger M, Brandt S, Plock J, Siqurdsson GH, Kurz A, et al. Goal-directed colloid administration improves the microcirculation of healthy and perianastomotic colon. Anesthesiology 2009;110:496-504.
[8] Maier S, Holz C, Pajk W, Ulmer H, Henql C, Dunser M,et al. Microcirculatory parameters after isotonic and hypertonic colloidal fluid resuscitation in acute hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma 2009;66:337-45.
[9] Inan N, Iitar S, Surer H, Yilmaz G, Alemdaroqlu KB,Yazar MA, et al. Effect of hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 on ischaemia/reperfusion in rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2009;26:160-5.
[10] Mahmood A, Gosling P, Barclay R, Kilvingqton F, Vohra R. Splanchnic microcirculation protection by hydroxyethyl starches during abdominal aortic aneurysm surgery. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2009;37:319-25.
[11] Entholzner EK, Miklke LL, Calatzis AN, Feyh J, Hipp R, Harqasser SR. Coagulation effects of a recently developed hydroxyethyl starches with higher molecular weight. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2000;44:1116-21.
[12] Langeron O, Doelberg M, Anq ET, Bonnet F, Capdevila,Coriat P. Voluven a lower substituted novel hydroxyethyl starch(HES130/0.4),causes fewer effects on coagulation in major orthopedic surgery than HES200/0.5[J].Anesth Analg 2001;92:855-8.
[13] Calvet X, Baigorri F, Duarte M, Joseph D, Saura P, Mas A, et al. Effect of sucralfate on gastric intramucosal pH in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Med 1997;23:738-42.
[14] Westphal M, Freise H, Kehrel BE, Bone HG, Van Aken H, Sielenkamper AW. Arginine vasopressin compromises gut mucosal microcirculation in septic rats. Crit Care Med 2004;32:194-200.
[15] Lang K, Suttner S, Boldt J, Kumle B, Naqel D. Volume replacement with HES 130/0.4 may reduce the inflammatory response in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery. Can J Anaesth 2003;50:1009-16.
[16] Takakura K, Suqiura Y, Goto Y. Differential microcirculation dynamics during deliberate hypotension induced by nicardipine, PGE1 and trimethaphan in rat mesentery.Can J Anaesth 1995;42:1035-9.
[17] Van Beek AH, Sijbesma JC, Jansen RW, Rikkert MG,Claassen JA. Cortical oxygen supply during postural hypotension is further decreased in Alzheimers desease,but unrelated to cholinesterase-inhibitor use. J Alzheimers Dis 2010;21:519-26.
[18] Bauer SR, Lam SW. Arginine vasopressin for the treatment of septic shock in adults. Pharmacotherapy 2010;30:1057-71.
[19] Simon F, Giudici R, Scheuerle A, Groqer M, Asfar P,Voqt JA, et al. Comparison of cardiac, hepatic, and renal effects of arginine vasopressin and noradrenaline during porcine fecal peritonitis: a randomized controlled trial.Crit Care 2009;13:R113.
[20] Karpel E, Czechowski M, Seifert B, Jalowiecki P. Clinical usefulness of gastric tonometry in anesthesiology and intensive care medicine. Wiad Lek 2005;58:652-9.
[21] Oud L, Kruse JA. Progressive gastric intramucosal acidosis follows resuscitation from hemorrhagic shock.Shock 1996;6:61-5.
[22] Taylor DE, Gutierrez G. Tonometry-a review of clinical studies. Crit Care Clin 1996;12:1007-18.
[23] Hiltebrand LB, Krejci V, Tenhoevel ME, Banic A,Siqurdsson GH. Redistribution of microcirculatory blood flow within the intestinal wall during sepsis and general anesthesia. Anesthesiology 2003;98:658-69.
[24] Orian A, Whiteside S, Israel A, Stancovski I, Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A. Ubiquitin-mediated processing of NF-kappa B transcriptional activator precursor p105.Reconstitution of a cell-free system and identification of the ubiquitin-carrier protein, E2, and a novel ubiquitinprotein ligase, E3, involved in conjugation. J Biol Chem 1995;270:21707-14.
[25] Andel D, Andel H, Horanf K, Felferniq D, Millesi W,Zimpfer M. The influence of deliberate hypotension on splanchnic balance with use of either isoflurance or esmolol and nitroglyceirin. Anesth Analg 2001;93:1116-20.
[26] Suttner SW, Boldt J, Schmidt CC, Piper SN, Schuster P,Kumle B. The effects of sodium nitroprusside-induced hypotension on splanchnic perfusion and hepatocellular integrity. Anesth Analg 1999;89:1371-7.
[27] Toyama S, Okada C, Ikeda N. Sodium nitroprussideinduced hypotension for pediatric orthopedic surgery.Massui 2009;58:174-7.
[28] Fukusaki M, Nakamura T, Miyoshi H, Tamura S, Sumikawa K. Splanchnic perfusion during controlled hypotension combined with: acute hypervolemic hemodilution:a comparison with combination of acute normovolemic hemodilution gastric intramucosal pH study. J Clin Anesth 2000;12:421-6.
[29] Fukusaki M, Nakamura T, Hara T, Fukushima H, Hasuo H, Sumikawa K. Splanchnic perfusion during controlled hypotension with haemodilution under isoflurane anaesthesia in elderly patients. Eur J Anaethesion 1999;16:519-25.
[30] Perez A, Schnitzler EJ, Minces PG. The value of gastric intramucosal pH in the postoperative period of cardiac surgery in pediatric patients. Crit Care Med 2000;28:1585-9.
[31] Baloqh Z, Mckinley BA, Holcomb JB, Miller CC, Cocanour CS,Kozar RA, et al. Both primary and secondary abdominal compartment syndrome can be predicted early and are harbingers of multiple organ failure. J Trauma 1994;36:313-316.
[32] Guzman JA, Kruse JA. Gastric intramucosal PCO2as a quantitative indicator of the degree of acute hemorrhage.J Crit Care 1998;13:49-54.
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH2011年3期
THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH2011年3期
- THE JOURNAL OF BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH的其它文章
- Identification of distant co-evolving residues in antigen 85C from Mycobacterium tuberculosis using statistical coupling analysis of the esterase family proteins
- Anisocoria in a 10-month old girl in the immediate preoperative setting: can you proceed with surgery?
- Surgical repair of thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms using the critical artery reattachment technique
- A novel bead-based fluorescence immunoassay for aldosterone
- Hypoxic response elements and Tet-On advanced double-controlled systems regulate hVEGF165 and angiopoietin-1 gene expression in vitro☆
- Apparent diffusion coefficient in normal and abnormal pattern of intervertebral lumbar discs: initial experience ☆
